Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsELS Hard
ELS Hard
Uploaded by
mppsregistrarThe document discusses energy use in organisms at the cellular level. It explains that [1] cells constantly need energy to perform tasks like breaking down and synthesizing molecules, transporting products, and removing waste; [2] energy is provided by nutrients from food which are broken down to release energy through cellular respiration; and [3] photosynthesis and cellular respiration are key processes that power life on Earth by facilitating the exchange of matter and energy between organisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Chapter 47Document11 pagesChapter 47Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Utilizing Energy For LifeDocument41 pagesUtilizing Energy For LifeJOHN PAUL MACALLINGNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument14 pagesEnergy TransformationJoaquine ArateaNo ratings yet
- Cell EnergyDocument29 pagesCell EnergyKimberly Anne T. RinNo ratings yet
- Overview of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesOverview of PhotosynthesisChelsea Marie AntolinNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesPhotosynthesisJESSERYL MARGALLONo ratings yet
- Metabolism Is The Sum Total of All Chemical Processes Taking Place Within A Living SystemDocument5 pagesMetabolism Is The Sum Total of All Chemical Processes Taking Place Within A Living SystemFerdinand Arcangel Ebalo IiNo ratings yet
- Adenosine Triphosphate ATP ATP Currency Used Throughout The Cell. Energy Carrier For Cells Mechanical Work To Move Cilia and Vesicles Transport Substances Across The Membrane and Perform Variou 1Document4 pagesAdenosine Triphosphate ATP ATP Currency Used Throughout The Cell. Energy Carrier For Cells Mechanical Work To Move Cilia and Vesicles Transport Substances Across The Membrane and Perform Variou 1Kurt IgotNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationFatima DariaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 11 Energy and MetabolismDocument29 pagesLife Sciences Grade 11 Energy and MetabolismClaire WeerepasNo ratings yet
- G4 BIOENERGETICS and EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTIION 2Document6 pagesG4 BIOENERGETICS and EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTIION 2niru098No ratings yet
- Biology - Module 5Document11 pagesBiology - Module 5ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and CRDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis and CRKhyla Grace DijenoNo ratings yet
- Energy and The Cell: Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument45 pagesEnergy and The Cell: Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationlovepugsNo ratings yet
- Els Reviewer 2Document6 pagesEls Reviewer 2Kenjie kunNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis ReviewerDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis ReviewerLJ RacadioNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis & RespirationDocument32 pagesPhotosynthesis & RespirationCarson Schultz100% (1)
- 11 - Photosynthesis - COMPLETE PDFDocument14 pages11 - Photosynthesis - COMPLETE PDFToni HeaterNo ratings yet
- Genbio Quatter 2Document5 pagesGenbio Quatter 2Shakira UyNo ratings yet
- Pre-Labs 3: 1. What Are Autotrophs and Heterotrophs? Give Each One ExampleDocument4 pagesPre-Labs 3: 1. What Are Autotrophs and Heterotrophs? Give Each One ExampleGiao TranNo ratings yet
- Flow of Energy and Matter in Ecosystems: Prepared By: Mr. Joselito Christian Paulus M. VillanuevaDocument9 pagesFlow of Energy and Matter in Ecosystems: Prepared By: Mr. Joselito Christian Paulus M. VillanuevaPaulus VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Photosynthesis - Chap 7 NotesDocument14 pagesBiology - Photosynthesis - Chap 7 NotessarayoshicaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Seat of Wisdom Secondary School, Trans Ekulu, EnuguDocument20 pagesUnit 1: Seat of Wisdom Secondary School, Trans Ekulu, EnuguUkwuma Michael ChijiokeNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Mod 9-11Document7 pagesGen Bio Mod 9-11Arabella BrionesNo ratings yet
- Topic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument70 pagesTopic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeJai CataluñaNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Photosynthesis and Energy FlowDocument4 pagesBioenergetics Photosynthesis and Energy Flowvin ocangNo ratings yet
