Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 viewsNG Tube
NG Tube
Uploaded by
A HA nasogastric tube (NG tube) is inserted through the nose into the stomach to drain gastric contents or deliver feeding. There are different types of NG tubes used for various purposes. The Levin tube is most commonly used and has a single lumen with holes near the tip to prevent accumulation of fluids and gas. A Sump tube is double lumened to allow separate suction and air passageways. A Sengstaken-Blackmore tube is triple lumened and used to treat esophageal varices by inflating balloons in the stomach and esophagus. NG tubes are indicated for feeding, aspiration, medication, lavage, and analysis. Complications include epistaxis, erosions,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Philip Kotler, Nancy R. Lee - Success in Social Marketing - 100 Case Studies From Around The Globe (2022)Document403 pagesPhilip Kotler, Nancy R. Lee - Success in Social Marketing - 100 Case Studies From Around The Globe (2022)Yoelvis89No ratings yet
- Positive Behavior SupportsDocument10 pagesPositive Behavior Supportsapi-491244141No ratings yet
- Inbound 7669742920615241001Document4 pagesInbound 7669742920615241001Mae Loreen CapuyanNo ratings yet
- 10.5 Tracheostomies - Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient CareDocument31 pages10.5 Tracheostomies - Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient CareMeg AqNo ratings yet
- NGT Ogt-FeedingDocument14 pagesNGT Ogt-Feedingnibbles nibblesNo ratings yet
- Ncm116 Skills LabDocument17 pagesNcm116 Skills LabMarie Isabelle HerveraNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 MSN Prelim Topic 3 Care of Clients With Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument2 pagesNCM 112 MSN Prelim Topic 3 Care of Clients With Gastrointestinal DisordersKim Erida QuezonNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube Insertion: Notes: ComplicationsDocument2 pagesNasogastric Tube Insertion: Notes: ComplicationsAlyssandra LucenoNo ratings yet
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDocument4 pages2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedLeonardo Montemayor100% (3)
- Atlas of Laparoscopic Urologic Surgery, 1E (2007) PDFDocument340 pagesAtlas of Laparoscopic Urologic Surgery, 1E (2007) PDFAndreea Q. PopaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation General Objectives: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation General Objectives: IndependentEden Marie FranciscoNo ratings yet
- NCP Marilou.... SanitariumDocument9 pagesNCP Marilou.... SanitariumJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Gastric-Lavage-and-Gavage ReviewerDocument2 pagesGastric-Lavage-and-Gavage ReviewerPatricia AdiaoNo ratings yet
- NGT NotesDocument2 pagesNGT NoteshanhananicasNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationNichol John MalabananNo ratings yet
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDocument4 pages2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedZharm MayNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS How To Insert A NasogastricNG Tube For Gastric Decompression 03Document1 pageNursing CS How To Insert A NasogastricNG Tube For Gastric Decompression 03solisetherealNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaFaith CalimlimNo ratings yet
- MS LAB ReviewerDocument2 pagesMS LAB Reviewershachima0713No ratings yet
- Laboratory Examinations: Allen's Test Normal Finding: Hand Quickly BecomesDocument9 pagesLaboratory Examinations: Allen's Test Normal Finding: Hand Quickly BecomesShane GumaponNo ratings yet
- EnemaDocument2 pagesEnemaleksis09No ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube (NGT)Document31 pagesNasogastric Tube (NGT)annyeong_123No ratings yet
- Ineffective AIRWAY CLEARANCE RT Retained Mucus Secretions AEB The (+) Crackles On Both Lower Lung Field.Document2 pagesIneffective AIRWAY CLEARANCE RT Retained Mucus Secretions AEB The (+) Crackles On Both Lower Lung Field.Senyorita KHaye0% (1)
- Dysphagia Artifical Ventilation Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesDysphagia Artifical Ventilation Lecture NotesTaylor AckermanNo ratings yet
- Surgery 1. 3-Way Foley Catheter (Latex/silicon) : TherapeuticDocument5 pagesSurgery 1. 3-Way Foley Catheter (Latex/silicon) : TherapeuticMalvinder Singh DhillonNo ratings yet
- RespDisord (PART B & C)Document4 pagesRespDisord (PART B & C)GraceNo ratings yet
- DONE - NCM 116 RLE Week 7 ROXASDocument11 pagesDONE - NCM 116 RLE Week 7 ROXASBatiao Camille ClaireNo ratings yet
- Act2 - Additional Info and QuestionsDocument4 pagesAct2 - Additional Info and QuestionsMika SaldanaNo ratings yet
