Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stats Prob Review G12HL
Stats Prob Review G12HL
Uploaded by
Le Vu nguyenCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Statistics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 4: Statistical DistributionsDocument2 pagesStatistics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 4: Statistical Distributions11110000No ratings yet
- Probability Questions From Past IB Exams: P (A B) P (ADocument17 pagesProbability Questions From Past IB Exams: P (A B) P (Aridhi_puriNo ratings yet
- Massey - Spatial Divisions of Labor - Social Structures and The Geography of Production PDFDocument410 pagesMassey - Spatial Divisions of Labor - Social Structures and The Geography of Production PDFMaruclaNo ratings yet
- Math IB QuestionsDocument11 pagesMath IB QuestionsFei TengNo ratings yet
- The Perception of Luxury Cars MA Thesis 25 03Document60 pagesThe Perception of Luxury Cars MA Thesis 25 03Quaxi1954No ratings yet
- Discrete Binomial Normal ExtraDocument8 pagesDiscrete Binomial Normal Extraibrahim fadelNo ratings yet
- Test - Probability: X X K XDocument2 pagesTest - Probability: X X K XIlayda AltayNo ratings yet
- 2015 MidtermDocument2 pages2015 Midtermeddy ngNo ratings yet
- A and B Are Mutually Exclusive A and B Are Independent.: IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Document2 pagesA and B Are Mutually Exclusive A and B Are Independent.: IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Jose David KastilloNo ratings yet
- Probability Question BankDocument49 pagesProbability Question Banksebastianikeda25No ratings yet
- SJC F6 2011-12-06 M1 Half Yearly ExaminationDocument10 pagesSJC F6 2011-12-06 M1 Half Yearly ExaminationKelvin CheungNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions Discrete Probability DistributionsDocument8 pagesExam Questions Discrete Probability DistributionsDuygu KavvasNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1Document6 pagesWorksheet 1bogdanghiorghiu89No ratings yet
- Distribution QuestionsDocument5 pagesDistribution QuestionsChrystal BrownNo ratings yet
- A and B Are Mutually Exclusive A and B Are Independent.: IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Document2 pagesA and B Are Mutually Exclusive A and B Are Independent.: IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1carlNo ratings yet
- PMMT100 FT 10 2020 1Document3 pagesPMMT100 FT 10 2020 1Kaoma MofyaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Revision Probability Paper 2 Type Questions Name: DateDocument10 pagesGrade 12 Revision Probability Paper 2 Type Questions Name: DateNg JeraldNo ratings yet
- Distributions BinomialDocument4 pagesDistributions BinomialboostoberoiNo ratings yet
- Quiz Review 2015Document3 pagesQuiz Review 2015Komal JainNo ratings yet
- IB Prob Distribution QuestionsDocument4 pagesIB Prob Distribution QuestionsjleodennisNo ratings yet
- AS Stats Chapter 5 Probability Worksheet QPDocument5 pagesAS Stats Chapter 5 Probability Worksheet QPydhd9nkkfrNo ratings yet
- Emt 3127 Engineering Probability and StatisticsDocument3 pagesEmt 3127 Engineering Probability and StatisticsdelinaNo ratings yet
- 9FM0 3B Topic1 Discreteprobabilitydistributions QuestionDocument6 pages9FM0 3B Topic1 Discreteprobabilitydistributions QuestionmzkunchuNo ratings yet
- Test - 2 - Probability: IB Mathematics HLDocument2 pagesTest - 2 - Probability: IB Mathematics HLIlayda AltayNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 11.3: Addition Law of ProbabilityDocument4 pagesWorksheet 11.3: Addition Law of Probability伊貝P-No ratings yet
- Statistics - GeneralDocument2 pagesStatistics - GeneralSubhom LqhaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 For EngDocument2 pagesWorksheet 2 For EngAdmasuNo ratings yet
- Mid-1 Question BankDocument4 pagesMid-1 Question BankRevanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- 2018 Past Paper PDFDocument2 pages2018 Past Paper PDFeddy ngNo ratings yet