- Energy MetabolismDocument4 pagesEnergy MetabolismKaren ParkNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument15 pagesPhotosynthesishurainsahar21No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesisMina IbrahimNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-2-BioenergeticsDocument5 pagesCHAPTER-2-Bioenergeticsbendanomarky8No ratings yet
- Labbio Sat DangPhuongQuynh Prelab3Document3 pagesLabbio Sat DangPhuongQuynh Prelab3Quynh Dang PhuongNo ratings yet
- GN 3.3 - Cell RespirationDocument7 pagesGN 3.3 - Cell RespirationJuan CastellanosNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument3 pagesBIOENERGETICSJaemsNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesGrade 9 PhotosynthesisyannsegundinoNo ratings yet
- Module 8 PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesModule 8 PhotosynthesisSeann ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesCellular Respirationashleyjade.sundiam.sccNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration (Module 5)Document51 pagesPhotosynthesis Cellular Respiration (Module 5)Trisha DeniseNo ratings yet
- Concept of Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument3 pagesConcept of Cell Structures and FunctionsTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Lecturer: Yuyun Wirasasmita, M.Farm., Apt at Stikes Ist ButonDocument13 pagesLecturer: Yuyun Wirasasmita, M.Farm., Apt at Stikes Ist Butonsifa al rishalNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument10 pagesECOSYSTEMRyanKingjimDiezUyNo ratings yet
- ChloroplastDocument8 pagesChloroplastJerome GamitNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDocument46 pagesPhotosynthesis and RespirationCarmsNo ratings yet
- Week 17 ModuleDocument3 pagesWeek 17 Modulerose maryNo ratings yet
- Lecture: 2.3 PHOTOSYNTHESIS: Photosynthesis Converts Light Energy To Chemical Energy of FoodDocument2 pagesLecture: 2.3 PHOTOSYNTHESIS: Photosynthesis Converts Light Energy To Chemical Energy of FoodLorena DizonNo ratings yet
- 2 8 PhotosynthesisDocument27 pages2 8 Photosynthesisıamnıkolaı 4No ratings yet
- Bio 12 AModule 7Document7 pagesBio 12 AModule 7Ivan RamirezNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument2 pagesMetabolismcheryl tayasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesChapter 10 PhotosynthesisstarcandypricessNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 2Document4 pagesLesson1 2Cheradee AnimNo ratings yet
- Photosyntheis and RespirationDocument37 pagesPhotosyntheis and Respirationfelisilda.136571140273No ratings yet
- Photosenthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesPhotosenthesis and Cellular RespirationMonkey D. AilaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis DocsDocument81 pagesPhotosynthesis Docsnm0583167No ratings yet
- BIOL111 1st Sem, Final TermDocument40 pagesBIOL111 1st Sem, Final TermJasmine CatanaNo ratings yet
- Eals 11abma1 MangosingDocument34 pagesEals 11abma1 MangosingAndrea Mae V. MangosingNo ratings yet
- What Is Photosynthesis?: Cellular Respiration FermentationDocument8 pagesWhat Is Photosynthesis?: Cellular Respiration FermentationDiana Jean Alo-adNo ratings yet
- General Biology NotesDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology NotesjeayNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer (1) - CompressedDocument61 pagesBiology Reviewer (1) - CompressedkevinNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm and OrganellesDocument22 pagesCytoplasm and OrganellesKrishiaDeVeraNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument22 pagesPhotosynthesislaNo ratings yet
- Fitness Training Manual 7.0Document141 pagesFitness Training Manual 7.0Ishraq Dhaly100% (4)
- Carbohydrates Chemistry-3 - Sana'a UniversityDocument45 pagesCarbohydrates Chemistry-3 - Sana'a UniversityMazin Mohsen ali almolikyNo ratings yet
- Core CH 5 Food and HumansDocument9 pagesCore CH 5 Food and HumansommpNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculeDocument14 pagesBio MoleculeMohit KaushikNo ratings yet
- HEALING Heal Your Mind Heal Your Body Change Your LifeDocument25 pagesHEALING Heal Your Mind Heal Your Body Change Your Lifemiso100% (1)
- Applied Nutrition 2nd Semester BSN Complete Notes, Educational Platform-1Document299 pagesApplied Nutrition 2nd Semester BSN Complete Notes, Educational Platform-1john wickNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4, 2010Document28 pagesScheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4, 2010WanM.Syamim0% (1)
