Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology HW
Biology HW
Uploaded by
santhoshtupakula392Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 2-REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATUREDocument18 pagesChapter 2-REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATUREMaria Lovella Misolas Diaz100% (1)
- Fixed Film Anaerobic DigesterDocument3 pagesFixed Film Anaerobic DigesterTyan NufutomoNo ratings yet
- 101 Essential Tips Growing Vegetables - 2015 PDFDocument74 pages101 Essential Tips Growing Vegetables - 2015 PDFMara100% (10)
- Edinburgh Recycling Guide 2014Document9 pagesEdinburgh Recycling Guide 2014GreenerLeithNo ratings yet
- Module - 1/4 Class IX Prepared By-Punam Jyoti Lakra School - AECS TuramdihDocument16 pagesModule - 1/4 Class IX Prepared By-Punam Jyoti Lakra School - AECS TuramdihDanica S.JNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument12 pages09 Science Notes Ch15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDhiraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER IMPROVEMENT IN FOOD RESOURCE - Doc NewDocument10 pagesCHAPTER IMPROVEMENT IN FOOD RESOURCE - Doc New459sana.mNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources... Chapter .. Home Work QuestionsDocument6 pagesImprovement in Food Resources... Chapter .. Home Work Questionsthe pantherNo ratings yet
- Question Bank BioDocument19 pagesQuestion Bank BioMr Sony MathewNo ratings yet
- 15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument10 pages15 Improvement in Food Resourcestara tuitionNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15, Improvement in Food Resources Part IDocument10 pagesChapter - 15, Improvement in Food Resources Part IMonika Mehan100% (14)
- Improvement of Food ResourcesDocument13 pagesImprovement of Food ResourcesNaveed BeighNo ratings yet
- Improvement of Food ResourcesDocument6 pagesImprovement of Food ResourcesSanvi SinghNo ratings yet
- Ch-15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument9 pagesCh-15 Improvement in Food ResourcesAakankshaNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources-NotesDocument6 pagesImprovement in Food Resources-Notesyatharthdange131No ratings yet
- Improvement of Food Resources NotesDocument16 pagesImprovement of Food Resources NotesNandakeshava KaustubhNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources 15Document3 pagesImprovement in Food Resources 15Navdeep JindalNo ratings yet
- Biology Study MaterialDocument74 pagesBiology Study MaterialSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument11 pagesImprovement in Food Resourcesminakshi kalraNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 NotesDocument8 pagesImprovement in Food Resources Class 9 NotesRubeena VargheseNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 NotesDocument8 pagesImprovement in Food Resources Class 9 NotesANAYA SHARANNo ratings yet
- Page No: 204: Chapter 15 - Improvement in Food Resources in Text QuestionsDocument7 pagesPage No: 204: Chapter 15 - Improvement in Food Resources in Text Questionsmadhurreet jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument5 pagesImprovement in Food ResourcesJ.S CommercialNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Intext QuesionsDocument5 pagesChapter 15 - Intext QuesionsShailaja MestryNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Biology Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument13 pagesCBSE Class 9 Biology Improvement in Food ResourcesChander Bhan SharmaNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument3 pagesCH 13 Improvement in Food ResourcesPRAVEEN KUMARNo ratings yet
- IX-15-Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument14 pagesIX-15-Improvement in Food Resourcesvaishnav.shrot777No ratings yet
- Working of InstitutionsDocument11 pagesWorking of InstitutionsShiv KotadiyaNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food ResouresesDocument77 pagesImprovement in Food ResouresesRinita MitraNo ratings yet
