Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mood Stabilizer
Mood Stabilizer
Uploaded by
drjyosnabnpsychiatrist0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageTable 1 summarizes the main classes of mood stabilizers used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, including their proposed mechanisms of action and common side effects. The classes discussed are minerals (lithium), anti-epileptics (sodium valproate, lamotrigine, carbamazepine), and atypical antipsychotics (risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine, aripiprazole). The table lists each medication's proposed mechanisms such as enhancing serotonergic activity or blocking sodium channels. It also provides examples of common side effects for each class like gastrointestinal upset, tremor, or sexual dysfunction.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTable 1 summarizes the main classes of mood stabilizers used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, including their proposed mechanisms of action and common side effects. The classes discussed are minerals (lithium), anti-epileptics (sodium valproate, lamotrigine, carbamazepine), and atypical antipsychotics (risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine, aripiprazole). The table lists each medication's proposed mechanisms such as enhancing serotonergic activity or blocking sodium channels. It also provides examples of common side effects for each class like gastrointestinal upset, tremor, or sexual dysfunction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageMood Stabilizer
Mood Stabilizer
Uploaded by
drjyosnabnpsychiatristTable 1 summarizes the main classes of mood stabilizers used in the treatment of bipolar disorder, including their proposed mechanisms of action and common side effects. The classes discussed are minerals (lithium), anti-epileptics (sodium valproate, lamotrigine, carbamazepine), and atypical antipsychotics (risperidone, olanzapine, quetiapine, aripiprazole). The table lists each medication's proposed mechanisms such as enhancing serotonergic activity or blocking sodium channels. It also provides examples of common side effects for each class like gastrointestinal upset, tremor, or sexual dysfunction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
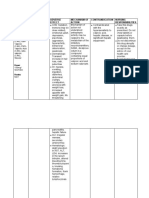
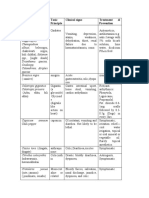
Table 1
Main classes of mood stabiliser (and alternatives to valproate in the treatment of bipolar disorder), mechanisms
of action and side effects (not including foetal or maternal risks). Compiled from various sources [10, 33, 34,
91–100]
Class Medication Proposed mechanism(s) of action Side effects
name
Mineral Lithium Enhances serotonergic neuron activity, Common: GI upset, fine tremor, polyuria,
inhibits pAp-phosphatase enzyme, polydipsia, metallic taste in mouth, ankle
interacts with nitric oxide signalling oedema, weight gain. Chronic: renal toxicity,
activity hypothyroidism.
Anti-epileptics Sodium GABA potentiation, blocks voltage Common: GI upset, hyperammonaemia
valproate gated sodium channels, epigenetically (causing nausea), weight gain, tremor, hair
inhibits histone deacetylase loss with curly regrowth.
In women: polycystic ovarian syndrome,
hyperandrogenism.
Rare: fulminant liver failure.
Lamotrigine GABA potentiation, suppresses Common: tremors, dizziness, tiredness, loss
glutamate release, inhibits serotonin of co-ordination, menstrual disturbance, dry
reuptake mouth, sleep problems.
Carbamazepine Blocks voltage gated sodium channels Common: dizziness, diplopia, drowsiness,
ataxia, nausea, headaches, dry mouth,
oedema, hyponatraemia, erythematous rash,
sexual dysfunction.
Rare: agranulocytosis.
Atypical Risperidone Dopaminergic (D1–5) receptor Common: sexual dysfunction
antipsychotics antagonist, serotonergic (5-HT2A/C) (hyperprolactinaemia).
Olanzapine receptor antagonist Long term: movement disorders (e.g. tardive
dyskinesia, akathisia, parkinsonism),
Quetiapine increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
Rare: neuroleptic malignant syndrome
Aripiprazole Dopaminergic (D2) and serotonergic (5- Common: weight gain, headache, agitation,
HT1A) receptor partial agonist insomnia, gastrointestinal effects,
disinhibition.