- Clinical Chemistry L 7Document151 pagesClinical Chemistry L 7adis alemNo ratings yet
- Alkyl PolyglycosideDocument16 pagesAlkyl PolyglycosidePrashantSoniNo ratings yet
- Project Geek To Freak 5-31-11Document43 pagesProject Geek To Freak 5-31-11Benny Carroll80% (5)
- Unit 3L.4:: Body Parts and FunctionsDocument27 pagesUnit 3L.4:: Body Parts and FunctionsAbhiday SinghNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy: UNP College of NursingDocument379 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy: UNP College of NursingrnrmmanphdNo ratings yet
- Aquaculture Set IDocument17 pagesAquaculture Set IClinton VillaflorNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Carbon Compounds: Unit 3: BiochemistryDocument21 pages3.1 Carbon Compounds: Unit 3: Biochemistryapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Infusion Therapy CompleteDocument93 pagesInfusion Therapy CompleteRafaelFreitasNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Performance NutritionDocument157 pagesComprehensive Performance NutritionJake100% (8)
- Nutritional and Medicinal Qualities of Sweetpotato Tops and LeavesDocument4 pagesNutritional and Medicinal Qualities of Sweetpotato Tops and LeavesAlfred YangaoNo ratings yet
- Pattern Matching Online VersionDocument35 pagesPattern Matching Online VersionBinay BrarNo ratings yet
- Biokar CatalogusDocument307 pagesBiokar Catalogusrheablack0% (2)
- Chep202 QPDocument5 pagesChep202 QPshamiksha dNo ratings yet
- 2018 Rashmietal TaroAnoverviewDocument7 pages2018 Rashmietal TaroAnoverviewKate TrespuerNo ratings yet
- Exam 1Document172 pagesExam 1Tara BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Green Credits For Sustainable LivingDocument8 pagesGreen Credits For Sustainable LivingPradeep Kumar KuncheNo ratings yet
- Carbs Handout PDFDocument4 pagesCarbs Handout PDFHM330No ratings yet
- TLE Part 3Document5 pagesTLE Part 3Jhoyvhie NolascoNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules RealnarealDocument19 pagesBiological Molecules RealnarealOyenx Garrix SulatorioNo ratings yet
- Nutri PrelimsDocument15 pagesNutri PrelimsGabNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- Proceeding International Conference 2019Document154 pagesProceeding International Conference 2019Prasetiyo Eko LaksonoNo ratings yet
ELS Hard
ELS Hard
Uploaded by
mppsregistrar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesThe document discusses energy use in organisms at the cellular level. It explains that [1] cells constantly need energy to perform tasks like breaking down and synthesizing molecules, transporting products, and removing waste; [2] energy is provided by nutrients from food which are broken down to release energy through cellular respiration; and [3] photosynthesis and cellular respiration are key processes that power life on Earth by facilitating the exchange of matter and energy between organisms.
Original Description:
Original Title
ELS-Hard-copy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses energy use in organisms at the cellular level. It explains that [1] cells constantly need energy to perform tasks like breaking down and synthesizing molecules, transporting products, and removing waste; [2] energy is provided by nutrients from food which are broken down to release energy through cellular respiration; and [3] photosynthesis and cellular respiration are key processes that power life on Earth by facilitating the exchange of matter and energy between organisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesELS Hard
ELS Hard
Uploaded by
mppsregistrarThe document discusses energy use in organisms at the cellular level. It explains that [1] cells constantly need energy to perform tasks like breaking down and synthesizing molecules, transporting products, and removing waste; [2] energy is provided by nutrients from food which are broken down to release energy through cellular respiration; and [3] photosynthesis and cellular respiration are key processes that power life on Earth by facilitating the exchange of matter and energy between organisms.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Use of Energy -bacteria decompose wastes
-dead organisms
Every task of the body requires the use of
energy. In the cellular level, body cells Energy - flows in one direction and transforms
constantly need a steady supply of energy to from one form to another.
keep the organism alive.
