Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Poster Bioscience TCHEUTCHOUA
Poster Bioscience TCHEUTCHOUA
Uploaded by
Loic MCCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ziehm Solo FD Service ManualDocument442 pagesZiehm Solo FD Service Manualdrakon100% (1)
- Kidney Kard - 6th EditionDocument4 pagesKidney Kard - 6th EditionHamlot100% (1)
- Metatonin & Pineal GlandDocument107 pagesMetatonin & Pineal GlandSoman100% (2)
- (A. Basak) Analogue Electronic Circuits and SystemDocument376 pages(A. Basak) Analogue Electronic Circuits and SystemRusman Santai KaawuNo ratings yet
- Cyprinus Carpio Cestrum SpeciesDocument4 pagesCyprinus Carpio Cestrum SpeciesDr. Jawale Chetan S.No ratings yet
- Dietary Modification For Reducing Electrical Conductivity of Piggery WastewaterDocument5 pagesDietary Modification For Reducing Electrical Conductivity of Piggery WastewaterApeng PangestuNo ratings yet
- Partial Replacement of Concentrate by Browse G Saraye 21 JN 2020Document3 pagesPartial Replacement of Concentrate by Browse G Saraye 21 JN 2020Rajesh ToolseeNo ratings yet
- University of Texas Water Anti AgingDocument5 pagesUniversity of Texas Water Anti AgingMichael DietrickNo ratings yet
- 2015 - Hristov, Mahon, DawsonDocument14 pages2015 - Hristov, Mahon, DawsonDương Minh MẫnNo ratings yet
- Dieudonné BISIMWA KAYEYE: BstractDocument8 pagesDieudonné BISIMWA KAYEYE: BstractBen Hamda FethiNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte MGT in SurgeryDocument40 pagesFluid and Electrolyte MGT in SurgeryJohn AgamahNo ratings yet
- Antihyperglycemic and Antihyperlipidemic Activities of Methanol-Water Isolated From Aqueous Extract of Syzygium AlternifoliumDocument7 pagesAntihyperglycemic and Antihyperlipidemic Activities of Methanol-Water Isolated From Aqueous Extract of Syzygium AlternifoliumMinyty LeNo ratings yet
- Paper 20Document4 pagesPaper 20GEORGE MIEBAKANo ratings yet
- Effect of Stocking Density Stress On The Hematological Profile ofDocument8 pagesEffect of Stocking Density Stress On The Hematological Profile ofdaniel cretuNo ratings yet
- Zanahoria 2Document5 pagesZanahoria 2Daniel felipeNo ratings yet
- Aegiceras CorniculatumDocument13 pagesAegiceras Corniculatumভাস্কর Vaskor0% (1)
- Bioresource Technology: Mariana Lucena Soares, Ester Ribeiro GouveiaDocument4 pagesBioresource Technology: Mariana Lucena Soares, Ester Ribeiro GouveiaJuan QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Wilt - Culture Media of Ralstonia Solanacearum - 2Document9 pagesBacterial Wilt - Culture Media of Ralstonia Solanacearum - 2PreuzNo ratings yet
- Glutaraldehyde PDFDocument83 pagesGlutaraldehyde PDFPariseerNo ratings yet
- Aspect To Consider in Fluid TherapyDocument34 pagesAspect To Consider in Fluid TherapyhanifahNo ratings yet
- b8c2 PDFDocument193 pagesb8c2 PDFRhIdho POetraNo ratings yet
- Molecules 19 06184Document18 pagesMolecules 19 06184Med AjNo ratings yet
- Nephroprotector Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Pods OfcanavaliagladiataDocument7 pagesNephroprotector Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Pods OfcanavaliagladiataspandanaNo ratings yet
- Culture Conditions For The Production of An Acidic Exopolysaccharide by The Nitrogen-Fixing Bacterium Burkholderia TropicaDocument5 pagesCulture Conditions For The Production of An Acidic Exopolysaccharide by The Nitrogen-Fixing Bacterium Burkholderia TropicanasrulNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report Of: Analysis of Food (FST 606)Document13 pagesLaboratory Report Of: Analysis of Food (FST 606)biokimia 2018No ratings yet
- In Vitro in Vivo Berberis Calliobotrys: Evaluation of and Anti-Arthritic Potential ofDocument14 pagesIn Vitro in Vivo Berberis Calliobotrys: Evaluation of and Anti-Arthritic Potential ofrocioNo ratings yet
- Environmental Eng'gDocument2 pagesEnvironmental Eng'gVaan100% (1)
- $RHZ3KN3Document39 pages$RHZ3KN3va.tmcbogorNo ratings yet
- Gupta and Jain - 1Document8 pagesGupta and Jain - 1Anonymous NEJodF0HXqNo ratings yet
- Wang2004 Article Anti-oxidationOfAgarOligosacchDocument8 pagesWang2004 Article Anti-oxidationOfAgarOligosacchYasmin EkapratiwiNo ratings yet
- Orange Peel: Organic Waste or Energetic Resource?: Martín M.A., Siles J.A., El Bari H., Chica A. F., Martín ADocument4 pagesOrange Peel: Organic Waste or Energetic Resource?: Martín M.A., Siles J.A., El Bari H., Chica A. F., Martín Amnegm2890No ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 2 - Fish Muscle ProteinDocument6 pagesLab Exercise 2 - Fish Muscle ProteinAcyl Chloride HaripremNo ratings yet
