Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Human Evolution
Human Evolution
Uploaded by
ajitrajput6078Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Human Evolution
Human Evolution
Uploaded by
ajitrajput6078Copyright:
Available Formats
S. N.
Kansagra School
Biology Department
http://tgesbiology.weebly.com/4-human-evolution.html
HUMAN
EVOLUTION Unit 1 chapter 4
NAME _____________________ DATE ________________
TGESBIOLOGY ISC 12 – HUMAN EVOLUTION 1
THE SCOPE OF SYLLABUS
Human evolution: Dryopithecus, Australopithecus, Homo erectus, Homo neanderthalensis,
Cromagnon man and Homo sapiens; differences between apes and man.
Evolution of man - brief idea of ancestors leading to man of today; comparison and homology
in chromosomes of apes and man.
THE FIRST HUMAN FOSSIL EVIDENCE
Found in Java, Indonesia
Homo erectus skull, Known as Java Man, this early human
species was identified based on fossil evidence first found in
1891 in archaeological sites along the Solo River, East Java,
Indonesia. This specimen is the Sangiran 17 skull, found in 1969
in the Sangiran Cave, Central Java. It has been dated to between
1.3 and 1 million years ago, though estimates vary.
EUGENE DUBOIS (1858-1940)
• In September 1890, his workers found a human, or human-like, fossil at Koedoeng Broeboes. This
consisted of the right side of the chin of a lower jaw and three attached teeth.
• In August 1891 he found a primate molar tooth. Two months later and one meter away was found an
intact skullcap, the fossil which would be known as Java Man.
• In August 1892, a third primate fossil, an almost complete left thigh bone, was found between 10 and
15 meters away from the skullcap
Human evolution- when and where.
TGESBIOLOGY ISC 12 – HUMAN EVOLUTION 2
FACTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR HUMAN EVOLUTION
• Increased aridity of climate.
• Dwindling of forests and replacement by grasslands
• Reduction in number of trees.
EARLY HUMAN ANCESTORS
Dryopithecus
The fossils were discovered from rocks of Miocene age (20 mya).
These resembled the great apes. Their arms and legs were of equal length.
They had semi-erect posture, large canines, and without brow ridges.
Australopithecus (African ape man)
Two million years ago fossil baby skull called Tuang baby was discovered by Raymond Dart and
named it (Australopithecus africanus).
Australopithecus were about 150cm and its skull was like that was like that of modern apes with
cranial capacity of 600cc. They lived during Pliocene and the Pleistocene in Africa.
Donald Johanson discovered another species of Australopithecus fossil “Lucy” in 1976.
Simian characters:
1. Small in size, average height- 4feet
2. Face prognathous.
3. Chin absent, forehead low.
4. Bulge of occipital region small.
5. Eyebrow ridges projected over the eyes.
6. Cranial capacity about 600 cc
Human characters:
1. Walked completely straight
2. Vertebral column with distinct lumbar curve
3. Pelvis broad and basin like.
4. Teeth man-like with dental arch in the form of
parabola.
5. Simian gap between incisors and canine absent.
6. Canines man-like and did not project beyond the level of other teeth
Advanced Australopithecus – Homo habilis
Louis Leakey discovered the fossils of Homo habilis or the handy
man in 1960.
These were found in rocks 1.6 to 1.8 million years old in east Africa.
They were slightly more advanced than Australopithecus.
TGESBIOLOGY ISC 12 – HUMAN EVOLUTION 3
Characters of Homo habilis
1. They were 120 -150cm tall.
2. They had cranial capacity of 730cc.
3. They had human like body with an ape like head.
4. They walked erect with bipedal gait.
They lived in caves were herbivores and used tools of stones to dig out tubers and led community life.
They are regarded as the last of the Australopithecus.
They originated about 3.5 million years ago
Homo erectus erectus (Java ape man)
Eugene Dubois discovered the fossil, in 1891. Dubois named the fossils as Pithecanthropus erectus or
Java ape-man. Later, Mayer (1950) renamed it as Homo erectus. They lived 1.7million years ago
(Pleistocene) on the banks of Solo River in Java.
