Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calamox Drops
Calamox Drops
Uploaded by
wardagsgl0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesThis document describes Calamox, an oral antibacterial combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. It provides details on the composition, mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, microbiology, therapeutic indications, dosage, administration and use in specific populations such as pediatric and renal patients. Calamox is indicated for short-term treatment of bacterial infections at various sites caused by organisms susceptible to amoxicillin or clavulanic acid. Dosing may require adjustment in renal or hepatic impairment based on the patient's condition and organ function.
Original Description:
Calamox prescription
Original Title
calamox-drops
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document describes Calamox, an oral antibacterial combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. It provides details on the composition, mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, microbiology, therapeutic indications, dosage, administration and use in specific populations such as pediatric and renal patients. Calamox is indicated for short-term treatment of bacterial infections at various sites caused by organisms susceptible to amoxicillin or clavulanic acid. Dosing may require adjustment in renal or hepatic impairment based on the patient's condition and organ function.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesCalamox Drops
Calamox Drops
Uploaded by
wardagsglThis document describes Calamox, an oral antibacterial combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. It provides details on the composition, mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, microbiology, therapeutic indications, dosage, administration and use in specific populations such as pediatric and renal patients. Calamox is indicated for short-term treatment of bacterial infections at various sites caused by organisms susceptible to amoxicillin or clavulanic acid. Dosing may require adjustment in renal or hepatic impairment based on the patient's condition and organ function.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
For Medical Professional only
DESCRIPTION: Gram-Negative Bacteria:
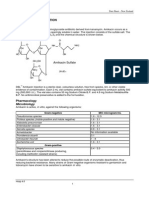
CALAMOX is an oral antibacterial combination consisting of amoxicillin and the beta-lactama- • Enterobacter species
se inhibitor, clavulanate potassium (the potassium salt of clavulanic acid). • Escherichia coli
• Haemophilus influenzae
Amoxicillin is an analog of ampicillin, derived from the basic penicillin nucleus, 6-aminopenicil- • Klebsiella species
lanic acid. The amoxicillin molecular formula is C16H19N3O5S•3H2O, and the molecular weight • Moraxella catarrhalis
is 419.46. Chemically, amoxicillin is (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(R)-(-)-2-Amino-2-(phydroxyphenyl)aceta- • Eikenella corrodens
mido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid trihydrate. • Proteus mirabilis
Clavulanic acid is produced by the fermentation of Streptomyces clavuligerus. It is a Anaerobic Bacteria:
beta-lactam structurally related to the penicillins and possesses the ability to inactivate some • Bacteroides species
beta-lactamases by blocking the active sites of these enzymes. The clavulanate potassium • Bacteroides fragilis
molecular formula is C8H8KNO5, and the molecular weight is 237.25. Chemically, clavulanate • Fusobacterium species
potassium is potassium (Z)(2R,5R)-3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-4-oxa-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0] • Peptostreptococcus species
-heptane-2-carboxylate.
Pharmacokinetic Properties
COMPOSITION: Absorption:
When reconstituted as directed each ml contains : Dosing in the fasted or fed state has minimal effect on the pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin.
Amoxicillin Trihydrate U.S.P. eq. to 50mg Amoxicillin While CALAMOX can be given without regard to meals, absorption of clavulanate potassium
Clavulanate Potassium U.S.P. eq. to 12.5mg Clavulanic acid when taken with food is greater relative to the fasted state. In one study, the relative
(Product Specs.: U.S.P.) bioavailability of clavulanate was reduced when CALAMOX was dosed at 30 and 150 minutes
after the start of a high-fat breakfast.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
Pharmacodynamic Properties: Distribution:
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Combinations of penicillins, incl. beta-lactamase inhibitors; ATC Neither component in CALAMOX is highly protein-bound; clavulanic acid is approximately
code: J01CR02 25% bound to human serum and amoxicillin approximately 18% bound. Amoxicillin diffuses
readily into most body tissues and fluids with the exception of the brain and spinal fluid. Two
Mechanism of Action: hours after oral administration of a single 35 mg/kg dose of suspension of CALAMOX to fasting
Amoxicillin is a semisynthetic penicillin (beta-lactam antibiotic) that inhibits one or more children, average concentrations of 3 mcg/mL of amoxicillin and 0.5 mcg/mL of clavulanic acid
enzymes (often referred to as penicillin-binding proteins, PBPs) in the biosynthetic pathway of were detected in middle ear effusions.
