Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 viewsFiveos PDF
Fiveos PDF
Uploaded by
shubhamsickriwal700moti1. The document discusses two covered option strategies - covered calls and covered puts. Covered calls involve buying a stock and writing call options against it to generate income from premiums. Covered puts involve writing cash-secured put options to generate income and hedge against declines in the price of an underlying stock.
2. The strategies provide income from option premiums while limiting downside risk. Covered calls are suitable for neutral to slightly bullish views, while covered puts work for bearish outlooks. Both strategies offer flexibility, downside protection, and can be part of broader risk management.
3. However, the strategies also have disadvantages like capped upside potential, assignment risks, opportunity costs, and transaction fees
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Practical Approaches To Applied Research and Program Evaluation For Helping Professionals 1St Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument50 pagesPractical Approaches To Applied Research and Program Evaluation For Helping Professionals 1St Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFrasmahjonaki34100% (5)
- Trading Options: The Ultimate Guide ToDocument25 pagesTrading Options: The Ultimate Guide ToHikmah Republika100% (1)
- Project On Option StrategiesDocument49 pagesProject On Option Strategieskamdica67% (9)
- CH 4 - Efficient Market HypothesesDocument48 pagesCH 4 - Efficient Market HypothesesNurul Khaleeda binti KamalNo ratings yet
- Options Strategies Quick GuideDocument36 pagesOptions Strategies Quick GuideParikshit KalyankarNo ratings yet
- Bodie8ce FormulaSheet PDFDocument24 pagesBodie8ce FormulaSheet PDFSandini Dharmasena PereraNo ratings yet
- Bullish: Option Strategies For Bullish ViewDocument10 pagesBullish: Option Strategies For Bullish ViewAshutosh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Equity Options Strategy: Naked PutDocument2 pagesEquity Options Strategy: Naked PutpkkothariNo ratings yet
- MCQ Set 2Document8 pagesMCQ Set 2judysaysNo ratings yet
- Option StrategiesDocument1 pageOption StrategiesUnnikrishnan ASNo ratings yet
- Bearish: Options Strategies For Bearish ViewDocument10 pagesBearish: Options Strategies For Bearish Viewukumar_657611No ratings yet
- 6 - Investment Prodcut and ServicesDocument33 pages6 - Investment Prodcut and Servicesmadhusudan2005No ratings yet
- IPM Reviewer For Nov 19Document3 pagesIPM Reviewer For Nov 19caylashinecerezoNo ratings yet
- IPM Webinar QuizzesDocument6 pagesIPM Webinar QuizzesPrincess Joy Andayan BorangNo ratings yet
- Slides Aymeric KALIFE - Vanilla StrategiesDocument38 pagesSlides Aymeric KALIFE - Vanilla StrategiesSlakeNo ratings yet
- Insider Strategies For Profiting With Options Max AnsbacherDocument13 pagesInsider Strategies For Profiting With Options Max AnsbacherbelewjoNo ratings yet
- Covered Strangle: Montréal ExchangeDocument3 pagesCovered Strangle: Montréal ExchangepkkothariNo ratings yet
- Swot Analysis of AssetsDocument8 pagesSwot Analysis of Assetsshinjan bhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- TestDocument13 pagesTestShiva oncNo ratings yet
- Cannon Trading Education: Options 101Document5 pagesCannon Trading Education: Options 101krolldoggNo ratings yet
- ExchangeDocument8 pagesExchangecool cookNo ratings yet
- Investment VehiclesDocument7 pagesInvestment Vehiclesapi-583759965No ratings yet
- Covered PutDocument3 pagesCovered PutpkkothariNo ratings yet
- Bus - Finance-Day 4Document24 pagesBus - Finance-Day 4Maricris AbundoNo ratings yet
- Visit For More Project Reports, Presentations, Notes Etc.: Option StrategiesDocument49 pagesVisit For More Project Reports, Presentations, Notes Etc.: Option StrategiesgrshneheteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Summary When To Use Each StrategyDocument6 pagesLesson 11 Summary When To Use Each StrategyMahesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Summary When To Use Each StrategyDocument6 pagesLesson 11 Summary When To Use Each StrategyadmsNo ratings yet
- FV PV (1+i) : Monthly Factor Rate MFRDocument4 pagesFV PV (1+i) : Monthly Factor Rate MFRSophia Joyce GonzaloNo ratings yet
- Equity Options Strategy: Naked CallDocument2 pagesEquity Options Strategy: Naked CallpkkothariNo ratings yet
- WM 2020 Wa 2Document7 pagesWM 2020 Wa 2Debanjan MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- 12 Options Strategies Special ReportDocument14 pages12 Options Strategies Special ReportalexescNo ratings yet
- 4 QuizDocument3 pages4 QuizAnandapadmanaban Muralidharan Muralidharan100% (1)
- Chapter 11Document8 pagesChapter 11алинаNo ratings yet
- IDFM Chapter 4Document76 pagesIDFM Chapter 4Little JainNo ratings yet
- CopyofIDFM Chapter 7Document107 pagesCopyofIDFM Chapter 7Little JainNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Notes: Financial MarketingDocument6 pagesWeek 1 Notes: Financial MarketingPulkit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Cash Secured PutDocument4 pagesCash Secured PutpkkothariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Money ManagementDocument25 pagesChapter 2: Money Managementapi-26130273No ratings yet
