Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Computer Science - Questions
Computer Science - Questions
Uploaded by
Adithya NathanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Final Exam - PROG1815 Programming Concepts IIDocument3 pagesFinal Exam - PROG1815 Programming Concepts IIKeerthi meher NadimpalliNo ratings yet
- DBMS Mini Project ...Document15 pagesDBMS Mini Project ...sandhya kondapurNo ratings yet
- Exam Az 303 Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies Skills MeasuredDocument5 pagesExam Az 303 Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies Skills MeasuredpradhyumnNo ratings yet
- Rockwell Automation PLCDocument212 pagesRockwell Automation PLCramorado0% (1)
- CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Syllabus 2023 24Document4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Computer Science Syllabus 2023 24Aanchal MakhijaniNo ratings yet
- 12 Computerscience Eng 2024 25Document4 pages12 Computerscience Eng 2024 25rahulkumar200721No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Syllabus 2022 23Document4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Computer Science Syllabus 2022 23Devansh ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Class-Xii Code No. 083 2021-22 1. Prerequisites 2. Learning OutcomesDocument4 pagesComputer Science Class-Xii Code No. 083 2021-22 1. Prerequisites 2. Learning OutcomesHarsh DugarNo ratings yet
- Cs MayDocument3 pagesCs Maytalktoarnab507No ratings yet
- 12 CSDocument107 pages12 CSrohitvk92No ratings yet
- Computer Science: I II IIIDocument5 pagesComputer Science: I II IIIAppan DNo ratings yet
- Xii Cs Study Material (2022-23)Document305 pagesXii Cs Study Material (2022-23)Arun SharmaNo ratings yet
- REVISED12 - SR - SEC. - Computer Science - 2020-21Document5 pagesREVISED12 - SR - SEC. - Computer Science - 2020-21Prasanta K PattadarNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Class-Xii Code No. 083 2021-22 1. Prerequisites 2. Learning OutcomesDocument5 pagesComputer Science Class-Xii Code No. 083 2021-22 1. Prerequisites 2. Learning OutcomesSiddharth NarsipurNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Cs 083 Syllabus 2023 24Document4 pagesClass Xii Cs 083 Syllabus 2023 24somojitroy80No ratings yet
- Class-Xii Code No. 083 2021-22 1. Prerequisites 2. Learning Outcomes CBSE Class 12 Term Wise Computer Science Syllabus 2021-22Document5 pagesClass-Xii Code No. 083 2021-22 1. Prerequisites 2. Learning Outcomes CBSE Class 12 Term Wise Computer Science Syllabus 2021-22Jazzy KingNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Class-Xii Code No. 083 2022-23: 1. PrerequisitesDocument4 pagesComputer Science Class-Xii Code No. 083 2022-23: 1. PrerequisitesKashvi BhatiaNo ratings yet
- 12 Syllabus 2023 Computer ScienceDocument4 pages12 Syllabus 2023 Computer ScienceAbhinavNo ratings yet
- Student Support Material For All Student - Class - XII - CSDocument238 pagesStudent Support Material For All Student - Class - XII - CSKaviya SankarNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School (Joka) South Kolkata: Class - Xii Computer ScienceDocument3 pagesDelhi Public School (Joka) South Kolkata: Class - Xii Computer Sciencesab108No ratings yet
- 2016 Syllabus 12 Computer ScienceDocument8 pages2016 Syllabus 12 Computer ScienceSamit BasuNo ratings yet
- Computer Science (Theory) : Class XII (Theory) - PythonDocument8 pagesComputer Science (Theory) : Class XII (Theory) - PythonVivaan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Class XII Study Material KV 2022-23Document183 pagesClass XII Study Material KV 2022-23Probably ArthNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Python 2020-21 LatestDocument3 pagesComputer Science Python 2020-21 LatestPriyanshu UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Computer Science (New) : Class-Xii Code No. 083 2019-20Document3 pagesComputer Science (New) : Class-Xii Code No. 083 2019-20TuaNo ratings yet
- PDF 5Document2 pagesPDF 5raj thoughtzzNo ratings yet