- Additional PracticeDocument2 pagesAdditional Practiceeryn corneliusNo ratings yet
- S2 Mock Exam August 2021Document4 pagesS2 Mock Exam August 2021Mohamed Nazeer Falah AhamadNo ratings yet
- 191HS42 - Probability & Statistics - Question Bank PDFDocument7 pages191HS42 - Probability & Statistics - Question Bank PDFKaleesNo ratings yet
- DPP-47 (Special DPP On Probability) 1.: Get 10% Instant Discount On Unacademy Plus (Use Referral Code: MCSIR)Document32 pagesDPP-47 (Special DPP On Probability) 1.: Get 10% Instant Discount On Unacademy Plus (Use Referral Code: MCSIR)Tushif RahmanNo ratings yet
- Test 8. ProbabilityDocument7 pagesTest 8. Probability台大人家教中心No ratings yet
- 12 Binom and NormalDocument6 pages12 Binom and NormalCaroline JohannesNo ratings yet
- Binomial Distribution IBSL QnsDocument6 pagesBinomial Distribution IBSL QnsPrestina Seena JacobiNo ratings yet
- Revision 12 IB Paper 1 PDFDocument293 pagesRevision 12 IB Paper 1 PDFAnonymous yjLUF9gDTSNo ratings yet
- West Bengal State University: AthematicsDocument4 pagesWest Bengal State University: AthematicsStudent CoordinatorNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Sample Space GCSE WorksheetDocument15 pagesThird Space Learning Sample Space GCSE Worksheetkucing sanguNo ratings yet
- STAT 290 ProbabilityDocument45 pagesSTAT 290 ProbabilityKinza IqbalNo ratings yet
- IB Questionbank Mathematical Studies 3rd Edition 1Document7 pagesIB Questionbank Mathematical Studies 3rd Edition 1Carlos QNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document16 pagesHW 1thewodrosNo ratings yet
- MIT6 041F10 Assn04Document3 pagesMIT6 041F10 Assn04M MovNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of TechnologyDocument3 pagesMassachusetts Institute of TechnologyM MovNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Binomial DistributionDocument5 pagesChapter 8 Binomial DistributionBid Hassan83% (6)
- Exam 1Document1 pageExam 1haninebayNo ratings yet
- 1 Distribución NormalDocument2 pages1 Distribución NormalDavid RomeroNo ratings yet
- Maths SL Worksheet Venn Conditional Combined Events PDFDocument40 pagesMaths SL Worksheet Venn Conditional Combined Events PDFtaimoor2No ratings yet
- Practice Test On Polynomials, Binomial Expansion, Counting Systems, Partial Fractions and AsymptotesDocument2 pagesPractice Test On Polynomials, Binomial Expansion, Counting Systems, Partial Fractions and Asymptotesuser980432No ratings yet
- Probability - Ibsl Math QuestionsDocument21 pagesProbability - Ibsl Math QuestionsAnanya Sanagavaram (yr. 18-20)No ratings yet
- This Paper Is Not To Be Removed From The Examination Hall: ST104B - ZA - 2016 - d0Document30 pagesThis Paper Is Not To Be Removed From The Examination Hall: ST104B - ZA - 2016 - d0Xinjie LinNo ratings yet
- Probability Practice 2 (Discrete & Continuous Distributions)Document13 pagesProbability Practice 2 (Discrete & Continuous Distributions)antonylukNo ratings yet
- Probability WroksheetDocument6 pagesProbability WroksheetjsarmientodcNo ratings yet
- (CC-206) (Elementary Statistics) - 2018Document4 pages(CC-206) (Elementary Statistics) - 2018Taniya BudhwaniNo ratings yet
- Stats Prob QPDocument33 pagesStats Prob QPAnsh Vanpariya100% (1)
- D.A.V. School: Affiliated To C.B.S.E., New Delhi) Sree Nandeeswarar Campus, Adambakkam, Chennai - 600 088Document3 pagesD.A.V. School: Affiliated To C.B.S.E., New Delhi) Sree Nandeeswarar Campus, Adambakkam, Chennai - 600 088Sai gokulNo ratings yet
- 12 Mathematics Ncert Ch13probability 13.4Document18 pages12 Mathematics Ncert Ch13probability 13.4AkshatNo ratings yet
- AssignmentProblems Ago18 2021Document4 pagesAssignmentProblems Ago18 2021RobertoNo ratings yet
- 2016 - 2017 H2 Maths Probability Tut FinalDocument10 pages2016 - 2017 H2 Maths Probability Tut Finalwee wooNo ratings yet
