Professional Documents
Culture Documents
QB Ch22
QB Ch22
Uploaded by
tateOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
QB Ch22
QB Ch22
Uploaded by
tateCopyright:
Available Formats
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
Chemistry: Chapter 22 Alkanes and alkenes
Multiple-choice questions
Section 22.1
~ |!|CMEMF0052200001|!| |!|CSEMF0052200001|!|
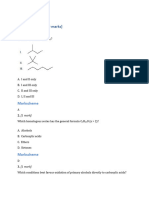
Which of the following compounds is saturated?
A. B.
C. D.
c
|!|CMEMF0052200002|!| |!|CSEMF0052200002|!|
Which of the following structural formulae represents an unsaturated hydrocarbon?
A. B.
C. D.
un &
|!|CMEMF0052200003|!| |!|CSEMF0052200003|!|
Which of the following formulae represent(s) a saturated straight-chain hydrocarbon?
(1) C3H6 Y Cultin +2
(2) C3H8 ~
(3) C4H10 ~
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only D
Section 22.2
|!|CMEMF0052200004|!| |!|CSEMF0052200004|!|
Which of the following statements about the gradual change in properties as the
number of carbon atoms in the members of the alkane series are INCORRECT?
(1) The reactivity with acids decreases.
(2) The molecular mass increases.
(3) The boiling point decreases.
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
|!|CMEMF0052200005|!| |!|CSEMF0052200005|!|
The following equation shows the complete combustion of propane.
C3H8(g) + xO2(g) → yCO2(g) + zH2O(l)
Which of the following combinations is correct?
x y z
A. 4 3 2
B. 5 3 4
C. 6 5 2
D. 7 5 4
|!|CMEMF0052200006|!| |!|CSEMF0052200006|!|
Which of the following substances are NOT produced during the combustion of
alkanes?
A. Carbon dioxide
B. Carbon monoxide
C. Hydrogen
D. Water
|!|CMEMF0052200007|!| |!|CSEMF0052200007|!|
Which of the following statements about alkanes is correct?
A. They have the same molecular formula.
B. They are unsaturated hydrocarbons.
C. They can undergo addition reaction.
D. They can undergo substitution reaction.
|!|CMEMF0052200008|!| |!|CSEMF0052200008|!|
Which of the following statements about substitution reaction are correct?
(1) It is the process of breaking down large molecules into smaller ones.
(2) It involves chemical change.
(3) The reaction between methane and bromine (dissolved in an organic solvent) in
the presence of light is a substitution reaction.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
|!|CMEMF0052200009|!| |!|CSEMF0052200009|!|
Which of the following are substitution reactions?
(1) CH4 + 4Cl2 → CCl4 + 4HCl
(2) CH4 + 2Cl2 → C + 4HCl
(3) CH2Br2 + Br2 → CHBr3 + HBr
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
|!|CMEMF0052200010|!| |!|CSEMF0052200010|!|
Which of the following statements about the reaction of propane with bromine
(dissolved in an organic solvent) are correct?
(1) The reaction does not occur in darkness.
(2) The reaction is a substitution reaction.
(3) The colour of the reaction mixture fades.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
|!|CMEMF0052200011|!| |!|CSEMF0052200011|!|
Which of the following compounds are the products of the reaction between chlorine
(dissolved in an organic solvent) and methane under sunlight?
(1) CH3Cl
(2) CHCl3
(3) CCl4
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
|!|CMEMF0052200012|!| |!|CSEMF0052200012|!|
Excess methane reacts with bromine in the presence of light to give a mixture of
products. Which of the following compounds is the major product?
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
A. Bromomethane
B. Dibromomethane
C. Tribromomethane
D. Tetrabromomethane
|!|CMEMH0052200013|!| |!|CSEMH0052200013|!|
In the presence of light, which of the following reaction mixtures will give the
if ar in excess + after frmony
greatest amount of CH3Cl? CHUT Un CHsUz easily attacked by
othe chlorine radicals
A. 1 mole of methane and 5 moles of chlorine
CHIC Cells -facoved
B. 1 mole of methane and 1 mole of chlorine -
if methas in excess , coloure
radicals will not chance to
C. 5 moles of methane and 1 mole of chlorine milide us methane molecules
D. The above mixture gives equal amounts of CH3Cl. yield of His 24
DXC
|!|CMEMF0052200014|!| |!|CSEMF0052200014|!| S
Which of the following statements about the propagation step of the chlorination of
ethane are correct?