- Covered CallDocument4 pagesCovered CallpkkothariNo ratings yet
- CFA Level 3 Book 5Document11 pagesCFA Level 3 Book 5sasasNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT 18Document2 pagesChatGPT 18ashaykosare.007No ratings yet
- Altana Optional View (June 2018) 'Skews'Document3 pagesAltana Optional View (June 2018) 'Skews'BlundersNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Chapter 3)Document3 pagesAssignment 1 (Chapter 3)Josef Galileo SibalaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Derivatives: Participants Can Enter Into Any Mutually Accepted ContractDocument4 pages1.1 Derivatives: Participants Can Enter Into Any Mutually Accepted ContractNg Jian LongNo ratings yet
- 10. CFA - L3 - 陳宏 - Risk Management Applications of DerivativesDocument6 pages10. CFA - L3 - 陳宏 - Risk Management Applications of DerivativesjanuarNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - SolutionDocument31 pagesCh3 - SolutionJeevan TejaNo ratings yet
- Flash CardDocument13 pagesFlash Cardkren24No ratings yet
- NISM Chapter 1Document2 pagesNISM Chapter 1akashpatelgameNo ratings yet
- Long PutDocument3 pagesLong PutpkkothariNo ratings yet
- Options Trading Strategies: Option Spread Strategy Description Reason To Use When To UseDocument6 pagesOptions Trading Strategies: Option Spread Strategy Description Reason To Use When To UseSGNo ratings yet
- Option Strstegies (Bullish Strategies) 1. Long CallDocument4 pagesOption Strstegies (Bullish Strategies) 1. Long CallObaid R.No ratings yet
- Option Strstegies (Bullish Strategies) 1. Long CallDocument4 pagesOption Strstegies (Bullish Strategies) 1. Long CallObaid R.No ratings yet
- Key Options Strategy GuideDocument18 pagesKey Options Strategy GuideAngelo PosillicoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2Shevon FortuneNo ratings yet
- Long Call: Montréal ExchangeDocument3 pagesLong Call: Montréal ExchangepkkothariNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes: 2.1 OptionsDocument10 pagesLearning Outcomes: 2.1 OptionsRajesh GargNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Corporate Financing Decisions and Efficient Capital MarketDocument49 pagesCH 4 - Corporate Financing Decisions and Efficient Capital Marketkk100% (1)
- Options Strategies For A Range Bound ViewDocument11 pagesOptions Strategies For A Range Bound ViewAshutosh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Answers To Problem Sets: Efficient Markets and Behavioral FinanceDocument8 pagesAnswers To Problem Sets: Efficient Markets and Behavioral Financemandy YiuNo ratings yet
- 5 QuizDocument3 pages5 QuizAnandapadmanaban Muralidharan MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time Scale IndonesiaDocument1 pageGeologic Time Scale IndonesiasyariefiqbalNo ratings yet
- Determinação BcarotenoDocument2 pagesDeterminação BcarotenoAna Verônica Menezes de AguiarNo ratings yet
- Infinitigeneralcatalog Compressed (1) CompressedDocument31 pagesInfinitigeneralcatalog Compressed (1) CompressedBilher SihombingNo ratings yet
- Urban Coherence: A Morphological DefinitionDocument19 pagesUrban Coherence: A Morphological DefinitionOlgu CaliskanNo ratings yet
- WMA12 01 Que 20211013Document32 pagesWMA12 01 Que 20211013Md Shahidul Islam IslamNo ratings yet
- NEPCon-CoC-Annual-Volume Summary-template-Nov17Document12 pagesNEPCon-CoC-Annual-Volume Summary-template-Nov17abraham alonso subiria cuetoNo ratings yet
- Comaroff, John L. Rules and Rulers. Political Processes in A Tswana ChiefdownDocument21 pagesComaroff, John L. Rules and Rulers. Political Processes in A Tswana ChiefdownDiego AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Jis S2147-1998Document35 pagesJis S2147-1998Xuan KhaiNo ratings yet
- Invitation Accp 2011Document5 pagesInvitation Accp 2011Klub 'Apoteker' IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- fmamsmlmflmlmlllmmlDUK DOSEN UNTAD AGUSTUS 2013bhvffyfDocument117 pagesfmamsmlmflmlmlllmmlDUK DOSEN UNTAD AGUSTUS 2013bhvffyfIsmail Sholeh Bahrun MakkaratteNo ratings yet
- R304 0307 Env HHDocument221 pagesR304 0307 Env HHsyamsundariitmiitmNo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram: Ecu A/7Document1 pageCircuit Diagram: Ecu A/7RubénNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy - G11Document62 pagesMedia and Information Literacy - G11Jerfel MAAMONo ratings yet
- JADWAL KULIAH TPB SMT GASAL TA 2020 2021 Rev 5Document49 pagesJADWAL KULIAH TPB SMT GASAL TA 2020 2021 Rev 5shin yongriNo ratings yet
- Resume Keerthana PG PDFDocument1 pageResume Keerthana PG PDFVivek GNo ratings yet
- CO2 CorrosionDocument18 pagesCO2 CorrosionShie OthongNo ratings yet
- Filipino American RelationshipDocument3 pagesFilipino American RelationshipSamuel Grant ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Logix SERCOS Tuning Tips v1.02 1Document6 pagesLogix SERCOS Tuning Tips v1.02 1José AlanizNo ratings yet