- 15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument24 pages15 Improvement in Food Resourcesjohn neil basasNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15: Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument14 pagesChapter - 15: Improvement in Food Resourcesanmolmuskan2020No ratings yet
- Babilon and WaganeshDocument9 pagesBabilon and WaganeshYomif NiguseNo ratings yet
- Food ResourcesDocument21 pagesFood ResourcesveenumorNo ratings yet
- Answer: Page No: 205Document6 pagesAnswer: Page No: 205apoorv saxenaNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Imp Ch15 3Document10 pages9 Science Imp Ch15 3deepakNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch15 Improvement in Food Resources-1Document7 pages09 Science Notes Ch15 Improvement in Food Resources-1Nirmal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources-NotesDocument9 pagesImprovement in Food Resources-NotesHemang NityantNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Important Questions 2022-23Document20 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Important Questions 2022-23abhishek singhNo ratings yet
- Crop Improvement UpDocument6 pagesCrop Improvement UpKrishna JaiswalNo ratings yet
- 2018 IFA Integrated Plant Nutrient Management HighlightsDocument9 pages2018 IFA Integrated Plant Nutrient Management Highlightscarlos mosqueraNo ratings yet
- Definition, Aim, Objectives and Scope of Plant Breeding DefinitionDocument155 pagesDefinition, Aim, Objectives and Scope of Plant Breeding DefinitionAayushi YadavNo ratings yet
- The Use of Organic FertilizerDocument15 pagesThe Use of Organic FertilizerAnnabelle Poniente HertezNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resource - Mat PDFDocument13 pagesImprovement in Food Resource - Mat PDFAyushman TripathyNo ratings yet
- Science UT 1Document99 pagesScience UT 1chitra sabarinathanNo ratings yet
- Sarthak Arora: - IX - C:-S.R.D.A.V. Public Scool: Made by ClassDocument15 pagesSarthak Arora: - IX - C:-S.R.D.A.V. Public Scool: Made by ClassNaman Gaur100% (1)
- Ganesh Project (Of) 2Document31 pagesGanesh Project (Of) 2Banty Chandresh DixitNo ratings yet
- Standard 9 Science BookDocument158 pagesStandard 9 Science Bookhero22No ratings yet
- Iesc 115Document13 pagesIesc 115obungaowoNo ratings yet
- BiofertilizersDocument8 pagesBiofertilizersUmer FarooqNo ratings yet
- Ncert Class 8 ScienceDocument12 pagesNcert Class 8 ScienceOjas SinghNo ratings yet
- FINAL Growth Response of Different Organic Fertilizer On Rice Oryza Sativa L. .Doc 2Document36 pagesFINAL Growth Response of Different Organic Fertilizer On Rice Oryza Sativa L. .Doc 2CHRIST IAN JAN PALGANNo ratings yet
- Imp Food ResDocument13 pagesImp Food ResIsaac PreethamNo ratings yet
- Biofertilizers - A Way To Organic AgricultureDocument4 pagesBiofertilizers - A Way To Organic AgricultureJesus DurangoNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer: Soran University Faculty of Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument9 pagesFertilizer: Soran University Faculty of Engineering Department of Chemical Engineeringموٴمن عبدالستار اسعدNo ratings yet
- 67 Topper 21 101 1 1 11 Improvement in Food Resources Up201807051759 1530793746 4459Document14 pages67 Topper 21 101 1 1 11 Improvement in Food Resources Up201807051759 1530793746 4459rakesh singhNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument11 pagesRRLERICA DOSADONo ratings yet
- Biology - Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources: Intext QuestionsDocument3 pagesBiology - Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources: Intext QuestionsShailaja MestryNo ratings yet
- Definition, Aim, Objectives and Scope of Plant BreedingDocument137 pagesDefinition, Aim, Objectives and Scope of Plant BreedingYosef AndualemNo ratings yet