- COMMON TERMS IN GI TREATMENT MODALITIES Part 1Document11 pagesCOMMON TERMS IN GI TREATMENT MODALITIES Part 1Mikee PaningbatanNo ratings yet
- NCP On Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Diagnosi S Planning Nursing Interventions Implementatio N Evaluation Subjective: IndependentDocument10 pagesNCP On Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Diagnosi S Planning Nursing Interventions Implementatio N Evaluation Subjective: IndependentSheryhan Tahir BayleNo ratings yet
- Test/Treatment What Is It? Complications To Monitor For Nursing Care NotesDocument5 pagesTest/Treatment What Is It? Complications To Monitor For Nursing Care NotesNieka WNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessm ENT Nursing Diagnos IS Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluati ON Subjectiv eDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessm ENT Nursing Diagnos IS Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluati ON Subjectiv eJ. TSNo ratings yet
- HW ncm102Document15 pagesHW ncm102maisidroNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric TubeDocument3 pagesNasogastric TubeFreddy PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- ENEMADocument4 pagesENEMAangelaNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube InsertionDocument9 pagesNasogastric Tube InsertionLjc JaslinNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Acute Epiglottis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Acute Epiglottis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Rigid Esophagoscopy (Complete)Document4 pagesRigid Esophagoscopy (Complete)Yukiko CalimutanNo ratings yet
- ENT TransDocument7 pagesENT TransanonymousNo ratings yet
- Barium Enema Edited FinalDocument9 pagesBarium Enema Edited FinalLouise Joy PlandoNo ratings yet
- SwabDocument1 pageSwabgaelNo ratings yet
- Inserting A Nasogastric Tube ChecklistDocument7 pagesInserting A Nasogastric Tube ChecklistAlyssa DeleonNo ratings yet
- TSCUH Trachy Bed Head PDFDocument4 pagesTSCUH Trachy Bed Head PDFTudistef Analize SanatateNo ratings yet
- Surgery OSCEDocument23 pagesSurgery OSCEsumith_gunawardhana100% (8)
- Ranula PDFDocument14 pagesRanula PDFsatya_mdsNo ratings yet
- Enteral Nutrition: Course OutlineDocument3 pagesEnteral Nutrition: Course OutlineAngeli IdrisNo ratings yet
- Jose, Leana Louisse D. BSN 2B1 Title: Enteric Nutrition Care of The Mother and Child at Risk or With ProblemsDocument3 pagesJose, Leana Louisse D. BSN 2B1 Title: Enteric Nutrition Care of The Mother and Child at Risk or With ProblemsLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- COMMON TERMS IN GI TREATMENT MODALITIES Part 1Document14 pagesCOMMON TERMS IN GI TREATMENT MODALITIES Part 1ninshiesungaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Action Rationale Preparatory PhaseDocument6 pagesNursing Action Rationale Preparatory Phasemarie100% (2)
- Radio - GitDocument19 pagesRadio - GitVon HippoNo ratings yet
- 20 Trauma Resuscitation Part 2 InterventionsDocument3 pages20 Trauma Resuscitation Part 2 InterventionssueNo ratings yet
- NCP-Combate-Risk For AspirationDocument2 pagesNCP-Combate-Risk For AspirationKayelyn-Rose CombateNo ratings yet
- Nasotracheal SuctioningDocument2 pagesNasotracheal Suctioningmarie100% (3)
- National Registry Skill SheetsDocument21 pagesNational Registry Skill SheetsKemzo AbarquezNo ratings yet
- Care To The Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesCare To The Digestive SystemSONGA AmriNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: SecretionsDocument4 pagesRespiratory System: SecretionsMarian FloresNo ratings yet
- Airway Masterclass 2 TOTW 043 2007Document11 pagesAirway Masterclass 2 TOTW 043 2007eryxspNo ratings yet
- Surgical Year 3 Sem2Document27 pagesSurgical Year 3 Sem2Gabriela GabrielaNo ratings yet
- NCP NRMFDocument2 pagesNCP NRMFJai CortezNo ratings yet
- Treatise on the Anatomy and Physiology of the Mucous Membranes: With Illustrative Pathological ObservationsFrom EverandTreatise on the Anatomy and Physiology of the Mucous Membranes: With Illustrative Pathological ObservationsNo ratings yet
- Writesonic Chatsonic 1709993519576Document1 pageWritesonic Chatsonic 1709993519576A HNo ratings yet
- Presentation1smoking 120603021549 Phpapp02Document12 pagesPresentation1smoking 120603021549 Phpapp02A HNo ratings yet
- Relationship of Nursing Management Functions With Missed Nursing Care: A Cross-Sectional StudyDocument16 pagesRelationship of Nursing Management Functions With Missed Nursing Care: A Cross-Sectional StudyA HNo ratings yet
- I. Patient Profile (2 Marks) :: Student Name: Student ID: Date: Instructor Name: Allotted Grade: Given GradeDocument4 pagesI. Patient Profile (2 Marks) :: Student Name: Student ID: Date: Instructor Name: Allotted Grade: Given GradeA HNo ratings yet