- Solutions l4 Chemistry Class 12 Cbse by Ashu SirDocument16 pagesSolutions l4 Chemistry Class 12 Cbse by Ashu Sirvedantu495No ratings yet
- 7451 Planiseal288 GBDocument4 pages7451 Planiseal288 GBHendyKoNo ratings yet
- NAA ItemNumber391518Document203 pagesNAA ItemNumber391518Jonathan ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- GSCFF APF TechniquesDocument18 pagesGSCFF APF TechniquesMaharaniNo ratings yet
- Lab 1a RASPlib Installation Instructions R5 2016b-2017aDocument10 pagesLab 1a RASPlib Installation Instructions R5 2016b-2017aaleNo ratings yet
- Jataka Tales 3 PDFDocument3 pagesJataka Tales 3 PDFGhosalNo ratings yet
- How Does Photodynamic Therapy WorkDocument13 pagesHow Does Photodynamic Therapy WorkLoredana VoiculescuNo ratings yet
- SES 100R (1450rpm)Document1 pageSES 100R (1450rpm)Jaeni GilangNo ratings yet
- Ca Q&aDocument129 pagesCa Q&aRavi TejaNo ratings yet
- Grade7 Final DemoDocument5 pagesGrade7 Final DemoMarygrace VictorioNo ratings yet
- Xenon 2.2 4x2 148HP DC PDFDocument4 pagesXenon 2.2 4x2 148HP DC PDFshiksha torooNo ratings yet
Fiveos PDF
Fiveos PDF
Uploaded by
shubhamsickriwal700moti0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 page1. The document discusses two covered option strategies - covered calls and covered puts. Covered calls involve buying a stock and writing call options against it to generate income from premiums. Covered puts involve writing cash-secured put options to generate income and hedge against declines in the price of an underlying stock.
2. The strategies provide income from option premiums while limiting downside risk. Covered calls are suitable for neutral to slightly bullish views, while covered puts work for bearish outlooks. Both strategies offer flexibility, downside protection, and can be part of broader risk management.
3. However, the strategies also have disadvantages like capped upside potential, assignment risks, opportunity costs, and transaction fees
Original Description:
Original Title
FIVEOS.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document discusses two covered option strategies - covered calls and covered puts. Covered calls involve buying a stock and writing call options against it to generate income from premiums. Covered puts involve writing cash-secured put options to generate income and hedge against declines in the price of an underlying stock.
2. The strategies provide income from option premiums while limiting downside risk. Covered calls are suitable for neutral to slightly bullish views, while covered puts work for bearish outlooks. Both strategies offer flexibility, downside protection, and can be part of broader risk management.
3. However, the strategies also have disadvantages like capped upside potential, assignment risks, opportunity costs, and transaction fees
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views1 pageFiveos PDF
Fiveos PDF
Uploaded by
shubhamsickriwal700moti1. The document discusses two covered option strategies - covered calls and covered puts. Covered calls involve buying a stock and writing call options against it to generate income from premiums. Covered puts involve writing cash-secured put options to generate income and hedge against declines in the price of an underlying stock.
2. The strategies provide income from option premiums while limiting downside risk. Covered calls are suitable for neutral to slightly bullish views, while covered puts work for bearish outlooks. Both strategies offer flexibility, downside protection, and can be part of broader risk management.
3. However, the strategies also have disadvantages like capped upside potential, assignment risks, opportunity costs, and transaction fees
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
1.
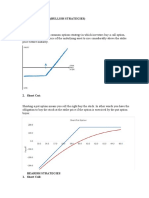
Cover call Strategy
1. View = Buillish / +ve Best Time to Execute:
a. Buy = Fut 1. Low Volatility: In a market with relatively
stable prices to maximize premium
b. Sell = OTM CE
collection.
2. Neutral to Slightly Bullish Outlook: When
you expect the underlying stock to maintain
1. View = Bearish / -ve or moderately increase in value.
a. Sell = Fut 3. Before Earnings Announcements: To
capitalize on heightened option premiums
b. Sell = OTM PE
before volatility increases.
4. Near Resistance Levels: If the stock is
approaching a resistance level, it might be a
Advantages: suitable time to execute covered calls.
1. Stable Market Conditions: Execute 5. When You're Willing to Sell: If you're
covered calls in stable markets to benefit comfortable with the possibility of selling
from premiums without excessive volatility. the underlying stock at the strike price.
2. Enhanced Income: Generate additional
income through premium collection,
boosting overall returns.
Disadvantages:
3. Risk Mitigation: Acts as a hedge, reducing
1. Capped Upside: Profit potential is limited
the overall risk of holding the underlying
to the premium received, missing out on
stock.
substantial gains.