You might also like
- Pocket NeurologyDocument6 pagesPocket NeurologyAlexandra BalanNo ratings yet
- Carlos Torrente Artero - Small Animal Emergency Care. Quick Reference Guide-Servet (2017)Document108 pagesCarlos Torrente Artero - Small Animal Emergency Care. Quick Reference Guide-Servet (2017)Jeferson BinladenNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ClozapineDocument2 pagesDrug Study ClozapineRobert Martin Rivera PuertaNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Pharmacology SummaryDocument25 pagesComprehensive Pharmacology Summarybhaveshnidhi64100% (1)
- Psychiatry Pharmacology J. Psychiatry' AntidepressantsDocument9 pagesPsychiatry Pharmacology J. Psychiatry' AntidepressantssumithjalyNo ratings yet
- Tufts Med ListDocument5 pagesTufts Med ListMarisa Deana Pontrelli100% (1)
- Comprehensive Pharmacology SummaryDocument25 pagesComprehensive Pharmacology Summarysubash p100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyizzieliciousNo ratings yet
- Anti Diabetic Agents In-Clude,: Ant PsychoticDocument1 pageAnti Diabetic Agents In-Clude,: Ant PsychoticDan PobanNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Actions Side Effects Adverse Effects Indications Contraindication S Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Actions Side Effects Adverse Effects Indications Contraindication S Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameMae Abigail Mallonga BunaganNo ratings yet
- Drugs Study Drugs Classification Adverse Effect Mechanism of Action Contrandication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesDrugs Study Drugs Classification Adverse Effect Mechanism of Action Contrandication Nursing ResponsibilitiesRachel BotonNo ratings yet
- Furosemide Drug StudyDocument4 pagesFurosemide Drug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- NURS 275 Meds Patient 3Document5 pagesNURS 275 Meds Patient 3Kai Yee GanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyDean Angelo BarrientosNo ratings yet
- NCMH Drug StudyDocument5 pagesNCMH Drug StudyHeartlee NapuranNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug Studyrubie ann tillorNo ratings yet
- NPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesDocument83 pagesNPLEX Combination Review Neurology - A: Paul S. Anderson, ND Medical Board Review ServicesValeria AcevedoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument106 pagesDrug StudyBlessie Mae Guinanghan AbuanNo ratings yet
- Benzodiazepines Drug StudyDocument4 pagesBenzodiazepines Drug Studyaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Epilepsy Is Due To Sudden, Excessive Depolarization Of: Some or All Cerebral NeuronsDocument19 pagesEpilepsy Is Due To Sudden, Excessive Depolarization Of: Some or All Cerebral NeuronsMourian AmanNo ratings yet
- Barbiturates: of Action of GABA. Independent of GABADocument10 pagesBarbiturates: of Action of GABA. Independent of GABAAvi WerdesheimNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric DrugsDocument42 pagesPsychiatric DrugsaartiNo ratings yet
- Parkinson's DiseaseDocument33 pagesParkinson's DiseasekapilNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyRubie Ann TillorNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument3 pagesAcetazolamideGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Parkinson - S Disease Case PresentationDocument39 pagesParkinson - S Disease Case PresentationAnonymous dpxYTE0% (1)
- Drugs Drugs Drugs STUDY GUIDEDocument13 pagesDrugs Drugs Drugs STUDY GUIDEAlexander Chamessian100% (1)
- DRG StudyDocument5 pagesDRG StudyCarlo ToledooNo ratings yet
- Medications Table 7.3: Common Medications Used To Treat Chronic Fatigue SyndromeDocument30 pagesMedications Table 7.3: Common Medications Used To Treat Chronic Fatigue SyndromeVujica ZivkovicNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Responsibilities: GenericArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- Risperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsDocument9 pagesRisperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Neurology AL QUDS Part 2Document73 pagesNeurology AL QUDS Part 2reem natshehNo ratings yet
- CC Rubie Ann G. Tillor: IM: (Schizophrenia)Document11 pagesCC Rubie Ann G. Tillor: IM: (Schizophrenia)Rubie Ann TillorNo ratings yet
- Medications NHBDocument40 pagesMedications NHBAnonymous 7hJgATNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideDocument6 pagesDrug Study: Labetalol Hydro ChlorideMark ToxNo ratings yet
- Drug 2Document4 pagesDrug 2Abie Jewel Joy RoqueNo ratings yet
- Pedia: Initial Therapy: 12.5 MGDocument3 pagesPedia: Initial Therapy: 12.5 MGVinz OñoNo ratings yet
- Clozapine Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 pagesClozapine Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComVinz OñoNo ratings yet
- Drug NameDocument31 pagesDrug Namelawha.chaand02No ratings yet
- Meds - KaplanDocument3 pagesMeds - KaplanJodi BairNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric DisordersDocument23 pagesPsychiatric DisordersRahul PatilNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Drugs - ZarinaDocument25 pagesPsychiatric Drugs - Zarinaszarina_7No ratings yet