- MMC 1Document6 pagesMMC 1A HNo ratings yet
- Shen Et Al. BMC Nursing (2023) 22:407Document13 pagesShen Et Al. BMC Nursing (2023) 22:407A HNo ratings yet
- Model Answers G4 Mid Term DTS 101 Fall 2017 - .PDF - 112317Document3 pagesModel Answers G4 Mid Term DTS 101 Fall 2017 - .PDF - 112317A HNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs - Docx-8-13Document6 pages2 1 Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs - Docx-8-13A HNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1DTS 101 - Model Answers - PDF - 109803Document2 pagesQuiz 1DTS 101 - Model Answers - PDF - 109803A HNo ratings yet
- Method fo-WPS OfficenDocument3 pagesMethod fo-WPS OfficenA HNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument4 pagesElectrochemistryA HNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ischemic Stoke PDFDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ischemic Stoke PDFA HNo ratings yet
- Status and Cost Analysis of Sabaki Tilapia FarmingDocument8 pagesStatus and Cost Analysis of Sabaki Tilapia FarmingA HNo ratings yet
- Mod. Ans G5 Mid Term Exam DTS 101 Fall 2017.Pdf - 114012Document3 pagesMod. Ans G5 Mid Term Exam DTS 101 Fall 2017.Pdf - 114012A HNo ratings yet
- 4 5915746627611529826Document4 pages4 5915746627611529826A HNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan StrokeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan StrokeA HNo ratings yet
- 19976251Document2 pages19976251A HNo ratings yet
- NPSG Chapter HAP Jan2021Document14 pagesNPSG Chapter HAP Jan2021A HNo ratings yet
- 2581 Fuel CellDocument6 pages2581 Fuel CellA HNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Stroke Care Plan PaperDocument12 pagesIschemic Stroke Care Plan PaperA HNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cell and Its Applications A ReviewDocument5 pagesFuel Cell and Its Applications A ReviewA HNo ratings yet
- 202004092006210179pavan Engg Electrolytic ProcessDocument9 pages202004092006210179pavan Engg Electrolytic ProcessA HNo ratings yet
- WA0054mmmDocument4 pagesWA0054mmmA HNo ratings yet
- Objective 1 - De-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesObjective 1 - De-WPS OfficeA HNo ratings yet
- Title-WPS OfficemjDocument1 pageTitle-WPS OfficemjA HNo ratings yet
- Turner's SyndromeDocument3 pagesTurner's SyndromeA HNo ratings yet
- Writing Portfolio 2 - CLO 2.7 - Descriptive ParagraphDocument12 pagesWriting Portfolio 2 - CLO 2.7 - Descriptive ParagraphA HNo ratings yet
- Practical For StudentsDocument50 pagesPractical For StudentsA HNo ratings yet
- PosterDocument2 pagesPosterA HNo ratings yet
- Wa0001Document4 pagesWa0001A HNo ratings yet
- JMO Handbook Updated 05 04 21 by Kate CushDocument31 pagesJMO Handbook Updated 05 04 21 by Kate CushCrystal ZawNo ratings yet
- Theory of Cultural Care and DiversityDocument16 pagesTheory of Cultural Care and DiversityJunne Rafaela NovalNo ratings yet
- Power of The Pinch Pinch Lower Lid BlepharoplastyDocument6 pagesPower of The Pinch Pinch Lower Lid BlepharoplastyBFF BotoxNo ratings yet
- Science Plan™ Puppy Healthy Development™ Large Breed Chicken - DryDocument3 pagesScience Plan™ Puppy Healthy Development™ Large Breed Chicken - DryDavina NaidooNo ratings yet
- Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy in The Brains of Military PersonnelDocument9 pagesChronic Traumatic Encephalopathy in The Brains of Military PersonnelBruce Fredy Chino ChambillaNo ratings yet
- Nitta Erlinda: Seminar Keperawatan RS Jantung Dan Pembuluh Darah "Harapan Kita" Jakarta 2019Document18 pagesNitta Erlinda: Seminar Keperawatan RS Jantung Dan Pembuluh Darah "Harapan Kita" Jakarta 2019Duas JourgieNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid: Kristoffer G. Villareal RN, LPTDocument23 pagesBasic First Aid: Kristoffer G. Villareal RN, LPTTopz VillarealNo ratings yet
- Lati Tubi Tingkatan 3: Left Atrium / Atrium Kiri Pulmonary Vein / Vena PeparuDocument3 pagesLati Tubi Tingkatan 3: Left Atrium / Atrium Kiri Pulmonary Vein / Vena PeparuTheMovingFingerNo ratings yet
- List of Members of Person's With Disability - Gulod (APWD-Gulod) Barangay Gulod, District 5, Quezon CityDocument33 pagesList of Members of Person's With Disability - Gulod (APWD-Gulod) Barangay Gulod, District 5, Quezon CityJurryNo ratings yet
- Molecular Laboratory ReportDocument1 pageMolecular Laboratory ReportCristina TorresNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: AmoxicillinDocument3 pagesDrug Study: AmoxicillinKrzia TehNo ratings yet
- Sample Case Study-2-1Document4 pagesSample Case Study-2-1visiniNo ratings yet