4. Capital Preservation: Ideal when seeking
2. Potential Stock Losses: If the stock
to protect capital while still participating in
declines significantly, losses on the
the market.
underlying position may offset premium
5. Flexibility: Offers flexibility in choosing gains.
strike prices and expiration dates based on
3. Obligation to Sell: Obligation to sell the
market outlook.
stock at the strike price, limiting future profit
6. Time Decay Benefit: Time decay works in participation.
your favor, eroding the option premium over
4. Opportunity Cost: Limits the ability to
time.
fully capitalize on a rapidly rising market.
7. Bullish to Neutral Outlook: Suitable for
5. Market Timing Risks: Timing the market
mildly bullish or neutral market
can be challenging, and executing at the
expectations.
wrong time may lead to losses.
6. Assignment Risk: There's a risk of the
option being exercised, forcing the sale of
WhatsApp "XMA" to +91 8141 8382 44 the underlying stock.
7. Limited Downside Protection: The
& lean XMA which can help you find
premium received may not fully offset
breakout to execute option trade with potential losses in a declining market.
appx 1:3 RR ratio.
8. Transaction Costs: Commissions and fees
associated with trading options can reduce
There are other copies of this card
overall returns.
9. Emotional Stress: Constant monitoring
and decision-making can be stressful for
some investors.
10. Market Fluctuations: Adverse market
movements can impact the value of both
the underlying stock and the option.
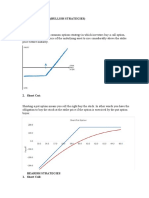
2. Cover Put Strategy
1. View = Buillish / +ve Best Time to Execute:
a. Buy = Fut 1. High Volatility Periods: When the market is
experiencing increased volatility, leading to
b. Buy = ATM PE
higher option premiums.
2. Bearish Outlook: During periods when you
anticipate a decline in the value of the
1. View = Bearish / -ve underlying stock.
a. Sell = Fut 3. Before Earnings Reports: To capitalize on
potential stock price drops associated with
b. BUY = ATM CE
earnings announcements.
4. Resistance Levels: When the stock
approaches resistance levels, indicating a
Advantages: potential downturn.
1. Profit from Stock Decline: Generates 5. Protective Strategy: As a protective
income if the underlying stock decreases in measure against an existing stock position
value. to hedge against potential losses.
2. Risk Mitigation: Acts as a hedge,
offsetting potential losses in the stock's
value.
3. Flexible Strike Selection: Allows flexibility
Disadvantages:
in choosing strike prices based on market
analysis. 1. Limited Profit Potential: Profit is capped at
the premium received, missing out on
4. Premium Collection: Similar to covered
potential gains.
calls, covered puts generate income
through premium collection. 2. Obligation to Buy Stock: There's an
obligation to buy the stock if the put option
5. Bearish Market Participation: Suitable for
is exercised.
investors with a bearish market outlook.
3. Potential Margin Requirements:
6. Time Decay Advantage: Time decay
Depending on the broker, executing covered
works in favor, eroding the option premium
puts may involve margin requirements.
over time.
4. Market Timing Risks: Timing the market
7. Downside Protection: Offers protection
correctly is crucial, and mistimed execution
against declining market conditions.
may lead to losses.
8. Partial Stock Profit: If the stock declines,
5. Transaction Costs: Commissions and fees
you can buy back the put and retain the
associated with options trading can reduce
remaining profit in the stock.
overall returns.
9. Versatility: Can be used as part of a
6. Opportunity Cost: Limits potential gains if
broader risk management strategy.
the stock experiences a significant rally.
10. Leverage in a Downtrend: Provides a
7. Emotional Stress: Regular monitoring and
degree of leverage in a market
decision-making may cause stress for some
characterized by a downward trend.
investors.
8. Unlimited Losses in a Stock Rally: If the
stock price rises significantly, losses can
WhatsApp "XMA" to +91 8141 8382 44 accumulate.
9. Assignment Risk: There's a risk of the
& lean XMA which can help you find
option being exercised, leading to the
breakout to execute option trade with obligation to buy the stock.
appx 1:3 RR ratio.
10. Requires Active Management: This
strategy necessitates ongoing attention and
adjustments based on market conditions.
3. Call Spread Strategy
1. View = Buillish / +ve Best Time to Execute:
a. Name = Long Call Spread 1. Low Volatility Periods: During times of
relatively low market volatility to benefit
b. Buy = ATM CE
from lower option premiums.
c. Sell = OTM CE
2. Bullish Outlook: When you expect a
moderate increase in the value of the
underlying stock.
1. View = Bearish / -ve 3. Before Expected Price Surges: Prior to
anticipated events or news that could lead
a. Name = Short Call Spread
to a bullish market movement.
b. Buy = OTM CE
4. Support Levels: When the stock is
c. Sell = ATM CE approaching support levels, suggesting
potential upward momentum.
5. Options Expiry Optimization: Executing
with a timeframe that aligns with your
Advantages:
outlook and objectives.