- 219 221 1 PB PDFDocument6 pages219 221 1 PB PDFVic KeyNo ratings yet
- 1.2.4 Fluid and Electrolyte Balance and Replacement Acid-Base BalanceDocument17 pages1.2.4 Fluid and Electrolyte Balance and Replacement Acid-Base BalanceZayan SyedNo ratings yet
- Hematology and Plasma Chemistry Reference Intervals For Cultured Tilapia (Oreochromis Hybrid)Document6 pagesHematology and Plasma Chemistry Reference Intervals For Cultured Tilapia (Oreochromis Hybrid)Ar RoshyiidNo ratings yet
- Enzym ProteazaDocument16 pagesEnzym Proteazavithuat1No ratings yet
- Electrolyzed Hydrogen Saturated Water For Drinking Use Elicits An Antioxidative Effect A Feeding Test With RatsDocument4 pagesElectrolyzed Hydrogen Saturated Water For Drinking Use Elicits An Antioxidative Effect A Feeding Test With RatsJoaqs JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Download Full Solution Manual For Introduction To General Organic And Biochemistry 12Th Edition Frederick A Bettelheim William H Brown Mary K Campbell Shawn O Farrell Omar Torres Is pdf docx full chapter chapterDocument36 pagesDownload Full Solution Manual For Introduction To General Organic And Biochemistry 12Th Edition Frederick A Bettelheim William H Brown Mary K Campbell Shawn O Farrell Omar Torres Is pdf docx full chapter chapterabnegatorbitterlye7wj594% (18)
- Water-Solubility of Chitosan and Its Antimicrobial ActivityDocument8 pagesWater-Solubility of Chitosan and Its Antimicrobial ActivityReemaNo ratings yet
- Molecules 19 09173 v2Document14 pagesMolecules 19 09173 v2Gautam NatrajanNo ratings yet
- Shinde2008 PDFDocument4 pagesShinde2008 PDFIndah WulansariNo ratings yet
- Vibrio CholeraeDocument3 pagesVibrio CholeraeBrycelle AlleraNo ratings yet
- Potassium Carbonate From Banana Skins: When Done With This Here Dobe Several Other IdeasDocument4 pagesPotassium Carbonate From Banana Skins: When Done With This Here Dobe Several Other Ideasteklemariam negashNo ratings yet
- Decaffeination. A Process To Detoxify Coffee PulpDocument5 pagesDecaffeination. A Process To Detoxify Coffee PulpKarime BGNo ratings yet
- Anti Hiv of Compounds Isolated From Polygonum CuspidatumDocument4 pagesAnti Hiv of Compounds Isolated From Polygonum CuspidatumAngga KusumaNo ratings yet
- Acute Toxicity Effect of Imidacloprid Insecticide On Serum BiochemicalDocument5 pagesAcute Toxicity Effect of Imidacloprid Insecticide On Serum Biochemicalkunalfcri09No ratings yet
- Phytotoxic and Nematicidal Components of Lavandula Luisieri Sup. InfDocument25 pagesPhytotoxic and Nematicidal Components of Lavandula Luisieri Sup. Influis fernando julio torresNo ratings yet
- Ijabr11 100 PDFDocument3 pagesIjabr11 100 PDFAjuogu PeterNo ratings yet
- Chin 1991Document5 pagesChin 1991Pedro RetamalNo ratings yet
- IsotachophoresisDocument7 pagesIsotachophoresisEka HerlinaNo ratings yet
- sc9b06008 Si 001Document18 pagessc9b06008 Si 001gigiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Aloes On Blood Glucose Levels in Normal and Alloxan Diabetic MiceDocument6 pagesEffect of Aloes On Blood Glucose Levels in Normal and Alloxan Diabetic MiceHaniya KhanNo ratings yet
- Статья Новиковой С.О. 25 тыс.Document17 pagesСтатья Новиковой С.О. 25 тыс.СнежанаNo ratings yet
- 10-Comparative Study of The Hypoglycemic Effects of Coconut Water Extract of Picralima Nitida Seeds and Daonil in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic RatsDocument3 pages10-Comparative Study of The Hypoglycemic Effects of Coconut Water Extract of Picralima Nitida Seeds and Daonil in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic RatsAditya Praja'schNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2352364620300092 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S2352364620300092 MainOktarian NandaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Endohyper On Biochemical Constituents of Freshwater Fish Mystus VittatusDocument7 pagesEffect of Endohyper On Biochemical Constituents of Freshwater Fish Mystus Vittatusc.kandeepanNo ratings yet
- Problems in BiochemDocument3 pagesProblems in BiochemIrish Marie Da-antonNo ratings yet
- Use of Bisphosphonates To Treat Severe Idiopathic Hypercalcaemia in A Young Ragdoll Cat 2011Document6 pagesUse of Bisphosphonates To Treat Severe Idiopathic Hypercalcaemia in A Young Ragdoll Cat 2011mariaNo ratings yet
- 731-Article Text-3619-2-10-20210121Document3 pages731-Article Text-3619-2-10-20210121Αβραξας ΓαβριήλNo ratings yet