- Pain Pada SyringomyeliaDocument6 pagesPain Pada Syringomyeliavico julendiNo ratings yet
- Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction - What Does The Single Heel Raise Test Mean in AssessmentDocument8 pagesPosterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction - What Does The Single Heel Raise Test Mean in AssessmentNegru TeodorNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214785321052202 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S2214785321052202 MainSudhi SureshNo ratings yet
- Added Sugars and Periodontal Disease in Young Adults: An Analysis of NHANES III DataDocument6 pagesAdded Sugars and Periodontal Disease in Young Adults: An Analysis of NHANES III DataNavaneethan GnanadesiganNo ratings yet
- ISQua Programme KL 2018 PDFDocument144 pagesISQua Programme KL 2018 PDFSuresh MikeNo ratings yet
- Medical Abbreviation Terms-2Document7 pagesMedical Abbreviation Terms-2Jmarie Brillantes PopiocoNo ratings yet
- What Is Vicarious Trauma 2018 05 20Document2 pagesWhat Is Vicarious Trauma 2018 05 20api-546034011No ratings yet
- Past Life RegressionDocument8 pagesPast Life RegressionGabriel AndradeNo ratings yet
- B.inggris3 7A Group Task10 Group 6Document7 pagesB.inggris3 7A Group Task10 Group 6Rosita DamayantiNo ratings yet
- ClaspDocument4 pagesClaspRebin AliNo ratings yet
- dm2022 0304Document2 pagesdm2022 0304Charlemagne Sabio GalamgamNo ratings yet
- PDF Medical Language Instant Translator 6 Ed Edition Davi Ellen Chabner Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Medical Language Instant Translator 6 Ed Edition Davi Ellen Chabner Ebook Full Chapterdaniel.mann336100% (4)
- Narrative Lyphedema and ElephantiasisDocument1 pageNarrative Lyphedema and ElephantiasisKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Comms 310 Strategic Message Planner Part 1Document7 pagesComms 310 Strategic Message Planner Part 1api-508434828No ratings yet
- The Four Terrible Things That Are Destroying Boys in Our CultureDocument4 pagesThe Four Terrible Things That Are Destroying Boys in Our CultureСаша МироноваNo ratings yet
- Shang Han LunDocument94 pagesShang Han LunDENo ratings yet
NG Tube
NG Tube
Uploaded by
A H0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views2 pagesA nasogastric tube (NG tube) is inserted through the nose into the stomach to drain gastric contents or deliver feeding. There are different types of NG tubes used for various purposes. The Levin tube is most commonly used and has a single lumen with holes near the tip to prevent accumulation of fluids and gas. A Sump tube is double lumened to allow separate suction and air passageways. A Sengstaken-Blackmore tube is triple lumened and used to treat esophageal varices by inflating balloons in the stomach and esophagus. NG tubes are indicated for feeding, aspiration, medication, lavage, and analysis. Complications include epistaxis, erosions,
Original Description:
Surgery
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentA nasogastric tube (NG tube) is inserted through the nose into the stomach to drain gastric contents or deliver feeding. There are different types of NG tubes used for various purposes. The Levin tube is most commonly used and has a single lumen with holes near the tip to prevent accumulation of fluids and gas. A Sump tube is double lumened to allow separate suction and air passageways. A Sengstaken-Blackmore tube is triple lumened and used to treat esophageal varices by inflating balloons in the stomach and esophagus. NG tubes are indicated for feeding, aspiration, medication, lavage, and analysis. Complications include epistaxis, erosions,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
47 views2 pagesNG Tube
NG Tube
Uploaded by
A HA nasogastric tube (NG tube) is inserted through the nose into the stomach to drain gastric contents or deliver feeding. There are different types of NG tubes used for various purposes. The Levin tube is most commonly used and has a single lumen with holes near the tip to prevent accumulation of fluids and gas. A Sump tube is double lumened to allow separate suction and air passageways. A Sengstaken-Blackmore tube is triple lumened and used to treat esophageal varices by inflating balloons in the stomach and esophagus. NG tubes are indicated for feeding, aspiration, medication, lavage, and analysis. Complications include epistaxis, erosions,
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
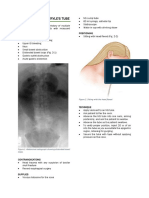
NASOGASTRIC TUBE (NG/RYLE’S TUBE)
LEVIN TUBE Single lumen, holes near tip
Prevents accumulation of intestinal liquids and gas
during and following surgery.
Prevents nausea, vomiting and distention due to
reduced peristaltic action.
