Professional Documents
Culture Documents
LVDT RTD
LVDT RTD
Uploaded by
Ajit PatraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
LVDT RTD
LVDT RTD
Uploaded by
Ajit PatraCopyright:
Available Formats
Electronic Measurement & Instrumentation (EE-323-F)
EXPERIMENT No.5
AIM:- Measurement of displacement using LVDT.
APPARATUS REQUIRED: - LVDT kit, multimeter, connecting wires.
THEORY: -
The differential transformer is a passive inductive transformer also known as Linear Variable Differential
Transformer (LVDT). LVDT has a soft iron core which slides within the hollow transformer & therefore
affects magnetic coupling between the primary and two secondaries. The displacement to be measured is
applied at its arm attached to soft iron core. When core is in normal position (null), equal voltages are
induced in the two secondaries. The frequency of ac applied to the primary winding ranges from 50Hz to
20KHz.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
1
PRIMARY WINDING
2
DISPLACEMENT
LVDT CORE
SECONDARY WINDING
S2 S1
O/P
PROCEDURE: -
1. Connect the circuit according to circuit diagram.
2. Switch on the power supply.
3. The core is initially brought to null position.
4. First turn the nut in clockwise direction to move core inwards i.e. left of null position & take
respective voltage readings on the voltmeter.
5. Now turn nut in anticlockwise direction to move the core towards right of null point & again take
respective voltage reading from voltmeter.
6. Plot the graph from the observations taken.
LAB MANUAL(V SEM ECE) Page 20
Electronic Measurement & Instrumentation (EE-323-F)
OBSERVATIONS TABLE
S.No. Displacement Displacement Reading Analog o/p
Micrometer (mm)
(mm)
GRAPH
RESULT: - Graph between voltage and displacement is plotted.
LAB MANUAL(V SEM ECE) Page 21
Electronic Measurement & Instrumentation (EE-323-F)
PRECAUTIONS: -
1. Handle all equipments with care.
2. Make connections according to the circuit diagram.
3. Take the readings carefully.
4. The connections should be tight.
QUIZ/ANSWERS:-
Q1 What is LVDT?
A1 Linear Variable Differential Transformer.
Q2 Uses of LVDT
A2 Measurement of displacement, thickness measurement, level indicators
Q3 Core of LVDT is made up of which material?
A3 Soft iron
Q4 LVDT is active transducer or passive?
A4 Passive
Q5 what is the working principle of LVDT?
A5 Mutual Induction
Q6 Write any two advantages of LVDT.
A6 can tolerate vibrations and shocks, Good linearity
Q7 Any one disadvantage of LVDT.
A7 Affected due to stray magnetic fields.
Q8 How many secondaries are there in LVDT?
A8 Two
Q9 LVDT is which type of transducer?
A9 Inductive type
Q10 How do we take the output of LVDT?
A10 We take differential output of the two secondary.
LAB MANUAL(V SEM ECE) Page 22
Electronic Measurement & Instrumentation (EE-323-F)
EXPERIMENT No.6
AIM:- Measurement of temperature using thermocouple,thermistor and RTD.
APPARATUS REQUIRED: - Thermocouple kit, Thermistor kit, RTD kit, heating arrangement,
Ice, Thermometer, H2O.
THEORY: -
THERMOCOUPLE
This transducer is widely used in industrial applications for temperature measurement.
Thermocouple is active transducer because there is no need of voltage source and transducer
bridge circuitry. The working principle of thermocouple is explained below: - When two
dissimilar metals A & B are joined together to form a closed circuit and the junctions J 1 and J2
are kept at two different temperatures T1 and T2 then an e.m.f. is generated resulting flow of
current in the loop or circuit. The two junctions in the loop are reference or cold junction which
is generally kept at 00C and the other is hot junction at which the temperature is to be measured.