1. Limited Risk: Defined risk as losses are
capped at the initial premium paid for the
spread.
2. Lower Cost: Compared to buying a single
call option, call spreads require less upfront Disadvantages:
capital.
1. Limited Profit Potential: Profit is capped at
3. Profit from Moderate Price Increase: the difference between the strike prices,
Generates profit if the stock's price minus the premium paid.
increases but within a specified range.
2. Possible Loss of Entire Premium: If the
4. Reduced Time Decay Impact: Time decay stock price doesn't move favorably, the
is less severe compared to buying a single premium paid could be lost entirely.
call option.
3. Underperformance in Strong Rally: May
5. Flexibility in Strike Selection: Allows for underperform in a significant stock price
flexibility in choosing strike prices based on rally as gains are capped.
market expectations.
4. Potential for Assignment: There's a risk of
6. Risk Mitigation: Acts as a risk being assigned the short call, obligating you
management strategy in a bullish market by to sell the stock.
limiting potential losses.
5. Transaction Costs: Commissions and fees
7. Versatility: Can be adapted to different associated with options trading can impact
market conditions by adjusting strike prices overall returns.
and expiration dates.
6. Market Timing Risks: Timing the market
8. Clear Exit Strategy: The defined risk and correctly is crucial for the strategy's
reward structure provides a clear exit success.
strategy.
7. Requires Active Management: Monitoring
9. Combination of Premiums: By selling a and adjusting the position may be
call option against a purchased call, you necessary based on market conditions.
offset some of the cost.
8. Not Ideal in High Volatility: In highly
10. Partial Profit-Taking: You can close the volatile markets, the strategy may be less
position early for a partial profit if your price effective due to increased option premiums.
target is reached.
9. Rolling Costs: Rolling the position to a
later expiration may incur additional costs.
10. Potential for Early Assignment: The short
call option may be exercised early, leading
to an obligation to sell the stock.
4. Put Spread Strategy
1. View = Buillish / +ve Best Time to Execute:
a. Name = Long Put Spread 1. High Volatility Periods: During times of
increased market volatility to benefit from
b. Buy = OTM PE
higher option premiums.
c. Sell = ATM PE
2. Bearish Outlook: When you expect a
moderate decline in the value of the
underlying stock.
1. View = Bearish / -ve 3. Before Expected Negative Events: Prior to
anticipated events or news that could lead
a. Name = Short Put Spread
to a bearish market movement.
b. Buy = OTM PE
4. Resistance Levels: When the stock is
c. Sell = ATM PE approaching resistance levels, suggesting
potential downward momentum.
5. Options Expiry Optimization: Executing
with a timeframe that aligns with your
Advantages:
outlook and risk tolerance.
1. Limited Risk: Defined risk as losses are
capped at the initial premium paid for the
spread.
Disadvantages:
2. Lower Cost: Compared to buying a single
put option, put spreads require less upfront 1. Limited Profit Potential: Profit is capped at
capital. the difference between the strike prices,
minus the premium paid.
3. Profit from Moderate Price Decrease:
Generates profit if the stock's price 2. Possible Loss of Entire Premium: If the
decreases but within a specified range. stock price doesn't move favorably, the
premium paid could be lost entirely.
4. Reduced Time Decay Impact: Time decay
is less severe compared to buying a single 3. Underperformance in Strong Decline: May
put option. underperform in a significant stock price
decline as gains are capped.
5. Flexibility in Strike Selection: Allows for
flexibility in choosing strike prices based on 4. Potential for Assignment: There's a risk of
market expectations. being assigned the short put, obligating you
to buy the stock.
6. Risk Mitigation: Acts as a risk
management strategy in a bearish market 5. Transaction Costs: Commissions and fees
by limiting potential losses. associated with options trading can impact
overall returns.
7. Versatility: Can be adapted to different
market conditions by adjusting strike prices 6. Market Timing Risks: Timing the market
and expiration dates. correctly is crucial for the strategy's
success.
8. Clear Exit Strategy: The defined risk and
reward structure provides a clear exit 7. Requires Active Management: Monitoring
strategy. and adjusting the position may be
necessary based on market conditions.
9. Combination of Premiums: By selling a
put option against a purchased put, you 8. Not Ideal in Low Volatility: In low-volatility
offset some of the cost. markets, the strategy may be less effective
due to lower option premiums.
10. Partial Profit-Taking: You can close the
position early for a partial profit if your price 9. Rolling Costs: Rolling the position to a
target is reached. later expiration may incur additional costs.
10. Potential for Early Assignment: The short
put option may be exercised early, leading
to an obligation to buy the stock.
5. Synthetic Future Strategy
1. View = Buillish / +ve Best Time to Execute:
2. Buy = ATM CE 1. Strong Market Trend: During periods of a
clear and strong market trend for better
3. Buy = ATM PE
directional accuracy.
4. Buy = Fut
2. Anticipated Price Movement: Before
expected significant price movements to
capitalize on the expected trend.
1. View = Bearish / -ve 3. Volatility Expansion: In times of increased
market volatility for enhanced option
2. Buy = ATM CE
premiums.