Energy - is required to produce and breakdown -flows through the ecosystem as plants absorb
molecules, as well as to transport products in light energy into chemical energy in the form of
and out of the cell. sugars
Removing pathogenic bacteria and Energy Conversion - in this process some
viruses and exporting toxins and energy is converted as heat.
poisons out of the cell also require the
use of energy. Specialized cell organelles
Energy is provided for by the nutrients
received via the digestive system. Living organisms - one or more cells.
Complex molecules from food,
specifically complex carbohydrates, are All organisms function using the chemical
broken down into simple sugars such as energy found in the form of carbohydrates
glucose. molecules.
In the cellular level, the synthesis and
breakdown of complex molecules occur Photoautotrophs - autotrophs that use sunlight
through chemical reactions that release and carbon from carbon dioxide to synthesize
energy or require energy to occur. This chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates
is the reason why food must be
consumed so that cells are replenished Plants - are the common photoautotrophs
and supplied with nutrients.
All these chemical reactions taking place Marine Algae - world’s largest oxygen
inside the cells are collectively called producers
metabolism.
All these chemical reactions taking place - lives in the ocean
inside the cells are collectively called
metabolism. Humans or plants - specialized organelles that
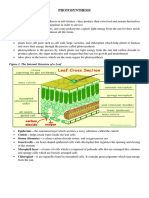
Figure 6.1 shows the relationship of two function for harvesting energy.
important processes that power life on
Earth or simply help organisms survive – Mitochondria - small specialized cellular
the exchange of matter and energy. organelles that produce energy from food by
breaking down carbon-containing molecules
Autotrophs (plants) - producers in a food chain
and releasing energy packets in the form of
which take water and minerals from the soil
ATP.
and carbon dioxide from the air.
Heterotrophs (consumers) - eat plants and - this is known as “powerhouse of the cell”
other animals
Capabilities of mitochondria - provides
Respiration - results in the release of carbon chemical fuels that power the cell to do certain
dioxide and return of wastes to the processes such as moving cells and their parts
environment.
- copying DNA
Decomposers
- synthesizing proteins and dividing in half,
-small animals
-fungi
Plant cells - possess different types of plastids Light-Dependent Stage -
that can harvest solar energy, store nutrients, involves photophosphorylation of ADP to form
and manufacture nutrient molecules. ATP. This is catalyzed by the enzyme ATP
synthase, which couples this reaction with the
Chloroplast - most common type of plastid. movement of hydrogen ( H + ) ions through the
enzyme. This can happen in a cyclic process or
- responsible for trapping light energy in a
chemical form. a noncyclic process.
Light-Independent Stage - is also known as the
Chlorophyll - a green pigment in innermost Calvin cycle or Calvin-Benson cycle. It consists
membrane of chloroplast.
of reactions that use the energy stored and
carried in the light-dependent reaction to build
PHOTOSYNTHESIS
glucose. Carbon dioxide enter the chloroplast
- converts solar energy into chemical energy of plant cells through the stomata of the leaves.
stored in sugar molecules (glucose). This
chemical energy is then released when certain CELLULAR RESPIRATION
organisms eat plants. In addition,
photosynthesis also releases essential oxygen, This process could be compared to
which humans and animals need for survival. using the energy from food. In a global
scale, this can be observed in an
- requires sunlight, carbon dioxide, and organism feeding on another.
water – the materials needed in the chemical There are two pathways by which
reaction energy is harvested from food: with or
without oxygen.
-takes place in the plant leaves
Aerobic pathway - also known as cellular
-occurs in the middle layer called mesophyll. respiration
Mesophyll - contains tiny openings has 2 pathways:
called stomata
Stomata - where gases enter and exit 1. Aerobic
Thylakoid membrane - is enclosed 2. Anaerobic Pathway
within a thylakoid space. A stack of
thylakoids is called a granum, which is 3 stages of Aerobic Pathway:
surrounded by a space known as the
stroma. 1. Glycolysis – series of enzymes-
controlled reactions that occur inside the
- Embedded inside the thylakoids are green cytoplasm.
pigment molecules, called chlorophyll, that
absorb light. The process continues on involving the
formation of two 3-C compound called
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages: pyruvate (ionized pyruvic acid)
Pyruvate - results in the release of two
1. Light-dependent - occurs in the thylakoid ATP molecules. This contains some
membrane of the chloroplast, where the stored chemical energy that acts as an
chlorophyll pigment absorbs the light intermediate or a reactant for the next
energy from the sun and converts it into part of the metabolic pathway.
chemical energy together with water.