The e.m.f. generated is proportional to the difference of temperatures, the materials used for
thermocouple. This phenomenon is called as Seeback effect. Thermocouple is having a lot of
advantages like low cost, mechanically rigid and strong, high range etc. But the main
disadvantage is that it requires a compensation arrangement.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
IRON LEAD a
c COPPER LEAD
d
b CONSTANTUN LEAD
TEMPERATURE CONTROLLED
FUNCTION BOX
THERMISTORS:
LAB MANUAL(V SEM ECE) Page 23
Electronic Measurement & Instrumentation (EE-323-F)
Thermistors are also called thermal resistors. For thermistor the absolute temperature- resistance
relationship is given by
RT=RT1exp [(1/T1-1/T2)]
Where RT=Resistance of the thermistor at absolute temperature T
RT1= Resistance of the thermistor at absolute temperature T1
= Constant
T1 and T2= Absolute temperatures
Thermistors are made up of semiconductor materials. As temperature changes the resistance of
materials also changes. The temperature range for thermistor is –600C to +150C. Its resistance
varies from 0.5 to 0.75M. Thermistor is placed in contact with the media whose temperature
is to be measured. As the temperature of the media changes, the resistance of the thermistor gets
changed. This change of resistance can be measured by connecting the thermistor in any one arm
of the Wheat stone bridge.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
THERMISTOR
2
BATTERY
MICROMETER CALIBRATED
1
IN TERMS OF TEMPERATURE
RTD:
This type of transducer is used for temperature measurement. Here the basic concept used is that
electrical resistance of different metal changes in accordance with the temperature i.e. for
temperature measurement. Principle used is that the resistance of a conductor changes in
proportion with the change in temperature. The unknown temperature is determined in terms of
electrical resistance of the conductor, which senses the temperature. The change in resistance of
this device is precisely determined either by bridge circuit or by ohmmeter. Resistance of a
conductor changes with change in temperature. This property is used for the measurement of
temperature and each transducer is called Resistive Thermometer and falls in the category of
electrical resistive transducer. The variation of resistance ‘R’ with temperature ‘T’ can be
presented as:
LAB MANUAL(V SEM ECE) Page 24
Electronic Measurement & Instrumentation (EE-323-F)
R=R0 (1+1T+2T2+…)
Where R0 resistance at 00C
1,2 constant
Generally the metals used are Platinum. This is used because of following features:
1. Platinum provides good stability and accuracy.
2. It can operate on wide range of temperature.
3. It has good linearity over wide temperature range.
4. Less errors during operation.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
Element Head Support Connecting Leads
Sheath
Mounting Thread
PROCEDURE: -
THERMOCOUPLE
1. Connect the main power cord at I/P main socket.
2. Switch ON the power supply
3. Connect the thermocouple sensor at the pin connector.
4. Keep the thermocouple in boiling water & adjust the display ranging 100 by the
adjustment span knob.
THERMISTOR
1. Connect the main power cord at I/P main socket.
2. Switch ON the power supply
3. Connect the thermistor sensor at the pin connector.
4. Keep the thermistor in boiling water & adjust the display ranging 100 by the adjustment
span knob.
RTD
LAB MANUAL(V SEM ECE) Page 25
Electronic Measurement & Instrumentation (EE-323-F)
1. Connect the input power supply to main power.
2. Switch on the power supply, the red LED will glow.
3. Connect the RTD source/sensor at a pin connector & 1000C temperature is calibrated.
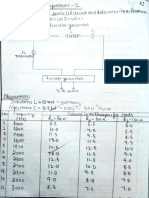
OBSERVATION TABLE
S.No. Temperature Display Reading Display Display
(mv) Reading (mv) Reading
Thermocouple Thermistor (mv)
RTD
Temp with Ice
point
Temp with Boiling
Point
RESULT: - We have measured the temperature using Thermocouple,Thermistor and RTD.
PRECAUTIONS: -
5. Handle all equipments with care.
6. Make connections according to the circuit diagram.
7. Take the readings carefully.
8. The connections should be tight.
QUIZ / ANSWERS: -
Q1 What is the working principle of thermocouple?
A1 When two dissimilar metals A & B are joined together to form a closed circuit and the
junctions J1 and J2 are kept at two different temperatures T1 and T2 then an e.m.f. is generated
resulting flow of current in the loop or circuit.
Q2 What are the types of thermocouple?
A2 J, K, E, T, S, R.
Q3 What is the cold junction compensation techniques?
A3 1. Hardware compensation.
2. Software compensation.
Q4 What are the advantages of thermistors?
A4 Small size, Compact, Good stability.