- 12 IpDocument127 pages12 Ipallyourneeds8682No ratings yet
- Computer ScienceDocument9 pagesComputer ScienceammullubNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Computer Science 2024 XIIDocument4 pagesSyllabus Computer Science 2024 XIIharshsingh14oct2006No ratings yet
- Computer Science (New) : Class-Xii Code No. 083 2019-20Document4 pagesComputer Science (New) : Class-Xii Code No. 083 2019-20Gaurav BhattNo ratings yet
- Computer Science (Theory) Class XII (Theory) - PythonDocument8 pagesComputer Science (Theory) Class XII (Theory) - PythonAnu RadhaNo ratings yet
- Class - Xii: Split-Up Syllabus Sub: Computer ScienceDocument3 pagesClass - Xii: Split-Up Syllabus Sub: Computer ScienceTech ArmyNo ratings yet
- 98 Ne HF 3 e We Eokqq IWMx 4Document2 pages98 Ne HF 3 e We Eokqq IWMx 4mp9414751No ratings yet
- 12 Class Syllabus 2011Document7 pages12 Class Syllabus 2011Chandresh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Computer Science SyllabusDocument1 pageClass 12 Computer Science Syllabusanubhavdas552006No ratings yet
- Termwise Syllabus Class - XI Computer Science (New) Code No. 083 Session 2019-20Document3 pagesTermwise Syllabus Class - XI Computer Science (New) Code No. 083 Session 2019-20Mobin Ahmed KingNo ratings yet
- CS Term II Cochin Region XII NOTESDocument139 pagesCS Term II Cochin Region XII NOTESoneplus3liteNo ratings yet
- Cbse CurriculumDocument6 pagesCbse CurriculumTechbuzz dav14ggmNo ratings yet
- Informatics Practices 2021-22Document9 pagesInformatics Practices 2021-22Aayush KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit No Unit Name Marks Periods Theory Periods Practical Total PeriodDocument9 pagesUnit No Unit Name Marks Periods Theory Periods Practical Total PeriodParineeta SinghNo ratings yet
- IP Gr12 StudyMaterialsDocument130 pagesIP Gr12 StudyMaterialsworksheet215No ratings yet
- Class Xii Computer Science Split Up 2024Document3 pagesClass Xii Computer Science Split Up 2024shreyasinghchampNo ratings yet
- 2 Computer Science and Application 1Document5 pages2 Computer Science and Application 1samiranchawrokNo ratings yet
- ADP Module-1Document116 pagesADP Module-1Vikas RNo ratings yet
- INT213Document2 pagesINT213Md. SakeelNo ratings yet
- Ip 12Document4 pagesIp 12sahusoubhagyaranjan72No ratings yet
- Core SyllabusDocument28 pagesCore SyllabusNìkèt SαínìNo ratings yet
- 1st Semester B.SC (H) Computer Science SyllabusDocument10 pages1st Semester B.SC (H) Computer Science SyllabusmaakaffNo ratings yet
- 15 Information Practices NewDocument6 pages15 Information Practices NewJAGANNATH THAWAITNo ratings yet
- Computer ScienceDocument3 pagesComputer ScienceAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- Informatics PracticesDocument9 pagesInformatics Practicesdadan vishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- CSGE 101 Programming Using Python 32345104Document7 pagesCSGE 101 Programming Using Python 32345104Aditya VashisthNo ratings yet
- 11 Informationpractices Eng 2024 25Document3 pages11 Informationpractices Eng 2024 25kiransharmmaa937No ratings yet
- 11 Informationpractices Eng 2024 25Document3 pages11 Informationpractices Eng 2024 25singhragho020No ratings yet
- Question Bank 2023-24 Computer ScienceDocument146 pagesQuestion Bank 2023-24 Computer Sciencekalpanapradhan1179No ratings yet
- Python SyllabusDocument3 pagesPython SyllabusSamaksh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 PythonDocument10 pagesUnit 5 PythonVikas PareekNo ratings yet
- Student Support Material - Comp. Sc. XII (2024-25)Document175 pagesStudent Support Material - Comp. Sc. XII (2024-25)DEV 8CNo ratings yet
- Informatics Practices: Class Xii Code No. 065 2021-2022Document5 pagesInformatics Practices: Class Xii Code No. 065 2021-2022Dhruv jainNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Computer Science 2023Document2 pagesCBSE Class 12 Computer Science 2023vaishnavisoni32No ratings yet
- Informatics PracticesDocument4 pagesInformatics PracticesAtanuBhandaryNo ratings yet