2. Light-independent - also known as 2. Krebs Cycle – also known as the citric
Calvin cycle or Calvin-Benson cycle acid cycle
occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast.
3. Electron transport chain – also involves
a series of enzyme-controlled reactions
that convert the 2kinetic energy present
in hydrogen electrons into energy (ATP).
In the mitochondrial membrane are iron-
containing enzyme molecules called
cytochrome.
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Anaerobic pathway - an anaerobic pathway
may be used to supply body cells with an
immediate energy source.
Fermentation - important in the global recycling
of carbon in the environment.
Without the presence of anaerobic
microorganisms, Earth would become oxygen-
poor.
You might also like
- Biology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideFrom EverandBiology: a QuickStudy Laminated Reference GuideRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Chapter 47Document11 pagesChapter 47Aziil LiizaNo ratings yet
- Utilizing Energy For LifeDocument41 pagesUtilizing Energy For LifeJOHN PAUL MACALLINGNo ratings yet
- Energy TransformationDocument14 pagesEnergy TransformationJoaquine ArateaNo ratings yet
- Cell EnergyDocument29 pagesCell EnergyKimberly Anne T. RinNo ratings yet
- Overview of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesOverview of PhotosynthesisChelsea Marie AntolinNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesPhotosynthesisJESSERYL MARGALLONo ratings yet
- Metabolism Is The Sum Total of All Chemical Processes Taking Place Within A Living SystemDocument5 pagesMetabolism Is The Sum Total of All Chemical Processes Taking Place Within A Living SystemFerdinand Arcangel Ebalo IiNo ratings yet
- Adenosine Triphosphate ATP ATP Currency Used Throughout The Cell. Energy Carrier For Cells Mechanical Work To Move Cilia and Vesicles Transport Substances Across The Membrane and Perform Variou 1Document4 pagesAdenosine Triphosphate ATP ATP Currency Used Throughout The Cell. Energy Carrier For Cells Mechanical Work To Move Cilia and Vesicles Transport Substances Across The Membrane and Perform Variou 1Kurt IgotNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument8 pagesPhotosynthesis and Cellular RespirationFatima DariaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 11 Energy and MetabolismDocument29 pagesLife Sciences Grade 11 Energy and MetabolismClaire WeerepasNo ratings yet
- G4 BIOENERGETICS and EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTIION 2Document6 pagesG4 BIOENERGETICS and EVIDENCE OF EVOLUTIION 2niru098No ratings yet
- Biology - Module 5Document11 pagesBiology - Module 5ASHLEY MONICA PLATANo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and CRDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis and CRKhyla Grace DijenoNo ratings yet
- Energy and The Cell: Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument45 pagesEnergy and The Cell: Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationlovepugsNo ratings yet
- Els Reviewer 2Document6 pagesEls Reviewer 2Kenjie kunNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis ReviewerDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis ReviewerLJ RacadioNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis & RespirationDocument32 pagesPhotosynthesis & RespirationCarson Schultz100% (1)
- 11 - Photosynthesis - COMPLETE PDFDocument14 pages11 - Photosynthesis - COMPLETE PDFToni HeaterNo ratings yet
- Genbio Quatter 2Document5 pagesGenbio Quatter 2Shakira UyNo ratings yet
- Pre-Labs 3: 1. What Are Autotrophs and Heterotrophs? Give Each One ExampleDocument4 pagesPre-Labs 3: 1. What Are Autotrophs and Heterotrophs? Give Each One ExampleGiao TranNo ratings yet