- 2) Chapter 4 PreparationDocument16 pages2) Chapter 4 PreparationTasniimNo ratings yet
- Geography Internal Assessment: How Does Water Quality in The Silver Mine River Change With Distance Downstream?Document41 pagesGeography Internal Assessment: How Does Water Quality in The Silver Mine River Change With Distance Downstream?Le Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Study of The Aerofoil-Shaped Formula One Rear WingDocument36 pagesAn Experimental Study of The Aerofoil-Shaped Formula One Rear WingLe Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Answer key-IGCSE Acid Base WorkhseetDocument1 pageAnswer key-IGCSE Acid Base WorkhseetLe Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 - Educational Theatre For The SDGs LinkedIn-1Document16 pagesAssignment2 - Educational Theatre For The SDGs LinkedIn-1Le Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Vu Nguyen LE - Word Processing Skills - 1Document5 pagesVu Nguyen LE - Word Processing Skills - 1Le Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Bonding Questions Mark SchemeDocument2 pagesBonding Questions Mark SchemeLe Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Test: Coordinate Geometry and Quadratic Functions: Score 49Document7 pagesTest: Coordinate Geometry and Quadratic Functions: Score 49Le Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Components of Research DesignDocument2 pagesComponents of Research DesignRakib Hossain100% (1)
- 7 Journal of Manufacturing Technology Mana-1-1Document23 pages7 Journal of Manufacturing Technology Mana-1-1VITA SARASINo ratings yet
- Final Research Paper PR Ii Group 1 (1) 2Document45 pagesFinal Research Paper PR Ii Group 1 (1) 2Aesthetics MinNo ratings yet
- CH 3. Theory of Errors in ObservationsDocument7 pagesCH 3. Theory of Errors in ObservationsNancyRossNo ratings yet
- Job No.5: To Determine The Grading or The Size Distribution of The Aggregates Using The Sieve AnalysisDocument4 pagesJob No.5: To Determine The Grading or The Size Distribution of The Aggregates Using The Sieve AnalysisFiazNo ratings yet
- Research Design MethodologyDocument26 pagesResearch Design MethodologyTadele DandenaNo ratings yet
- The Next Stage of Psychographic Segmentation Usage of EnneagramDocument7 pagesThe Next Stage of Psychographic Segmentation Usage of EnneagramJaba BokuchavaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Total StationDocument2 pagesCourse Outline Total StationBebinmNo ratings yet
- 104 BRMDocument37 pages104 BRMAmol KareNo ratings yet
- JBW Group - IB - Supply Chain and ISO 28000 V1-N1.0Document4 pagesJBW Group - IB - Supply Chain and ISO 28000 V1-N1.0HUNTER DEL CARIBENo ratings yet
- Debby Willar ThesisDocument0 pagesDebby Willar ThesisAjay MalikNo ratings yet
- FormulaDocument27 pagesFormulaSadia KausarNo ratings yet
- Critical Chain Project ManagementDocument187 pagesCritical Chain Project ManagementMonali VarpeNo ratings yet
- Nicole Anderson - Inquiry - Te 808Document33 pagesNicole Anderson - Inquiry - Te 808api-523371519No ratings yet
- PR Statement of The ProblemDocument6 pagesPR Statement of The ProblemJulienne BigorniaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Dissertation TitlesDocument9 pagesClimate Change Dissertation TitlesBestPaperWritingServicesUK100% (1)
- HRM CaseDocument24 pagesHRM CaseSimli MisraNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Virtual Models (3shape Ortho System) in Assessing Accuracy and Duration of Model Analyses Based On The Severity of CrowdingDocument8 pagesEvaluation of Virtual Models (3shape Ortho System) in Assessing Accuracy and Duration of Model Analyses Based On The Severity of CrowdingRebin AliNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research CH 1Document16 pagesMarketing Research CH 1Dalia ElarabyNo ratings yet