LAB MANUAL(V SEM ECE) Page 26
You might also like
- Generator BasicsDocument100 pagesGenerator BasicsTravis Chesna100% (6)
- How To Create and Configure DME FileDocument3 pagesHow To Create and Configure DME FilesairamsapNo ratings yet
- 2020 07 18 Transformer Bushing FailuresDocument34 pages2020 07 18 Transformer Bushing FailuresPradeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Emi Lab Sem V (Ece) Experiment No.: 1Document19 pagesEmi Lab Sem V (Ece) Experiment No.: 1neha sharmaNo ratings yet
- Circuital ArrangementDocument31 pagesCircuital ArrangementRahul RaaghavNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation - Unit 5Document125 pagesInstrumentation - Unit 5Rinki KeswaniNo ratings yet
- Ch.3-3. Temperature Measurement EET 238 InstrumentationDocument8 pagesCh.3-3. Temperature Measurement EET 238 InstrumentationAbeyu AssefaNo ratings yet
- Exp 6 Process Measurements TemperatureDocument17 pagesExp 6 Process Measurements TemperatureHardik AgravattNo ratings yet
- EC335 Power Electronics & Instrumentation Lab PDFDocument33 pagesEC335 Power Electronics & Instrumentation Lab PDFAnu RajNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.:-1: AIM:-To Measure Output Voltage W.R.T The Displacement of The Core On The LVDT Kit andDocument29 pagesExperiment No.:-1: AIM:-To Measure Output Voltage W.R.T The Displacement of The Core On The LVDT Kit andSanjeev kumarNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurment and Instrumentation Mcqs CH 2Document16 pagesElectrical Measurment and Instrumentation Mcqs CH 2kibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- Running (Test-1) EC 322 SensorsDocument68 pagesRunning (Test-1) EC 322 SensorsSaurabh MauryaNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Training Tutorial Part2Document25 pagesInstrumentation Training Tutorial Part2Gary8100% (1)
- Temperature, Light & AccousticDocument50 pagesTemperature, Light & AccousticCakra BhirawaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 RamsesDocument12 pagesLecture 8 RamseschetanNo ratings yet
- 2 RTDDocument6 pages2 RTDRAHUL DARANDALENo ratings yet
- Module 4 Sesion 1 Temperature and Displacement SensorsDocument39 pagesModule 4 Sesion 1 Temperature and Displacement SensorsManav Jain100% (3)
- Study of Temp. Transducers.Document13 pagesStudy of Temp. Transducers.Dr. Poonamlata YadavNo ratings yet
- Sensors and TransducersDocument15 pagesSensors and TransducersNirjhar FilmsNo ratings yet
- Experiment-15 Aim: - Study and Use Various Temperature Sensing Elements. Apparatus UsedDocument4 pagesExperiment-15 Aim: - Study and Use Various Temperature Sensing Elements. Apparatus UsedHem DaveNo ratings yet
- 1 EO 102 Transducers and Instrumentation PDFDocument102 pages1 EO 102 Transducers and Instrumentation PDFFarhan Ahmad60% (5)
- UntitledDocument13 pagesUntitledrejianbuNo ratings yet
- Temp RTDDocument8 pagesTemp RTDShambhavi VarmaNo ratings yet
- Study of TransducersDocument11 pagesStudy of TransducersSrg Perumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Basic Control System Equipments: TransducersDocument21 pagesBasic Control System Equipments: TransducersBurak OğuzNo ratings yet
- Temp TransducerDocument32 pagesTemp TransducerGunjan VarshneyNo ratings yet
- EmtDocument12 pagesEmtrajasree Marine Engg-Asst ProfNo ratings yet
- Emi 7Document79 pagesEmi 7viju_310No ratings yet
- Thermocouple TheoryDocument6 pagesThermocouple TheorySamuël VaillancourtNo ratings yet
- Active TransducerDocument29 pagesActive TransducerBabasrinivas GuduruNo ratings yet
- PDC Lab ReportDocument13 pagesPDC Lab Reportarslan_uetanNo ratings yet
- Temperatue and DiplacementDocument63 pagesTemperatue and Diplacementaregawi weleabezgi100% (1)
- Industrial VariablesDocument59 pagesIndustrial VariablesMuhamad RidzwanNo ratings yet
- Biomedical instrumentation-LR 3Document21 pagesBiomedical instrumentation-LR 3jonathan stevenNo ratings yet
- Ep3291 - Ep Lab - Iv Lab Report: Adil Sidan EP20B003Document3 pagesEp3291 - Ep Lab - Iv Lab Report: Adil Sidan EP20B003Adil Sidan ep20b003No ratings yet
- Temperature SensorsDocument5 pagesTemperature SensorsDatabase BimbinganNo ratings yet
- Analoge Signal Thermo CoupleDocument12 pagesAnaloge Signal Thermo CouplemohamedNo ratings yet
