Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 viewsBIO270 Tuto 5
BIO270 Tuto 5
Uploaded by
Mirza Karmila1. The document differentiates between innate and acquired immunity in 3 sentences: Innate immunity is the first line of defense and is effective from birth with no memory and an immediate but non-specific response. Acquired immunity is the second line of defense and develops after exposure, has memory, and a delayed but specific response.
2. T-cells and B-cells are differentiated in 3 sentences: T-cells have TCRs and are long-lived, developing in the bone marrow before migrating to the thymus and secreting cytokines and cellular effectors. B-cells have BCRs, are short-lived, develop in the bone marrow, and secrete Ig and cytokines as well as
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Hematologic Disorders NotesDocument19 pagesHematologic Disorders Notesmikkagreen95% (22)
- 130 Immunology Questions and AnswersDocument46 pages130 Immunology Questions and Answers成失86% (14)
- Bio320 Lab 2Document4 pagesBio320 Lab 2Mirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Immunology Flash CardsDocument46 pagesImmunology Flash CardsRickyNoviantoNo ratings yet
- Third Line of Defense: Acquired or Developed or Adaptive ImmunityDocument7 pagesThird Line of Defense: Acquired or Developed or Adaptive Immunityهند نهاد سلمان حسينNo ratings yet
- Body'S Defenses Mechanisms: by Anmaw Shite (DVM, MSC) Assistant Professor ofDocument48 pagesBody'S Defenses Mechanisms: by Anmaw Shite (DVM, MSC) Assistant Professor ofgetnet gizachewNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Immunology - Ranjan ShawDocument9 pagesBasic Concept of Immunology - Ranjan ShawRanjan ShawNo ratings yet
- 53 PDFDocument29 pages53 PDFBrunoNo ratings yet
- Immuno - Immunology QnADocument15 pagesImmuno - Immunology QnANashrah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09. Host Response To InfectionDocument51 pagesChapter 09. Host Response To InfectionZin LimNo ratings yet
- Disease and DefenceDocument5 pagesDisease and DefenceNabindra Ruwali100% (1)
- Biology Class NotesDocument4 pagesBiology Class NotesAngelica ANo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument15 pagesImmunologyAnik MazumderNo ratings yet
- Micp Lec (Week - 4) Host Response To InfectionDocument15 pagesMicp Lec (Week - 4) Host Response To Infectioncaitie miracleNo ratings yet
- Immunology BookDocument35 pagesImmunology BookMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Overview and Cells of The Immune SystemDocument5 pagesOverview and Cells of The Immune SystemAmanda AmiraultNo ratings yet
- Prelim - Adaptive Immune ResponseDocument12 pagesPrelim - Adaptive Immune ResponseJustin BellosaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ImmunoooDocument10 pagesReviewer ImmunoooTWINKLE MAE EGAYNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Document8 pagesIsabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Charlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument7 pagesIntroduction To ImmunologyPRECY MAE VALETENo ratings yet
- MicpLec 28week 429UpdatedCANVASJan2024HostResponsetoInfectionDocument11 pagesMicpLec 28week 429UpdatedCANVASJan2024HostResponsetoInfectionRaven Joyce LabayenNo ratings yet
- Management of Clients With Immune DisordersDocument75 pagesManagement of Clients With Immune DisordersRatih Purnamasari Nu AmooreaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Dynamic Equilibrium Section 6-Immune System: Biology 2201Document23 pagesUnit 3 - Dynamic Equilibrium Section 6-Immune System: Biology 2201nurulallizzwellNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Immunologic Disorders: Immune SystemDocument7 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Immunologic Disorders: Immune SystemIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Immunity 1Document55 pagesImmunity 1itsminisimmerNo ratings yet
- Disease and The Immune SystemDocument44 pagesDisease and The Immune SystemBaydaa Hameed Al AbdaliNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITYDocument58 pagesIMMUNITYkamala 123No ratings yet