3. Buy = ATM PE
4. Economic Events: Prior to anticipated
4. Sell = Fut economic events that could impact the
underlying asset's price.
5. Options Expiry Optimization: Executing
with a timeframe that aligns with your
Advantages:
market outlook and objectives
1. Cost Efficiency: Requires less initial
capital compared to buying the underlying
asset outright.
Disadvantages:
2. Leverage: Provides significant leverage,
allowing for amplified returns (and losses) 1. Time Decay Impact: Options experience
compared to owning the asset. time decay, which can erode the value of
the position over time.
3. Flexibility: Allows for both bullish and
bearish positions through the use of call and 2. Limited Upside in Strong Trends: Profits
put options. are capped, limiting gains in a strong and
sustained market trend.
4. Reduced Capital Outlay: Lower upfront
cost compared to purchasing the actual 3. Potential for Loss of Premium: If the
asset. anticipated price movement doesn't occur,
the premium paid could be lost.
5. Defined Risk: Limited risk as the
maximum loss is the initial premium paid for 4. Complexity: Requires a good
the options. understanding of options and their pricing
dynamics.
6. Profit Potential in Both Directions: Can
profit from both upward and downward 5. Transaction Costs: Commissions and fees
price movements. associated with options trading can impact
overall returns.
7. No Margin Requirements: Unlike
traditional futures, synthetic futures don't 6. Risk of Early Assignment: The short
usually require margin accounts. option may be exercised early, leading to an
obligation to buy or sell the asset.
8. Adjustable Leverage: You can adjust the
level of leverage by choosing different strike 7. Market Timing Risks: Timing the market is
prices and expiration dates. crucial for success, and mistimed execution
may lead to losses.
9. Versatility: Can be used as a speculative
tool or as a part of more complex trading 8. Limited Dividend Capture: Does not
strategies. capture dividends, unlike owning the actual
asset.
10. Mitigates Timing Risk: The use of
options allows for more forgiving timing in 9. Rolling Costs: Rolling the position to a
predicting price movements. later expiration may incur additional costs.
10. Not Suitable for All Investors: Requires
careful risk management and may not be
suitable for all investors.
WhatsApp "XMA" to +91 8141 8382 44
& lean XMA which can help you find
breakout to execute option trade with
appx 1:3 RR ratio.
Share this PDF with all your friends and family. JAI HIND
Thanks and Regards, Can you give me 5 Star
Office of Mitul Mehta.
www.mitulmehta.in | +91 814183824
rating at
www.mitul.pro/5star
🔳 Follow us on:
🔸 Telegram: https://t.me/xperttechnicals
🔹 Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/XpertNifty/
🔸 Twitter: https://www.twitter.com/XpertNifty
🔹 Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/xpertniftyonline/
🔸 YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/c/XpertNifty
🔹 Linked in: https://www.linkedin.com/company/13423518/
🔸 Website: https://www.mitulmehta.in
Join our Telegram channel for live market updates 💸
👉 https://t.me/xperttechnicals
or search in telegram 👉 @xperttechnicals
Mitul Mehta's Free Strategies
🔸 M2B2 🔹 STARMA 🔸 Xpert Doji 🔹 Crude Oil Strategy 🔸 VWAP 🔹 FIBONACCI
🔹 Super Trend 🔸 Option Trading Strategies 🔹 Pivot Point
🌐 Free Strategy - Web : mitul.pro/free | 📱 Free Strategy - Android App : mitul.pro/app
You might also like
- Practical Approaches To Applied Research and Program Evaluation For Helping Professionals 1St Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument50 pagesPractical Approaches To Applied Research and Program Evaluation For Helping Professionals 1St Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFrasmahjonaki34100% (5)
- Trading Options: The Ultimate Guide ToDocument25 pagesTrading Options: The Ultimate Guide ToHikmah Republika100% (1)
- Project On Option StrategiesDocument49 pagesProject On Option Strategieskamdica67% (9)
- CH 4 - Efficient Market HypothesesDocument48 pagesCH 4 - Efficient Market HypothesesNurul Khaleeda binti KamalNo ratings yet
- Options Strategies Quick GuideDocument36 pagesOptions Strategies Quick GuideParikshit KalyankarNo ratings yet
- Bodie8ce FormulaSheet PDFDocument24 pagesBodie8ce FormulaSheet PDFSandini Dharmasena PereraNo ratings yet
- Bullish: Option Strategies For Bullish ViewDocument10 pagesBullish: Option Strategies For Bullish ViewAshutosh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Equity Options Strategy: Naked PutDocument2 pagesEquity Options Strategy: Naked PutpkkothariNo ratings yet