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument43 pagesAntiepileptic DrugsdrpraneethpremkumarNo ratings yet
- Psychotropic Medication ReviewDocument7 pagesPsychotropic Medication ReviewAakash Shah100% (2)
- Pertimbangan Pemilihan Obat Anti Epilepsi DR Nelly Edit 23 JanDocument53 pagesPertimbangan Pemilihan Obat Anti Epilepsi DR Nelly Edit 23 Janvenus002No ratings yet
- Mayra Pagan: Pharmacology-NursingDocument50 pagesMayra Pagan: Pharmacology-NursingmayraNo ratings yet
- Anti ParkinsonDocument43 pagesAnti ParkinsonSasya pashaNo ratings yet
- HTTPDocument3 pagesHTTPChon 앙드레 BalanayNo ratings yet
- Step 3 - PharmacologyDocument10 pagesStep 3 - PharmacologyLauren LevyNo ratings yet
- Antineoplastic AgentsDocument3 pagesAntineoplastic AgentsJan Patrick ArrietaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Reporting-1Document32 pagesPharmacology Reporting-1Mj TalentNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic Drugs 2019 Elearning PDFDocument39 pagesAntiepileptic Drugs 2019 Elearning PDFMalvika BabuNo ratings yet
- Antiepileptic DrugsDocument7 pagesAntiepileptic DrugsFatima Asim 922-FSS/BSPSY/F17No ratings yet
- AntiepilepticiDocument29 pagesAntiepilepticiIskraNo ratings yet
- Age Drug StudyDocument13 pagesAge Drug StudyLadybelle GototosNo ratings yet
- Wearing Off in PD - Dr. Rocksy Fransisca VS, SPS (K), PHDDocument52 pagesWearing Off in PD - Dr. Rocksy Fransisca VS, SPS (K), PHDFebrian TanNo ratings yet
- Mood Stabilisers: PsychopharmacologyDocument50 pagesMood Stabilisers: Psychopharmacologymeno321No ratings yet
- Common Plants Poisonous To LivestockDocument88 pagesCommon Plants Poisonous To LivestockSunilNo ratings yet
- List of Poisonous Plants of Veterinary Importance 2Document5 pagesList of Poisonous Plants of Veterinary Importance 2SunilNo ratings yet
- Endocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsFrom EverandEndocrinology Notes for Medical StudentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Leoncio General Hospital: Medical CertificateDocument10 pagesLeoncio General Hospital: Medical Certificatefranchiser6No ratings yet
- Diabetic Foot Hajera FinalDocument38 pagesDiabetic Foot Hajera FinalAfifah SelamatNo ratings yet
- Medicare GuideDocument3 pagesMedicare GuideyigaplusoneNo ratings yet
- Superhero AssignmentDocument5 pagesSuperhero Assignmentprathibha asok kumarNo ratings yet
- Notes On Meniere's DiseaseDocument5 pagesNotes On Meniere's DiseaseDipson HamalNo ratings yet
- Medicinal Chemistry I Sovan Sarkar 186012111012Document11 pagesMedicinal Chemistry I Sovan Sarkar 186012111012Sovan SarkarNo ratings yet
- Domingo LucianiDocument13 pagesDomingo LucianiAlex AlbornozNo ratings yet
- SFH PPT 1Document14 pagesSFH PPT 1Mohit anandNo ratings yet
- How To Write A Research Paper On Prostate CancerDocument4 pagesHow To Write A Research Paper On Prostate Cancertus0zaz1b1g3No ratings yet
- Case Report - An Uncommon Association of Ebstein's Anomaly and Rheumatic Mitral StenosisDocument4 pagesCase Report - An Uncommon Association of Ebstein's Anomaly and Rheumatic Mitral StenosisRJMNo ratings yet
- Psoriasis and Aging: Paul S. YamauchiDocument7 pagesPsoriasis and Aging: Paul S. YamauchiAngélica MacielNo ratings yet
- WSSFN Program 1 1Document9 pagesWSSFN Program 1 1standmaker0No ratings yet
- Common Newborn Problems (2) C1Document39 pagesCommon Newborn Problems (2) C1ZmNo ratings yet
- Granuloma Anulare 2Document4 pagesGranuloma Anulare 2Ahmad Ligar SuhermanNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA LampiranDocument3 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA Lampiransiska putri utamaNo ratings yet
- Health 7 Activity SheetsDocument31 pagesHealth 7 Activity SheetsGABINO ELECTRONIC REPAIR & PRINTING SERVICESNo ratings yet
- Sarkis 2014Document6 pagesSarkis 2014druga godinaNo ratings yet
- JRomero - Alcohol - and - Opioid - Abuse - Case - Study - 28 - Days - 1Document3 pagesJRomero - Alcohol - and - Opioid - Abuse - Case - Study - 28 - Days - 1Camille SindayNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Cancer Chemotherapy - Skeel, Roland TDocument813 pagesHandbook of Cancer Chemotherapy - Skeel, Roland TJesús BlancoNo ratings yet
- The Blue BookDocument53 pagesThe Blue BookTammy BoudNo ratings yet
- Regular 20 Regular 30 Regular 50 Urgent 20 Urgent 30 Urgent 50Document1 pageRegular 20 Regular 30 Regular 50 Urgent 20 Urgent 30 Urgent 50VishwaNo ratings yet
- E Scleroderma Ye Scleroderma LikeDocument31 pagesE Scleroderma Ye Scleroderma LikeHmn07No ratings yet
- Zerihun FigaDocument46 pagesZerihun FigaMoges desaleNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - DS03 - Paper - 1.1Document8 pagesMicrosoft Word - DS03 - Paper - 1.1kuridisanjeevNo ratings yet
- AlopeciaDocument12 pagesAlopeciasonamNo ratings yet
- Trauma and Adverse Childhood Experiences (Aces) : The Impact of TraumaDocument2 pagesTrauma and Adverse Childhood Experiences (Aces) : The Impact of TraumaInfante SanndyNo ratings yet
- Mineral, Vitamin, and Herbal SupplementsDocument18 pagesMineral, Vitamin, and Herbal SupplementsismailcemNo ratings yet
- Pulpal DiseasesDocument34 pagesPulpal Diseasessamar yousif mohamedNo ratings yet
- Bennett 2020Document19 pagesBennett 2020Olga MichailidouNo ratings yet