bacterial peptidoglycan, which is an integral structural component of the bacterial cell wall.
Inhibition of peptidoglycan synthesis leads to weakening of the cell wall, which is usually Metabolism and Excretion:
followed by cell lysis and death. The half-life of amoxicillin after the oral administration of CALAMOX is 1.3 hours and that of
clavulanic acid is 1 hour. Approximately 50% to 70% of the amoxicillin and approximately 25%
Amoxicillin is susceptible to degradation by beta-lactamases produced by resistant bacteria to 40% of the clavulanic acid are excreted unchanged in urine during the first 6 hours after
and therefore the spectrum of activity of amoxicillin alone does not include organisms which administration of a single 250-mg or 500-mg tablet of CALAMOX.
produce these enzymes.
SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Clavulanic acid is a beta-lactam structurally related to penicillins. It inactivates some Renal Impairment
beta-lactamase enzymes thereby preventing inactivation of amoxicillin. Clavulanic acid alone The total serum clearance of amoxicillin/clavulanic acid decreases proportionately with
does not exert a clinically useful antibacterial effect. decreasing renal function. The reduction in drug clearance is more pronounced for amoxicillin
than for clavulanic acid, as a higher proportion of amoxicillin is excreted via the renal route.
Microbiology: Doses in renal impairment must therefore prevent undue accumulation of amoxicillin while
Gram-Positive Bacteria: maintaining adequate levels of clavulanic acid.
• Staphylococcus aureus
• Enterococcus faecalis Hepatic Impairment
• Staphylococcus epidermidis Hepatically impaired patients should be dosed with caution and hepatic function monitored at
• Staphylococcus saprophyticus regular intervals.
• Streptococcus pneumoniae
• Streptococcus pyogenes
• Viridans group Streptococcus
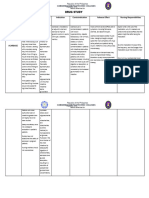
Pediatrics: Dosage in renal impairment
The elimination half-life of amoxicillin is similar for children aged around 3 months to 2 years Moderate impairment
and older children and adults. For very young children (including preterm newborns) in the first Mild impairment (Crea�nine Severe impairment (Creatinine
(Creatinine clearance 10-30
week of life the interval of administration should not exceed twice daily administration due to clearance >30 ml/min) clearance <10ml/min)
ml/min)
immaturity of the renal pathway of elimination.
No change in dosage, i.e., the The recommended dose given The recommended dose given
Elderly:
recommended dose given three twice daily instead of three once daily instead of three
Elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose
selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. �mes daily* �mes per day* �mes per day*
THERAPEUTIC INDICATIONS: * In more serious cases this dose may be doubled.
CALAMOX infant drops are indicated for short-term treatment of bacterial infections at the
following sites: Upper respiratory tract Infections (including ENT) e.g. recurrent tonsillitis, Dosage in hepatic impairment
sinusitis, otitis media. Lower respiratory tract infections e.g. acute exacerbation of chronic Dose with caution; monitor hepatic function at regular intervals.
bronchitis, lobar and bronchopneumonia. Genitourinary tract infections e.g. cystitis, urethritis,
pyelonephritis. Skin and soft tissue infections, e.g. boils, abscesses, cellulitis, wound Administration:
infections. Bone and joint infections e.g. osteomyelitis. Other infections e.g. intra abdominal To minimise potential gastrointestinal intolerance, administer at the start of a meal. The
sepsis. Infections caused by amoxicillin-susceptible organisms are amenable to CALAMOX absorption of CALAMOX is optimised when taken at the start of a meal. Duration of therapy
treatment due to its amoxicillin content. Mixed infections caused by amoxicillin-susceptible should be appropriate to the indication and should not be extended beyond 14 days without
organisms in conjunction with CALAMOX-susceptible β-lactamase producing organisms may review.
therefore be treated with CALAMOX.