Most common type used.
SUMP (SALEM) TUBE Double lumen, radiopaque
- 1st lumen: suction of gastric contents
- 2nd lumen: blue extension (pig tail) open to
room air to maintain a continuous flow of
atmospheric air into the stomach.
Controls the amount of suction pressure placed on
stomach walls.
Prevents injury, ulcers.
SENGSTAKEN-BLACKMORE TUBE Triple lumen
- 1st lumen: Inflates the balloon in the stomach to
press against the esophagogastric junction.
- 2nd lumen: Inflates the balloon in the
esophagus to press directly against varices.
- 3rd lumen: Used for aspiration and lavage.
©AzreenSyazlin SurgicalPosting 2014/2015, RoadToFinalPro
INDICATION
COMPLICATION
Feeding : for pt who cannot drink/sip liquid
Epistaxis
feed/unconscious/on ventilator
Erosions in the nasal cavity, and
Aspiration: to provide samples of gastric
nasopharynx
contents
More dangerous complications include:
Lab analysis : to keep stomach free of gastric
Esophageal
contents and air- post operation
penetration
Lavage : in cases of poisoning or overdose
Intracranial insertion
Medication
Aspiration
HOW TO INSERT NG TUBE?
1. Wash your hands, introduce to the patient and clarify their identity. Explain the procedure and get consent.
2. Gather your equipment:
3. Position the patient on the bed upright and facing forward.
4. Estimate the length of the tube to be inserted (measure the NG tube from the tip of the nose, to the earlobe and then
to xiphisternum).
5. Lubricate the tip of the tube and begin to insert through one of the nostrils. If any resistance is encountered, change
to the other nostril.
6. Ask the patient to keep on swallowing (saliva?)
7. Aspirate/ Blow air from/into the tube using a syringe.
8. Test the aspirate using pH indicator paper. The pH should be 1 – 5.5/ hear the air sound in the stomach by
stethoscope.
9. If satisfied that the pH is correct, and the tube is draining gastric fluid, secure the tube with tape and attach a bile bag
to allow drainage.
10. Ensure your patient is comfortable, thank them and wash hands.
©AzreenSyazlin SurgicalPosting 2014/2015, RoadToFinalPro
You might also like
- Philip Kotler, Nancy R. Lee - Success in Social Marketing - 100 Case Studies From Around The Globe (2022)Document403 pagesPhilip Kotler, Nancy R. Lee - Success in Social Marketing - 100 Case Studies From Around The Globe (2022)Yoelvis89No ratings yet
- Positive Behavior SupportsDocument10 pagesPositive Behavior Supportsapi-491244141No ratings yet
- Inbound 7669742920615241001Document4 pagesInbound 7669742920615241001Mae Loreen CapuyanNo ratings yet
- 10.5 Tracheostomies - Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient CareDocument31 pages10.5 Tracheostomies - Clinical Procedures For Safer Patient CareMeg AqNo ratings yet
- NGT Ogt-FeedingDocument14 pagesNGT Ogt-Feedingnibbles nibblesNo ratings yet
- Ncm116 Skills LabDocument17 pagesNcm116 Skills LabMarie Isabelle HerveraNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 MSN Prelim Topic 3 Care of Clients With Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument2 pagesNCM 112 MSN Prelim Topic 3 Care of Clients With Gastrointestinal DisordersKim Erida QuezonNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube Insertion: Notes: ComplicationsDocument2 pagesNasogastric Tube Insertion: Notes: ComplicationsAlyssandra LucenoNo ratings yet
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDocument4 pages2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedLeonardo Montemayor100% (3)
- Atlas of Laparoscopic Urologic Surgery, 1E (2007) PDFDocument340 pagesAtlas of Laparoscopic Urologic Surgery, 1E (2007) PDFAndreea Q. PopaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation General Objectives: IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation General Objectives: IndependentEden Marie FranciscoNo ratings yet
- NCP Marilou.... SanitariumDocument9 pagesNCP Marilou.... SanitariumJerry AbleNo ratings yet
- Gastric-Lavage-and-Gavage ReviewerDocument2 pagesGastric-Lavage-and-Gavage ReviewerPatricia AdiaoNo ratings yet
- NGT NotesDocument2 pagesNGT NoteshanhananicasNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Inference Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationNichol John MalabananNo ratings yet
- 2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedDocument4 pages2 NCP Impaired Swallowing EditedZharm MayNo ratings yet