- XI-CS Study Material 2023-24Document142 pagesXI-CS Study Material 2023-242pwxanqt8aNo ratings yet
- Mastering Python Programming: A Comprehensive Guide: The IT CollectionFrom EverandMastering Python Programming: A Comprehensive Guide: The IT CollectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mastering Python: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners and ExpertsFrom EverandMastering Python: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners and ExpertsNo ratings yet
- Pre - Board 2 STD 10 ScienceDocument9 pagesPre - Board 2 STD 10 ScienceMihir MishraNo ratings yet
- English ProjectDocument19 pagesEnglish ProjectMihir MishraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - SrSec - 2023 24 Pages 7 13Document7 pagesChemistry - SrSec - 2023 24 Pages 7 13Mihir MishraNo ratings yet
- English - Core - SrSec - 2023 24 Pages 10 12Document3 pagesEnglish - Core - SrSec - 2023 24 Pages 10 12Mihir MishraNo ratings yet
- pg168 GtwizardDocument154 pagespg168 GtwizardNguyễn HạnhNo ratings yet
- Abb Irc5 Application ManualDocument64 pagesAbb Irc5 Application ManualRAFAEL CARDOSONo ratings yet
- Vira Jaya Computer Mangga Dua Mal LTDocument6 pagesVira Jaya Computer Mangga Dua Mal LTPapa Beatrix100% (1)
- Fault Recorder120 071Document21 pagesFault Recorder120 071O P Sridharan PerumalNo ratings yet
- PPIF0542-014 Payshield 9000 Software and License Update ProcedureDocument9 pagesPPIF0542-014 Payshield 9000 Software and License Update ProcedureAlexey KhotulevNo ratings yet
- Oracle: Question & AnswersDocument11 pagesOracle: Question & AnswersRafael BarrosNo ratings yet
- What Is BootingDocument3 pagesWhat Is Bootingramanan_rapiddNo ratings yet
- AppssynonymsDocument42 pagesAppssynonymsEmilia RomeroNo ratings yet
- Final Part OneDocument14 pagesFinal Part OneVishavjeetDevganNo ratings yet
- Progress ReportDocument3 pagesProgress Reportapi-581166535No ratings yet
- SNAP Load InstructionsDocument1 pageSNAP Load InstructionsDaniel ChiriacNo ratings yet
- b0193wq MDocument84 pagesb0193wq MAnonymous nVMYT3AEO100% (2)
- How To Upgrade Esxi 6Document4 pagesHow To Upgrade Esxi 6Kiệt Trần TrungNo ratings yet
- New PPT Nursing InfromaticsDocument35 pagesNew PPT Nursing InfromaticsSusi SeptianiNo ratings yet
- Slip PP ProtocolDocument3 pagesSlip PP Protocolabhishektanu87No ratings yet
- DTE MicroprojectDocument22 pagesDTE MicroprojectShreyas Bagate100% (1)
- Django Money Readthedocs Io en StableDocument29 pagesDjango Money Readthedocs Io en Stablemuhammad safwanNo ratings yet
- 1670 Petra UMA MB-Aspire V5-531 V5-571-11324Document103 pages1670 Petra UMA MB-Aspire V5-531 V5-571-11324juan carlosNo ratings yet
- Vonino Firmware Upgrade ProcedureDocument8 pagesVonino Firmware Upgrade ProcedureIonut GrigoreNo ratings yet
- Emu LogDocument1 pageEmu LogMayke OchoaNo ratings yet
- TMF1434 - Data Structure & Algorithms Assignment - UNIMAS Kiosk Point of Sale System Sem 02, 2022/2023Document2 pagesTMF1434 - Data Structure & Algorithms Assignment - UNIMAS Kiosk Point of Sale System Sem 02, 2022/2023Adry NietzscheNo ratings yet
- AWS Command Line Interface Part 1Document22 pagesAWS Command Line Interface Part 1Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Polycab End User Manual V1 PDFDocument6 pagesPolycab End User Manual V1 PDFrkl007No ratings yet
- Cloudguard Cnapp Final - DesignedDocument36 pagesCloudguard Cnapp Final - DesignedGfact MailNo ratings yet
- Connectivity Screening FormDocument3 pagesConnectivity Screening Form1304 RecordsNo ratings yet
- Send A Smartform Through Mail Using OopsDocument8 pagesSend A Smartform Through Mail Using OopsRicky DasNo ratings yet
Computer Science - Questions
Computer Science - Questions
Uploaded by
Adithya NathanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Science - Questions
Computer Science - Questions
Uploaded by
Adithya NathanCopyright:
Available Formats
Computer Science
CLASS-XII
Code No. 083
2023-24
1. Prerequisites
Computer Science- Class XI
2. Learning Outcomes
Student should be able to
a) apply the concept of function.