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION: Hypersensitivity to the active substances, to any of the penicillins or to any of the excipients.
The usual recommended daily dosage is 25 mg/kg/day in divided doses every eight hours. In History of a severe immediate hypersensitivity reaction (e.g. anaphylaxis) to another
more serious infections the dosage may be increased up to 50 mg/kg/day in divided doses beta-lactam agent (e.g. a cephalosporin, carbapenem or monobactam). History of
every eight hours. Each 25 mg CALAMOX provides 20mg amoxicillin and 5 mg clavulanate. jaundice/hepatic impairment due to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid.
Calamox Drops should be administered by using the supplied dropper. The Dropper has
marking according to the volume per drop providing convenience of dosing. For example at a WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS:
marking of 1ml (equivalent to approx. 25 drops) should then be orally administered to the child. Before initiating therapy with co-amoxiclav, careful enquiry should be made concerning
A similar dose should be administered after 8 hours interval according to the weight of the previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillin, cephalosporin or other allergens. Serious and
child. The dosage chart of Calamox Drops which corresponds to the weight (Kg) and Age occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactoid) reactions have been reported in patients on
(months) are shown below: penicillin therapy. These reactions are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of
penicillin hypersensitivity. Co-amoxiclav should be avoided if infectious mononucleosis is
Weight of child (kg) Volume (ml) of Co-amoxiclav (Calamox) infant suspected since the occurrence of a morbilliform rash has been associated with this condition
drops* following the use of amoxicillin. Prolonged use may also occasionally result in overgrowth of
non-susceptible organisms. Prolongation of prothrombin time has been reported rarely in
1 0.13 patients receiving Co-amoxiclav. Appropriate monitoring should be undertaken when
anticoagulants are prescribed concomitantly. Changes in liver function tests have been
1.5 0.20 observed in some patients receiving Co-amoxiclav. The clinical significance of these changes
is uncertain but Co-amoxiclav should be used with caution in patients with evidence of hepatic
2 0.27 dysfunction. Cholestatic jaundice, which may be severe, but is usually reversible, has been
reported rarely. Signs and symptoms may not become apparent for up to six weeks after
2.5 0.33 treatment has ceased. In patients with renal impairment Co-amoxiclav dosage should be
adjusted as recommended in the Dosage and Administration section. In patients with reduced
3 0.40
urine output, crystalluria has been observed very rarely predominantly with parenteral therapy.
During the administration of high doses of amoxicillin, it is advisable to maintain adequate fluid
3.5 0.47
intake and urinary output in order to reduce the possibility of amoxicillin crystalluria.
4 0.53
DRUG INTERACTIONS:
4.5 0.60 Use of probenecid is not recommended. Probenecid decreases the renal tubular secretion of
amoxicillin. Concomitant use with CALAMOX may result in increased and prolonged blood
5 0.67 levels of amoxicillin but not of clavulanate. Concomitant use of allopurinol during treatment
with amoxicillin can increase the likelihood of allergic skin reactions. There are no data on the
5.5 0.73 concomitant use of Co-amoxiclav and allopurinol. In common with other antibiotics,
Co-amoxiclav may affect the gut flora, leading to lower estrogen reabsorption and reduced
6 0.80 efficacy of combined oral contraceptives.
6.5 0.87 ADVERSE EFFECTS:
Common:
7 0.93 Mucocutaneous candidiasis, Blood and lymphatic system disorders, Diarrhoea, nausea,
vomiting.