- Flow of Energy and Matter in Ecosystems: Prepared By: Mr. Joselito Christian Paulus M. VillanuevaDocument9 pagesFlow of Energy and Matter in Ecosystems: Prepared By: Mr. Joselito Christian Paulus M. VillanuevaPaulus VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Biology - Photosynthesis - Chap 7 NotesDocument14 pagesBiology - Photosynthesis - Chap 7 NotessarayoshicaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: Seat of Wisdom Secondary School, Trans Ekulu, EnuguDocument20 pagesUnit 1: Seat of Wisdom Secondary School, Trans Ekulu, EnuguUkwuma Michael ChijiokeNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio Mod 9-11Document7 pagesGen Bio Mod 9-11Arabella BrionesNo ratings yet
- Topic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeDocument70 pagesTopic I: Cell: The Basic Unit of LifeJai CataluñaNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Photosynthesis and Energy FlowDocument4 pagesBioenergetics Photosynthesis and Energy Flowvin ocangNo ratings yet
- Energy MetabolismDocument4 pagesEnergy MetabolismKaren ParkNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument15 pagesPhotosynthesishurainsahar21No ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument13 pagesPhotosynthesisMina IbrahimNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-2-BioenergeticsDocument5 pagesCHAPTER-2-Bioenergeticsbendanomarky8No ratings yet
- Labbio Sat DangPhuongQuynh Prelab3Document3 pagesLabbio Sat DangPhuongQuynh Prelab3Quynh Dang PhuongNo ratings yet
- GN 3.3 - Cell RespirationDocument7 pagesGN 3.3 - Cell RespirationJuan CastellanosNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICSDocument3 pagesBIOENERGETICSJaemsNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 PhotosynthesisDocument20 pagesGrade 9 PhotosynthesisyannsegundinoNo ratings yet
- Module 8 PhotosynthesisDocument6 pagesModule 8 PhotosynthesisSeann ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesCellular Respirationashleyjade.sundiam.sccNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration (Module 5)Document51 pagesPhotosynthesis Cellular Respiration (Module 5)Trisha DeniseNo ratings yet
- Concept of Cell Structures and FunctionsDocument3 pagesConcept of Cell Structures and FunctionsTyron ChuaNo ratings yet
- Lecturer: Yuyun Wirasasmita, M.Farm., Apt at Stikes Ist ButonDocument13 pagesLecturer: Yuyun Wirasasmita, M.Farm., Apt at Stikes Ist Butonsifa al rishalNo ratings yet
- ECOSYSTEMDocument10 pagesECOSYSTEMRyanKingjimDiezUyNo ratings yet
- ChloroplastDocument8 pagesChloroplastJerome GamitNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis and RespirationDocument46 pagesPhotosynthesis and RespirationCarmsNo ratings yet
- Week 17 ModuleDocument3 pagesWeek 17 Modulerose maryNo ratings yet
- Lecture: 2.3 PHOTOSYNTHESIS: Photosynthesis Converts Light Energy To Chemical Energy of FoodDocument2 pagesLecture: 2.3 PHOTOSYNTHESIS: Photosynthesis Converts Light Energy To Chemical Energy of FoodLorena DizonNo ratings yet
- 2 8 PhotosynthesisDocument27 pages2 8 Photosynthesisıamnıkolaı 4No ratings yet
- Bio 12 AModule 7Document7 pagesBio 12 AModule 7Ivan RamirezNo ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument2 pagesMetabolismcheryl tayasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 PhotosynthesisDocument12 pagesChapter 10 PhotosynthesisstarcandypricessNo ratings yet
- Lesson1 2Document4 pagesLesson1 2Cheradee AnimNo ratings yet
- Photosyntheis and RespirationDocument37 pagesPhotosyntheis and Respirationfelisilda.136571140273No ratings yet
- Photosenthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument3 pagesPhotosenthesis and Cellular RespirationMonkey D. AilaNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis DocsDocument81 pagesPhotosynthesis Docsnm0583167No ratings yet
- BIOL111 1st Sem, Final TermDocument40 pagesBIOL111 1st Sem, Final TermJasmine CatanaNo ratings yet
- Eals 11abma1 MangosingDocument34 pagesEals 11abma1 MangosingAndrea Mae V. MangosingNo ratings yet