b) explain and use the concept of file handling.
c) use basic data structure: Stacks
d) explain basics of computer networks.
e) use Database concepts, SQL along with connectivity between Python and SQL.
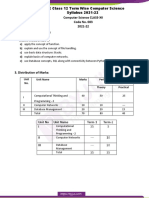
3. Distribution of Marks:
Unit No. Unit Name Marks Periods
Theory Practical
I Computational Thinking and 40 70 50
Programming – 2
II Computer Networks 10 15 …
III Database Management 20 25 20
Total 70 110 70
4. Unit wise Syllabus
Unit I: Computational Thinking and Programming – 2
● Revision of Python topics covered in Class XI.
● Functions: types of function (built-in functions, functions defined in module, user
defined functions), creating user defined function, arguments and parameters, default
parameters, positional parameters, function returning value(s), flow of execution, scope
of a variable (global scope, local scope)
● Exception Handling: Introduction, handling exceptions using try-except-finally blocks
● Introduction to files, types of files (Text file, Binary file, CSV file), relative
and absolute paths
● Text file: opening a text file, text file open modes (r, r+, w, w+, a, a+), closing a text
file, opening a file using with clause, writing/appending data to a text file using write()
and writelines(), reading from a text file using read(), readline() and readlines(), seek
and tell methods, manipulation of data in a text file
● Binary file: basic operations on a binary file: open using file open modes (rb, rb+, wb,
wb+, ab, ab+), close a binary file, import pickle module, dump() and load() method,
read, write/create, search, append and update operations in a binary file
● CSV file: import csv module, open / close csv file, write into a csv file using
writer(),writerow(),writerows() and read from a csv file using reader()
● Data Structure: Stack, operations on stack (push & pop), implementation of stack
using list.
Unit II: Computer Networks
● Evolution of networking: introduction to computer networks, evolution of networking
(ARPANET, NSFNET, INTERNET)
● Data communication terminologies: concept of communication, components of data
communication (sender,receiver, message, communication media, protocols),
measuring capacity of communication media (bandwidth, data transfer rate), IP
address, switching techniques (Circuit switching, Packet switching)
● Transmission media: Wired communication media (Twisted pair cable, Co-axial cable,
Fiber-optic cable), Wireless media (Radio waves, Micro waves, Infrared waves)
● Network devices (Modem, Ethernet card, RJ45, Repeater, Hub, Switch, Router,
Gateway, WIFI card)
● Network topologies and Network types: types of networks (PAN, LAN, MAN, WAN),
networking topologies (Bus, Star, Tree)
● Network protocol: HTTP, FTP, PPP, SMTP, TCP/IP, POP3, HTTPS, TELNET, VoIP
● Introduction to web services: WWW, Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML),
Extensible Markup Language (XML), domain names, URL, website, web browser,
web servers, web hosting
Unit III: Database Management
● Database concepts: introduction to database concepts and its need
● Relational data model: relation, attribute, tuple, domain, degree, cardinality, keys
(candidate key, primary key, alternate key, foreign key)
● Structured Query Language: introduction, Data Definition Language and Data
Manipulation Language, data type (char(n), varchar(n), int, float, date), constraints (not
null, unique, primary key), create database, use database, show databases, drop
database, show tables, create table, describe table, alter table (add and remove an
attribute, add and remove primary key), drop table, insert, delete, select, operators
(mathematical, relational and logical), aliasing, distinct clause, where clause, in,
between, order by, meaning of null, is null, is not null, like, update command, delete
command, aggregate functions (max, min, avg, sum, count), group by, having clause,
joins: cartesian product on two tables, equi-join and natural join
● Interface of python with an SQL database: connecting SQL with Python, performing
insert, update, delete queries using cursor, display data by using connect(), cursor(),
execute(), commit(), fetchone(), fetchall(), rowcount, creating database connectivity
applications, use of %s format specifier or format() to perform queries
5. Practical
S.No Unit Name Marks
(Total=30)
1 Lab Test: 8
1. Python program (60% logic + 20%
documentation + 20% code quality)
2. SQL queries (4 queries based on one or 4
two tables)
2 Report file: 7
● Minimum 15 Python programs.