Characters-
1. They stood upright to a height of 150cms.
2. They had receding forehead with prominent brow ridges
3. The jaws were prognathous without a distinct chin.
4. The cranial capacity was 900cc.
They were hunters and food gatherers, used stone tools for hunting,
lived in caves, learned the use of fire for cooking and used animal skin
for clothing themselves and probably used sign language.
Homo sapiens neanderthalensis (Neanderthal man)
C. Fuhirott discovered fossil in 1856.
They arose about 1,00,000 years ago and became extinct 25,000 years ago.
Characters-
• Thick skull bones.
• Low slanting forehead.
• Strong lower jaw muscles and no chin.
• Short of stature 1.5 to 1.6m height.
• Semi-erect stooping posture.
• Cranial capacity of 1450cc.
TGESBIOLOGY ISC 12 – HUMAN EVOLUTION 4
They used flint tools and animal skin for clothing. They buried the dead and performed ceremonies
and constructed dwelling structure.
State three structural features by which Neanderthal man differed from Homo sapiens. 3M2007
Homo sapiens fossilis (early modern man or cro-magnon man)
Mac Gregor discovered fossil in 1868 from the caves of northwest Italy.
They originated 50,000 years ago and existed for about
30,000 years. They became extinct 10-20 thousand years
ago.
Characters-
• They were about 1.8m tall.
• They had perfect posture.
• The cranial capacity was 1660 cc.
• They are prominent chin and narrow elevated nose.
• Face was prognathous.
They were cave dwellers and hunters; they buried the dead
and could make paint. They learnt to shape stones and bones into excellent tools. They had religious
beliefs and burial customs. They developed the Paleolithic culture.
Give the characteristics of cro-magnon man. 4M ISC 2005
Give reasons to show that Cro-magnon man is the direct ancestor of man today. 4M ISC 2002
Homo sapiens sapiens (Modern man)
It is the living modern man, evolved 25 thousand years ago.
Their evolution includes cultural evolution rather than
anatomical evolution. He learned to cultivate plants and
domesticate animals. Modern man is associated with
Neolithic culture. They settled down near lakes and ocean
shores to catch fishes, and also started domesticating plants
and animals.
The modern man is known to have appeared around the
Caspian Sea and evolved into following races-
Negroid- Africa and Malaysia.
Caucasian- Europe and North America.
Mongoloids- China, Siberia and Japan.
TGESBIOLOGY ISC 12 – HUMAN EVOLUTION 5
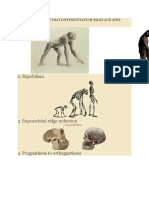
CHARACTERS THAT DIFFERENTIATE APES AND HUMANS
1. Erect posture: Bend posture to straight or erect posture.
2. Bipedalism: Walking on all four limbs to walking on two legs.
3. Supraorbital ridge reduction: Apes have prominent supra-orbital ridge.
TGESBIOLOGY ISC 12 – HUMAN EVOLUTION 6
4. Prognathous to orthognathous:
Face of apes protrudes out into a muzzle due to In Homo sapiens here is a prominent chin and is
the broad and long teeth row. without a muzzle.
5. Opposable thumb- that helps in grasping.
6. Shape of the jaw
The dental arch is in the shape of parabola in apes whereas it is U shaped in humans
TGESBIOLOGY ISC 12 – HUMAN EVOLUTION 7
Other trends in Human evolution
• Development of distinct lumbar curve.
• Development of broad pelvic bones
• Acetabular cavities shifted inside, to give straight posture.