- Antioxidant Activity of Ethyl Acetate Soluble.8Document6 pagesAntioxidant Activity of Ethyl Acetate Soluble.8Yasmeen AliNo ratings yet
- Fuels, Chemicals and Materials from the Oceans and Aquatic SourcesFrom EverandFuels, Chemicals and Materials from the Oceans and Aquatic SourcesFrancesca M. KertonNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterFrom EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNo ratings yet
- 10 11648 J JDMP 20160206 11Document7 pages10 11648 J JDMP 20160206 11Loic MCNo ratings yet
- Job Hunting in The Development Sector Presentation by Kathy KooDocument22 pagesJob Hunting in The Development Sector Presentation by Kathy KooLoic MCNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Ginger On Testis of Broiler BreedersDocument6 pagesThe Effect of Ginger On Testis of Broiler BreedersLoic MCNo ratings yet
- 10 11648 J BMB 20210603 15Document12 pages10 11648 J BMB 20210603 15Loic MCNo ratings yet
- La Cirrhose Alcoolique: Aspects Épidémiologiques, Diagnostiques Et ÉvolutifsDocument3 pagesLa Cirrhose Alcoolique: Aspects Épidémiologiques, Diagnostiques Et ÉvolutifsLoic MCNo ratings yet
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) SA ELISA: ReferencesDocument2 pagesFollicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) SA ELISA: ReferencesLoic MCNo ratings yet
- Protective Effects of Alendronate in Triton X-100-Induced Hyperlipidemia in RatsDocument8 pagesProtective Effects of Alendronate in Triton X-100-Induced Hyperlipidemia in RatsLoic MCNo ratings yet
- A New Dammarane Type Triterpene Glucoside From The Aerial Parts of Gouania Longipetala (Rhamnaceae)Document13 pagesA New Dammarane Type Triterpene Glucoside From The Aerial Parts of Gouania Longipetala (Rhamnaceae)Loic MCNo ratings yet
- Chemopreventive Effect of A Novel, Selective TACE Inhibitor On DMBA-and TPA-induced Skin CarcinogenesisDocument8 pagesChemopreventive Effect of A Novel, Selective TACE Inhibitor On DMBA-and TPA-induced Skin CarcinogenesisLoic MCNo ratings yet
- AGNES Intra Africa Mobility Grant - 2021 Call For Applications - EnglishDocument4 pagesAGNES Intra Africa Mobility Grant - 2021 Call For Applications - EnglishLoic MCNo ratings yet
- Anastrozole CLN 75 1643Document5 pagesAnastrozole CLN 75 1643Loic MCNo ratings yet
- TUNEL ASSAY Kyrylkova2012Document7 pagesTUNEL ASSAY Kyrylkova2012Loic MCNo ratings yet
- 2012 Theneuroprotectiveroleof TERTviaanantiapoptoticDocument6 pages2012 Theneuroprotectiveroleof TERTviaanantiapoptoticLoic MCNo ratings yet
- Three Dimensional GeometryDocument3 pagesThree Dimensional GeometryTaqi IsmailNo ratings yet
- Repro enDocument20 pagesRepro enWai Mei TeeNo ratings yet
- CCDS Parent Letter - Letter For Student-Contact To CaseDocument1 pageCCDS Parent Letter - Letter For Student-Contact To CaseActionNewsJaxNo ratings yet
- Valorisation of Spent Coffee Grounds Production of Biodiesel Via Enzimatic Catalisis With Ethanol and Co-SolventDocument14 pagesValorisation of Spent Coffee Grounds Production of Biodiesel Via Enzimatic Catalisis With Ethanol and Co-SolventAline GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Observations From The Plant VisitDocument2 pagesObservations From The Plant VisitAniket ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ME Engines: Electronic Headway of Two-Stroke DieselsDocument4 pagesME Engines: Electronic Headway of Two-Stroke DieselsSalwan ShubhamNo ratings yet
- English FinalDocument71 pagesEnglish FinalKhadeeja MarjanNo ratings yet
- CPS - Data Intensive Distributed ComputingDocument11 pagesCPS - Data Intensive Distributed ComputingManoj KavediaNo ratings yet
- PTCL Stormfiber Packages - Google SearchDocument1 pagePTCL Stormfiber Packages - Google Searchmachinekicking63No ratings yet
- Project Documentation SandeepDocument19 pagesProject Documentation SandeepFYIT80Sultan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics PDFDocument48 pagesFluid Mechanics PDFrakib hasanNo ratings yet
- Metasploit FrameworkDocument1 pageMetasploit FrameworkPAUL VINCENT FAJARDONo ratings yet
- The Prince of Evolution - Lee Alan DugatkinDocument68 pagesThe Prince of Evolution - Lee Alan DugatkinDjordje78No ratings yet
- ISEN 330 Final Exam ReviewDocument2 pagesISEN 330 Final Exam ReviewDaniel MedranoNo ratings yet
- Covellite PDFDocument1 pageCovellite PDFRyoga RizkyNo ratings yet
- 132kv, 1200sqmm UNDER GROUND CABLE WORKSDocument4 pages132kv, 1200sqmm UNDER GROUND CABLE WORKSBadhur ZamanNo ratings yet