7.5 1.00
Uncommon:
8 1.07 Dizziness, headache, Indigestion, A moderate rise in AST and/or ALT, Skin rash, pruritus,
urticaria.
8.5 1.14
Rare:
9 1.20
Reversible leucopenia (including neutropenia) and thrombocytopenia, Erythema multiforme.
9.5 1.27
Very Rare:
10 1.34 Reversible agranulocytosis and haemolytic anaemia. Prolongation of bleeding time and
prothrombin time, Angioneurotic oedema, anaphylaxis, serum sickness-like syndrome,
* These doses may be doubled in cases of severe infection. hypersensitivity vasculitis, Reversible hyperactivity and convulsions. Convulsions may occur
in patients with impaired renal function or in those receiving high doses, Antibiotic-associated
colitis (including pseudomembranous colitis and haemorrhagic colitis). Superficial tooth INSTRUCTIONS:
discolouration has been reported very rarely in children. Good oral hygiene may help to Do not take if seal is Broken.
prevent tooth discolouration as it can usually be removed by brushing, Hepatitis and Before reconstitution protect from heat, sunlight & moisture, store below 25°C.
cholestatic jaundice. These events have been noted with other penicillins and cephalosporins, Reconstituted suspension should be stored in a refrigerator (2°C-8°C) and used within seven
Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, bullous exfoliative-dermatitis, acute days. Do not freeze.
generalised exanthemous pustulosis (AGEP), Interstitial nephritis, crystalluria. The Expiration date refer to the product correctly stored at required condition.
Patients and healthcare professionals can also report suspected adverse drug reaction at
USE IN PREGNANCY AND LACTATION: ade@bosch-pharma.com.
Pregnancy: Keep out of the reach of children.
Teratogenic Effects: Pregnancy Category B To be sold on prescription of a registered medical practitioner only.
There are, however, no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women. This drug
should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. PRESENTATION:
Calamox Drops 62.5mg/ml: 20ml (after reconstitution) in 30ml Amber Glass Bottle.
Lactation:
Both substances are excreted into breast milk. Consequently, diarrhoea and fungus infection
of the mucous membranes are possible in the breast-fed infant, so that breast-feeding might
have to be discontinued. Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid should only be used during breast-feeding
after benefit/risk assessment by the physician in charge.
OVERDOSE:
Gastrointestinal symptoms may be treated symptomatically, with attention to the water/electro-
lyte balance. Amoxicillin/clavulanic acid can be removed from the circulation by haemodialysis.
SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS FOR DISPOSAL AND OTHER HANDLING:
Add a small quantity of pre boiled cool water in the bottle and shake well, then add more water
upto the mark given on the label and shake well to make suspension. Once reconstituted, the
plastic dropper dosing device should then be used in place of the screw cap. The device is
used to dose patients upto 6 months according to the schedule in the Dosage and
Administration section.
Manufactured by:
Bosch Pharmaceuticals (Pvt) Ltd.