- MT701Document14 pagesMT701Monica Louise EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Internship Report Format King'sDocument15 pagesInternship Report Format King'sDawa Lakje SherpaNo ratings yet
- Air TrafficDocument96 pagesAir TrafficSixsigma TqmNo ratings yet
- TQM-Unit IIIDocument39 pagesTQM-Unit IIITharun Kumar U100% (1)
- The Last ProjectDocument68 pagesThe Last Projectsidac_coolNo ratings yet
- JMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Marbel University Integrated Basic Education Department City of Koronadal, South CotabatoDocument5 pagesJMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Marbel University Integrated Basic Education Department City of Koronadal, South CotabatoNestor Gerotape DiosanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: The Linear Time Selection in The Worst CaseDocument7 pagesLecture 5: The Linear Time Selection in The Worst CaseRonak ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Delivering and Performing ServicesDocument35 pagesDelivering and Performing ServicesKumar RebelNo ratings yet
- THESIS DWCC UlitDocument28 pagesTHESIS DWCC UlitJay-R NuestroNo ratings yet
Stats Prob Review G12HL
Stats Prob Review G12HL
Uploaded by
Le Vu nguyenOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stats Prob Review G12HL
Stats Prob Review G12HL
Uploaded by
Le Vu nguyenCopyright:
Available Formats
Statistics & Probability Review Questions
1. Events A and B are such that P(A) = 0.3 and P(B) = 0.4.
(a) Find the value of P(A B) when
(i) A and B are mutually exclusive;
(ii) A and B are independent.
(4)
(b) Given that P(A B) = 0.6, find P(A | B).
(3)
(Total 7 marks)
2. In a population of rabbits, 1 % are known to have a particular disease. A test is developed for
the disease that gives a positive result for a rabbit that does have the disease in 99 % of cases. It
is also known that the test gives a positive result for a rabbit that does not have the disease in
0.1 % of cases. A rabbit is chosen at random from the population.
(a) Find the probability that the rabbit tests positive for the disease.
(2)
(b) Given that the rabbit tests positive for the disease, show that the probability that the rabbit
does not have the disease is less than 10 %.
(3)
(Total 5 marks)
3. Two players, A and B, alternately throw a fair six–sided dice, with A starting, until one of them
obtains a six. Find the probability that A obtains the first six.
(Total 7 marks)
4
4. A biased coin is weighted such that the probability of obtaining a head is 7 . The coin is tossed
P( X 3)
6 times and X denotes the number of heads observed. Find the value of the ratio P( X 2) .
(Total 4 marks)
IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd edition 1
5.
A discrete random variable X has a probability distribution given in the following table.
x 0.5 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5 5.5
P(X = x) 0.15 0.21 p q 0.13 0.07
(a) If E(X) = 2.61, determine the value of p and of q.
(4)
(b) Calculate Var (X) to three significant figures.
(2)
(Total 6 marks)
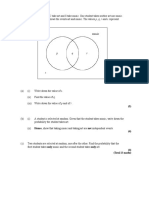
6. In a class of 20 students, 12 study Biology, 15 study History and 2 students study neither
Biology nor History.
(a) Illustrate this information on a Venn diagram.
(2)
(b) Find the probability that a randomly selected student from this class is studying both
Biology and History.
(1)
(c) Given that a randomly selected student studies Biology, find the probability that this
student also studies History.
(1)
(Total 4 marks)
7. The probability distribution of a discrete random variable X is defined by
P(X = x) = cx(5 − x), x = 1, 2, 3, 4.
(a) Find the value of c.
(3)
(b) Find E(X).
(3)
(Total 6 marks)
IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd edition 2
8. Over a one month period, Ava and Sven play a total of n games of tennis.
The probability that Ava wins any game is 0.4. The result of each game played is independent
of any other game played.