- Research On Sustainable Development of Textile Industrial Clusters in The Process of GlobalizationDocument5 pagesResearch On Sustainable Development of Textile Industrial Clusters in The Process of GlobalizationSam AbdulNo ratings yet
- Dance VolumeDocument11 pagesDance VolumeuiuiuiuNo ratings yet
- ECE Workshop Practicals Exp No.2Document6 pagesECE Workshop Practicals Exp No.2msdineshpaiNo ratings yet
- Nabcep AppendixesDocument32 pagesNabcep AppendixeshockpinNo ratings yet
- Modding For Ysflight - Scenery EditorDocument92 pagesModding For Ysflight - Scenery Editordecaff_42No ratings yet
- Summary of Rock Armour Cost For Option A, B & C S/No Description Unit Rate Qty AmountDocument3 pagesSummary of Rock Armour Cost For Option A, B & C S/No Description Unit Rate Qty AmountHerbert P. BacosaNo ratings yet
- Living in The I.T Era Module 2Document18 pagesLiving in The I.T Era Module 2Aivee GatzzNo ratings yet
- Project 1 - School - Architecture Design - HandoutDocument6 pagesProject 1 - School - Architecture Design - Handoutawais anjumNo ratings yet
- 07 - Chapter-4. Land DegradationDocument92 pages07 - Chapter-4. Land DegradationKristhian GalárragaNo ratings yet
- XPR 300 Manual HyperthermDocument106 pagesXPR 300 Manual HyperthermDawitt BadilloNo ratings yet
- Serial Adder Mealy Modelling ProgramDocument22 pagesSerial Adder Mealy Modelling ProgrambcemailidNo ratings yet
Poster Bioscience TCHEUTCHOUA
Poster Bioscience TCHEUTCHOUA
Uploaded by
Loic MCOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Poster Bioscience TCHEUTCHOUA
Poster Bioscience TCHEUTCHOUA
Uploaded by
Loic MCCopyright:
Available Formats
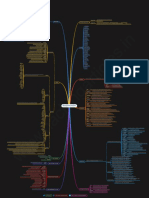
30e Conférence annuelle du Comité Camerounais de Biosciences (CCB)
Preventive Potential of the Aqueous Extract of the Mixture of
Bidens pilosa (Asteraceae) and Cymbopogon citratus (Poaceae)
Aerial Parts on Hypertension Induced by a Chronic Salt and
Alcohol Consumption on the Rats
Tcheutchoua Y.C, Bilanda D.C, Dzeufiet D.P.D, Djunie N.C.O, Owona P.E, Bidingha G.R, Ngapout
F.R, Mbolang N.L, Dimo T and Kamtchouing P.
Département de Biologie et Physiologie Animales, Laboratoire de Physiologie Animale, Université de Yaoundé I,
B.P.812 Yaoundé, Cameroun
INTRODUCTION
High blood pressure (HBP) is currently one of the main risk factors for cardiovascular and kidney diseases. Nowadays, populations make extensive use of alternative medicine for their health problems.
Bidens pilosa (Asteraceae) and Cymbopogon citratus (Poaceae) are used individually in the traditional treatment of cardiovascular disorders.
OBJECTIVE
This study assessed the effects of the mixture of the aqueous extract of Bidens pilosa (B. pilosa) and Cymbopogon citratus (C. citratus) on HBP in rats.
METHODOLOGY
Male rats (42) were divided into 7 groups of 6 rats each. Normotensive rats received only distilled water and formed group 1. The other animals received ethanol + salt preceded by distilled water (10 mL/ kg;
group 2) and spironolactone (10 mg/kg; group 3); the aqueous extracts of the mixture (100 and 200 mg/kg; groups 4 and 5) isolated plants B. pilosa (200 mg/kg; group 6) and C. citratus (200 mg/kg; group 7).
Animals were treated for 7 weeks during which water consumption and urine volume were assessed; then, hemodynamic parameters were recorded, and rats were sacrificed. Serum and some organs (liver,
kidney, heart, and aorta) were used to evaluate biochemical parameters.
RESULTS
Ingestion of ethanol + salt leads to a significant increase in urinary volume and water intake that were significantly prevented by the extracts from the mixture and isolated plants. Ethanol + salt solution
significantly increased the blood pressure, heart rate, triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-chol), very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (VLDL-chol), and
malondialdehyde (MDA) levels. However, the levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-chol), reduced glutathione (GSH), catalase, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity were significantly
reduced. The extracts of the mixture and isolated plants significantly prevented all these variations with a more pronounced action for the lowest dose of the mixture on the lipid profile, oxidative stress, and
kidney function.
Figure 1: Effects of the aqueous extract of the mixture of B. pilosa and C. citratus on blood pressure (a) and heart rate (b).