- MCQ Set 2Document8 pagesMCQ Set 2judysaysNo ratings yet
- Option StrategiesDocument1 pageOption StrategiesUnnikrishnan ASNo ratings yet
- Bearish: Options Strategies For Bearish ViewDocument10 pagesBearish: Options Strategies For Bearish Viewukumar_657611No ratings yet
- 6 - Investment Prodcut and ServicesDocument33 pages6 - Investment Prodcut and Servicesmadhusudan2005No ratings yet
- IPM Reviewer For Nov 19Document3 pagesIPM Reviewer For Nov 19caylashinecerezoNo ratings yet
- IPM Webinar QuizzesDocument6 pagesIPM Webinar QuizzesPrincess Joy Andayan BorangNo ratings yet
- Slides Aymeric KALIFE - Vanilla StrategiesDocument38 pagesSlides Aymeric KALIFE - Vanilla StrategiesSlakeNo ratings yet
- Insider Strategies For Profiting With Options Max AnsbacherDocument13 pagesInsider Strategies For Profiting With Options Max AnsbacherbelewjoNo ratings yet
- Covered Strangle: Montréal ExchangeDocument3 pagesCovered Strangle: Montréal ExchangepkkothariNo ratings yet
- Swot Analysis of AssetsDocument8 pagesSwot Analysis of Assetsshinjan bhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- TestDocument13 pagesTestShiva oncNo ratings yet
- Cannon Trading Education: Options 101Document5 pagesCannon Trading Education: Options 101krolldoggNo ratings yet
- ExchangeDocument8 pagesExchangecool cookNo ratings yet
- Investment VehiclesDocument7 pagesInvestment Vehiclesapi-583759965No ratings yet
- Covered PutDocument3 pagesCovered PutpkkothariNo ratings yet
- Bus - Finance-Day 4Document24 pagesBus - Finance-Day 4Maricris AbundoNo ratings yet
- Visit For More Project Reports, Presentations, Notes Etc.: Option StrategiesDocument49 pagesVisit For More Project Reports, Presentations, Notes Etc.: Option StrategiesgrshneheteNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Summary When To Use Each StrategyDocument6 pagesLesson 11 Summary When To Use Each StrategyMahesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11 Summary When To Use Each StrategyDocument6 pagesLesson 11 Summary When To Use Each StrategyadmsNo ratings yet
- FV PV (1+i) : Monthly Factor Rate MFRDocument4 pagesFV PV (1+i) : Monthly Factor Rate MFRSophia Joyce GonzaloNo ratings yet
- Equity Options Strategy: Naked CallDocument2 pagesEquity Options Strategy: Naked CallpkkothariNo ratings yet
- WM 2020 Wa 2Document7 pagesWM 2020 Wa 2Debanjan MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- 12 Options Strategies Special ReportDocument14 pages12 Options Strategies Special ReportalexescNo ratings yet
- 4 QuizDocument3 pages4 QuizAnandapadmanaban Muralidharan Muralidharan100% (1)
- Chapter 11Document8 pagesChapter 11алинаNo ratings yet
- IDFM Chapter 4Document76 pagesIDFM Chapter 4Little JainNo ratings yet
- CopyofIDFM Chapter 7Document107 pagesCopyofIDFM Chapter 7Little JainNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Notes: Financial MarketingDocument6 pagesWeek 1 Notes: Financial MarketingPulkit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Cash Secured PutDocument4 pagesCash Secured PutpkkothariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Money ManagementDocument25 pagesChapter 2: Money Managementapi-26130273No ratings yet
- Covered CallDocument4 pagesCovered CallpkkothariNo ratings yet
- CFA Level 3 Book 5Document11 pagesCFA Level 3 Book 5sasasNo ratings yet
- ChatGPT 18Document2 pagesChatGPT 18ashaykosare.007No ratings yet
- Altana Optional View (June 2018) 'Skews'Document3 pagesAltana Optional View (June 2018) 'Skews'BlundersNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 (Chapter 3)Document3 pagesAssignment 1 (Chapter 3)Josef Galileo SibalaNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Derivatives: Participants Can Enter Into Any Mutually Accepted ContractDocument4 pages1.1 Derivatives: Participants Can Enter Into Any Mutually Accepted ContractNg Jian LongNo ratings yet
- 10. CFA - L3 - 陳宏 - Risk Management Applications of DerivativesDocument6 pages10. CFA - L3 - 陳宏 - Risk Management Applications of DerivativesjanuarNo ratings yet
- Ch3 - SolutionDocument31 pagesCh3 - SolutionJeevan TejaNo ratings yet
- Flash CardDocument13 pagesFlash Cardkren24No ratings yet
- NISM Chapter 1Document2 pagesNISM Chapter 1akashpatelgameNo ratings yet
- Long PutDocument3 pagesLong PutpkkothariNo ratings yet
- Options Trading Strategies: Option Spread Strategy Description Reason To Use When To UseDocument6 pagesOptions Trading Strategies: Option Spread Strategy Description Reason To Use When To UseSGNo ratings yet