● SQL Queries – Minimum 5 sets using
one table / two tables.
● Minimum 4 programs based on Python -
SQL connectivity
3 Project (using concepts learnt in Classes 11 8
and 12)
4 Viva voce 3
6. Suggested Practical List:
Python Programming
● Read a text file line by line and display each word separated by a #.
● Read a text file and display the number of vowels/consonants/uppercase/lowercase
characters in the file.
● Remove all the lines that contain the character 'a' in a file and write it to another file.
● Create a binary file with name and roll number. Search for a given roll number and
display the name, if not found display appropriate message.
● Create a binary file with roll number, name and marks. Input a roll number and update
the marks.
● Write a random number generator that generates random numbers between 1 and 6
(simulates a dice).
● Write a Python program to implement a stack using list.
● Create a CSV file by entering user-id and password, read and search the password for
given userid.
Database Management
● Create a student table and insert data. Implement the following SQL commands on the
student table:
o ALTER table to add new attributes / modify data type / drop attribute
o UPDATE table to modify data
o ORDER By to display data in ascending / descending order
o DELETE to remove tuple(s)
o GROUP BY and find the min, max, sum, count and average
● Similar exercise may be framed for other cases.
● Integrate SQL with Python by importing suitable module.
7. Suggested Reading Material
● NCERT Textbook for COMPUTER SCIENCE (Class XII)
● Support Materials on the CBSE website.
8. Project
The aim of the class project is to create something that is tangible and useful using Python
file handling/ Python-SQL connectivity. This should be done in groups of two to three
students and should be started by students at least 6 months before the submission
deadline. The aim here is to find a real world problem that is worthwhile to solve.
Students are encouraged to visit local businesses and ask them about the problems that
they are facing. For example, if a business is finding it hard to create invoices for filing GST
claims, then students can do a project that takes the raw data (list of transactions), groups
the transactions by category, accounts for the GST tax rates, and creates invoices in the
appropriate format. Students can be extremely creative here. They can use a wide variety of
Python libraries to create user friendly applications such as games, software for their school,
software for their disabled fellow students, and mobile applications, of course to do some of
these projects, some additional learning is required; this should be encouraged. Students
should know how to teach themselves.
The students should be sensitized to avoid plagiarism and violations of copyright issues while
working on projects. Teachers should take necessary measures for this.