- The Immune System:: Innate and Acquired ImmunityDocument47 pagesThe Immune System:: Innate and Acquired ImmunityBad BunnyNo ratings yet
- Bt302 Current SolvedDocument5 pagesBt302 Current SolvedMuzamil RazaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Aquired ImmunDocument34 pages1 - Aquired Immunعبدالرحمن الماحيNo ratings yet
- Components of The Immune SystemDocument8 pagesComponents of The Immune Systemبراءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- Class XII Human Health and Disease Chapter 8Document15 pagesClass XII Human Health and Disease Chapter 8sahilNo ratings yet
- SB025 11. ImmunityDocument21 pagesSB025 11. ImmunityNur SafirahNo ratings yet
- Shakira Ghazanfar: PHD ScholarDocument22 pagesShakira Ghazanfar: PHD ScholarLord SivaNo ratings yet
- Immunity of Parasitic InfectionsDocument4 pagesImmunity of Parasitic InfectionsCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- 143 SG 9Document43 pages143 SG 9cake girlsNo ratings yet
- MLS 021 - Immunology & Serology - Lecture - NotesDocument1 pageMLS 021 - Immunology & Serology - Lecture - NotesFrancine UriarteNo ratings yet
- Immunobiology NIOSDocument16 pagesImmunobiology NIOSChetan MitraNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System HandoutDocument4 pagesThe Lymphatic System HandoutLleana TanNo ratings yet
- Immunology Lecturs 27Document27 pagesImmunology Lecturs 27Rolls SaeedNo ratings yet
- AQA Immunity Booklet AnswersDocument6 pagesAQA Immunity Booklet AnswersJames ChongNo ratings yet
- Crawford Hes Lec Sas 10Document6 pagesCrawford Hes Lec Sas 10Divo SkyeNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Basic and Clinical Principles: First EditionDocument112 pagesMicrobiology: Basic and Clinical Principles: First EditionDawn DixonNo ratings yet
- CBS Imm1Document31 pagesCBS Imm1tyhbbhhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesDocument2 pagesChapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesChryza Faith QuicoyNo ratings yet
- L 2 Adaptive Immunity To Infection REVISEDDocument15 pagesL 2 Adaptive Immunity To Infection REVISEDaugustongoviNo ratings yet
- Elements of The Immune System and Their Roles in DefenseDocument55 pagesElements of The Immune System and Their Roles in Defensenokate konkoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 To 3 - Introduction and Adaptive Immunity PDFDocument30 pagesLecture 1 To 3 - Introduction and Adaptive Immunity PDFNamam VasaveNo ratings yet
- Inmunidad y SepsisDocument6 pagesInmunidad y SepsisAmmarie SanchezNo ratings yet
- Immunity System Health and Defense CH 57 & 58Document19 pagesImmunity System Health and Defense CH 57 & 58NaNo ratings yet
- 47.2 Specific Defenses, The Immune System: Chapter 47: The Body's Defense SystemsDocument20 pages47.2 Specific Defenses, The Immune System: Chapter 47: The Body's Defense Systemsapi-520057338No ratings yet
- IVB Immune SystemDocument11 pagesIVB Immune Systembarathkumar amidalaNo ratings yet
- Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis ADEM AtfDocument4 pagesAcute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis ADEM AtfAfrah AbdulNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument65 pagesDiseases of The Immune Systemanon_62816775No ratings yet
- PMT WeeblyDocument10 pagesPMT WeeblyAdam BeyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Immunologykaiyeol exoNo ratings yet
- Micro F2.Chapter 4 - 2022Document3 pagesMicro F2.Chapter 4 - 2022عبدالرحمن عابدNo ratings yet
- Immunity DR Ahmed KamelDocument35 pagesImmunity DR Ahmed KamelMostafa EidNo ratings yet
- 12 13 2006 Life Science Introduction To Immune 2006Document99 pages12 13 2006 Life Science Introduction To Immune 2006api-3696530No ratings yet
- Cell Mediated and Humoral Immunity. Cytokines & The Immune Responses, Hypersensitivity ReactionsDocument40 pagesCell Mediated and Humoral Immunity. Cytokines & The Immune Responses, Hypersensitivity ReactionsAjaga RuqayyahNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Physical BarriersDocument6 pagesImmunology: Physical BarriersFarhana AktharNo ratings yet