Each bar represents the mean ± SEM (n 6). SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; MBP, mean blood pressure; DW, normal
rats receiving only distilled water (10 mL/kg); DW + Al-salt, rats receiving distilled water (10 mL/kg) and the inducer (alcohol + salt solution)
concomitantly; BC 100+Al-salt and BC 200+Al-salt, rats receiving the aqueous extract of B. pilosa and C. citratus mixture at 100 and 200 mg/ kg,
respectively, and the inducer concomitantly; SPIRO + Al-salt, rats receiving spironolactone (10 mg/kg) and the inducer simultaneously; B 200+Al-
salt, rats receiving B. pilosa aqueous extract (200 mg/kg) and the inducer simultaneously; C 200+Al-salt, rats receiving C. citratus extract (200
mg/kg) and the inducer; 3p< 0.001, significant difference compared to normotensive rats receiving only distilled water; ap< 0.05; bp< 0.05; cp<
0.001, significant difference compared to rats given distilled water and the inducer
Table 4: Effects of the aqueous extract of the mixture of B. pilosa and C. citratus on the lipid profile. Figure 2: Effects of the aqueous extract of the mixture of B. pilosa
Parameters DW DW + Al-salt SPIRO + Al-salt BC 100 ± Al-salt BC 200 ± Al-salt B 200 ± Al-salt C 200 ± Al-salt and C. citratus on the level of GSH, catalase, and SOD activity, on the
concentration of MDA and on the level of nitrites. Each bar represents
the mean ± SEM (n 6). DW, normal rats receiving only distilled water (10 mL/kg);
TC (mg/dL) 66.20 ± 1.02 94.27 ± 4.203 82.64 ± 0.222b 67.88 ± 2.22c 79.17 ± 4.261a 88.06 ± 3.883 92.75 ± 0.203 DW + Al-salt, rats receiving distilled water (10 mL/kg) and the inducer (alcohol +
salt solution) simultaneously; BC 100+Al-salt and BC 200+Al-salt, rats receiving the
TG (mg/dL) 27.80 ± 1.95 60.39 ± 5.963 28.15 ± 3.88c 22.76 ± 1.87c 40.17 ± 3.36b 23.68 ± 1.21c 27.89 ± 3.92c aqueous extract of the mixture of B. pilosa and C. citratus, respectively, at doses
of 100 and 200 mg/kg and the inducer simultaneously; SPIRO + Al-salt, rats
HDL-chol (mg/dL) 57.07 ± 2.18 47.81 ± 4.30 56.87 ± 1.02 48.80 ± 1.78 63.69 ± 2.50b 49.56 ± 1.72 71.92 ± 3.93c2 receiving spironolactone (10 mg/kg) and the inducer simultaneously; B 200+Al-
salt, rats receiving the aqueous extract of B. pilosa (200 mg/kg) and the inducer
simultaneously; C 200 + Al-salt, rats receiving concurrent the aqueous extract of C.
LDL-chol (mg/dL) 3.57 ± 0.81 34.38 ± 4.023 20.14 ± 1.623a 14.53 ± 1.763b 7.45 ± 1.581c 33.76 ± 0.983 15.24 ± 1.033b citratus (200 mg/kg) and the inducer. 1p< 0.05; 2p< 0.01; 3p< 0.001, significant
difference compared to normal rats treated with only distilled water; ap< 0.05;
VLDL-chol (mg/dL) 5.56 ± 0.39 12.08 ± 1.193 5.63 ± 0.78c 4.55 ± 0.37c 8.03 ± 0.67b 4.74 ± 0.24c 5.58 ± 0.78c bp< 0.01; cp< 0.001, significant difference compared to rats receiving distilled
water
CONCLUSION REFERENCES
D. C. Bilanda, P. D. D. Dzeufiet, and L. Kouakep, “Bidens pilosa ethylene acetate extract can protect
The extracts of the mixture and isolated plants significantly prevented all these variations with a more
against L-NAME induced hypertension on the rats,” BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine, vol. 17,
pronounced action for the lowest dose of the mixture on the blood pressure, lipid profile, and oxidative no. 1, pp. 1–7, 2017.
stress. These observations confirm the beneficial effects of B. pilosa and C. citratus to manage J. F. Bastos, I. J. Moreira, T. P. Ribeiro et al., “Hypotensive and vasorelaxant effects of citronellol, a
monoterpene alcohol, in rats,” Basic and Clinical Pharmacology and Toxicology, vol. 106, no. 4, pp. 331–
hypertension. 337, 2010.