CLICK ON IMAGE TO
JOIN US ON TELEGRAM
CLICK HERE TO JOIN
US ON TELEGRAM
You might also like
- Final Exam - PROG1815 Programming Concepts IIDocument3 pagesFinal Exam - PROG1815 Programming Concepts IIKeerthi meher NadimpalliNo ratings yet
- DBMS Mini Project ...Document15 pagesDBMS Mini Project ...sandhya kondapurNo ratings yet
- Exam Az 303 Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies Skills MeasuredDocument5 pagesExam Az 303 Microsoft Azure Architect Technologies Skills MeasuredpradhyumnNo ratings yet
- Rockwell Automation PLCDocument212 pagesRockwell Automation PLCramorado0% (1)
- CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Syllabus 2023 24Document4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Computer Science Syllabus 2023 24Aanchal MakhijaniNo ratings yet
- 12 Computerscience Eng 2024 25Document4 pages12 Computerscience Eng 2024 25rahulkumar200721No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Syllabus 2022 23Document4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Computer Science Syllabus 2022 23Devansh ChawlaNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Class-Xii Code No. 083 2021-22 1. Prerequisites 2. Learning OutcomesDocument4 pagesComputer Science Class-Xii Code No. 083 2021-22 1. Prerequisites 2. Learning OutcomesHarsh DugarNo ratings yet
- Cs MayDocument3 pagesCs Maytalktoarnab507No ratings yet
- 12 CSDocument107 pages12 CSrohitvk92No ratings yet
- Computer Science: I II IIIDocument5 pagesComputer Science: I II IIIAppan DNo ratings yet
- Xii Cs Study Material (2022-23)Document305 pagesXii Cs Study Material (2022-23)Arun SharmaNo ratings yet
- REVISED12 - SR - SEC. - Computer Science - 2020-21Document5 pagesREVISED12 - SR - SEC. - Computer Science - 2020-21Prasanta K PattadarNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Class-Xii Code No. 083 2021-22 1. Prerequisites 2. Learning OutcomesDocument5 pagesComputer Science Class-Xii Code No. 083 2021-22 1. Prerequisites 2. Learning OutcomesSiddharth NarsipurNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Cs 083 Syllabus 2023 24Document4 pagesClass Xii Cs 083 Syllabus 2023 24somojitroy80No ratings yet
- Class-Xii Code No. 083 2021-22 1. Prerequisites 2. Learning Outcomes CBSE Class 12 Term Wise Computer Science Syllabus 2021-22Document5 pagesClass-Xii Code No. 083 2021-22 1. Prerequisites 2. Learning Outcomes CBSE Class 12 Term Wise Computer Science Syllabus 2021-22Jazzy KingNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Class-Xii Code No. 083 2022-23: 1. PrerequisitesDocument4 pagesComputer Science Class-Xii Code No. 083 2022-23: 1. PrerequisitesKashvi BhatiaNo ratings yet
- 12 Syllabus 2023 Computer ScienceDocument4 pages12 Syllabus 2023 Computer ScienceAbhinavNo ratings yet
- Student Support Material For All Student - Class - XII - CSDocument238 pagesStudent Support Material For All Student - Class - XII - CSKaviya SankarNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School (Joka) South Kolkata: Class - Xii Computer ScienceDocument3 pagesDelhi Public School (Joka) South Kolkata: Class - Xii Computer Sciencesab108No ratings yet
- 2016 Syllabus 12 Computer ScienceDocument8 pages2016 Syllabus 12 Computer ScienceSamit BasuNo ratings yet
- Computer Science (Theory) : Class XII (Theory) - PythonDocument8 pagesComputer Science (Theory) : Class XII (Theory) - PythonVivaan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Class XII Study Material KV 2022-23Document183 pagesClass XII Study Material KV 2022-23Probably ArthNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Python 2020-21 LatestDocument3 pagesComputer Science Python 2020-21 LatestPriyanshu UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Computer Science (New) : Class-Xii Code No. 083 2019-20Document3 pagesComputer Science (New) : Class-Xii Code No. 083 2019-20TuaNo ratings yet