- Altered Immune ResponseDocument20 pagesAltered Immune Responsesho bartNo ratings yet
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityFrom EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityNo ratings yet
- Bio270 Tutorial Week 11Document1 pageBio270 Tutorial Week 11Mirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Active Learning Activity 1 Bms551 Principles of BioinformaticsDocument2 pagesActive Learning Activity 1 Bms551 Principles of BioinformaticsMirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Faculty OF Applied Sciences Diploma in Science (AS120) : CapacitenceDocument10 pagesFaculty OF Applied Sciences Diploma in Science (AS120) : CapacitenceMirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- CHM256 Case Study (Mirza Karmila, Nurul Izzati)Document12 pagesCHM256 Case Study (Mirza Karmila, Nurul Izzati)Mirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- BIO270 Written AssignmentDocument3 pagesBIO270 Written AssignmentMirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Bio320 Lab 4Document6 pagesBio320 Lab 4Mirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Applied Sciences Diploma in Science (AS120) : Coulomb'S LawDocument10 pagesFaculty of Applied Sciences Diploma in Science (AS120) : Coulomb'S LawMirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Workbook: Laboratory BIO320: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm)Document4 pagesWorkbook: Laboratory BIO320: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm)Mirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Workbook: Laboratory BIO32: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm) Branch Sabah Campus Kota KinabaluDocument6 pagesWorkbook: Laboratory BIO32: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm) Branch Sabah Campus Kota KinabaluMirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Bio320 Lab 4Document6 pagesBio320 Lab 4Mirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- 11 Compressed Notes ImmunityDocument9 pages11 Compressed Notes ImmunityLIM ZHI SHUENNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Case Study On Malignant MelanomaDocument7 pagesGroup 4 Case Study On Malignant MelanomaLance JardiolinNo ratings yet
- A Brief Journey Through The Immune System: Karim M. Yatim and Fadi G. LakkisDocument8 pagesA Brief Journey Through The Immune System: Karim M. Yatim and Fadi G. LakkisMaximeNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IV Lecture Notes BP205T Computer Applications in Pharmacy-Updated 07.08.2020Document31 pagesUNIT-IV Lecture Notes BP205T Computer Applications in Pharmacy-Updated 07.08.2020B.MAHAALAKSHMINo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument10 pagesConcept MapStephen Yor100% (1)
- Immunology and SerologyDocument66 pagesImmunology and SerologyDenver CarbonNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument86 pagesPDFXuan TuanNo ratings yet
- SBL100-Immunology Lectures 1-3Document92 pagesSBL100-Immunology Lectures 1-3B.simhachalam100% (1)
- Immunology 9Th Edition Male David Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pagesImmunology 9Th Edition Male David Full Chapter PDFvisbystoss100% (4)
- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses: Elaine N. MariebDocument75 pagesThe Lymphatic System and Body Defenses: Elaine N. MariebReysa Manulat100% (1)
- Mock Test of 3rd GroupDocument7 pagesMock Test of 3rd GroupSelvia PutriNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Lymph Nodes: Norman Levy, MDDocument92 pagesPathology of Lymph Nodes: Norman Levy, MDDocAxi Maximo Jr AxibalNo ratings yet
- The Recognition of Antigen: Antigen Recognition by B-Cell and T-Cell ReceptorsDocument2 pagesThe Recognition of Antigen: Antigen Recognition by B-Cell and T-Cell ReceptorsIsSis0% (1)
- Non-Hodgkins LymphomaDocument22 pagesNon-Hodgkins LymphomaNyoman TapayanaNo ratings yet
- Ammar K. Daoud: Haneen Ibrahim Hamza Al-SleatiDocument10 pagesAmmar K. Daoud: Haneen Ibrahim Hamza Al-SleatiInnocent L NdambakuwaNo ratings yet