Let X denote the number of games won by Ava over a one month period.
(a) Find an expression for P(X = 2) in terms of n.
(3)
(b) If the probability that Ava wins two games is 0.121 correct to three decimal places, find
the value of n.
(3)
(Total 6 marks)
9. The cumulative frequency graph below represents the weight in grams of 80 apples picked from
a particular tree.
(a) Estimate the
(i) median weight of the apples;
th
(ii) 30 percentile of the weight of the apples.
(2)
(b) Estimate the number of apples that weigh more than 110 grams.
(2)
(Total 4 marks)
IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd edition 3
10. The company Fresh Water produces one-litre bottles of mineral water. The company wants to
determine the amount of magnesium, in milligrams, in these bottles.
A random sample of ten bottles is analysed and the results are as follows:
6.7, 7.2, 6.7, 6.8, 6.9, 7.0, 6.8, 6.6, 7.1, 7.3.
Find unbiased estimates of the population mean and variance of the amount of magnesium in
the one-litre bottles.
(Total 4 marks)
11. Consider the data set {k − 2, k, k +1, k + 4}, where k .
(a) Find the mean of this data set in terms of k.
(3)
Each number in the above data set is now decreased by 3.
(b) Find the mean of this new data set in terms of k.
(2)
(Total 5 marks)
12. (a) The random variable Y is such that E(2Y + 3) = 6 and Var (2 – 3Y) = 11.
Calculate
(i) E(Y);
(ii) Var(Y);
2
(iii) E(Y ).
(Total 6 marks)
IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd edition 4
13. Tim throws two identical fair dice simultaneously. Each die has six faces: two faces numbered
1, two faces numbered 2 and two faces numbered 3. His score is the sum of the two numbers
shown on the dice.
(a) (i) Calculate the probability that Tim obtains a score of 6.
(ii) Calculate the probability that Tim obtains a score of at least 3.
(3)
Tim plays a game with his friend Bill, who also has two dice numbered in the same way. Bill’s
score is the sum of the two numbers shown on his dice.
(b) (i) Calculate the probability that Tim and Bill both obtain a score of 6.
(ii) Calculate the probability that Tim and Bill obtain the same score.
(4)
(c) Let X denote the largest number shown on the four dice.
16
(i) Show that P(X ≤ 2) = 81 .
(ii) Copy and complete the following probability distribution table.
x 1 2 3
1
P(X = x)
81
2
(iii) Calculate E(X) and E(X ) and hence find Var(X).
(10)
(d) Given that X = 3, find the probability that the sum of the numbers shown on the four dice
is 8.
(4)
(Total 21 marks)
IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd edition 5
You might also like
- Statistics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 4: Statistical DistributionsDocument2 pagesStatistics Year 1 (AS) Unit Test 4: Statistical Distributions11110000No ratings yet
- Probability Questions From Past IB Exams: P (A B) P (ADocument17 pagesProbability Questions From Past IB Exams: P (A B) P (Aridhi_puriNo ratings yet
- Massey - Spatial Divisions of Labor - Social Structures and The Geography of Production PDFDocument410 pagesMassey - Spatial Divisions of Labor - Social Structures and The Geography of Production PDFMaruclaNo ratings yet
- Math IB QuestionsDocument11 pagesMath IB QuestionsFei TengNo ratings yet
- The Perception of Luxury Cars MA Thesis 25 03Document60 pagesThe Perception of Luxury Cars MA Thesis 25 03Quaxi1954No ratings yet
- Discrete Binomial Normal ExtraDocument8 pagesDiscrete Binomial Normal Extraibrahim fadelNo ratings yet
- Test - Probability: X X K XDocument2 pagesTest - Probability: X X K XIlayda AltayNo ratings yet
- 2015 MidtermDocument2 pages2015 Midtermeddy ngNo ratings yet