- Change CropDocument37 pagesChange CropChristopher Ryan GalganaNo ratings yet
- Physiological Response of Glutinous Corn To Rates of Fermented SeaweedDocument20 pagesPhysiological Response of Glutinous Corn To Rates of Fermented SeaweedMark Iandy Lumamig100% (1)
- Heirloom Gardening and Biodiversity_ Cultivating a Time : Honored Legacy for a Sustainable FutureFrom EverandHeirloom Gardening and Biodiversity_ Cultivating a Time : Honored Legacy for a Sustainable FutureNo ratings yet
- Tomato Factsheet 2013Document4 pagesTomato Factsheet 2013Crystal Redhead-GouldNo ratings yet
- Daphnia e MoinaDocument6 pagesDaphnia e MoinaRosangela D Magalhaes LopesNo ratings yet
- Growth and Yield Perpormance of Pechay FinalDocument25 pagesGrowth and Yield Perpormance of Pechay FinalJaimeh Annabelle100% (2)
- Zeolita EstudiosDocument5 pagesZeolita EstudiosVulcano JerezNo ratings yet
- Coconut Farm Diversification Gasa Engl Corrected 2016 09 15Document33 pagesCoconut Farm Diversification Gasa Engl Corrected 2016 09 15W_ScheeweNo ratings yet
- Pdf2text - 64954ca6d7f9e (AutoRecovered)Document13 pagesPdf2text - 64954ca6d7f9e (AutoRecovered)Shalumaria GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Coconut Cultivators GuideDocument21 pagesCoconut Cultivators GuideArunNo ratings yet
- On-Farm Composting Methods 2003 BOOKDocument51 pagesOn-Farm Composting Methods 2003 BOOKlalibNo ratings yet
- Industrial Survey Report by Sudhershan Gundeti On Ankapur A Model VillageDocument35 pagesIndustrial Survey Report by Sudhershan Gundeti On Ankapur A Model Villagekiranreddy9999No ratings yet
- Ncert Sol For Cbse Class 9 Sci Chapter 15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument8 pagesNcert Sol For Cbse Class 9 Sci Chapter 15 Improvement in Food ResourcesShah RukhNo ratings yet
- The Production Problems Include Raw Material AvailabilityDocument46 pagesThe Production Problems Include Raw Material AvailabilityankitsonigaraNo ratings yet
- Composite Fish Culture in HillsDocument20 pagesComposite Fish Culture in HillsSullip MajhiNo ratings yet
- Almanac Start A GardenDocument21 pagesAlmanac Start A GardenAlice Henry0% (1)
- Journal of EcologyDocument324 pagesJournal of EcologyyellowNo ratings yet
- Grade Vi Epp Agri TQ Tos Answers KeyDocument9 pagesGrade Vi Epp Agri TQ Tos Answers Keyanthony100% (1)
- Joel Salatin at Stanford (Feb 2009) Talk NotesDocument11 pagesJoel Salatin at Stanford (Feb 2009) Talk Noteslwu.two100% (4)
- Journal Sukartono 2011, Basic and AppliedDocument6 pagesJournal Sukartono 2011, Basic and AppliedmonikaNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Crops Production and ManagementDocument7 pagesCh-1 Crops Production and ManagementAryan RoyNo ratings yet
- Sangha Lam ChanchinDocument8 pagesSangha Lam ChanchinKca Khawlhring ChunthangNo ratings yet
- CoffeeDocument10 pagesCoffeepandaypiraNo ratings yet
- Focal Point - Agri-Crop ProductionDocument27 pagesFocal Point - Agri-Crop ProductionGina Baranda Artates100% (1)
- PAES Terms Compilation - PDF Version 1 2Document52 pagesPAES Terms Compilation - PDF Version 1 2RAFAEL TAYO JR.No ratings yet
- Evaluation of Spent Biogas Silage As Casing Soil inDocument3 pagesEvaluation of Spent Biogas Silage As Casing Soil inShailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- Afa Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesAfa Lesson PlanVincent Jay Maat100% (3)
- 8cropproduction101 BieDocument56 pages8cropproduction101 BieDan RicksNo ratings yet
- 14 Dr. Cho 2007 Korean NF - InputsDocument6 pages14 Dr. Cho 2007 Korean NF - InputsRoy Basbas ResurreccionNo ratings yet
- On-Farm Composting: A GuideDocument44 pagesOn-Farm Composting: A GuideGreater Charlotte Harbor Sierra ClubNo ratings yet
Biology HW
Biology HW
Uploaded by
santhoshtupakula392Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biology HW
Biology HW
Uploaded by
santhoshtupakula392Copyright:
Available Formats
1. .Differentiate between Rabi and Kharif crops.