(1) It involves the breaking of covalent bonds.
(2) It involves the formation of covalent bonds.
(3) It involves the formation of free radicals.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
Section 22.3
|!|CMEMF0052200015|!| |!|CSEMF0052200015|!|
Which of the following statements about the cracking of alkane is INCORRECT?
A. It is a chemical change.
B. It is carried out in the absence of oxygen. ~
->
C. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced.
D. Carbon dioxide is produced. Or is absem
*
X Wr
|!|CMEMF0052200016|!| |!|CSEMF0052200016|!|
P
Which of the following are the reasons for cracking heavy oil fractions?
(1) Heavy oil fractions are in less demand and so they are cracked to produce extra
petrol.
(2) Cracking produces alkenes, which can be used to make many useful organic
compounds.
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
(3) Cracking can separate oil fractions with different boiling point ranges.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
|!|CMEMF0052200017|!| |!|CSEMF0052200017|!|
The following diagram shows a fractionating column in oil refining.
fraction W
fraction X
fraction Y
fraction Z
crude oil
Which of the following fractions can be cracked to produce more useful products?
(1) Fraction X
(2) Fraction Y
(3) Fraction Z
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
o
|!|CMEMF0052200018|!| |!|CSEMF0052200018|!|
The equation below shows the cracking of a hydrocarbon.
C20H42 → X + 2C4H8 + H2
What is the molecular formula of compound X?
A. C12H24
B. C12H26
C. C16H34
D. C16H32
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
|!|CMEMF0052200019|!| |!|CSEMF0052200019|!|
Upon cracking, one molecule of octane (C8H18) gives two molecules of ethene and
one molecule of Y. Which of the following is the possible skeletal formula of Y?
A. B.
C. D.
|!|CMEMF0052200020|!| |!|CSEMF0052200020|!|
Consider the following process.
catalyst
C8H18 C6H14 + Y
heat
Which of the following combinations is correct?
Y Process
A. An alkene Cracking
B. An alkene Fractional distillation
C. An alkane Cracking
D. An alkane Fractional distillation
|!|CMEMF0052200021|!| |!|CSEMF0052200021|!|
C18H38 is cracked to C9H20, C4H10, C and 2X when heated with a catalyst. Which of
the following substances would X be?
A. C2H4
B. C2H6
C. C3H8
D. C4H8
|!|CMEMH0052200022|!| |!|CSEMH0052200022|!|
A long-chain alkane, heptadecane (C17H36), is cracked. One possible reaction can be
represented by the following equation:
C17H36 → X + Y + Z + C
In the equation, X and Y are saturated hydrocarbons and Z is an unsaturated
hydrocarbon. Which of the following combinations is INCORRECT?
X Y Z
A. C4H10 C9H20 C3H6
B. C5H12 C9H18 C2H4
C. C9H20 C3H8 C4H8
D. C6H14 C8H18 C2H4
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
|!|CMEMH0052200023|!| |!|CSEMH0052200023|!|
The following equation represents the cracking of a straight-chained alkane.
C22H46 → 2X + 3Y
It is known that Y reacts with bromine to give a steamy fume. Which of the following
is the possible chemical formula of Y?
A. C4H8
B. C4H10
C. C5H10
D. C5H12
|!|CMEMF0052200024|!| |!|CSEMF0052200024|!|
The following diagram shows the cracking of paraffin.
broken pieces of porous pot
glass wool soaked
with paraffin heat
tube X tube Y
universal bromine (dissolved in
indicator tetrachloromethane)
Which of the following statements about the experiment is/are correct?
(1) Universal indicator in tube X turns red.