- A and B Are Mutually Exclusive A and B Are Independent.: IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Document2 pagesA and B Are Mutually Exclusive A and B Are Independent.: IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Jose David KastilloNo ratings yet
- Probability Question BankDocument49 pagesProbability Question Banksebastianikeda25No ratings yet
- SJC F6 2011-12-06 M1 Half Yearly ExaminationDocument10 pagesSJC F6 2011-12-06 M1 Half Yearly ExaminationKelvin CheungNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions Discrete Probability DistributionsDocument8 pagesExam Questions Discrete Probability DistributionsDuygu KavvasNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1Document6 pagesWorksheet 1bogdanghiorghiu89No ratings yet
- Distribution QuestionsDocument5 pagesDistribution QuestionsChrystal BrownNo ratings yet
- A and B Are Mutually Exclusive A and B Are Independent.: IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1Document2 pagesA and B Are Mutually Exclusive A and B Are Independent.: IB Questionbank Mathematics Higher Level 3rd Edition 1carlNo ratings yet
- PMMT100 FT 10 2020 1Document3 pagesPMMT100 FT 10 2020 1Kaoma MofyaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 Revision Probability Paper 2 Type Questions Name: DateDocument10 pagesGrade 12 Revision Probability Paper 2 Type Questions Name: DateNg JeraldNo ratings yet
- Distributions BinomialDocument4 pagesDistributions BinomialboostoberoiNo ratings yet
- Quiz Review 2015Document3 pagesQuiz Review 2015Komal JainNo ratings yet
- IB Prob Distribution QuestionsDocument4 pagesIB Prob Distribution QuestionsjleodennisNo ratings yet
- AS Stats Chapter 5 Probability Worksheet QPDocument5 pagesAS Stats Chapter 5 Probability Worksheet QPydhd9nkkfrNo ratings yet
- Emt 3127 Engineering Probability and StatisticsDocument3 pagesEmt 3127 Engineering Probability and StatisticsdelinaNo ratings yet
- 9FM0 3B Topic1 Discreteprobabilitydistributions QuestionDocument6 pages9FM0 3B Topic1 Discreteprobabilitydistributions QuestionmzkunchuNo ratings yet
- Test - 2 - Probability: IB Mathematics HLDocument2 pagesTest - 2 - Probability: IB Mathematics HLIlayda AltayNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 11.3: Addition Law of ProbabilityDocument4 pagesWorksheet 11.3: Addition Law of Probability伊貝P-No ratings yet
- Statistics - GeneralDocument2 pagesStatistics - GeneralSubhom LqhaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 For EngDocument2 pagesWorksheet 2 For EngAdmasuNo ratings yet
- Mid-1 Question BankDocument4 pagesMid-1 Question BankRevanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- 2018 Past Paper PDFDocument2 pages2018 Past Paper PDFeddy ngNo ratings yet
- Additional PracticeDocument2 pagesAdditional Practiceeryn corneliusNo ratings yet
- S2 Mock Exam August 2021Document4 pagesS2 Mock Exam August 2021Mohamed Nazeer Falah AhamadNo ratings yet
- 191HS42 - Probability & Statistics - Question Bank PDFDocument7 pages191HS42 - Probability & Statistics - Question Bank PDFKaleesNo ratings yet
- DPP-47 (Special DPP On Probability) 1.: Get 10% Instant Discount On Unacademy Plus (Use Referral Code: MCSIR)Document32 pagesDPP-47 (Special DPP On Probability) 1.: Get 10% Instant Discount On Unacademy Plus (Use Referral Code: MCSIR)Tushif RahmanNo ratings yet
- Test 8. ProbabilityDocument7 pagesTest 8. Probability台大人家教中心No ratings yet
- 12 Binom and NormalDocument6 pages12 Binom and NormalCaroline JohannesNo ratings yet
- Binomial Distribution IBSL QnsDocument6 pagesBinomial Distribution IBSL QnsPrestina Seena JacobiNo ratings yet
- Revision 12 IB Paper 1 PDFDocument293 pagesRevision 12 IB Paper 1 PDFAnonymous yjLUF9gDTSNo ratings yet
- West Bengal State University: AthematicsDocument4 pagesWest Bengal State University: AthematicsStudent CoordinatorNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Sample Space GCSE WorksheetDocument15 pagesThird Space Learning Sample Space GCSE Worksheetkucing sanguNo ratings yet