- Immunology Exam Q S With AnswersDocument28 pagesImmunology Exam Q S With AnswersIceBearNo ratings yet
- Full HD English Editorials 2-1-2022Document25 pagesFull HD English Editorials 2-1-2022uihuyhyubuhbNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument3 pagesImmunologybhawana bhattNo ratings yet
- A Less Brief Guide To The Pfizer and Moderna VaccinesDocument7 pagesA Less Brief Guide To The Pfizer and Moderna VaccinesAnika Jane BeamerNo ratings yet
- The Immune SystemDocument31 pagesThe Immune SystemYesiana Lilis Sugiarti100% (1)
- Communicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5Document461 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5Jordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Car-T Cell Receptors (7758)Document8 pagesCar-T Cell Receptors (7758)Saradha PellatiNo ratings yet
- Limfoproliferari Cronice MaligneDocument18 pagesLimfoproliferari Cronice MaligneAlice MuscaNo ratings yet
- CAR-T e LESDocument5 pagesCAR-T e LESSpanna Lo SpamNo ratings yet
- 11 ImmunityDocument5 pages11 ImmunityTina EtoileNo ratings yet
- Grupp Et Al - 2013 - Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells For AcuDocument16 pagesGrupp Et Al - 2013 - Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells For AcuChae SonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 3 1 First Line of DefenseDocument33 pagesChapter 3 3 1 First Line of Defenseapi-237856591No ratings yet
- Rhinitis Allergy and ElderlyDocument26 pagesRhinitis Allergy and ElderlyPutri Rizky AmaliaNo ratings yet
BIO270 Tuto 5
BIO270 Tuto 5
Uploaded by
Mirza Karmila0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pages1. The document differentiates between innate and acquired immunity in 3 sentences: Innate immunity is the first line of defense and is effective from birth with no memory and an immediate but non-specific response. Acquired immunity is the second line of defense and develops after exposure, has memory, and a delayed but specific response.
2. T-cells and B-cells are differentiated in 3 sentences: T-cells have TCRs and are long-lived, developing in the bone marrow before migrating to the thymus and secreting cytokines and cellular effectors. B-cells have BCRs, are short-lived, develop in the bone marrow, and secrete Ig and cytokines as well as
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document differentiates between innate and acquired immunity in 3 sentences: Innate immunity is the first line of defense and is effective from birth with no memory and an immediate but non-specific response. Acquired immunity is the second line of defense and develops after exposure, has memory, and a delayed but specific response.
2. T-cells and B-cells are differentiated in 3 sentences: T-cells have TCRs and are long-lived, developing in the bone marrow before migrating to the thymus and secreting cytokines and cellular effectors. B-cells have BCRs, are short-lived, develop in the bone marrow, and secrete Ig and cytokines as well as
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views3 pagesBIO270 Tuto 5
BIO270 Tuto 5
Uploaded by
Mirza Karmila1. The document differentiates between innate and acquired immunity in 3 sentences: Innate immunity is the first line of defense and is effective from birth with no memory and an immediate but non-specific response. Acquired immunity is the second line of defense and develops after exposure, has memory, and a delayed but specific response.
2. T-cells and B-cells are differentiated in 3 sentences: T-cells have TCRs and are long-lived, developing in the bone marrow before migrating to the thymus and secreting cytokines and cellular effectors. B-cells have BCRs, are short-lived, develop in the bone marrow, and secrete Ig and cytokines as well as
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
1.
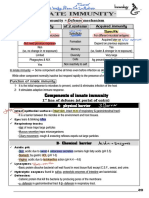
Differentiate between innate and acquired immunity (5m)
Innate immunity Acquired immunity
1st line of defense 2nd line of defense
Effective from the time of birth Develops after esxposure to inducing agents.