Ans. Rabi and Kharif are two distinct cropping
seasons in India. Rabi crops are sown in winter,
typically between October and December, and
harvested in spring, around March to May.
Wheat, barley, and mustard are examples of
Rabi crops. In contrast, Kharif crops are planted
with the onset of the monsoon, from June to July, and are harvested in the autumn,
between September and October. Rice, maize, and cotton are common examples of
Kharif crops.
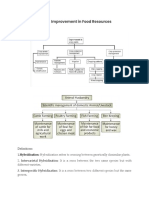
2. What are the various ways to improve the variety of crops?
Ans. Crop variety improvement: It can be done either by hybridisation or by
introducing a gene.
(i) Hybridisation: Hybridisation refers to crossing between genetically dissimilar
plants.
(ii) Crop improvement by introducing a gene: This provides the desired
characteristics and results in genetically modified crops.
3. What is hybridization? Name the various types of hybridization.
Ans. Hybridization is a breeding technique that involves crossing two genetically
different individuals to create offspring with desirable traits
Intraspecific Hybridization: Crossing individuals of the same species with distinct
characteristics to obtain improved traits.
Interspecific Hybridization: Breeding between individuals of different species, aiming to
combine advantageous traits from both species.
Intergeneric Hybridization: Crossing individuals from different genera, often employed
to create hybrids with novel characteristics.
Intragenic Hybridization (or Line Breeding): Repeatedly crossing and selecting within a
specific line or population to enhance and stabilize desirable traits.
4. What do you mean by genetically modified crops?
Ans. Genetically modified crops, often referred to as GMOs
(Genetically Modified Organisms), are plants whose genetic
material has been altered through genetic engineering
techniques. Scientists modify the DNA of these crops to
introduce specific traits, such as resistance to pests, diseases,
or environmental conditions, as well as enhanced nutritional
content. The purpose of genetically modifying crops is to improve their overall
performance, yield, and resilience
5. What are the purposes of crop variety improvement?
Ans. Crop variety improvement seeks to enhance agricultural productivity by developing
resilient, high-yielding varieties with resistance to diseases and tolerance to
environmental stresses. This effort also addresses nutritional deficiencies, adapts to
climate change, and reduces environmental impact.
6. What are the desired agronomic characters for fodder crops and cereal crops?
Ans. Desired agronomic traits for fodder crops include high biomass yield, nutritional
value, and palatability for livestock. For cereal crops, key traits involve high grain
yield, disease resistance, and adaptability to varied environmental conditions, ensuring
robust and reliable harvests.
7. What are macronutrients and micronutrients?
Ans. Macronutrients are essential nutrients required by plants and organisms in
relatively large quantities, including nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Micronutrients
are vital elements needed in smaller amounts, such as iron, zinc, and copper. Both are
crucial for the healthy growth and development of plants.
8. List the nutrients required by the plants and their sources?
Ans. Plants require macronutrients like nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K)
sourced from fertilizers and organic matter. Micronutrients such as iron (Fe), zinc (Zn),
and copper (Cu) are needed in smaller amounts and are often supplied through soil and
organic amendments. These nutrients collectively support plant growth and development.
9. Differentiate between manure and fertilizer.(Any two). Why are manure considered
better than fertilizers?
Ans. Manure is organic, derived from animal and plant decomposition, gradually releasing
nutrients to enhance soil health. Fertilizers, synthetic or natural, provide quick nutrient
availability but may lack organic content. Manure is favoured for its sustainable, soil-
improving qualities, including organic matter and microbial support, leading to reduced
environmental impact compared to fertilizers.