- STAT 290 ProbabilityDocument45 pagesSTAT 290 ProbabilityKinza IqbalNo ratings yet
- IB Questionbank Mathematical Studies 3rd Edition 1Document7 pagesIB Questionbank Mathematical Studies 3rd Edition 1Carlos QNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document16 pagesHW 1thewodrosNo ratings yet
- MIT6 041F10 Assn04Document3 pagesMIT6 041F10 Assn04M MovNo ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of TechnologyDocument3 pagesMassachusetts Institute of TechnologyM MovNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Binomial DistributionDocument5 pagesChapter 8 Binomial DistributionBid Hassan83% (6)
- Exam 1Document1 pageExam 1haninebayNo ratings yet
- 1 Distribución NormalDocument2 pages1 Distribución NormalDavid RomeroNo ratings yet
- Maths SL Worksheet Venn Conditional Combined Events PDFDocument40 pagesMaths SL Worksheet Venn Conditional Combined Events PDFtaimoor2No ratings yet
- Practice Test On Polynomials, Binomial Expansion, Counting Systems, Partial Fractions and AsymptotesDocument2 pagesPractice Test On Polynomials, Binomial Expansion, Counting Systems, Partial Fractions and Asymptotesuser980432No ratings yet
- Probability - Ibsl Math QuestionsDocument21 pagesProbability - Ibsl Math QuestionsAnanya Sanagavaram (yr. 18-20)No ratings yet
- This Paper Is Not To Be Removed From The Examination Hall: ST104B - ZA - 2016 - d0Document30 pagesThis Paper Is Not To Be Removed From The Examination Hall: ST104B - ZA - 2016 - d0Xinjie LinNo ratings yet
- Probability Practice 2 (Discrete & Continuous Distributions)Document13 pagesProbability Practice 2 (Discrete & Continuous Distributions)antonylukNo ratings yet
- Probability WroksheetDocument6 pagesProbability WroksheetjsarmientodcNo ratings yet
- (CC-206) (Elementary Statistics) - 2018Document4 pages(CC-206) (Elementary Statistics) - 2018Taniya BudhwaniNo ratings yet
- Stats Prob QPDocument33 pagesStats Prob QPAnsh Vanpariya100% (1)
- D.A.V. School: Affiliated To C.B.S.E., New Delhi) Sree Nandeeswarar Campus, Adambakkam, Chennai - 600 088Document3 pagesD.A.V. School: Affiliated To C.B.S.E., New Delhi) Sree Nandeeswarar Campus, Adambakkam, Chennai - 600 088Sai gokulNo ratings yet
- 12 Mathematics Ncert Ch13probability 13.4Document18 pages12 Mathematics Ncert Ch13probability 13.4AkshatNo ratings yet
- AssignmentProblems Ago18 2021Document4 pagesAssignmentProblems Ago18 2021RobertoNo ratings yet
- 2016 - 2017 H2 Maths Probability Tut FinalDocument10 pages2016 - 2017 H2 Maths Probability Tut Finalwee wooNo ratings yet
- 2) Chapter 4 PreparationDocument16 pages2) Chapter 4 PreparationTasniimNo ratings yet
- Geography Internal Assessment: How Does Water Quality in The Silver Mine River Change With Distance Downstream?Document41 pagesGeography Internal Assessment: How Does Water Quality in The Silver Mine River Change With Distance Downstream?Le Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Study of The Aerofoil-Shaped Formula One Rear WingDocument36 pagesAn Experimental Study of The Aerofoil-Shaped Formula One Rear WingLe Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Answer key-IGCSE Acid Base WorkhseetDocument1 pageAnswer key-IGCSE Acid Base WorkhseetLe Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Assignment2 - Educational Theatre For The SDGs LinkedIn-1Document16 pagesAssignment2 - Educational Theatre For The SDGs LinkedIn-1Le Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Vu Nguyen LE - Word Processing Skills - 1Document5 pagesVu Nguyen LE - Word Processing Skills - 1Le Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Bonding Questions Mark SchemeDocument2 pagesBonding Questions Mark SchemeLe Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Test: Coordinate Geometry and Quadratic Functions: Score 49Document7 pagesTest: Coordinate Geometry and Quadratic Functions: Score 49Le Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- Components of Research DesignDocument2 pagesComponents of Research DesignRakib Hossain100% (1)