- Option Strstegies (Bullish Strategies) 1. Long CallDocument4 pagesOption Strstegies (Bullish Strategies) 1. Long CallObaid R.No ratings yet
- Option Strstegies (Bullish Strategies) 1. Long CallDocument4 pagesOption Strstegies (Bullish Strategies) 1. Long CallObaid R.No ratings yet
- Key Options Strategy GuideDocument18 pagesKey Options Strategy GuideAngelo PosillicoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document15 pagesChapter 2Shevon FortuneNo ratings yet
- Long Call: Montréal ExchangeDocument3 pagesLong Call: Montréal ExchangepkkothariNo ratings yet
- Learning Outcomes: 2.1 OptionsDocument10 pagesLearning Outcomes: 2.1 OptionsRajesh GargNo ratings yet
- CH 4 - Corporate Financing Decisions and Efficient Capital MarketDocument49 pagesCH 4 - Corporate Financing Decisions and Efficient Capital Marketkk100% (1)
- Options Strategies For A Range Bound ViewDocument11 pagesOptions Strategies For A Range Bound ViewAshutosh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Answers To Problem Sets: Efficient Markets and Behavioral FinanceDocument8 pagesAnswers To Problem Sets: Efficient Markets and Behavioral Financemandy YiuNo ratings yet
- 5 QuizDocument3 pages5 QuizAnandapadmanaban Muralidharan MuralidharanNo ratings yet
- Geologic Time Scale IndonesiaDocument1 pageGeologic Time Scale IndonesiasyariefiqbalNo ratings yet
- Determinação BcarotenoDocument2 pagesDeterminação BcarotenoAna Verônica Menezes de AguiarNo ratings yet
- Infinitigeneralcatalog Compressed (1) CompressedDocument31 pagesInfinitigeneralcatalog Compressed (1) CompressedBilher SihombingNo ratings yet
- Urban Coherence: A Morphological DefinitionDocument19 pagesUrban Coherence: A Morphological DefinitionOlgu CaliskanNo ratings yet
- WMA12 01 Que 20211013Document32 pagesWMA12 01 Que 20211013Md Shahidul Islam IslamNo ratings yet
- NEPCon-CoC-Annual-Volume Summary-template-Nov17Document12 pagesNEPCon-CoC-Annual-Volume Summary-template-Nov17abraham alonso subiria cuetoNo ratings yet
- Comaroff, John L. Rules and Rulers. Political Processes in A Tswana ChiefdownDocument21 pagesComaroff, John L. Rules and Rulers. Political Processes in A Tswana ChiefdownDiego AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Jis S2147-1998Document35 pagesJis S2147-1998Xuan KhaiNo ratings yet
- Invitation Accp 2011Document5 pagesInvitation Accp 2011Klub 'Apoteker' IndonesiaNo ratings yet
- fmamsmlmflmlmlllmmlDUK DOSEN UNTAD AGUSTUS 2013bhvffyfDocument117 pagesfmamsmlmflmlmlllmmlDUK DOSEN UNTAD AGUSTUS 2013bhvffyfIsmail Sholeh Bahrun MakkaratteNo ratings yet
- R304 0307 Env HHDocument221 pagesR304 0307 Env HHsyamsundariitmiitmNo ratings yet
- Circuit Diagram: Ecu A/7Document1 pageCircuit Diagram: Ecu A/7RubénNo ratings yet
- Media and Information Literacy - G11Document62 pagesMedia and Information Literacy - G11Jerfel MAAMONo ratings yet
- JADWAL KULIAH TPB SMT GASAL TA 2020 2021 Rev 5Document49 pagesJADWAL KULIAH TPB SMT GASAL TA 2020 2021 Rev 5shin yongriNo ratings yet
- Resume Keerthana PG PDFDocument1 pageResume Keerthana PG PDFVivek GNo ratings yet
- CO2 CorrosionDocument18 pagesCO2 CorrosionShie OthongNo ratings yet
- Filipino American RelationshipDocument3 pagesFilipino American RelationshipSamuel Grant ZabalaNo ratings yet
- Logix SERCOS Tuning Tips v1.02 1Document6 pagesLogix SERCOS Tuning Tips v1.02 1José AlanizNo ratings yet
- Solutions l4 Chemistry Class 12 Cbse by Ashu SirDocument16 pagesSolutions l4 Chemistry Class 12 Cbse by Ashu Sirvedantu495No ratings yet
- 7451 Planiseal288 GBDocument4 pages7451 Planiseal288 GBHendyKoNo ratings yet
- NAA ItemNumber391518Document203 pagesNAA ItemNumber391518Jonathan ArmstrongNo ratings yet
- GSCFF APF TechniquesDocument18 pagesGSCFF APF TechniquesMaharaniNo ratings yet
- Lab 1a RASPlib Installation Instructions R5 2016b-2017aDocument10 pagesLab 1a RASPlib Installation Instructions R5 2016b-2017aaleNo ratings yet
- Jataka Tales 3 PDFDocument3 pagesJataka Tales 3 PDFGhosalNo ratings yet
- How Does Photodynamic Therapy WorkDocument13 pagesHow Does Photodynamic Therapy WorkLoredana VoiculescuNo ratings yet
- SES 100R (1450rpm)Document1 pageSES 100R (1450rpm)Jaeni GilangNo ratings yet
- Ca Q&aDocument129 pagesCa Q&aRavi TejaNo ratings yet
- Grade7 Final DemoDocument5 pagesGrade7 Final DemoMarygrace VictorioNo ratings yet
- Xenon 2.2 4x2 148HP DC PDFDocument4 pagesXenon 2.2 4x2 148HP DC PDFshiksha torooNo ratings yet