10. What do you mean by compost and green manure?
Ans. Compost is humus-like material created from decomposed
organic matter, enhancing soil structure and fertility. Green
manure involves growing specific crops, like legumes, to be
incorporated into the soil, providing nutrients and preventing erosion. Both practices
contribute to sustainable soil management and improved agricultural productivity.
x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x-x
You might also like
- Chapter 2-REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATUREDocument18 pagesChapter 2-REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATUREMaria Lovella Misolas Diaz100% (1)
- Fixed Film Anaerobic DigesterDocument3 pagesFixed Film Anaerobic DigesterTyan NufutomoNo ratings yet
- 101 Essential Tips Growing Vegetables - 2015 PDFDocument74 pages101 Essential Tips Growing Vegetables - 2015 PDFMara100% (10)
- Edinburgh Recycling Guide 2014Document9 pagesEdinburgh Recycling Guide 2014GreenerLeithNo ratings yet
- Module - 1/4 Class IX Prepared By-Punam Jyoti Lakra School - AECS TuramdihDocument16 pagesModule - 1/4 Class IX Prepared By-Punam Jyoti Lakra School - AECS TuramdihDanica S.JNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument12 pages09 Science Notes Ch15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDhiraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER IMPROVEMENT IN FOOD RESOURCE - Doc NewDocument10 pagesCHAPTER IMPROVEMENT IN FOOD RESOURCE - Doc New459sana.mNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources... Chapter .. Home Work QuestionsDocument6 pagesImprovement in Food Resources... Chapter .. Home Work Questionsthe pantherNo ratings yet
- Question Bank BioDocument19 pagesQuestion Bank BioMr Sony MathewNo ratings yet
- 15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument10 pages15 Improvement in Food Resourcestara tuitionNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15, Improvement in Food Resources Part IDocument10 pagesChapter - 15, Improvement in Food Resources Part IMonika Mehan100% (14)
- Improvement of Food ResourcesDocument13 pagesImprovement of Food ResourcesNaveed BeighNo ratings yet
- Improvement of Food ResourcesDocument6 pagesImprovement of Food ResourcesSanvi SinghNo ratings yet
- Ch-15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument9 pagesCh-15 Improvement in Food ResourcesAakankshaNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources-NotesDocument6 pagesImprovement in Food Resources-Notesyatharthdange131No ratings yet
- Improvement of Food Resources NotesDocument16 pagesImprovement of Food Resources NotesNandakeshava KaustubhNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources 15Document3 pagesImprovement in Food Resources 15Navdeep JindalNo ratings yet
- Biology Study MaterialDocument74 pagesBiology Study MaterialSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument11 pagesImprovement in Food Resourcesminakshi kalraNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 NotesDocument8 pagesImprovement in Food Resources Class 9 NotesRubeena VargheseNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources Class 9 NotesDocument8 pagesImprovement in Food Resources Class 9 NotesANAYA SHARANNo ratings yet
- Page No: 204: Chapter 15 - Improvement in Food Resources in Text QuestionsDocument7 pagesPage No: 204: Chapter 15 - Improvement in Food Resources in Text Questionsmadhurreet jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument5 pagesImprovement in Food ResourcesJ.S CommercialNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Intext QuesionsDocument5 pagesChapter 15 - Intext QuesionsShailaja MestryNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Biology Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument13 pagesCBSE Class 9 Biology Improvement in Food ResourcesChander Bhan SharmaNo ratings yet