- 7 Journal of Manufacturing Technology Mana-1-1Document23 pages7 Journal of Manufacturing Technology Mana-1-1VITA SARASINo ratings yet
- Final Research Paper PR Ii Group 1 (1) 2Document45 pagesFinal Research Paper PR Ii Group 1 (1) 2Aesthetics MinNo ratings yet
- CH 3. Theory of Errors in ObservationsDocument7 pagesCH 3. Theory of Errors in ObservationsNancyRossNo ratings yet
- Job No.5: To Determine The Grading or The Size Distribution of The Aggregates Using The Sieve AnalysisDocument4 pagesJob No.5: To Determine The Grading or The Size Distribution of The Aggregates Using The Sieve AnalysisFiazNo ratings yet
- Research Design MethodologyDocument26 pagesResearch Design MethodologyTadele DandenaNo ratings yet
- The Next Stage of Psychographic Segmentation Usage of EnneagramDocument7 pagesThe Next Stage of Psychographic Segmentation Usage of EnneagramJaba BokuchavaNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Total StationDocument2 pagesCourse Outline Total StationBebinmNo ratings yet
- 104 BRMDocument37 pages104 BRMAmol KareNo ratings yet
- JBW Group - IB - Supply Chain and ISO 28000 V1-N1.0Document4 pagesJBW Group - IB - Supply Chain and ISO 28000 V1-N1.0HUNTER DEL CARIBENo ratings yet
- Debby Willar ThesisDocument0 pagesDebby Willar ThesisAjay MalikNo ratings yet
- FormulaDocument27 pagesFormulaSadia KausarNo ratings yet
- Critical Chain Project ManagementDocument187 pagesCritical Chain Project ManagementMonali VarpeNo ratings yet
- Nicole Anderson - Inquiry - Te 808Document33 pagesNicole Anderson - Inquiry - Te 808api-523371519No ratings yet
- PR Statement of The ProblemDocument6 pagesPR Statement of The ProblemJulienne BigorniaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Dissertation TitlesDocument9 pagesClimate Change Dissertation TitlesBestPaperWritingServicesUK100% (1)
- HRM CaseDocument24 pagesHRM CaseSimli MisraNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Virtual Models (3shape Ortho System) in Assessing Accuracy and Duration of Model Analyses Based On The Severity of CrowdingDocument8 pagesEvaluation of Virtual Models (3shape Ortho System) in Assessing Accuracy and Duration of Model Analyses Based On The Severity of CrowdingRebin AliNo ratings yet
- Marketing Research CH 1Document16 pagesMarketing Research CH 1Dalia ElarabyNo ratings yet
- MT701Document14 pagesMT701Monica Louise EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Internship Report Format King'sDocument15 pagesInternship Report Format King'sDawa Lakje SherpaNo ratings yet
- Air TrafficDocument96 pagesAir TrafficSixsigma TqmNo ratings yet
- TQM-Unit IIIDocument39 pagesTQM-Unit IIITharun Kumar U100% (1)
- The Last ProjectDocument68 pagesThe Last Projectsidac_coolNo ratings yet
- JMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Marbel University Integrated Basic Education Department City of Koronadal, South CotabatoDocument5 pagesJMJ Marist Brothers Notre Dame of Marbel University Integrated Basic Education Department City of Koronadal, South CotabatoNestor Gerotape DiosanaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5: The Linear Time Selection in The Worst CaseDocument7 pagesLecture 5: The Linear Time Selection in The Worst CaseRonak ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Delivering and Performing ServicesDocument35 pagesDelivering and Performing ServicesKumar RebelNo ratings yet
- THESIS DWCC UlitDocument28 pagesTHESIS DWCC UlitJay-R NuestroNo ratings yet