• Increase in size of cranial cavity
• Flattening of face
• Straightening of forehead
• Narrowing of nose
• Thinning of jaw bones
• Reduction in jaw musculature
• Reduction in size of canines
• Loss of tail
• Articulated speech
State the main morphological changes that occurred in the ancestors of modern man. 3M 2011
State two similarities between the chromosomes of man and apes. 2M 2011
Differentiate between apes and man with respect to the following characteristic- 4M 2009
a. Posture, b. cranium c. brow ridges d. locomotion
What are the characteristics that have developed in human beings during evolution? 4 M 2004
Cultural evolution in man
Cultural evolution started in the Pleistocene period with the early
human ancestors leading a community life.
They lived in caves to protect themselves from the predators.
They started using tools for digging tubers etc. for food. They then
started making tools for hunting animals.
As evolution took place in the late Pleistocene, the used fire for
defense and cooking.
These early humans also used sign language for communication.
The tools were more sophisticated and animal skin used for clothing.
They followed religious customs and burial patterns.
TGESBIOLOGY ISC 12 – HUMAN EVOLUTION 8
Homology in chromosomes of man and ape
Modern man showed more of cultural evolution than anatomical evolution. For improved hunting, good tools
were produced, later domestication of plants and animals led to the agricultural revolution and finally the latest
industrial and scientific revolution.
The diploid chromosome number in man is 46 and that in apes (chimpanzee, gorilla and orangutan are
48. Comparing the banding technique, the pattern is similar in chromosome number 3 and 6. The
nucleotide sequence between the DNA molecules is also similar. The difference between the sequence
in man and chimpanzee is only 2.5%.
Evidences in support of common ancestors
1. Anatomical: These include the various morphological similarities posture, teeth, locomotion etc. Vestigial
organs present in humans are also present in apes.
2. Physiological: blood groups, menstrual cycle in female (no. of days same), gestation period (270-90
humans,265-80 –gorilla and 210-52 chimpanzee)
3. Embryological: eggs and sperms are similar, mammae in six-week-old human embryo, hairs on the embryos
What are the chromosomal similarities found in man and apes? What do such similarities indicate?3M 2001
Give the characteristic features that suggest a close phylogenetic relationship between man and apes. 4M
2003
Give an account of the evidence, which shows the common ancestry of man and apes. 4M 2006
TGESBIOLOGY ISC 12 – HUMAN EVOLUTION 9
SOURCES-
http://www.creationism.org/books/TaylorInMindsMen/TaylorIMMhmEugeneDuboisM.jpg
http://blogs.smithsonianmag.com/hominids/files/2012/09/picresized_1347204858_Pithecanthropus-erectus.jpg
http://img.gawkerassets.com/img/18666jebis5bljpg/original.jpg
http://cdn0.cosmosmagazine.com/wp-content/uploads/20070717_bipedalism.jpg
http://i.livescience.com/images/i/000/025/831/i02/human-evolution.jpg
http://www.cryptomundo.com/wp-content/dryopithecus.jpg
http://www.metaprimate.com/IMG/Australopithecus-afarensis.jpg
http://www.sciencephoto.com/image/170967/350wm/E4380068-Homo_habilis_making_stone_tool-SPL.jpg
http://www.metaprimate.com/ancestral-species/
http://mr_sedivy.tripod.com/world/w_cavemen.jpg
http://25.media.tumblr.com/tumblr_m44lbjc6PR1rwpqlio1_400.jpg
http://www.detectingdesign.org/wp-content/uploads/2011/05/Java-Man-2.jpg
TGESBIOLOGY ISC 12 – HUMAN EVOLUTION 10
You might also like