You might also like
- Ziehm Solo FD Service ManualDocument442 pagesZiehm Solo FD Service Manualdrakon100% (1)
- Kidney Kard - 6th EditionDocument4 pagesKidney Kard - 6th EditionHamlot100% (1)
- Metatonin & Pineal GlandDocument107 pagesMetatonin & Pineal GlandSoman100% (2)
- (A. Basak) Analogue Electronic Circuits and SystemDocument376 pages(A. Basak) Analogue Electronic Circuits and SystemRusman Santai KaawuNo ratings yet
- Cyprinus Carpio Cestrum SpeciesDocument4 pagesCyprinus Carpio Cestrum SpeciesDr. Jawale Chetan S.No ratings yet
- Dietary Modification For Reducing Electrical Conductivity of Piggery WastewaterDocument5 pagesDietary Modification For Reducing Electrical Conductivity of Piggery WastewaterApeng PangestuNo ratings yet
- Partial Replacement of Concentrate by Browse G Saraye 21 JN 2020Document3 pagesPartial Replacement of Concentrate by Browse G Saraye 21 JN 2020Rajesh ToolseeNo ratings yet
- University of Texas Water Anti AgingDocument5 pagesUniversity of Texas Water Anti AgingMichael DietrickNo ratings yet
- 2015 - Hristov, Mahon, DawsonDocument14 pages2015 - Hristov, Mahon, DawsonDương Minh MẫnNo ratings yet
- Dieudonné BISIMWA KAYEYE: BstractDocument8 pagesDieudonné BISIMWA KAYEYE: BstractBen Hamda FethiNo ratings yet
- Fluid and Electrolyte MGT in SurgeryDocument40 pagesFluid and Electrolyte MGT in SurgeryJohn AgamahNo ratings yet
- Antihyperglycemic and Antihyperlipidemic Activities of Methanol-Water Isolated From Aqueous Extract of Syzygium AlternifoliumDocument7 pagesAntihyperglycemic and Antihyperlipidemic Activities of Methanol-Water Isolated From Aqueous Extract of Syzygium AlternifoliumMinyty LeNo ratings yet
- Paper 20Document4 pagesPaper 20GEORGE MIEBAKANo ratings yet
- Effect of Stocking Density Stress On The Hematological Profile ofDocument8 pagesEffect of Stocking Density Stress On The Hematological Profile ofdaniel cretuNo ratings yet
- Zanahoria 2Document5 pagesZanahoria 2Daniel felipeNo ratings yet
- Aegiceras CorniculatumDocument13 pagesAegiceras Corniculatumভাস্কর Vaskor0% (1)
- Bioresource Technology: Mariana Lucena Soares, Ester Ribeiro GouveiaDocument4 pagesBioresource Technology: Mariana Lucena Soares, Ester Ribeiro GouveiaJuan QuintanaNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Wilt - Culture Media of Ralstonia Solanacearum - 2Document9 pagesBacterial Wilt - Culture Media of Ralstonia Solanacearum - 2PreuzNo ratings yet
- Glutaraldehyde PDFDocument83 pagesGlutaraldehyde PDFPariseerNo ratings yet
- Aspect To Consider in Fluid TherapyDocument34 pagesAspect To Consider in Fluid TherapyhanifahNo ratings yet
- b8c2 PDFDocument193 pagesb8c2 PDFRhIdho POetraNo ratings yet
- Molecules 19 06184Document18 pagesMolecules 19 06184Med AjNo ratings yet
- Nephroprotector Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Pods OfcanavaliagladiataDocument7 pagesNephroprotector Activity of Ethanolic Extract of Pods OfcanavaliagladiataspandanaNo ratings yet
- Culture Conditions For The Production of An Acidic Exopolysaccharide by The Nitrogen-Fixing Bacterium Burkholderia TropicaDocument5 pagesCulture Conditions For The Production of An Acidic Exopolysaccharide by The Nitrogen-Fixing Bacterium Burkholderia TropicanasrulNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report Of: Analysis of Food (FST 606)Document13 pagesLaboratory Report Of: Analysis of Food (FST 606)biokimia 2018No ratings yet
- In Vitro in Vivo Berberis Calliobotrys: Evaluation of and Anti-Arthritic Potential ofDocument14 pagesIn Vitro in Vivo Berberis Calliobotrys: Evaluation of and Anti-Arthritic Potential ofrocioNo ratings yet
- Environmental Eng'gDocument2 pagesEnvironmental Eng'gVaan100% (1)
- $RHZ3KN3Document39 pages$RHZ3KN3va.tmcbogorNo ratings yet
- Gupta and Jain - 1Document8 pagesGupta and Jain - 1Anonymous NEJodF0HXqNo ratings yet
- Wang2004 Article Anti-oxidationOfAgarOligosacchDocument8 pagesWang2004 Article Anti-oxidationOfAgarOligosacchYasmin EkapratiwiNo ratings yet
- Orange Peel: Organic Waste or Energetic Resource?: Martín M.A., Siles J.A., El Bari H., Chica A. F., Martín ADocument4 pagesOrange Peel: Organic Waste or Energetic Resource?: Martín M.A., Siles J.A., El Bari H., Chica A. F., Martín Amnegm2890No ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 2 - Fish Muscle ProteinDocument6 pagesLab Exercise 2 - Fish Muscle ProteinAcyl Chloride HaripremNo ratings yet
- 219 221 1 PB PDFDocument6 pages219 221 1 PB PDFVic KeyNo ratings yet
- 1.2.4 Fluid and Electrolyte Balance and Replacement Acid-Base BalanceDocument17 pages1.2.4 Fluid and Electrolyte Balance and Replacement Acid-Base BalanceZayan SyedNo ratings yet
- Hematology and Plasma Chemistry Reference Intervals For Cultured Tilapia (Oreochromis Hybrid)Document6 pagesHematology and Plasma Chemistry Reference Intervals For Cultured Tilapia (Oreochromis Hybrid)Ar RoshyiidNo ratings yet
- Enzym ProteazaDocument16 pagesEnzym Proteazavithuat1No ratings yet