(2) The bromine solution in tube Y is decolorized.
(3) The broken pieces of porous pot can be replaced by aluminium oxide.
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
|!|CMEMF0052200025|!| |!|CSEMF0052200025|!|
The following diagram shows the set-up of an experiment.
pumice stones
glass wool soaked
with kerosene heat
solution X
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
Which of the following combinations about solution X is correct?
Solution X Colour change
A. Acidified potassium dichromate From orange to green
B. Acidified potassium permanganate From purple to colourless
C. Bromine From colourless to red-orange
D. Phenolphthalein From pink to colourless
|!|CMEMF0052200026|!| |!|CSEMF0052200026|!|
Which of the following is NOT the safety precaution for cracking experiment in the
school laboratory?
A. Wear safety goggles.
B. Perform the experiment in the fume cupboard.
C. Heat the catalyst evenly.
D. Stop heating before pulling the delivery tube out of the water.
Section 22.4
|!|CMEMF0052200027|!| |!|CSEMF0052200027|!|
Which of the following statements about propene are correct?
(1) The chemical formula of propene is C3H8.
(2) It is an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
(3) It has the same number of carbon atoms as propane.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
|!|CMEMF0052200028|!| |!|CSEMF0052200028|!|
Organic compound G is an acid and can decolorize bromine (dissolved in an organic
solvent) in the dark. Which of the following formulae may G be?
A. CH3CH2CH=CH2
B. CH3CH2CH2CO2H
C. CH3CH2CO2CH3
D. CH2=CHCH2CO2H
|!|CMEMF0052200029|!| |!|CSEMF0052200029|!|
Which of the following statements about ethene and ethane is correct?
A. They can undergo addition reaction with halogens (dissolved in an organic
solvent).
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
B. They can undergo substitution reaction with halogens.
C. They can undergo combustion to give carbon dioxide and water.
D. They can be oxidized by acidified potassium permanganate solution.
ethane X react
permanganate
us audited potassium
solution
c
|!|CMEMF0052200030|!| |!|CSEMF0052200030|!|
Which of the following methods can be used to distinguish between ethane and
ethene?
(1) Bubbling the gases into bromine (dissolved in an organic solvent) in the dark.
(2) Bubbling the gases into universal indicator.
(3) Bubbling the gases into acidified potassium permanganate solution.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
|!|CMEMF0052200031|!| |!|CSEMF0052200031|!| alkene
Which
we
of the following statements about two straight-chain hydrocarbons C6H12 and
all
C7H16 is correct?
A. They belong to the same homologous series.
liquid
B. They are gases at room conditions.
Cli2
C. They can undergo addition reaction.
D. They can undergo redox reaction.
D
|!|CMEMF0052200032|!| |!|CSEMF0052200032|!|
Consider the following reaction:
Which of the following types of reaction is/are involved in the above reaction?
(1) Addition reaction
(2) Substitution reaction
(3) Redox reaction
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
|!|CMEMF0052200033|!| |!|CSEMF0052200033|!|
Which of the following statements concerning the reaction of chlorine with propene
is/are correct?
(1) The reaction is an addition reaction.
(2) 1,3-dichloropropane is the organic product of the reaction.
(3) Sunlight is required for the reaction to occur.
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
|!|CMEMF0052200034|!| |!|CSEMF0052200034|!|
Which of the following compounds is the product of the following reaction?
A. B.
C. D.
|!|CMEMH0052200035|!| |!|CSEMH0052200035|!|
Which of the following compounds is the product of the reaction between
1-chlorobut-2-ene and bromine?
A. B.
C. D.
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
|!|CMEMF0052200036|!| |!|CSEMF0052200036|!|
Gas A is bubbled into B as shown in the following diagram. B shows a colour change.
Which of the following combinations is correct?
A B
(1) Ammonia Dilute sulphuric acid
(2) Propene Acidified potassium permanganate solution
(3) Carbon dioxide Phenolphthalein
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
|!|CMEMF0052200037|!| |!|CSEMF0052200037|!|
1 mole of an alkene reacts completely with 2 moles of chlorine. Which of the
following is probably the structure of the alkene?