- Lesson Plan For Teaching GrammarDocument9 pagesLesson Plan For Teaching Grammarruszita75% (4)
- Investigatory ProjectDocument21 pagesInvestigatory ProjectDiya 2788% (86)
- Human EvolutionDocument10 pagesHuman EvolutionAdelinaAliman100% (1)
- Human Evolution ZOOLOGY PROJECTDocument11 pagesHuman Evolution ZOOLOGY PROJECTpravenkumar100% (2)
- Sixth Grade Social Science (For Homeschool or Extra Practice)From EverandSixth Grade Social Science (For Homeschool or Extra Practice)No ratings yet
- Overview of ProjectDocument14 pagesOverview of Projectofmephotos4No ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument20 pagesBio Projectsaudaminipadhan423No ratings yet
- To Trace Back The Evolutionary History of Homo Sapiens SapiensDocument15 pagesTo Trace Back The Evolutionary History of Homo Sapiens SapiensgrafixitisNo ratings yet
- UCSP 2ND Quarter Module5Document65 pagesUCSP 2ND Quarter Module5Romar FloresNo ratings yet
- Human Evolution and Human Experimentation: Presented byDocument51 pagesHuman Evolution and Human Experimentation: Presented byHAZEL LEELA A P RICHARDNo ratings yet
- Cultural, Social, Political and Economic Symbols and PracticesDocument25 pagesCultural, Social, Political and Economic Symbols and PracticesMiko SantosNo ratings yet
- F1 - Early ManDocument4 pagesF1 - Early MandevNo ratings yet
- Bio Niranjan FinalDocument16 pagesBio Niranjan Finalkirubasankaran22606No ratings yet
- From The Beginning of Time: Sources To Understand Early Human HistoryDocument5 pagesFrom The Beginning of Time: Sources To Understand Early Human HistoryarchanaNo ratings yet
- History - XI Notes-Chapter-1 - From The Beginning of TimeDocument8 pagesHistory - XI Notes-Chapter-1 - From The Beginning of TimePeeyush SinhaNo ratings yet
- Ucsp ExamDocument150 pagesUcsp ExamBernadette ZaragozaNo ratings yet
- UCSP Quarter 1 Module 4Document19 pagesUCSP Quarter 1 Module 4Jerwinasmr TabujaraNo ratings yet
- Anthropological Concepts in Clinical OrthodonticsDocument42 pagesAnthropological Concepts in Clinical Orthodonticsayesha rathore100% (1)
- Theme1 From The Beginning of TimeDocument8 pagesTheme1 From The Beginning of TimeZafar AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Infos Ape To ManDocument8 pagesInfos Ape To Manjosh salahidNo ratings yet
- Block-1 HISTORYDocument72 pagesBlock-1 HISTORYdanish mohammadNo ratings yet
- Part-1 Early SocietiesDocument89 pagesPart-1 Early SocietiesZafar AkhtarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 BiologicalDocument55 pagesLesson 1 BiologicalCheska LimsonNo ratings yet
- SS2 LG 2.1 Introduction To Prehistory Students Copy 1Document6 pagesSS2 LG 2.1 Introduction To Prehistory Students Copy 1WengNo ratings yet
- Human AncestersDocument4 pagesHuman AncestersVenkatesan RamalingamNo ratings yet
- Origin of Huan RaceDocument6 pagesOrigin of Huan RaceJenell F. LumaluNo ratings yet
- Human EvolutionDocument10 pagesHuman Evolution11 E Harsh dagarNo ratings yet
- 4-Origin of Man & SocietyDocument4 pages4-Origin of Man & SocietyJerica TamayoNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document17 pagesCH 1Siddharth SinghNo ratings yet
- Evolution of ManDocument2 pagesEvolution of ManHennessy Shania Gallera ArdienteNo ratings yet
- Class XI NotesDocument6 pagesClass XI Notesdipankar90% (10)
- Human Biocultural and Social Evolution: (From Homo Habilis To Homo Sapiens)Document10 pagesHuman Biocultural and Social Evolution: (From Homo Habilis To Homo Sapiens)Philipjommel MilanoNo ratings yet
- Implications For The WorldDocument18 pagesImplications For The WorldMukesh KaliramanNo ratings yet