221-223, Sector 23, Korangi Industrial Area,
Karachi - Pakistan
You might also like
- Antibacterial AgentsDocument31 pagesAntibacterial AgentsdragajojicNo ratings yet
- 10.beta Lactamase InhibitorsDocument15 pages10.beta Lactamase InhibitorsJagirNo ratings yet
- MoxaclavDocument3 pagesMoxaclavAshish SharmaNo ratings yet
- New Zealand Data Sheet: Amoxiclav MultichemDocument17 pagesNew Zealand Data Sheet: Amoxiclav MultichemdoodrillNo ratings yet
- 20120613Document16 pages20120613ALi Rḿ ḾöhẳḿḿẳdNo ratings yet
- Penicillins and Betalaktamase InhibitorDocument23 pagesPenicillins and Betalaktamase InhibitorHanung PujanggaNo ratings yet
- AugmentinDocument7 pagesAugmentinImran KhanNo ratings yet
- Liceo de Cagayan University: College of PharmacyDocument8 pagesLiceo de Cagayan University: College of PharmacyPrecious Grace CabahugNo ratings yet
- Calamox Tablets SuspensionsDocument4 pagesCalamox Tablets SuspensionsAbdurrahman DarmanNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of AmoxicillinDocument15 pagesPharmacology of AmoxicillinWilliamNo ratings yet
- OgminDocument7 pagesOgminSharar KalayliehNo ratings yet
- 0208 Sulfa SlideDocument24 pages0208 Sulfa SlidetvvsagarNo ratings yet
- Augmentin in JDocument15 pagesAugmentin in JChutharat SucharitNo ratings yet
- Nurse Round - AugmentinDocument15 pagesNurse Round - AugmentinkyokeungkennethNo ratings yet
- Composition: Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets USPDocument5 pagesComposition: Amoxicillin and Clavulanate Potassium Tablets USPManjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Mefenamic AcidDocument1 pagePharmacology of Mefenamic AcidNida AdillahNo ratings yet
- GDL 01240Document7 pagesGDL 01240Christian KosiNo ratings yet
- Hikma Pharmaceuticals: AmoclanDocument5 pagesHikma Pharmaceuticals: AmoclanBest ManNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Penicillins, CephalosporinsDocument44 pagesWeek 4 - Penicillins, CephalosporinsTiko JomidavaNo ratings yet
- DBL Amikacin Injection DescriptionDocument9 pagesDBL Amikacin Injection Descriptionnela sharonNo ratings yet
- GENERIC NAME: Co-Amoxiclav (Amoxicillin & Clavulanic Acid) BRAND NAMES: Natravox, AddexDocument4 pagesGENERIC NAME: Co-Amoxiclav (Amoxicillin & Clavulanic Acid) BRAND NAMES: Natravox, AddexDRANo ratings yet
- Augmentin Duo TabletsDocument10 pagesAugmentin Duo TabletsRajat Kumar YadavNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic Acid Capsules, USP 250 MG RX Only: Reference ID: 3928117Document20 pagesMefenamic Acid Capsules, USP 250 MG RX Only: Reference ID: 3928117Riska AuliahNo ratings yet
- Augmentin ES 600 MDS006Document18 pagesAugmentin ES 600 MDS006JeneshNo ratings yet
- AugmentinDocument24 pagesAugmentinKaren Ann M. EstradaNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Co-Amoxiclav Brand Name: Nursing ResponsibilityDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Co-Amoxiclav Brand Name: Nursing ResponsibilityScribdScirbdNo ratings yet
- Protein Synthesis InhibitorsDocument59 pagesProtein Synthesis InhibitorsApurba Sarker Apu100% (1)
- Chapter 43 - Beta-LactamDocument7 pagesChapter 43 - Beta-LactamErika De JesusNo ratings yet
- Pocket Guide Antimicrobial Dosing in Renal Failure PDFDocument16 pagesPocket Guide Antimicrobial Dosing in Renal Failure PDFReynaldo BinsarNo ratings yet
- ACARBOSEDocument2 pagesACARBOSEJohn Carlo SamsonNo ratings yet
- Mecobalamin Tablet Capsule Prescribing InformationDocument5 pagesMecobalamin Tablet Capsule Prescribing InformationShemul IslamNo ratings yet
- Augmentin 375 UsesDocument10 pagesAugmentin 375 UseskalelNo ratings yet
- AminoacidopathyDocument44 pagesAminoacidopathydrsoker2012No ratings yet