- CH 13 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument3 pagesCH 13 Improvement in Food ResourcesPRAVEEN KUMARNo ratings yet
- IX-15-Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument14 pagesIX-15-Improvement in Food Resourcesvaishnav.shrot777No ratings yet
- Working of InstitutionsDocument11 pagesWorking of InstitutionsShiv KotadiyaNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food ResouresesDocument77 pagesImprovement in Food ResouresesRinita MitraNo ratings yet
- 15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument24 pages15 Improvement in Food Resourcesjohn neil basasNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 15: Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument14 pagesChapter - 15: Improvement in Food Resourcesanmolmuskan2020No ratings yet
- Babilon and WaganeshDocument9 pagesBabilon and WaganeshYomif NiguseNo ratings yet
- Food ResourcesDocument21 pagesFood ResourcesveenumorNo ratings yet
- Answer: Page No: 205Document6 pagesAnswer: Page No: 205apoorv saxenaNo ratings yet
- 9 Science Imp Ch15 3Document10 pages9 Science Imp Ch15 3deepakNo ratings yet
- 09 Science Notes Ch15 Improvement in Food Resources-1Document7 pages09 Science Notes Ch15 Improvement in Food Resources-1Nirmal SharmaNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resources-NotesDocument9 pagesImprovement in Food Resources-NotesHemang NityantNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Important Questions 2022-23Document20 pagesCBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources Important Questions 2022-23abhishek singhNo ratings yet
- Crop Improvement UpDocument6 pagesCrop Improvement UpKrishna JaiswalNo ratings yet
- 2018 IFA Integrated Plant Nutrient Management HighlightsDocument9 pages2018 IFA Integrated Plant Nutrient Management Highlightscarlos mosqueraNo ratings yet
- Definition, Aim, Objectives and Scope of Plant Breeding DefinitionDocument155 pagesDefinition, Aim, Objectives and Scope of Plant Breeding DefinitionAayushi YadavNo ratings yet
- The Use of Organic FertilizerDocument15 pagesThe Use of Organic FertilizerAnnabelle Poniente HertezNo ratings yet
- Improvement in Food Resource - Mat PDFDocument13 pagesImprovement in Food Resource - Mat PDFAyushman TripathyNo ratings yet
- Science UT 1Document99 pagesScience UT 1chitra sabarinathanNo ratings yet
- Sarthak Arora: - IX - C:-S.R.D.A.V. Public Scool: Made by ClassDocument15 pagesSarthak Arora: - IX - C:-S.R.D.A.V. Public Scool: Made by ClassNaman Gaur100% (1)
- Ganesh Project (Of) 2Document31 pagesGanesh Project (Of) 2Banty Chandresh DixitNo ratings yet
- Standard 9 Science BookDocument158 pagesStandard 9 Science Bookhero22No ratings yet
- Iesc 115Document13 pagesIesc 115obungaowoNo ratings yet
- BiofertilizersDocument8 pagesBiofertilizersUmer FarooqNo ratings yet
- Ncert Class 8 ScienceDocument12 pagesNcert Class 8 ScienceOjas SinghNo ratings yet
- FINAL Growth Response of Different Organic Fertilizer On Rice Oryza Sativa L. .Doc 2Document36 pagesFINAL Growth Response of Different Organic Fertilizer On Rice Oryza Sativa L. .Doc 2CHRIST IAN JAN PALGANNo ratings yet
- Imp Food ResDocument13 pagesImp Food ResIsaac PreethamNo ratings yet
- Biofertilizers - A Way To Organic AgricultureDocument4 pagesBiofertilizers - A Way To Organic AgricultureJesus DurangoNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer: Soran University Faculty of Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument9 pagesFertilizer: Soran University Faculty of Engineering Department of Chemical Engineeringموٴمن عبدالستار اسعدNo ratings yet
- 67 Topper 21 101 1 1 11 Improvement in Food Resources Up201807051759 1530793746 4459Document14 pages67 Topper 21 101 1 1 11 Improvement in Food Resources Up201807051759 1530793746 4459rakesh singhNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument11 pagesRRLERICA DOSADONo ratings yet