No memory Memory present
Immediate response Not immediate response
Non-specific response to pathogens Specific response to pathogens
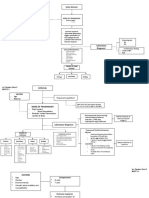
2. Differentiate between T-cell and B-cell receptors (5m)
*klw dpt lukis,lukis yah.
*sbb lukisan ada markah
*bole ikut point dkt miss punya simple notes
T-cells B-cells
TCRs BCRs
Long-lived Short lived
Developed in red bone marrow before Developed in red bone marrow
migrating to thymus
Secretes cytokinesis Secrets ig and cytokinesis
Cellular and humoral effectors Humoral effector only
3. Differentiate between humoral and cell mediated acquired immunity (5m)
*buat mcm apa miss ckp dkt discussion for tutorial.
*tambah table utk classes dia
Humural Immunity Cell Mediated Immunity
mediated by antibody Mediated by cytotoxic lymphocyets
Main cells are B-cells Main cells are T-cells
The onset is rapid The onset is delayed
Protect againts extracellular pathogens Protect againts intracellular pathogens
The end of the result of activation is the
The end of the result of the activation is the
differentiation of plasma B-cells, secreting
secretion of cytokines
antibodies
4. Explain and give examples of 5 classes of antibodies (10m)
*klw bole buat jadual spaya senang.
I. igG (monomer)
-secreted by plasma cells in the blood
-able to cross placenta to fetus
-promote opsonization, neurtralization and agglutination of antigents and less effective in
complement activation than igM
II. igA (dimer)
-found in mucus, saliva tears and breast milk.
-provides localized defense of mucous membranes by agglutination and neutralization of
antigens
-protects againts pathogens
III. IgM (pentamer)
-May be attached to the surface of B-cell in blood.
-promotes neutralization and agglutination of antigents which is very effective in complement
activation.
IV. igE (monomer)
-triggers release from mast cells and basophils of histamnie and other chemicals that cause
allergic reactions.
V. igD (monomer)
-parts of the B-cell receptor
-act as antigen receptor in antigen-stimulated proliferation and differentiation of B cells.
You might also like
- Hematologic Disorders NotesDocument19 pagesHematologic Disorders Notesmikkagreen95% (22)
- 130 Immunology Questions and AnswersDocument46 pages130 Immunology Questions and Answers成失86% (14)
- Bio320 Lab 2Document4 pagesBio320 Lab 2Mirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Immunology Flash CardsDocument46 pagesImmunology Flash CardsRickyNoviantoNo ratings yet
- Third Line of Defense: Acquired or Developed or Adaptive ImmunityDocument7 pagesThird Line of Defense: Acquired or Developed or Adaptive Immunityهند نهاد سلمان حسينNo ratings yet
- Body'S Defenses Mechanisms: by Anmaw Shite (DVM, MSC) Assistant Professor ofDocument48 pagesBody'S Defenses Mechanisms: by Anmaw Shite (DVM, MSC) Assistant Professor ofgetnet gizachewNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of Immunology - Ranjan ShawDocument9 pagesBasic Concept of Immunology - Ranjan ShawRanjan ShawNo ratings yet
- 53 PDFDocument29 pages53 PDFBrunoNo ratings yet
- Immuno - Immunology QnADocument15 pagesImmuno - Immunology QnANashrah HusnaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 09. Host Response To InfectionDocument51 pagesChapter 09. Host Response To InfectionZin LimNo ratings yet
- Disease and DefenceDocument5 pagesDisease and DefenceNabindra Ruwali100% (1)
- Biology Class NotesDocument4 pagesBiology Class NotesAngelica ANo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument15 pagesImmunologyAnik MazumderNo ratings yet
- Micp Lec (Week - 4) Host Response To InfectionDocument15 pagesMicp Lec (Week - 4) Host Response To Infectioncaitie miracleNo ratings yet