A. B.
C. D.
|!|CMEMF0052200038|!| |!|CSEMF0052200038|!|
Consider the following compound.
(a) What is the systematic name of the compound?
A. 1-chloro-5-hydroxylpenta-1,3-diene
B. 5-chloro-1-hydroxylpenta-2,4-diene
C. 1-chloropen-1,3-dien-5-ol
D. 5-chloropen-2,4-dien-1-ol
(b) Which of the following statements about the compound is correct?
A. It is a saturated compound.
B. It is a hydrocarbon.
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
C. It is an alkali.
D. It can decolorize bromine solution in the dark.
|!|CMEMF0052200039|!| |!|CSEMF0052200039|!|
What is the systematic name of the product for the reaction between but-2-ene and
acidified potassium permanganate solution?
A. Butan-1-ol
B. Butan-2-ol
C. Butane-1,2-diol
D. Butane-2,3-diol
Sections 44.1−44.2
|!|CMEMF0114400001|!|
Which of the following conditions are required for alkanes to undergo substitution
reactions with bromine?
(1) Sunlight
(2) High temperature
(3) High pressure
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
|!|CMEMF0114400002|!|
Which of the following compounds is the major product of the reaction between
excess methane and chlorine?
A. Chloromethane
B. Dichloromethane
C. Trichloromethane
D. Tetrachloromethane
|!|CMEMF0114400003|!|
Which of the following compounds are the products from the reaction between
methane and chlorine in the presence of light?
(1) Chloromethane
(2) Chloroform
(3) Hydrogen chloride
A. (1) and (2) only
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
|!|CMEMF0114400004|!|
Which of the following statements about the substitution reaction between propane
and chlorine are correct?
(1) It does not take place in the dark. ~
(2) It involves the breaking of C−H bonds in the initiation step. X
(3) Hydrogen chloride is one of the products of the reaction. ~
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
B-
|!|CMEMF0114400005|!|
Which of the following statements about the substitution reaction between methane
and chlorine are correct?
(1) The product of the reaction is a mixture of chloroalkanes.
(2) The major product is tetrachloromethane if excess chlorine is used.
(3) Free radicals are produced during the reaction.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
|!|CMEMF0114400006|!|
Ethane gas and chlorine gas are allowed to react. Which of the following statements
about the reaction is/are correct?
(1) It is a substitution reaction.
(2) It is a polymerization reaction. X
(3) It is a chain reaction.
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
u
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
Section 44.3
|!|CMEMF0114400007|!|
Which of the following compounds is the major product of the addition reaction
between hydrogen chloride and propene?
A. 1-chloropropane
B. 2-chloropropane
C. 1,2-dichloropropane
D. 2,2-dichloropropane
|!|CMEMF0114400008|!|
Which of the following combinations about addition reactions is correct?
Addition reaction Major product
A. CH3CH=CH2 + HBr CH3CH2CH2Br
B. (CH3)2C=CH2 + HBr (CH3)3CBr
C. BrCH=CH2 + HBr BrCH2CH2Br
D. (CH3)3CCH=CH2 + HBr (CH3)3CCH2CH2Br
|!|CMEMF0114400009|!|
Which of the following statements about but-1-ene are correct?
(1) It reacts with hydrogen chloride to give 1-chlorobutane as the major product.
(2) It can decolorize acidified potassium permanganate solution.
(3) It undergoes hydrogenation in the presence of platinum.
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
|!|CMEMF0114400010|!|
Which of the following compounds is the major product of the reaction between
2,5-dimethylhex-2,4-diene and excess hydrogen bromide?
A. 3,5-dibromo-2,5-dimethylhexane
B. 2,4-dibromo-2,5-dimethylhexane
C. 3,4-dibromo-2,5-dimethylhexane
D. 2,5-dibromo-2,5-dimethylhexane
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
|!|CMEMF0114400011|!|
Hydrogen bromide is allowed to react with excess 2,4,7,7-tetramethylhept-2,4-diene:
+ HBr
Which of the following compounds is/are the possible major product(s) of the
reaction?