- Biology - Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources: Intext QuestionsDocument3 pagesBiology - Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources: Intext QuestionsShailaja MestryNo ratings yet
- Definition, Aim, Objectives and Scope of Plant BreedingDocument137 pagesDefinition, Aim, Objectives and Scope of Plant BreedingYosef AndualemNo ratings yet
- Change CropDocument37 pagesChange CropChristopher Ryan GalganaNo ratings yet
- Physiological Response of Glutinous Corn To Rates of Fermented SeaweedDocument20 pagesPhysiological Response of Glutinous Corn To Rates of Fermented SeaweedMark Iandy Lumamig100% (1)
- Heirloom Gardening and Biodiversity_ Cultivating a Time : Honored Legacy for a Sustainable FutureFrom EverandHeirloom Gardening and Biodiversity_ Cultivating a Time : Honored Legacy for a Sustainable FutureNo ratings yet
- Tomato Factsheet 2013Document4 pagesTomato Factsheet 2013Crystal Redhead-GouldNo ratings yet
- Daphnia e MoinaDocument6 pagesDaphnia e MoinaRosangela D Magalhaes LopesNo ratings yet
- Growth and Yield Perpormance of Pechay FinalDocument25 pagesGrowth and Yield Perpormance of Pechay FinalJaimeh Annabelle100% (2)
- Zeolita EstudiosDocument5 pagesZeolita EstudiosVulcano JerezNo ratings yet
- Coconut Farm Diversification Gasa Engl Corrected 2016 09 15Document33 pagesCoconut Farm Diversification Gasa Engl Corrected 2016 09 15W_ScheeweNo ratings yet
- Pdf2text - 64954ca6d7f9e (AutoRecovered)Document13 pagesPdf2text - 64954ca6d7f9e (AutoRecovered)Shalumaria GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Coconut Cultivators GuideDocument21 pagesCoconut Cultivators GuideArunNo ratings yet
- On-Farm Composting Methods 2003 BOOKDocument51 pagesOn-Farm Composting Methods 2003 BOOKlalibNo ratings yet
- Industrial Survey Report by Sudhershan Gundeti On Ankapur A Model VillageDocument35 pagesIndustrial Survey Report by Sudhershan Gundeti On Ankapur A Model Villagekiranreddy9999No ratings yet
- Ncert Sol For Cbse Class 9 Sci Chapter 15 Improvement in Food ResourcesDocument8 pagesNcert Sol For Cbse Class 9 Sci Chapter 15 Improvement in Food ResourcesShah RukhNo ratings yet
- The Production Problems Include Raw Material AvailabilityDocument46 pagesThe Production Problems Include Raw Material AvailabilityankitsonigaraNo ratings yet
- Composite Fish Culture in HillsDocument20 pagesComposite Fish Culture in HillsSullip MajhiNo ratings yet
- Almanac Start A GardenDocument21 pagesAlmanac Start A GardenAlice Henry0% (1)
- Journal of EcologyDocument324 pagesJournal of EcologyyellowNo ratings yet
- Grade Vi Epp Agri TQ Tos Answers KeyDocument9 pagesGrade Vi Epp Agri TQ Tos Answers Keyanthony100% (1)
- Joel Salatin at Stanford (Feb 2009) Talk NotesDocument11 pagesJoel Salatin at Stanford (Feb 2009) Talk Noteslwu.two100% (4)
- Journal Sukartono 2011, Basic and AppliedDocument6 pagesJournal Sukartono 2011, Basic and AppliedmonikaNo ratings yet
- Ch-1 Crops Production and ManagementDocument7 pagesCh-1 Crops Production and ManagementAryan RoyNo ratings yet
- Sangha Lam ChanchinDocument8 pagesSangha Lam ChanchinKca Khawlhring ChunthangNo ratings yet
- CoffeeDocument10 pagesCoffeepandaypiraNo ratings yet
- Focal Point - Agri-Crop ProductionDocument27 pagesFocal Point - Agri-Crop ProductionGina Baranda Artates100% (1)
- PAES Terms Compilation - PDF Version 1 2Document52 pagesPAES Terms Compilation - PDF Version 1 2RAFAEL TAYO JR.No ratings yet
- Evaluation of Spent Biogas Silage As Casing Soil inDocument3 pagesEvaluation of Spent Biogas Silage As Casing Soil inShailendra RajanNo ratings yet
- Afa Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesAfa Lesson PlanVincent Jay Maat100% (3)
- 8cropproduction101 BieDocument56 pages8cropproduction101 BieDan RicksNo ratings yet
- 14 Dr. Cho 2007 Korean NF - InputsDocument6 pages14 Dr. Cho 2007 Korean NF - InputsRoy Basbas ResurreccionNo ratings yet
- On-Farm Composting: A GuideDocument44 pagesOn-Farm Composting: A GuideGreater Charlotte Harbor Sierra ClubNo ratings yet