- PDF 5Document2 pagesPDF 5raj thoughtzzNo ratings yet
- 12 IpDocument127 pages12 Ipallyourneeds8682No ratings yet
- Computer ScienceDocument9 pagesComputer ScienceammullubNo ratings yet
- Syllabus Computer Science 2024 XIIDocument4 pagesSyllabus Computer Science 2024 XIIharshsingh14oct2006No ratings yet
- Computer Science (New) : Class-Xii Code No. 083 2019-20Document4 pagesComputer Science (New) : Class-Xii Code No. 083 2019-20Gaurav BhattNo ratings yet
- Computer Science (Theory) Class XII (Theory) - PythonDocument8 pagesComputer Science (Theory) Class XII (Theory) - PythonAnu RadhaNo ratings yet
- Class - Xii: Split-Up Syllabus Sub: Computer ScienceDocument3 pagesClass - Xii: Split-Up Syllabus Sub: Computer ScienceTech ArmyNo ratings yet
- 98 Ne HF 3 e We Eokqq IWMx 4Document2 pages98 Ne HF 3 e We Eokqq IWMx 4mp9414751No ratings yet
- 12 Class Syllabus 2011Document7 pages12 Class Syllabus 2011Chandresh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Computer Science SyllabusDocument1 pageClass 12 Computer Science Syllabusanubhavdas552006No ratings yet
- Termwise Syllabus Class - XI Computer Science (New) Code No. 083 Session 2019-20Document3 pagesTermwise Syllabus Class - XI Computer Science (New) Code No. 083 Session 2019-20Mobin Ahmed KingNo ratings yet
- CS Term II Cochin Region XII NOTESDocument139 pagesCS Term II Cochin Region XII NOTESoneplus3liteNo ratings yet
- Cbse CurriculumDocument6 pagesCbse CurriculumTechbuzz dav14ggmNo ratings yet
- Informatics Practices 2021-22Document9 pagesInformatics Practices 2021-22Aayush KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit No Unit Name Marks Periods Theory Periods Practical Total PeriodDocument9 pagesUnit No Unit Name Marks Periods Theory Periods Practical Total PeriodParineeta SinghNo ratings yet
- IP Gr12 StudyMaterialsDocument130 pagesIP Gr12 StudyMaterialsworksheet215No ratings yet
- Class Xii Computer Science Split Up 2024Document3 pagesClass Xii Computer Science Split Up 2024shreyasinghchampNo ratings yet
- 2 Computer Science and Application 1Document5 pages2 Computer Science and Application 1samiranchawrokNo ratings yet
- ADP Module-1Document116 pagesADP Module-1Vikas RNo ratings yet
- INT213Document2 pagesINT213Md. SakeelNo ratings yet
- Ip 12Document4 pagesIp 12sahusoubhagyaranjan72No ratings yet
- Core SyllabusDocument28 pagesCore SyllabusNìkèt SαínìNo ratings yet
- 1st Semester B.SC (H) Computer Science SyllabusDocument10 pages1st Semester B.SC (H) Computer Science SyllabusmaakaffNo ratings yet
- 15 Information Practices NewDocument6 pages15 Information Practices NewJAGANNATH THAWAITNo ratings yet
- Computer ScienceDocument3 pagesComputer ScienceAnkit YadavNo ratings yet
- Informatics PracticesDocument9 pagesInformatics Practicesdadan vishwakarmaNo ratings yet
- CSGE 101 Programming Using Python 32345104Document7 pagesCSGE 101 Programming Using Python 32345104Aditya VashisthNo ratings yet
- 11 Informationpractices Eng 2024 25Document3 pages11 Informationpractices Eng 2024 25kiransharmmaa937No ratings yet
- 11 Informationpractices Eng 2024 25Document3 pages11 Informationpractices Eng 2024 25singhragho020No ratings yet
- Question Bank 2023-24 Computer ScienceDocument146 pagesQuestion Bank 2023-24 Computer Sciencekalpanapradhan1179No ratings yet
- Python SyllabusDocument3 pagesPython SyllabusSamaksh KhannaNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 PythonDocument10 pagesUnit 5 PythonVikas PareekNo ratings yet
- Student Support Material - Comp. Sc. XII (2024-25)Document175 pagesStudent Support Material - Comp. Sc. XII (2024-25)DEV 8CNo ratings yet
- Informatics Practices: Class Xii Code No. 065 2021-2022Document5 pagesInformatics Practices: Class Xii Code No. 065 2021-2022Dhruv jainNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Computer Science 2023Document2 pagesCBSE Class 12 Computer Science 2023vaishnavisoni32No ratings yet