(1)
(2)
(3)
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
|!|CMEMF0114400012|!|
Which of the following can be classified as addition reactions?
(1) Reaction between methane and chlorine
(2) Reaction between ethene and hydrogen
(3) Reaction between chloroethene and hydrogen chloride
A. (1) only
B. (2) only
C. (1) and (3) only
D. (2) and (3) only
|!|CMEMF0114400013|!|
Which of the following statements about propene are correct?
(1) It reacts with hydrogen in the presence of platinum to give propane.
(2) It reacts with hydrogen chloride to give 1-chloropropane as the major product.
(3) It decolorizes bromine solution in the dark.
A. (1) and (2) only
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
|!|CMEMF0114400014|!|
Which of the following compounds is the major product for the reaction between
2-methylpropene and hydrogen chloride?
A. 1-chloro-2-methylpropane CHs
B. 1,2-dichloro-2-methylpropane S
C-0-f MU
C. 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
D. 2-methylpropane
-
|!|CMEMF0114400015|!|
Which of the following compounds is the product for the reaction between
penta-1,4-diene and excess bromine?
A. 1,2-dibromopentane
B. 2,4-dibromopentane
C. 4,5-dibromopentane
D. 1,2,4,5-tetrabromopentane
|!|CMEMF0114400016|!|
Which of the following compounds is the major product for the reaction between
buta-1,3-diene and hydrogen iodide?
A. 1,4-diiodobutane
B 2,4-diiodobutane C 1 1 =2
=
-
C. 1,3-diiodobutane
D. 2,3-diiodobutane
D
|!|CMEMF0114400017|!|
Which of the following reactions are addition reactions?
(1) CH2=CHCH=CH2 + HI
(2) CH3CH2CH2CH3 + Cl2
(3) CH2=CHCH2CH3 + H2
A. (1) and (2) only
B. (1) and (3) only
C. (2) and (3) only
D. (1), (2) and (3)
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
HKDSE CHEMISTRY — A Modern View (Second Edition)
Part V Fossil fuels and carbon compounds
|!|CMEMF0114400018|!|
Consider the following compound:
Which of the following statements about the compound is INCORRECT?
A. The systematic name of the compound is 2,3-dichloropropene.
B. The compound is insoluble in water.
C. It reacts with hydrogen bromide to give 1-bromo-2,3-dichloropropane as the
major product.
D. It reacts with chlorine (dissolved in an organic solvent) to give a
1,2,2,3-tetrachloropropane.
|!|CMEMF0114400020|!|
Which of the following statements about propene is correct?
A. It can decolorize acidified potassium dichromate solution.
B. It can be prepared by heating propan-1-ol with dilute sulphuric acid.
C. It reacts with hydrogen in the presence of platinum to give propane.
D. It reacts with hydrogen chloride to give 1-chloropropane as the major
product.
Chemistry: Chapter 22 Alkanes and alkenes
Combined Science (Chemistry Part): Chapter 22 Alkanes and alkenes
Structured questions
Sections 22.1−22.2
|!|CMELF0052200001|!| |!|CSELF0052200001|!|
The table below shows some information of the first four members of the alkane
series.