- What Is Photosynthesis?: Cellular Respiration FermentationDocument8 pagesWhat Is Photosynthesis?: Cellular Respiration FermentationDiana Jean Alo-adNo ratings yet
- General Biology NotesDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology NotesjeayNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer (1) - CompressedDocument61 pagesBiology Reviewer (1) - CompressedkevinNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm and OrganellesDocument22 pagesCytoplasm and OrganellesKrishiaDeVeraNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument22 pagesPhotosynthesislaNo ratings yet
- Fitness Training Manual 7.0Document141 pagesFitness Training Manual 7.0Ishraq Dhaly100% (4)
- Carbohydrates Chemistry-3 - Sana'a UniversityDocument45 pagesCarbohydrates Chemistry-3 - Sana'a UniversityMazin Mohsen ali almolikyNo ratings yet
- Core CH 5 Food and HumansDocument9 pagesCore CH 5 Food and HumansommpNo ratings yet
- Bio MoleculeDocument14 pagesBio MoleculeMohit KaushikNo ratings yet
- HEALING Heal Your Mind Heal Your Body Change Your LifeDocument25 pagesHEALING Heal Your Mind Heal Your Body Change Your Lifemiso100% (1)
- Applied Nutrition 2nd Semester BSN Complete Notes, Educational Platform-1Document299 pagesApplied Nutrition 2nd Semester BSN Complete Notes, Educational Platform-1john wickNo ratings yet
- Scheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4, 2010Document28 pagesScheme of Work BIOLOGY FORM 4, 2010WanM.Syamim0% (1)
- Clinical Chemistry L 7Document151 pagesClinical Chemistry L 7adis alemNo ratings yet
- Alkyl PolyglycosideDocument16 pagesAlkyl PolyglycosidePrashantSoniNo ratings yet
- Project Geek To Freak 5-31-11Document43 pagesProject Geek To Freak 5-31-11Benny Carroll80% (5)
- Unit 3L.4:: Body Parts and FunctionsDocument27 pagesUnit 3L.4:: Body Parts and FunctionsAbhiday SinghNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Therapy: UNP College of NursingDocument379 pagesNutrition and Diet Therapy: UNP College of NursingrnrmmanphdNo ratings yet
- Aquaculture Set IDocument17 pagesAquaculture Set IClinton VillaflorNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Carbon Compounds: Unit 3: BiochemistryDocument21 pages3.1 Carbon Compounds: Unit 3: Biochemistryapi-520057338No ratings yet
- Infusion Therapy CompleteDocument93 pagesInfusion Therapy CompleteRafaelFreitasNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Performance NutritionDocument157 pagesComprehensive Performance NutritionJake100% (8)
- Nutritional and Medicinal Qualities of Sweetpotato Tops and LeavesDocument4 pagesNutritional and Medicinal Qualities of Sweetpotato Tops and LeavesAlfred YangaoNo ratings yet
- Pattern Matching Online VersionDocument35 pagesPattern Matching Online VersionBinay BrarNo ratings yet
- Biokar CatalogusDocument307 pagesBiokar Catalogusrheablack0% (2)
- Chep202 QPDocument5 pagesChep202 QPshamiksha dNo ratings yet
- 2018 Rashmietal TaroAnoverviewDocument7 pages2018 Rashmietal TaroAnoverviewKate TrespuerNo ratings yet
- Exam 1Document172 pagesExam 1Tara BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- Green Credits For Sustainable LivingDocument8 pagesGreen Credits For Sustainable LivingPradeep Kumar KuncheNo ratings yet
- Carbs Handout PDFDocument4 pagesCarbs Handout PDFHM330No ratings yet
- TLE Part 3Document5 pagesTLE Part 3Jhoyvhie NolascoNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules RealnarealDocument19 pagesBiological Molecules RealnarealOyenx Garrix SulatorioNo ratings yet
- Nutri PrelimsDocument15 pagesNutri PrelimsGabNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument16 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Levelmstudy123456No ratings yet
- Proceeding International Conference 2019Document154 pagesProceeding International Conference 2019Prasetiyo Eko LaksonoNo ratings yet