- 21246LBLDocument13 pages21246LBLDr-Dalya ShakirNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin SulbactamDocument5 pagesAmpicillin SulbactamtitiNo ratings yet
- Beta Lactamase Inhibitors - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument6 pagesBeta Lactamase Inhibitors - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfRaffaharianggaraNo ratings yet
- Neuromuscular Blocking DrugsDocument5 pagesNeuromuscular Blocking DrugsTherese Jane TiradorNo ratings yet
- KANAMYCIN - Kanamycin Injection, S Olution Fres Enius Kabi USA, LLCDocument15 pagesKANAMYCIN - Kanamycin Injection, S Olution Fres Enius Kabi USA, LLCheristiana pratiwiNo ratings yet
- VancomycinDocument16 pagesVancomycinSakandar TalibNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin (: INN BAN β-lactam antibiotic bacterial infections microorganismsDocument17 pagesAmoxicillin (: INN BAN β-lactam antibiotic bacterial infections microorganismsNiks KanungoNo ratings yet
- Cell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors: Pharmacology Seminar Group: A1Document113 pagesCell Wall Synthesis Inhibitors: Pharmacology Seminar Group: A1Lola KhatimNo ratings yet
- 083082s050lbl PDFDocument2 pages083082s050lbl PDFSonali DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides KunjDocument17 pagesAminoglycosides KunjDeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin and Clavula NateDocument4 pagesAmoxicillin and Clavula NateRoberto BenziNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - MC 3Document58 pagesUnit 1 - MC 3Shreyas ShreyuNo ratings yet
- OgminDocument9 pagesOgminelcapitano vegetaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate Dosage PlusDocument8 pagesCalcium Gluconate Dosage PlusJaved ArifNo ratings yet
- March 2023 Recalls Solved by Nazia RafiqueDocument18 pagesMarch 2023 Recalls Solved by Nazia RafiqueelgafarypharmacyNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin Has A Good Pharmacokinetic Profile by Which It Is Well AbsorbedDocument1 pageCephalexin Has A Good Pharmacokinetic Profile by Which It Is Well AbsorbedJameseu KimNo ratings yet
- Antibacterial Drugs: B.K. SatriyasaDocument56 pagesAntibacterial Drugs: B.K. SatriyasaVicNo ratings yet
- CHLOROQUINEDocument6 pagesCHLOROQUINEKarla Camille de LeonNo ratings yet
- ZAINAB JAVED dp-108-240Document17 pagesZAINAB JAVED dp-108-240Zainab JavaidNo ratings yet
- Myrin P ForteDocument3 pagesMyrin P ForteJohn Zedric Villanueva ArciagaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacokinetic Training Packet For PharmacistsDocument24 pagesPharmacokinetic Training Packet For PharmacistsGlory Claudia KarundengNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Protein Synthesis InhibitorDocument71 pagesBacterial Protein Synthesis InhibitorpuriNo ratings yet
- Drug InfoDocument11 pagesDrug InfoArjun SinghNo ratings yet
- Suggamadex Remifentanyl PalonosetronDocument28 pagesSuggamadex Remifentanyl PalonosetronSai TejeswiNo ratings yet
- 5 6339302665821881285Document5 pages5 6339302665821881285Adrija SenNo ratings yet
- Keto LogDocument7 pagesKeto LogKim Justin InfantadoNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic AcidDocument6 pagesMefenamic AcidArisa VijungcoNo ratings yet
- Continuous and Extended Infusion Beta Lactams PDFDocument3 pagesContinuous and Extended Infusion Beta Lactams PDFarnaldops333No ratings yet
- Isolation of Pathogens Causing Sepsis Pus and Infected Wounds From Critical Care Unit A Retrospective Study - 2Document8 pagesIsolation of Pathogens Causing Sepsis Pus and Infected Wounds From Critical Care Unit A Retrospective Study - 2Omoding EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Emergency Department Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument8 pagesEmergency Department Urinary Tract InfectionsPrimasari DiahNo ratings yet