- Immunology BookDocument35 pagesImmunology BookMuhammad AliNo ratings yet
- Overview and Cells of The Immune SystemDocument5 pagesOverview and Cells of The Immune SystemAmanda AmiraultNo ratings yet
- Prelim - Adaptive Immune ResponseDocument12 pagesPrelim - Adaptive Immune ResponseJustin BellosaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer ImmunoooDocument10 pagesReviewer ImmunoooTWINKLE MAE EGAYNo ratings yet
- Isabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Document8 pagesIsabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Charlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument7 pagesIntroduction To ImmunologyPRECY MAE VALETENo ratings yet
- MicpLec 28week 429UpdatedCANVASJan2024HostResponsetoInfectionDocument11 pagesMicpLec 28week 429UpdatedCANVASJan2024HostResponsetoInfectionRaven Joyce LabayenNo ratings yet
- Management of Clients With Immune DisordersDocument75 pagesManagement of Clients With Immune DisordersRatih Purnamasari Nu AmooreaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 - Dynamic Equilibrium Section 6-Immune System: Biology 2201Document23 pagesUnit 3 - Dynamic Equilibrium Section 6-Immune System: Biology 2201nurulallizzwellNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Clients With Immunologic Disorders: Immune SystemDocument7 pagesNursing Care of Clients With Immunologic Disorders: Immune SystemIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Immunity 1Document55 pagesImmunity 1itsminisimmerNo ratings yet
- Disease and The Immune SystemDocument44 pagesDisease and The Immune SystemBaydaa Hameed Al AbdaliNo ratings yet
- IMMUNITYDocument58 pagesIMMUNITYkamala 123No ratings yet
- The Immune System:: Innate and Acquired ImmunityDocument47 pagesThe Immune System:: Innate and Acquired ImmunityBad BunnyNo ratings yet
- Bt302 Current SolvedDocument5 pagesBt302 Current SolvedMuzamil RazaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Aquired ImmunDocument34 pages1 - Aquired Immunعبدالرحمن الماحيNo ratings yet
- Components of The Immune SystemDocument8 pagesComponents of The Immune Systemبراءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- Class XII Human Health and Disease Chapter 8Document15 pagesClass XII Human Health and Disease Chapter 8sahilNo ratings yet
- SB025 11. ImmunityDocument21 pagesSB025 11. ImmunityNur SafirahNo ratings yet
- Shakira Ghazanfar: PHD ScholarDocument22 pagesShakira Ghazanfar: PHD ScholarLord SivaNo ratings yet
- Immunity of Parasitic InfectionsDocument4 pagesImmunity of Parasitic InfectionsCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- 143 SG 9Document43 pages143 SG 9cake girlsNo ratings yet
- MLS 021 - Immunology & Serology - Lecture - NotesDocument1 pageMLS 021 - Immunology & Serology - Lecture - NotesFrancine UriarteNo ratings yet
- Immunobiology NIOSDocument16 pagesImmunobiology NIOSChetan MitraNo ratings yet
- The Lymphatic System HandoutDocument4 pagesThe Lymphatic System HandoutLleana TanNo ratings yet
- Immunology Lecturs 27Document27 pagesImmunology Lecturs 27Rolls SaeedNo ratings yet
- AQA Immunity Booklet AnswersDocument6 pagesAQA Immunity Booklet AnswersJames ChongNo ratings yet
- Crawford Hes Lec Sas 10Document6 pagesCrawford Hes Lec Sas 10Divo SkyeNo ratings yet
- Microbiology: Basic and Clinical Principles: First EditionDocument112 pagesMicrobiology: Basic and Clinical Principles: First EditionDawn DixonNo ratings yet
- CBS Imm1Document31 pagesCBS Imm1tyhbbhhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesDocument2 pagesChapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesChryza Faith QuicoyNo ratings yet
- L 2 Adaptive Immunity To Infection REVISEDDocument15 pagesL 2 Adaptive Immunity To Infection REVISEDaugustongoviNo ratings yet