- Nursing CS How To Insert A NasogastricNG Tube For Gastric Decompression 03Document1 pageNursing CS How To Insert A NasogastricNG Tube For Gastric Decompression 03solisetherealNo ratings yet
- NCP Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaDocument2 pagesNCP Ineffective Airway Clearance PediaFaith CalimlimNo ratings yet
- MS LAB ReviewerDocument2 pagesMS LAB Reviewershachima0713No ratings yet
- Laboratory Examinations: Allen's Test Normal Finding: Hand Quickly BecomesDocument9 pagesLaboratory Examinations: Allen's Test Normal Finding: Hand Quickly BecomesShane GumaponNo ratings yet
- EnemaDocument2 pagesEnemaleksis09No ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube (NGT)Document31 pagesNasogastric Tube (NGT)annyeong_123No ratings yet
- Ineffective AIRWAY CLEARANCE RT Retained Mucus Secretions AEB The (+) Crackles On Both Lower Lung Field.Document2 pagesIneffective AIRWAY CLEARANCE RT Retained Mucus Secretions AEB The (+) Crackles On Both Lower Lung Field.Senyorita KHaye0% (1)
- Dysphagia Artifical Ventilation Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesDysphagia Artifical Ventilation Lecture NotesTaylor AckermanNo ratings yet
- Surgery 1. 3-Way Foley Catheter (Latex/silicon) : TherapeuticDocument5 pagesSurgery 1. 3-Way Foley Catheter (Latex/silicon) : TherapeuticMalvinder Singh DhillonNo ratings yet
- RespDisord (PART B & C)Document4 pagesRespDisord (PART B & C)GraceNo ratings yet
- DONE - NCM 116 RLE Week 7 ROXASDocument11 pagesDONE - NCM 116 RLE Week 7 ROXASBatiao Camille ClaireNo ratings yet
- Act2 - Additional Info and QuestionsDocument4 pagesAct2 - Additional Info and QuestionsMika SaldanaNo ratings yet
- COMMON TERMS IN GI TREATMENT MODALITIES Part 1Document11 pagesCOMMON TERMS IN GI TREATMENT MODALITIES Part 1Mikee PaningbatanNo ratings yet
- NCP On Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Diagnosi S Planning Nursing Interventions Implementatio N Evaluation Subjective: IndependentDocument10 pagesNCP On Ineffective Airway Clearance Nursing Diagnosi S Planning Nursing Interventions Implementatio N Evaluation Subjective: IndependentSheryhan Tahir BayleNo ratings yet
- Test/Treatment What Is It? Complications To Monitor For Nursing Care NotesDocument5 pagesTest/Treatment What Is It? Complications To Monitor For Nursing Care NotesNieka WNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessm ENT Nursing Diagnos IS Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluati ON Subjectiv eDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessm ENT Nursing Diagnos IS Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluati ON Subjectiv eJ. TSNo ratings yet
- HW ncm102Document15 pagesHW ncm102maisidroNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric TubeDocument3 pagesNasogastric TubeFreddy PanjaitanNo ratings yet
- ENEMADocument4 pagesENEMAangelaNo ratings yet
- Nasogastric Tube InsertionDocument9 pagesNasogastric Tube InsertionLjc JaslinNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Acute Epiglottis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii Acute Epiglottis: St. Paul College of Ilocos SurCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Rigid Esophagoscopy (Complete)Document4 pagesRigid Esophagoscopy (Complete)Yukiko CalimutanNo ratings yet
- ENT TransDocument7 pagesENT TransanonymousNo ratings yet
- Barium Enema Edited FinalDocument9 pagesBarium Enema Edited FinalLouise Joy PlandoNo ratings yet
- SwabDocument1 pageSwabgaelNo ratings yet
- Inserting A Nasogastric Tube ChecklistDocument7 pagesInserting A Nasogastric Tube ChecklistAlyssa DeleonNo ratings yet
- TSCUH Trachy Bed Head PDFDocument4 pagesTSCUH Trachy Bed Head PDFTudistef Analize SanatateNo ratings yet
- Surgery OSCEDocument23 pagesSurgery OSCEsumith_gunawardhana100% (8)
- Ranula PDFDocument14 pagesRanula PDFsatya_mdsNo ratings yet
- Enteral Nutrition: Course OutlineDocument3 pagesEnteral Nutrition: Course OutlineAngeli IdrisNo ratings yet
- Jose, Leana Louisse D. BSN 2B1 Title: Enteric Nutrition Care of The Mother and Child at Risk or With ProblemsDocument3 pagesJose, Leana Louisse D. BSN 2B1 Title: Enteric Nutrition Care of The Mother and Child at Risk or With ProblemsLiana Louisse JoseNo ratings yet