- Stages of Evolution of ManDocument3 pagesStages of Evolution of ManJuanjo Alonso Tresguerres89% (9)
- Name - Yash Narayan Patil STD-X Div-D Roll No - 19 Project Name - Human Evolution Subject - ScienceDocument7 pagesName - Yash Narayan Patil STD-X Div-D Roll No - 19 Project Name - Human Evolution Subject - SciencePrachi PatilNo ratings yet
- Curs - I.1103 - World PrehistoryDocument54 pagesCurs - I.1103 - World PrehistoryCristina MariaNo ratings yet
- The Earliest Possible Hominids: Sahelanthropus TchadensisDocument7 pagesThe Earliest Possible Hominids: Sahelanthropus Tchadensisdod_nurNo ratings yet
- Biological Evolution of Early Humans and Modern Humans: Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument24 pagesBiological Evolution of Early Humans and Modern Humans: Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsJansenn PastorNo ratings yet
- Bio-Cultural Evolution of HumansDocument8 pagesBio-Cultural Evolution of Humanstyagiishika216No ratings yet
- Ucsp Summary ReportDocument6 pagesUcsp Summary ReportDani AmorteiaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Culture, Society and Politics: Week - 6 Jaime J. GilbuenaDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Culture, Society and Politics: Week - 6 Jaime J. Gilbuenajosel DiwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-12 Human Evolution: Topic-1Document3 pagesChapter-12 Human Evolution: Topic-1Wizard BroNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 UcspDocument32 pagesChapter-3 UcspGabriela LopezNo ratings yet
- 11th His Chapter 1Document17 pages11th His Chapter 1Nitish DhenwalNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Prehistory - TheoryDocument11 pagesUnit 5 Prehistory - Theorylucia.benito.sanz12No ratings yet
- General Scope and Uses of Physical/Biological AnthropologyDocument23 pagesGeneral Scope and Uses of Physical/Biological AnthropologybhushantintinNo ratings yet
- The Beginnings of ManDocument50 pagesThe Beginnings of ManPehedenNo ratings yet
- Biological and Cultural Evolution by Jeff 103612Document63 pagesBiological and Cultural Evolution by Jeff 103612ClaiireNo ratings yet
- The Human Origin and Capacity For CultureDocument54 pagesThe Human Origin and Capacity For CultureJiwon Park100% (1)
- Sociology and Anthropology 2Document6 pagesSociology and Anthropology 2ashleycummingsmithNo ratings yet
- OK Lesson 3 - Looking Back at Human Biocultural and Social EvolutionDocument46 pagesOK Lesson 3 - Looking Back at Human Biocultural and Social EvolutionAdrian DimaunahanNo ratings yet
- Biological and Cultural EvolutionDocument55 pagesBiological and Cultural EvolutionKarl Rigo Andrino100% (3)
- Unit 1 Hunting and Gathering: StructureDocument16 pagesUnit 1 Hunting and Gathering: Structurebedanta04No ratings yet
- Emergence of Human and Major RacesDocument10 pagesEmergence of Human and Major RacesNikhil WandheNo ratings yet
- The Story of HumansDocument19 pagesThe Story of HumansSathyav VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- G.D.Goenka Public School, Siliguri: On-Line Learning Portal Class: Xi Subject: HistoryDocument3 pagesG.D.Goenka Public School, Siliguri: On-Line Learning Portal Class: Xi Subject: HistoryAayushi TomarNo ratings yet
- Human EvulotionDocument3 pagesHuman EvulotionAngelica GrantosNo ratings yet
- Stages of Human EvolutionDocument3 pagesStages of Human EvolutionHarley AdanzaNo ratings yet
- Australopiticus and Homo HabilisDocument17 pagesAustralopiticus and Homo HabilisThea SprouseNo ratings yet
- Human EvolutionDocument4 pagesHuman Evolutionbil5ingh05No ratings yet