- Electrolyzed Hydrogen Saturated Water For Drinking Use Elicits An Antioxidative Effect A Feeding Test With RatsDocument4 pagesElectrolyzed Hydrogen Saturated Water For Drinking Use Elicits An Antioxidative Effect A Feeding Test With RatsJoaqs JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Download Full Solution Manual For Introduction To General Organic And Biochemistry 12Th Edition Frederick A Bettelheim William H Brown Mary K Campbell Shawn O Farrell Omar Torres Is pdf docx full chapter chapterDocument36 pagesDownload Full Solution Manual For Introduction To General Organic And Biochemistry 12Th Edition Frederick A Bettelheim William H Brown Mary K Campbell Shawn O Farrell Omar Torres Is pdf docx full chapter chapterabnegatorbitterlye7wj594% (18)
- Water-Solubility of Chitosan and Its Antimicrobial ActivityDocument8 pagesWater-Solubility of Chitosan and Its Antimicrobial ActivityReemaNo ratings yet
- Molecules 19 09173 v2Document14 pagesMolecules 19 09173 v2Gautam NatrajanNo ratings yet
- Shinde2008 PDFDocument4 pagesShinde2008 PDFIndah WulansariNo ratings yet
- Vibrio CholeraeDocument3 pagesVibrio CholeraeBrycelle AlleraNo ratings yet
- Potassium Carbonate From Banana Skins: When Done With This Here Dobe Several Other IdeasDocument4 pagesPotassium Carbonate From Banana Skins: When Done With This Here Dobe Several Other Ideasteklemariam negashNo ratings yet
- Decaffeination. A Process To Detoxify Coffee PulpDocument5 pagesDecaffeination. A Process To Detoxify Coffee PulpKarime BGNo ratings yet
- Anti Hiv of Compounds Isolated From Polygonum CuspidatumDocument4 pagesAnti Hiv of Compounds Isolated From Polygonum CuspidatumAngga KusumaNo ratings yet
- Acute Toxicity Effect of Imidacloprid Insecticide On Serum BiochemicalDocument5 pagesAcute Toxicity Effect of Imidacloprid Insecticide On Serum Biochemicalkunalfcri09No ratings yet
- Phytotoxic and Nematicidal Components of Lavandula Luisieri Sup. InfDocument25 pagesPhytotoxic and Nematicidal Components of Lavandula Luisieri Sup. Influis fernando julio torresNo ratings yet
- Ijabr11 100 PDFDocument3 pagesIjabr11 100 PDFAjuogu PeterNo ratings yet
- Chin 1991Document5 pagesChin 1991Pedro RetamalNo ratings yet
- IsotachophoresisDocument7 pagesIsotachophoresisEka HerlinaNo ratings yet
- sc9b06008 Si 001Document18 pagessc9b06008 Si 001gigiNo ratings yet
- Effect of Aloes On Blood Glucose Levels in Normal and Alloxan Diabetic MiceDocument6 pagesEffect of Aloes On Blood Glucose Levels in Normal and Alloxan Diabetic MiceHaniya KhanNo ratings yet
- Статья Новиковой С.О. 25 тыс.Document17 pagesСтатья Новиковой С.О. 25 тыс.СнежанаNo ratings yet
- 10-Comparative Study of The Hypoglycemic Effects of Coconut Water Extract of Picralima Nitida Seeds and Daonil in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic RatsDocument3 pages10-Comparative Study of The Hypoglycemic Effects of Coconut Water Extract of Picralima Nitida Seeds and Daonil in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic RatsAditya Praja'schNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2352364620300092 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S2352364620300092 MainOktarian NandaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Endohyper On Biochemical Constituents of Freshwater Fish Mystus VittatusDocument7 pagesEffect of Endohyper On Biochemical Constituents of Freshwater Fish Mystus Vittatusc.kandeepanNo ratings yet
- Problems in BiochemDocument3 pagesProblems in BiochemIrish Marie Da-antonNo ratings yet
- Use of Bisphosphonates To Treat Severe Idiopathic Hypercalcaemia in A Young Ragdoll Cat 2011Document6 pagesUse of Bisphosphonates To Treat Severe Idiopathic Hypercalcaemia in A Young Ragdoll Cat 2011mariaNo ratings yet
- 731-Article Text-3619-2-10-20210121Document3 pages731-Article Text-3619-2-10-20210121Αβραξας ΓαβριήλNo ratings yet
- Antioxidant Activity of Ethyl Acetate Soluble.8Document6 pagesAntioxidant Activity of Ethyl Acetate Soluble.8Yasmeen AliNo ratings yet
- Fuels, Chemicals and Materials from the Oceans and Aquatic SourcesFrom EverandFuels, Chemicals and Materials from the Oceans and Aquatic SourcesFrancesca M. KertonNo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterFrom EverandPlant and Animal Bio-Chemistry - Including Information on Amino Acids, Proteins, Pigments and Other Chemical Constituents of Organic MatterNo ratings yet
- 10 11648 J JDMP 20160206 11Document7 pages10 11648 J JDMP 20160206 11Loic MCNo ratings yet
- Job Hunting in The Development Sector Presentation by Kathy KooDocument22 pagesJob Hunting in The Development Sector Presentation by Kathy KooLoic MCNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Ginger On Testis of Broiler BreedersDocument6 pagesThe Effect of Ginger On Testis of Broiler BreedersLoic MCNo ratings yet
- 10 11648 J BMB 20210603 15Document12 pages10 11648 J BMB 20210603 15Loic MCNo ratings yet