- COMMON TERMS IN GI TREATMENT MODALITIES Part 1Document14 pagesCOMMON TERMS IN GI TREATMENT MODALITIES Part 1ninshiesungaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Action Rationale Preparatory PhaseDocument6 pagesNursing Action Rationale Preparatory Phasemarie100% (2)
- Radio - GitDocument19 pagesRadio - GitVon HippoNo ratings yet
- 20 Trauma Resuscitation Part 2 InterventionsDocument3 pages20 Trauma Resuscitation Part 2 InterventionssueNo ratings yet
- NCP-Combate-Risk For AspirationDocument2 pagesNCP-Combate-Risk For AspirationKayelyn-Rose CombateNo ratings yet
- Nasotracheal SuctioningDocument2 pagesNasotracheal Suctioningmarie100% (3)
- National Registry Skill SheetsDocument21 pagesNational Registry Skill SheetsKemzo AbarquezNo ratings yet
- Care To The Digestive SystemDocument16 pagesCare To The Digestive SystemSONGA AmriNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System: SecretionsDocument4 pagesRespiratory System: SecretionsMarian FloresNo ratings yet
- Airway Masterclass 2 TOTW 043 2007Document11 pagesAirway Masterclass 2 TOTW 043 2007eryxspNo ratings yet
- Surgical Year 3 Sem2Document27 pagesSurgical Year 3 Sem2Gabriela GabrielaNo ratings yet
- NCP NRMFDocument2 pagesNCP NRMFJai CortezNo ratings yet
- Treatise on the Anatomy and Physiology of the Mucous Membranes: With Illustrative Pathological ObservationsFrom EverandTreatise on the Anatomy and Physiology of the Mucous Membranes: With Illustrative Pathological ObservationsNo ratings yet
- Writesonic Chatsonic 1709993519576Document1 pageWritesonic Chatsonic 1709993519576A HNo ratings yet
- Presentation1smoking 120603021549 Phpapp02Document12 pagesPresentation1smoking 120603021549 Phpapp02A HNo ratings yet
- Relationship of Nursing Management Functions With Missed Nursing Care: A Cross-Sectional StudyDocument16 pagesRelationship of Nursing Management Functions With Missed Nursing Care: A Cross-Sectional StudyA HNo ratings yet
- I. Patient Profile (2 Marks) :: Student Name: Student ID: Date: Instructor Name: Allotted Grade: Given GradeDocument4 pagesI. Patient Profile (2 Marks) :: Student Name: Student ID: Date: Instructor Name: Allotted Grade: Given GradeA HNo ratings yet
- MMC 1Document6 pagesMMC 1A HNo ratings yet
- Shen Et Al. BMC Nursing (2023) 22:407Document13 pagesShen Et Al. BMC Nursing (2023) 22:407A HNo ratings yet
- Model Answers G4 Mid Term DTS 101 Fall 2017 - .PDF - 112317Document3 pagesModel Answers G4 Mid Term DTS 101 Fall 2017 - .PDF - 112317A HNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs - Docx-8-13Document6 pages2 1 Chemistry and Pharmacology of Anticancer Drugs - Docx-8-13A HNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1DTS 101 - Model Answers - PDF - 109803Document2 pagesQuiz 1DTS 101 - Model Answers - PDF - 109803A HNo ratings yet
- Method fo-WPS OfficenDocument3 pagesMethod fo-WPS OfficenA HNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument4 pagesElectrochemistryA HNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Ischemic Stoke PDFDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Ischemic Stoke PDFA HNo ratings yet
- Status and Cost Analysis of Sabaki Tilapia FarmingDocument8 pagesStatus and Cost Analysis of Sabaki Tilapia FarmingA HNo ratings yet
- Mod. Ans G5 Mid Term Exam DTS 101 Fall 2017.Pdf - 114012Document3 pagesMod. Ans G5 Mid Term Exam DTS 101 Fall 2017.Pdf - 114012A HNo ratings yet
- 4 5915746627611529826Document4 pages4 5915746627611529826A HNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan StrokeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan StrokeA HNo ratings yet
- 19976251Document2 pages19976251A HNo ratings yet
- NPSG Chapter HAP Jan2021Document14 pagesNPSG Chapter HAP Jan2021A HNo ratings yet
- 2581 Fuel CellDocument6 pages2581 Fuel CellA HNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Stroke Care Plan PaperDocument12 pagesIschemic Stroke Care Plan PaperA HNo ratings yet
- Fuel Cell and Its Applications A ReviewDocument5 pagesFuel Cell and Its Applications A ReviewA HNo ratings yet
- 202004092006210179pavan Engg Electrolytic ProcessDocument9 pages202004092006210179pavan Engg Electrolytic ProcessA HNo ratings yet
- WA0054mmmDocument4 pagesWA0054mmmA HNo ratings yet
- Objective 1 - De-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesObjective 1 - De-WPS OfficeA HNo ratings yet
- Title-WPS OfficemjDocument1 pageTitle-WPS OfficemjA HNo ratings yet
- Turner's SyndromeDocument3 pagesTurner's SyndromeA HNo ratings yet