- Elements of The Immune System and Their Roles in DefenseDocument55 pagesElements of The Immune System and Their Roles in Defensenokate konkoorNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 To 3 - Introduction and Adaptive Immunity PDFDocument30 pagesLecture 1 To 3 - Introduction and Adaptive Immunity PDFNamam VasaveNo ratings yet
- Inmunidad y SepsisDocument6 pagesInmunidad y SepsisAmmarie SanchezNo ratings yet
- Immunity System Health and Defense CH 57 & 58Document19 pagesImmunity System Health and Defense CH 57 & 58NaNo ratings yet
- 47.2 Specific Defenses, The Immune System: Chapter 47: The Body's Defense SystemsDocument20 pages47.2 Specific Defenses, The Immune System: Chapter 47: The Body's Defense Systemsapi-520057338No ratings yet
- IVB Immune SystemDocument11 pagesIVB Immune Systembarathkumar amidalaNo ratings yet
- Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis ADEM AtfDocument4 pagesAcute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis ADEM AtfAfrah AbdulNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument65 pagesDiseases of The Immune Systemanon_62816775No ratings yet
- PMT WeeblyDocument10 pagesPMT WeeblyAdam BeyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To ImmunologyDocument14 pagesIntroduction To Immunologykaiyeol exoNo ratings yet
- Micro F2.Chapter 4 - 2022Document3 pagesMicro F2.Chapter 4 - 2022عبدالرحمن عابدNo ratings yet
- Immunity DR Ahmed KamelDocument35 pagesImmunity DR Ahmed KamelMostafa EidNo ratings yet
- 12 13 2006 Life Science Introduction To Immune 2006Document99 pages12 13 2006 Life Science Introduction To Immune 2006api-3696530No ratings yet
- Cell Mediated and Humoral Immunity. Cytokines & The Immune Responses, Hypersensitivity ReactionsDocument40 pagesCell Mediated and Humoral Immunity. Cytokines & The Immune Responses, Hypersensitivity ReactionsAjaga RuqayyahNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Physical BarriersDocument6 pagesImmunology: Physical BarriersFarhana AktharNo ratings yet
- Altered Immune ResponseDocument20 pagesAltered Immune Responsesho bartNo ratings yet
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityFrom EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityNo ratings yet
- Bio270 Tutorial Week 11Document1 pageBio270 Tutorial Week 11Mirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Active Learning Activity 1 Bms551 Principles of BioinformaticsDocument2 pagesActive Learning Activity 1 Bms551 Principles of BioinformaticsMirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Faculty OF Applied Sciences Diploma in Science (AS120) : CapacitenceDocument10 pagesFaculty OF Applied Sciences Diploma in Science (AS120) : CapacitenceMirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- CHM256 Case Study (Mirza Karmila, Nurul Izzati)Document12 pagesCHM256 Case Study (Mirza Karmila, Nurul Izzati)Mirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- BIO270 Written AssignmentDocument3 pagesBIO270 Written AssignmentMirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Bio320 Lab 4Document6 pagesBio320 Lab 4Mirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Applied Sciences Diploma in Science (AS120) : Coulomb'S LawDocument10 pagesFaculty of Applied Sciences Diploma in Science (AS120) : Coulomb'S LawMirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Workbook: Laboratory BIO320: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm)Document4 pagesWorkbook: Laboratory BIO320: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm)Mirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Workbook: Laboratory BIO32: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm) Branch Sabah Campus Kota KinabaluDocument6 pagesWorkbook: Laboratory BIO32: Universiti Teknologi Mara (Uitm) Branch Sabah Campus Kota KinabaluMirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- Bio320 Lab 4Document6 pagesBio320 Lab 4Mirza KarmilaNo ratings yet