- La Cirrhose Alcoolique: Aspects Épidémiologiques, Diagnostiques Et ÉvolutifsDocument3 pagesLa Cirrhose Alcoolique: Aspects Épidémiologiques, Diagnostiques Et ÉvolutifsLoic MCNo ratings yet
- Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) SA ELISA: ReferencesDocument2 pagesFollicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) SA ELISA: ReferencesLoic MCNo ratings yet
- Protective Effects of Alendronate in Triton X-100-Induced Hyperlipidemia in RatsDocument8 pagesProtective Effects of Alendronate in Triton X-100-Induced Hyperlipidemia in RatsLoic MCNo ratings yet
- A New Dammarane Type Triterpene Glucoside From The Aerial Parts of Gouania Longipetala (Rhamnaceae)Document13 pagesA New Dammarane Type Triterpene Glucoside From The Aerial Parts of Gouania Longipetala (Rhamnaceae)Loic MCNo ratings yet
- Chemopreventive Effect of A Novel, Selective TACE Inhibitor On DMBA-and TPA-induced Skin CarcinogenesisDocument8 pagesChemopreventive Effect of A Novel, Selective TACE Inhibitor On DMBA-and TPA-induced Skin CarcinogenesisLoic MCNo ratings yet
- AGNES Intra Africa Mobility Grant - 2021 Call For Applications - EnglishDocument4 pagesAGNES Intra Africa Mobility Grant - 2021 Call For Applications - EnglishLoic MCNo ratings yet
- Anastrozole CLN 75 1643Document5 pagesAnastrozole CLN 75 1643Loic MCNo ratings yet
- TUNEL ASSAY Kyrylkova2012Document7 pagesTUNEL ASSAY Kyrylkova2012Loic MCNo ratings yet
- 2012 Theneuroprotectiveroleof TERTviaanantiapoptoticDocument6 pages2012 Theneuroprotectiveroleof TERTviaanantiapoptoticLoic MCNo ratings yet
- Three Dimensional GeometryDocument3 pagesThree Dimensional GeometryTaqi IsmailNo ratings yet
- Repro enDocument20 pagesRepro enWai Mei TeeNo ratings yet
- CCDS Parent Letter - Letter For Student-Contact To CaseDocument1 pageCCDS Parent Letter - Letter For Student-Contact To CaseActionNewsJaxNo ratings yet
- Valorisation of Spent Coffee Grounds Production of Biodiesel Via Enzimatic Catalisis With Ethanol and Co-SolventDocument14 pagesValorisation of Spent Coffee Grounds Production of Biodiesel Via Enzimatic Catalisis With Ethanol and Co-SolventAline GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Observations From The Plant VisitDocument2 pagesObservations From The Plant VisitAniket ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- ME Engines: Electronic Headway of Two-Stroke DieselsDocument4 pagesME Engines: Electronic Headway of Two-Stroke DieselsSalwan ShubhamNo ratings yet
- English FinalDocument71 pagesEnglish FinalKhadeeja MarjanNo ratings yet
- CPS - Data Intensive Distributed ComputingDocument11 pagesCPS - Data Intensive Distributed ComputingManoj KavediaNo ratings yet
- PTCL Stormfiber Packages - Google SearchDocument1 pagePTCL Stormfiber Packages - Google Searchmachinekicking63No ratings yet
- Project Documentation SandeepDocument19 pagesProject Documentation SandeepFYIT80Sultan ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics PDFDocument48 pagesFluid Mechanics PDFrakib hasanNo ratings yet
- Metasploit FrameworkDocument1 pageMetasploit FrameworkPAUL VINCENT FAJARDONo ratings yet
- The Prince of Evolution - Lee Alan DugatkinDocument68 pagesThe Prince of Evolution - Lee Alan DugatkinDjordje78No ratings yet
- ISEN 330 Final Exam ReviewDocument2 pagesISEN 330 Final Exam ReviewDaniel MedranoNo ratings yet
- Covellite PDFDocument1 pageCovellite PDFRyoga RizkyNo ratings yet
- 132kv, 1200sqmm UNDER GROUND CABLE WORKSDocument4 pages132kv, 1200sqmm UNDER GROUND CABLE WORKSBadhur ZamanNo ratings yet
- Research On Sustainable Development of Textile Industrial Clusters in The Process of GlobalizationDocument5 pagesResearch On Sustainable Development of Textile Industrial Clusters in The Process of GlobalizationSam AbdulNo ratings yet
- Dance VolumeDocument11 pagesDance VolumeuiuiuiuNo ratings yet
- ECE Workshop Practicals Exp No.2Document6 pagesECE Workshop Practicals Exp No.2msdineshpaiNo ratings yet
- Nabcep AppendixesDocument32 pagesNabcep AppendixeshockpinNo ratings yet
- Modding For Ysflight - Scenery EditorDocument92 pagesModding For Ysflight - Scenery Editordecaff_42No ratings yet
- Summary of Rock Armour Cost For Option A, B & C S/No Description Unit Rate Qty AmountDocument3 pagesSummary of Rock Armour Cost For Option A, B & C S/No Description Unit Rate Qty AmountHerbert P. BacosaNo ratings yet
- Living in The I.T Era Module 2Document18 pagesLiving in The I.T Era Module 2Aivee GatzzNo ratings yet
- Project 1 - School - Architecture Design - HandoutDocument6 pagesProject 1 - School - Architecture Design - Handoutawais anjumNo ratings yet
- 07 - Chapter-4. Land DegradationDocument92 pages07 - Chapter-4. Land DegradationKristhian GalárragaNo ratings yet
- XPR 300 Manual HyperthermDocument106 pagesXPR 300 Manual HyperthermDawitt BadilloNo ratings yet
- Serial Adder Mealy Modelling ProgramDocument22 pagesSerial Adder Mealy Modelling ProgrambcemailidNo ratings yet