Formula Relative molecular mass Boiling point (C)
CH4 16.0 −161
C2H6 30.0 −89
C3H8 44.0 −42
C4H10 58.0 −0.5
(a) Alkanes are hydrocarbons. What is meant by ‘hydrocarbons’? (1 mark)
(b) (i) What is the general formula of alkanes? (1 mark)
© Aristo Educational Press Ltd 2014 Chapter 22
You might also like
- Pub A History of Everyday Life in Scotland 1800 1900Document345 pagesPub A History of Everyday Life in Scotland 1800 1900MioaraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Structure and Preparation of Alkenes - Elimination ReactionsDocument13 pagesChapter 5: Structure and Preparation of Alkenes - Elimination ReactionsRahma AshrafNo ratings yet
- 3) DNA Replication-GenesDocument6 pages3) DNA Replication-GenesAlbertoNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Interference and CompatibilityDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Interference and CompatibilityYuvaraja50% (2)
- QB Ch23Document8 pagesQB Ch23tateNo ratings yet
- Trial Chemistry Sem 3Document14 pagesTrial Chemistry Sem 3Nurul FarhanaNo ratings yet
- Đề Cương Học Phần Hoá Hữu Cơ Lớp D2022Document17 pagesĐề Cương Học Phần Hoá Hữu Cơ Lớp D2022Cảnh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Alkanes and AlkenesDocument8 pagesAlkanes and Alkenesskylar chanNo ratings yet
- Ch46 Reactions of Various Function MCQDocument22 pagesCh46 Reactions of Various Function MCQtoperissaNo ratings yet
- DSE 5-8 MC - AnsDocument24 pagesDSE 5-8 MC - AnsSherry LeeNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument18 pagesChemLINDSAY PALAGANASNo ratings yet
- De Cuong HHCDocument42 pagesDe Cuong HHCNguyễn DuyênNo ratings yet
- Radicals PDFDocument34 pagesRadicals PDFadelNo ratings yet
- ALKANES Sheet-1Document4 pagesALKANES Sheet-1Vinod AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Alkanes Alkenes AlkynesDocument10 pagesAlkanes Alkenes AlkynesPanda Boy100% (2)
- Topic 10 SL CHEM QuestionsDocument32 pagesTopic 10 SL CHEM QuestionsWalter Jose Velasquez100% (1)
- Alka NetDocument13 pagesAlka Netjonida88No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes HaloarenesDocument12 pagesHaloalkanes Haloarenessameerkumargupta74No ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry 9Th Edition Carey Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesOrganic Chemistry 9Th Edition Carey Test Bank Full Chapter PDFtonya.paongo686100% (11)
- Alkyl Halides, Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides: 1. What Is The IUPAC Name For CHDocument17 pagesAlkyl Halides, Alcohols, Ethers and Epoxides: 1. What Is The IUPAC Name For CHEllaŠtrbacNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde KetoneDocument5 pagesAldehyde Ketonehareharanbt22No ratings yet
- uSiUkKOBYNXsDocument9 pagesuSiUkKOBYNXsrashidnazir1918No ratings yet
- Safari - 24 Apr 2020 at 1:57 AMDocument1 pageSafari - 24 Apr 2020 at 1:57 AMAgatha chilesheNo ratings yet
- 15 CHEMISTRY Some Basic Principles & Techniques HydrocarbonsDocument3 pages15 CHEMISTRY Some Basic Principles & Techniques HydrocarbonsHasan shaikhNo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-12-28 at 6.20.02 PMDocument35 pagesScreenshot 2023-12-28 at 6.20.02 PM20191g070No ratings yet
- Topic 10 20 MC PracticeDocument17 pagesTopic 10 20 MC PracticePipen 5No ratings yet
- Chem Test No. 4 (Alkyl Halides, Alcohol and Phenols)Document4 pagesChem Test No. 4 (Alkyl Halides, Alcohol and Phenols)fahadmustafa100% (1)
- PB Xii Chem 2023-24Document6 pagesPB Xii Chem 2023-24NehaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem Intro Qs 3.: (Total 1 Mark)Document7 pagesOrganic Chem Intro Qs 3.: (Total 1 Mark)Nika Johanne SCHOLTENo ratings yet