- 11 Compressed Notes ImmunityDocument9 pages11 Compressed Notes ImmunityLIM ZHI SHUENNo ratings yet
- Group 4 Case Study On Malignant MelanomaDocument7 pagesGroup 4 Case Study On Malignant MelanomaLance JardiolinNo ratings yet
- A Brief Journey Through The Immune System: Karim M. Yatim and Fadi G. LakkisDocument8 pagesA Brief Journey Through The Immune System: Karim M. Yatim and Fadi G. LakkisMaximeNo ratings yet
- UNIT-IV Lecture Notes BP205T Computer Applications in Pharmacy-Updated 07.08.2020Document31 pagesUNIT-IV Lecture Notes BP205T Computer Applications in Pharmacy-Updated 07.08.2020B.MAHAALAKSHMINo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument10 pagesConcept MapStephen Yor100% (1)
- Immunology and SerologyDocument66 pagesImmunology and SerologyDenver CarbonNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument86 pagesPDFXuan TuanNo ratings yet
- SBL100-Immunology Lectures 1-3Document92 pagesSBL100-Immunology Lectures 1-3B.simhachalam100% (1)
- Immunology 9Th Edition Male David Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pagesImmunology 9Th Edition Male David Full Chapter PDFvisbystoss100% (4)
- The Lymphatic System and Body Defenses: Elaine N. MariebDocument75 pagesThe Lymphatic System and Body Defenses: Elaine N. MariebReysa Manulat100% (1)
- Mock Test of 3rd GroupDocument7 pagesMock Test of 3rd GroupSelvia PutriNo ratings yet
- Pathology of Lymph Nodes: Norman Levy, MDDocument92 pagesPathology of Lymph Nodes: Norman Levy, MDDocAxi Maximo Jr AxibalNo ratings yet
- The Recognition of Antigen: Antigen Recognition by B-Cell and T-Cell ReceptorsDocument2 pagesThe Recognition of Antigen: Antigen Recognition by B-Cell and T-Cell ReceptorsIsSis0% (1)
- Non-Hodgkins LymphomaDocument22 pagesNon-Hodgkins LymphomaNyoman TapayanaNo ratings yet
- Ammar K. Daoud: Haneen Ibrahim Hamza Al-SleatiDocument10 pagesAmmar K. Daoud: Haneen Ibrahim Hamza Al-SleatiInnocent L NdambakuwaNo ratings yet
- Immunology Exam Q S With AnswersDocument28 pagesImmunology Exam Q S With AnswersIceBearNo ratings yet
- Full HD English Editorials 2-1-2022Document25 pagesFull HD English Editorials 2-1-2022uihuyhyubuhbNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument3 pagesImmunologybhawana bhattNo ratings yet
- A Less Brief Guide To The Pfizer and Moderna VaccinesDocument7 pagesA Less Brief Guide To The Pfizer and Moderna VaccinesAnika Jane BeamerNo ratings yet
- The Immune SystemDocument31 pagesThe Immune SystemYesiana Lilis Sugiarti100% (1)
- Communicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5Document461 pagesCommunicable Disease Nursing Ca1 July 2018 5Jordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Car-T Cell Receptors (7758)Document8 pagesCar-T Cell Receptors (7758)Saradha PellatiNo ratings yet
- Limfoproliferari Cronice MaligneDocument18 pagesLimfoproliferari Cronice MaligneAlice MuscaNo ratings yet
- CAR-T e LESDocument5 pagesCAR-T e LESSpanna Lo SpamNo ratings yet
- 11 ImmunityDocument5 pages11 ImmunityTina EtoileNo ratings yet
- Grupp Et Al - 2013 - Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells For AcuDocument16 pagesGrupp Et Al - 2013 - Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells For AcuChae SonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 3 1 First Line of DefenseDocument33 pagesChapter 3 3 1 First Line of Defenseapi-237856591No ratings yet
- Rhinitis Allergy and ElderlyDocument26 pagesRhinitis Allergy and ElderlyPutri Rizky AmaliaNo ratings yet