- Informatics PracticesDocument4 pagesInformatics PracticesAtanuBhandaryNo ratings yet
- XI-CS Study Material 2023-24Document142 pagesXI-CS Study Material 2023-242pwxanqt8aNo ratings yet
- Mastering Python Programming: A Comprehensive Guide: The IT CollectionFrom EverandMastering Python Programming: A Comprehensive Guide: The IT CollectionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mastering Python: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners and ExpertsFrom EverandMastering Python: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners and ExpertsNo ratings yet
- Pre - Board 2 STD 10 ScienceDocument9 pagesPre - Board 2 STD 10 ScienceMihir MishraNo ratings yet
- English ProjectDocument19 pagesEnglish ProjectMihir MishraNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - SrSec - 2023 24 Pages 7 13Document7 pagesChemistry - SrSec - 2023 24 Pages 7 13Mihir MishraNo ratings yet
- English - Core - SrSec - 2023 24 Pages 10 12Document3 pagesEnglish - Core - SrSec - 2023 24 Pages 10 12Mihir MishraNo ratings yet
- pg168 GtwizardDocument154 pagespg168 GtwizardNguyễn HạnhNo ratings yet
- Abb Irc5 Application ManualDocument64 pagesAbb Irc5 Application ManualRAFAEL CARDOSONo ratings yet
- Vira Jaya Computer Mangga Dua Mal LTDocument6 pagesVira Jaya Computer Mangga Dua Mal LTPapa Beatrix100% (1)
- Fault Recorder120 071Document21 pagesFault Recorder120 071O P Sridharan PerumalNo ratings yet
- PPIF0542-014 Payshield 9000 Software and License Update ProcedureDocument9 pagesPPIF0542-014 Payshield 9000 Software and License Update ProcedureAlexey KhotulevNo ratings yet
- Oracle: Question & AnswersDocument11 pagesOracle: Question & AnswersRafael BarrosNo ratings yet
- What Is BootingDocument3 pagesWhat Is Bootingramanan_rapiddNo ratings yet
- AppssynonymsDocument42 pagesAppssynonymsEmilia RomeroNo ratings yet
- Final Part OneDocument14 pagesFinal Part OneVishavjeetDevganNo ratings yet
- Progress ReportDocument3 pagesProgress Reportapi-581166535No ratings yet
- SNAP Load InstructionsDocument1 pageSNAP Load InstructionsDaniel ChiriacNo ratings yet
- b0193wq MDocument84 pagesb0193wq MAnonymous nVMYT3AEO100% (2)
- How To Upgrade Esxi 6Document4 pagesHow To Upgrade Esxi 6Kiệt Trần TrungNo ratings yet
- New PPT Nursing InfromaticsDocument35 pagesNew PPT Nursing InfromaticsSusi SeptianiNo ratings yet
- Slip PP ProtocolDocument3 pagesSlip PP Protocolabhishektanu87No ratings yet
- DTE MicroprojectDocument22 pagesDTE MicroprojectShreyas Bagate100% (1)
- Django Money Readthedocs Io en StableDocument29 pagesDjango Money Readthedocs Io en Stablemuhammad safwanNo ratings yet
- 1670 Petra UMA MB-Aspire V5-531 V5-571-11324Document103 pages1670 Petra UMA MB-Aspire V5-531 V5-571-11324juan carlosNo ratings yet
- Vonino Firmware Upgrade ProcedureDocument8 pagesVonino Firmware Upgrade ProcedureIonut GrigoreNo ratings yet
- Emu LogDocument1 pageEmu LogMayke OchoaNo ratings yet
- TMF1434 - Data Structure & Algorithms Assignment - UNIMAS Kiosk Point of Sale System Sem 02, 2022/2023Document2 pagesTMF1434 - Data Structure & Algorithms Assignment - UNIMAS Kiosk Point of Sale System Sem 02, 2022/2023Adry NietzscheNo ratings yet
- AWS Command Line Interface Part 1Document22 pagesAWS Command Line Interface Part 1Muhammad AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Polycab End User Manual V1 PDFDocument6 pagesPolycab End User Manual V1 PDFrkl007No ratings yet
- Cloudguard Cnapp Final - DesignedDocument36 pagesCloudguard Cnapp Final - DesignedGfact MailNo ratings yet
- Connectivity Screening FormDocument3 pagesConnectivity Screening Form1304 RecordsNo ratings yet
- Send A Smartform Through Mail Using OopsDocument8 pagesSend A Smartform Through Mail Using OopsRicky DasNo ratings yet