- Writing Portfolio 2 - CLO 2.7 - Descriptive ParagraphDocument12 pagesWriting Portfolio 2 - CLO 2.7 - Descriptive ParagraphA HNo ratings yet
- Practical For StudentsDocument50 pagesPractical For StudentsA HNo ratings yet
- PosterDocument2 pagesPosterA HNo ratings yet
- Wa0001Document4 pagesWa0001A HNo ratings yet
- JMO Handbook Updated 05 04 21 by Kate CushDocument31 pagesJMO Handbook Updated 05 04 21 by Kate CushCrystal ZawNo ratings yet
- Theory of Cultural Care and DiversityDocument16 pagesTheory of Cultural Care and DiversityJunne Rafaela NovalNo ratings yet
- Power of The Pinch Pinch Lower Lid BlepharoplastyDocument6 pagesPower of The Pinch Pinch Lower Lid BlepharoplastyBFF BotoxNo ratings yet
- Science Plan™ Puppy Healthy Development™ Large Breed Chicken - DryDocument3 pagesScience Plan™ Puppy Healthy Development™ Large Breed Chicken - DryDavina NaidooNo ratings yet
- Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy in The Brains of Military PersonnelDocument9 pagesChronic Traumatic Encephalopathy in The Brains of Military PersonnelBruce Fredy Chino ChambillaNo ratings yet
- Nitta Erlinda: Seminar Keperawatan RS Jantung Dan Pembuluh Darah "Harapan Kita" Jakarta 2019Document18 pagesNitta Erlinda: Seminar Keperawatan RS Jantung Dan Pembuluh Darah "Harapan Kita" Jakarta 2019Duas JourgieNo ratings yet
- Basic First Aid: Kristoffer G. Villareal RN, LPTDocument23 pagesBasic First Aid: Kristoffer G. Villareal RN, LPTTopz VillarealNo ratings yet
- Lati Tubi Tingkatan 3: Left Atrium / Atrium Kiri Pulmonary Vein / Vena PeparuDocument3 pagesLati Tubi Tingkatan 3: Left Atrium / Atrium Kiri Pulmonary Vein / Vena PeparuTheMovingFingerNo ratings yet
- List of Members of Person's With Disability - Gulod (APWD-Gulod) Barangay Gulod, District 5, Quezon CityDocument33 pagesList of Members of Person's With Disability - Gulod (APWD-Gulod) Barangay Gulod, District 5, Quezon CityJurryNo ratings yet
- Molecular Laboratory ReportDocument1 pageMolecular Laboratory ReportCristina TorresNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: AmoxicillinDocument3 pagesDrug Study: AmoxicillinKrzia TehNo ratings yet
- Sample Case Study-2-1Document4 pagesSample Case Study-2-1visiniNo ratings yet
- Pain Pada SyringomyeliaDocument6 pagesPain Pada Syringomyeliavico julendiNo ratings yet
- Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction - What Does The Single Heel Raise Test Mean in AssessmentDocument8 pagesPosterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction - What Does The Single Heel Raise Test Mean in AssessmentNegru TeodorNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214785321052202 MainDocument5 pages1 s2.0 S2214785321052202 MainSudhi SureshNo ratings yet
- Added Sugars and Periodontal Disease in Young Adults: An Analysis of NHANES III DataDocument6 pagesAdded Sugars and Periodontal Disease in Young Adults: An Analysis of NHANES III DataNavaneethan GnanadesiganNo ratings yet
- ISQua Programme KL 2018 PDFDocument144 pagesISQua Programme KL 2018 PDFSuresh MikeNo ratings yet
- Medical Abbreviation Terms-2Document7 pagesMedical Abbreviation Terms-2Jmarie Brillantes PopiocoNo ratings yet
- What Is Vicarious Trauma 2018 05 20Document2 pagesWhat Is Vicarious Trauma 2018 05 20api-546034011No ratings yet
- Past Life RegressionDocument8 pagesPast Life RegressionGabriel AndradeNo ratings yet
- B.inggris3 7A Group Task10 Group 6Document7 pagesB.inggris3 7A Group Task10 Group 6Rosita DamayantiNo ratings yet
- ClaspDocument4 pagesClaspRebin AliNo ratings yet
- dm2022 0304Document2 pagesdm2022 0304Charlemagne Sabio GalamgamNo ratings yet
- PDF Medical Language Instant Translator 6 Ed Edition Davi Ellen Chabner Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Medical Language Instant Translator 6 Ed Edition Davi Ellen Chabner Ebook Full Chapterdaniel.mann336100% (4)
- Narrative Lyphedema and ElephantiasisDocument1 pageNarrative Lyphedema and ElephantiasisKim SunooNo ratings yet
- Comms 310 Strategic Message Planner Part 1Document7 pagesComms 310 Strategic Message Planner Part 1api-508434828No ratings yet
- The Four Terrible Things That Are Destroying Boys in Our CultureDocument4 pagesThe Four Terrible Things That Are Destroying Boys in Our CultureСаша МироноваNo ratings yet
- Shang Han LunDocument94 pagesShang Han LunDENo ratings yet