- Chemistry 2018 FinalDocument24 pagesChemistry 2018 FinalmilapdhruvcomputerworkNo ratings yet
- HydrocarbonsDocument116 pagesHydrocarbonsabhisheksingh27zxNo ratings yet
- Halo AlkaneDocument4 pagesHalo Alkanetechnicalgamerz818No ratings yet
- St. Mark's Sr. Sec. Public School, Janakpuri PA-II Exam Class XII Subject: ChemistryDocument22 pagesSt. Mark's Sr. Sec. Public School, Janakpuri PA-II Exam Class XII Subject: ChemistryPp PpNo ratings yet
- 2012 Hkdse Chem Mock 1aDocument10 pages2012 Hkdse Chem Mock 1aSiming Huang (。。。。。。)No ratings yet
- Chemistry Mock ExamDocument6 pagesChemistry Mock ExamLauraNo ratings yet
- Sri Bhagawan Mahaveer Jain Collge Chemistry: Mock Paper 1 Part A IDocument4 pagesSri Bhagawan Mahaveer Jain Collge Chemistry: Mock Paper 1 Part A IChiranjivi ChiruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23: Substitution Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds at The Alpha-CarbonDocument26 pagesChapter 23: Substitution Reactions of Carbonyl Compounds at The Alpha-CarboneliNo ratings yet
- 10th Foundation - Chemistry (23-09-2023)Document6 pages10th Foundation - Chemistry (23-09-2023)prince2216jNo ratings yet
- TimidDocument13 pagesTimid公孫堂傲100% (2)
- Grade 12 Chemistry Model Exam Final Version-OEB-2024Document10 pagesGrade 12 Chemistry Model Exam Final Version-OEB-2024bunniabebeNo ratings yet
- Organic Problems1Document9 pagesOrganic Problems1Sung-Eun KimNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry ExamDocument5 pagesOrganic Chemistry ExamfyajNo ratings yet
- ORGANIC20CHEMISTRY20POST20TESTDocument13 pagesORGANIC20CHEMISTRY20POST20TESTJan Mill100% (1)
- A (2e, 4e) B (2Z, 4Z) C (2Z, 4e) D (2e, 4Z)Document1 pageA (2e, 4e) B (2Z, 4Z) C (2Z, 4e) D (2e, 4Z)Agatha chilesheNo ratings yet
- 01 HydrocarbonsDocument6 pages01 HydrocarbonslingarajugowdaNo ratings yet
- Alkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes and Their Alicyclic Couterparts: 1. What Is The IUPAC Name For CHDocument17 pagesAlkanes, Alkenes, Alkynes and Their Alicyclic Couterparts: 1. What Is The IUPAC Name For CHEllaŠtrbac100% (1)
- HKDSE Chemistry 2014 Paper1ADocument12 pagesHKDSE Chemistry 2014 Paper1ABILLYNG33050% (2)
- Chemistry: Supportive Seminars For G.C.E. (A/L) - 2012 Revision PaperDocument10 pagesChemistry: Supportive Seminars For G.C.E. (A/L) - 2012 Revision Papersivalingam vasanNo ratings yet
- Examen 1Document12 pagesExamen 1Sahimara de JesúsNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument133 pagesQuestion BankBabar AliNo ratings yet
- Chem Practice Paper 3 QPDocument10 pagesChem Practice Paper 3 QPSANAJ BSNo ratings yet
- 英華女學校 2020 Mock Paper 1A Answer (at bottom) - TikadoDocument13 pages英華女學校 2020 Mock Paper 1A Answer (at bottom) - TikadoOof GucciNo ratings yet
- First Organic WorksheetDocument16 pagesFirst Organic WorksheetZoya AzeemNo ratings yet
- Topic 10 Paper 1Document30 pagesTopic 10 Paper 1RawanMazen SharifNo ratings yet
- Chemistry A Level Paper 2 2012Document12 pagesChemistry A Level Paper 2 2012Baiye RandolfNo ratings yet
- IsomerismDocument16 pagesIsomerismAnusmita MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Chem e TermDocument6 pagesChem e TermchituNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYCET-16thOCT Ixm5pzgcfy8k2ejcDocument7 pagesCHEMISTRYCET-16thOCT Ixm5pzgcfy8k2ejcanuNo ratings yet
- Ch12org MetalicoDocument21 pagesCh12org MetaliconicoleNo ratings yet