- Gutsy Girls Go For Science: Paleontologists: With Stem Projects for KidsFrom EverandGutsy Girls Go For Science: Paleontologists: With Stem Projects for KidsNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.1: Introduction To Lti Representation and Transfer Function ModelDocument7 pagesExperiment No.1: Introduction To Lti Representation and Transfer Function ModelIra CervoNo ratings yet
- Datron PRC-BC4 Multiple Battery Charger - Operator and Technical ManualDocument28 pagesDatron PRC-BC4 Multiple Battery Charger - Operator and Technical ManualAlexander J RokowetzNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Welding GuideDocument8 pagesAluminum Welding Guideharish3742No ratings yet
- Data Protection Policy EnglishEWDocument8 pagesData Protection Policy EnglishEWAnkurNo ratings yet
- Nw4install DHCPDocument10 pagesNw4install DHCPnitrorubyNo ratings yet
- Io-Link Hub For 8 Analog Input SignalsDocument2 pagesIo-Link Hub For 8 Analog Input SignalsGabriel CardosoNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Basic ConceptsDocument32 pagesAir Compressor Basic Conceptsjkahamed100% (11)
- Practice-Tests Correction: Estimated Grade BDocument1 pagePractice-Tests Correction: Estimated Grade BDr. Emad Elbadawy د عماد البدويNo ratings yet
- BiotedadNo 3Document2 pagesBiotedadNo 3Budok MercadoNo ratings yet
- Abap Webdynpro Tips For Beginners: Windows and ViewsDocument14 pagesAbap Webdynpro Tips For Beginners: Windows and ViewsEr.Tousif MollickNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: KDL-52V4100 KDL-52V4100 KDL-52W4100 KDL-52W4100Document114 pagesService Manual: KDL-52V4100 KDL-52V4100 KDL-52W4100 KDL-52W4100Carolina López GonzálezNo ratings yet
- Quiz PASDocument3 pagesQuiz PASZoey Alvin EstarejaNo ratings yet
- COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION 11th Feb 2024Document4 pagesCOMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION 11th Feb 2024Ddamulira CharlesNo ratings yet
- Tugas B Ing FaldoDocument1 pageTugas B Ing FaldoFaldo AlfaizaNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Review Physics 11 SolutionsDocument8 pagesDynamics Review Physics 11 SolutionsAiswariya Alagu SunderNo ratings yet
- Uw Madison PHD ThesisDocument4 pagesUw Madison PHD Thesiskimberlyjonesnaperville100% (2)
- Vibrotip Web PAM1Document8 pagesVibrotip Web PAM1Bahtiar YudhistiraNo ratings yet
- Senate Bill 1483Document15 pagesSenate Bill 1483SAS NwSSUNo ratings yet
- MV KairosDocument104 pagesMV KairosDominic VillamanteNo ratings yet
- Cortana Tutorial: Raphael Mudge, Strategic Cyber LLCDocument61 pagesCortana Tutorial: Raphael Mudge, Strategic Cyber LLCcastillo_leoNo ratings yet
- Important Safeguards. Instrucciones Importantes de SeguridadDocument2 pagesImportant Safeguards. Instrucciones Importantes de SeguridadLUISA MALDONADO ROANo ratings yet
- RSAL KEMENKES Sby1Document150 pagesRSAL KEMENKES Sby1WAY MINCANGNo ratings yet
- Laplace TransformsDocument22 pagesLaplace TransformsAustin JamesNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 2-8: Tudent EgreeDocument5 pagesPractice Test 2-8: Tudent EgreeThùy LinhNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Auf DeutschDocument8 pagesDissertation Auf DeutschWriteMyPaperForMeSpringfield100% (1)
- Ask A Question Create A Poll: Why Is The Number "13" Considered An "Unlucky" Number?Document28 pagesAsk A Question Create A Poll: Why Is The Number "13" Considered An "Unlucky" Number?Andres TugguinNo ratings yet
- Scap Assignment 2Document11 pagesScap Assignment 2ARYAN KESHRINo ratings yet
- D 2Document9 pagesD 2jhouvanNo ratings yet
- Sex Is Binary EssayDocument6 pagesSex Is Binary EssayAshleigh SchumanNo ratings yet