- CephalosporinDocument35 pagesCephalosporinGavin BirlaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy MCQSDocument132 pagesPharmacy MCQSomair zafar100% (6)
- Antimicrobial Resistance and Clinical Use in Respiratory InfectionsDocument23 pagesAntimicrobial Resistance and Clinical Use in Respiratory InfectionsWamique IzharNo ratings yet
- PenicillinsDocument21 pagesPenicillinssekarenthangavelNo ratings yet
- Brenner and Stevens, Pharmacology 3 © 2010Document5 pagesBrenner and Stevens, Pharmacology 3 © 2010PharAwayNo ratings yet
- CVV 46 V449 S02016042Document7 pagesCVV 46 V449 S02016042Quang TháiNo ratings yet
- DiverticulitisDocument15 pagesDiverticulitisElisabeth MelisaNo ratings yet
- Claforan (Cefotaxime) PDFDocument18 pagesClaforan (Cefotaxime) PDFdinniNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Bacterial Structure - Cell Wall 2020 PDFDocument59 pagesUnit 5 Bacterial Structure - Cell Wall 2020 PDFhellokittyNo ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases I: Eric W. Mueller, Pharm.D., FCCP, FCCMDocument52 pagesInfectious Diseases I: Eric W. Mueller, Pharm.D., FCCP, FCCMNhanLiNo ratings yet
- Keneuoe MohlakoanaDocument137 pagesKeneuoe MohlakoanaDurga BhavaniNo ratings yet
- All You Need To Know About Antibiotics: Tariq A. Madani, MBBS, FRCPCDocument89 pagesAll You Need To Know About Antibiotics: Tariq A. Madani, MBBS, FRCPCMansour AltalhiNo ratings yet
- Cephalosporins Quick ReviewDocument19 pagesCephalosporins Quick ReviewErinson Custodio PlasenciaNo ratings yet
- ESBL BrochureDocument2 pagesESBL BrochureChandra MohanNo ratings yet
- Mark Miguel P. Latras, RPHDocument11 pagesMark Miguel P. Latras, RPHLOLOLONo ratings yet
- 4 - Intravascular Catheter-Related Bloodstream InfectionsDocument23 pages4 - Intravascular Catheter-Related Bloodstream InfectionschiaraNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic 1-Terminology: 1. Inhibition of Cell Wall SynthesisDocument12 pagesAntibiotic 1-Terminology: 1. Inhibition of Cell Wall SynthesismidoNo ratings yet
- Aminoglycosides: Official Reprint From Uptodate ©2021 Uptodate, Inc. And/Or Its Affiliates. All Rights ReservedDocument17 pagesAminoglycosides: Official Reprint From Uptodate ©2021 Uptodate, Inc. And/Or Its Affiliates. All Rights ReservedVanessa GomesNo ratings yet
- Beta - Lactam Antibiotics: Prof. R. K. Dixit Pharmacology and Therapeutics K. G. M. U. LucknowDocument29 pagesBeta - Lactam Antibiotics: Prof. R. K. Dixit Pharmacology and Therapeutics K. G. M. U. LucknowHely PatelNo ratings yet
- We Are Intechopen, Open Access Books: The World'S Leading Publisher of Built by Scientists, For ScientistsDocument19 pagesWe Are Intechopen, Open Access Books: The World'S Leading Publisher of Built by Scientists, For ScientistsbapaknyanadlirNo ratings yet
- Drug Resistance: College of Ashur University Department of Pharmacy PharmacologyDocument12 pagesDrug Resistance: College of Ashur University Department of Pharmacy Pharmacologyمحمود محمدNo ratings yet
- AST by The CDS Methode PDFDocument88 pagesAST by The CDS Methode PDFari_nuswantoroNo ratings yet
- Bioeksen CatalogueDocument20 pagesBioeksen CatalogueMentor KurshumliuNo ratings yet
- Infectiuos Disease PDFDocument248 pagesInfectiuos Disease PDFntnquynhpro0% (1)
- Microbiolspec - Arba 0009 2017Document26 pagesMicrobiolspec - Arba 0009 2017Rossio Noelia Jurado NaciónNo ratings yet
- Mark M Calban MD MPM-HSDDocument58 pagesMark M Calban MD MPM-HSDZllison Mae Teodoro Mangabat100% (1)