- There Is No Negative MarkingDocument9 pagesThere Is No Negative MarkingDrk ZeusNo ratings yet
- A&B Education Centre: Chemistry Paper IDocument12 pagesA&B Education Centre: Chemistry Paper IUniversityJCNo ratings yet
- Hardware - SoftwareDocument12 pagesHardware - SoftwareMarie Kelsey Acena MacaraigNo ratings yet
- Unit Hydrographs: Transforming The RunoffDocument69 pagesUnit Hydrographs: Transforming The RunoffShriganesh ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Jasmine F Slaughter - Day&Zimmerman - Fall2011Document22 pagesJasmine F Slaughter - Day&Zimmerman - Fall2011studentATtempleNo ratings yet
- 20T Wheat Flour Milling PlantDocument12 pages20T Wheat Flour Milling Plantshio29100% (2)
- Ultra Tech CementDocument14 pagesUltra Tech CementRaunak Doshi71% (14)
- Receta PastelDocument5 pagesReceta PastelJesus BeltranNo ratings yet
- Quality Management Principles For Excellence: by - Sacchidanand Gogawale, Zen International SystemsDocument5 pagesQuality Management Principles For Excellence: by - Sacchidanand Gogawale, Zen International SystemsSanjeevani GogawaleNo ratings yet
- Diagnosisofmyasthenia Gravis: Mamatha Pasnoor,, Mazen M. Dimachkie,, Constantine Farmakidis,, Richard J. BarohnDocument14 pagesDiagnosisofmyasthenia Gravis: Mamatha Pasnoor,, Mazen M. Dimachkie,, Constantine Farmakidis,, Richard J. BarohnLilisNo ratings yet
- Hypertension Dash DietDocument32 pagesHypertension Dash DietKAUSHAL ARYA100% (1)
- Day 1 Exam 1Document3 pagesDay 1 Exam 1Cheng PasionNo ratings yet
- OHSAS Hazard Identification & Risk Assessment HIRADocument15 pagesOHSAS Hazard Identification & Risk Assessment HIRASwati joshiNo ratings yet
- Shindengen: Super Fast Recovery RectifiersDocument7 pagesShindengen: Super Fast Recovery Rectifiersjoroma58No ratings yet
- Arthropod Borne Infections - MHA (12 Files Merged)Document377 pagesArthropod Borne Infections - MHA (12 Files Merged)MariaNo ratings yet
- Shipping Container PreservationDocument16 pagesShipping Container PreservationMohamed Sahnoun100% (1)
- CuttackDocument6 pagesCuttackbaivabi priyadarshiniNo ratings yet
- Manuscript - Dark and Light Triad - 2022Document15 pagesManuscript - Dark and Light Triad - 2022Mihaela-AlexandraGhermanNo ratings yet
- Homeopathic Remedies For 'Flu - Flow ChartDocument1 pageHomeopathic Remedies For 'Flu - Flow Chartisadore97% (32)
- MTD REPAIR MANUAL FOR P90 ENGINE 769 - 06294 - p90 - EngineDocument120 pagesMTD REPAIR MANUAL FOR P90 ENGINE 769 - 06294 - p90 - EngineMalte BreitlowNo ratings yet
- At 221 Auto Service Shop Maintenance 1Document18 pagesAt 221 Auto Service Shop Maintenance 1Charlene Fernandez MutiaNo ratings yet
- Application Form For Registration of Job ContractingDocument1 pageApplication Form For Registration of Job ContractingKris Borlongan100% (1)
- Childhood EducationDocument19 pagesChildhood EducationCharlyn Mae Abedes EbuengaNo ratings yet
- VIVA - TarrifDocument1 pageVIVA - TarrifSrinivas VadtheNo ratings yet
- Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment WorksheetDocument4 pagesHazard Identification and Risk Assessment WorksheetNaveed Ahmed Get-InfoNo ratings yet
- Ict - Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesIct - Lesson Planapi-249343709100% (2)
- Sheep Diseases - The Farmers Guide - 2nd Edition - July 2015Document84 pagesSheep Diseases - The Farmers Guide - 2nd Edition - July 2015Raghu NathaNo ratings yet
- DCP082 Motorized Screw JackDocument3 pagesDCP082 Motorized Screw JackANAND KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Aecc 2 EnvsDocument12 pagesAecc 2 Envssaha7003810868No ratings yet