- AN-460 LM34/LM35 Precision Monolithic Temperature Sensors: Application ReportDocument20 pagesAN-460 LM34/LM35 Precision Monolithic Temperature Sensors: Application ReportpippoNo ratings yet
- Snoa 748 CDocument20 pagesSnoa 748 CAsistencia Técnica JLFNo ratings yet
- In Strut MentDocument8 pagesIn Strut MentAbcdNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 PDFDocument12 pagesLecture 8 PDFBelayneh Tadesse100% (1)
- ME6504 - Metrology & Measurements Unit 5 - Measurement of Power, Flow & TemperatureDocument40 pagesME6504 - Metrology & Measurements Unit 5 - Measurement of Power, Flow & TemperaturearunpdcNo ratings yet
- Embeded Based Human SecurityDocument57 pagesEmbeded Based Human SecuritysreeragpmNo ratings yet
- Temperature MeasurementDocument42 pagesTemperature MeasurementSaid OmanNo ratings yet
- Measurement_of_temp._with_thermistor (1)Document7 pagesMeasurement_of_temp._with_thermistor (1)Mahesh HNo ratings yet
- Hardware - Mini - Project (1) - RemovedDocument12 pagesHardware - Mini - Project (1) - RemovedAyushi singh PariharNo ratings yet
- Wollo University Kombolcha Institute of Technology Chemical Engineering DepartmentDocument39 pagesWollo University Kombolcha Institute of Technology Chemical Engineering Departmentየነበር ነበር በነበርNo ratings yet
- Sensors and Transducers PDFDocument10 pagesSensors and Transducers PDFdebasish beheraNo ratings yet
- Temperature SensorsDocument4 pagesTemperature SensorsVinnakota JyothirmaiNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Temperature TransducersDocument17 pagesCharacteristics of Temperature TransducersSubhadeep PatraNo ratings yet
- Sensors and TransducersDocument15 pagesSensors and TransducersWaqas AhmadNo ratings yet
- Een 11 Midterm Lec3Document67 pagesEen 11 Midterm Lec3Miggy VelasquezNo ratings yet
- 66 - 15575 - Ec410 - 2014 - 1 - 2 - 1 - Lecture 12Document31 pages66 - 15575 - Ec410 - 2014 - 1 - 2 - 1 - Lecture 12sijal2005No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Analog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13From EverandAnalog Dialogue, Volume 48, Number 1: Analog Dialogue, #13Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Assignment EdDocument19 pagesAssignment EdAjit PatraNo ratings yet
- Resonance ExperimentDocument10 pagesResonance ExperimentAjit PatraNo ratings yet
- LECTURE NOTES - 3rd ETC - EMI - A PradhanDocument74 pagesLECTURE NOTES - 3rd ETC - EMI - A PradhanAjit PatraNo ratings yet
- Measurement and Instrumentation Lab ManualDocument148 pagesMeasurement and Instrumentation Lab ManualAjit PatraNo ratings yet
- Electrical Measurement Lab by SK FinalDocument40 pagesElectrical Measurement Lab by SK FinalAjit PatraNo ratings yet
- 16ec416-Electronic Measurementsand InstrumentationDocument6 pages16ec416-Electronic Measurementsand InstrumentationAjit PatraNo ratings yet
- Is 459Document10 pagesIs 459AmbrishNo ratings yet
- BS en Iso 9934-2-2015 - MTDocument30 pagesBS en Iso 9934-2-2015 - MTKenny ELtor100% (2)
- 2015 Recent Achievements in Solidified Floating Organic Drop MicroextractionDocument30 pages2015 Recent Achievements in Solidified Floating Organic Drop MicroextractionDidier MauricioNo ratings yet
- Basu 1985Document18 pagesBasu 1985sandraNo ratings yet
- Lalit ISM FileDocument28 pagesLalit ISM Filelalit rawatNo ratings yet
- Technical Standards and Commentaries For Port and Harbours Faclilities in JapanDocument5 pagesTechnical Standards and Commentaries For Port and Harbours Faclilities in JapandalifyNo ratings yet
- Magic Quadrant For Data Integration Tools 2007Document16 pagesMagic Quadrant For Data Integration Tools 2007Sagardeep RoyNo ratings yet
- Silibus Diesel CommanrailDocument2 pagesSilibus Diesel CommanrailPokcik ZaidNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Lesson PlanDocument5 pagesGrade 7 Lesson PlanCorazon YcotNo ratings yet
- Superposition TheoremDocument18 pagesSuperposition TheoremShoubhik SahaNo ratings yet
- M-2023 MathematicsDocument32 pagesM-2023 Mathematicsomgraj6291No ratings yet
- ISA RP3.2-1960 Flange Mounted Sharp Edged Orifice Plate For Flow Measurement PDFDocument8 pagesISA RP3.2-1960 Flange Mounted Sharp Edged Orifice Plate For Flow Measurement PDFamshahNo ratings yet
- Assessment - 6: Question 1: Write The C Program To Implement A Linked List File Allocation MethodDocument6 pagesAssessment - 6: Question 1: Write The C Program To Implement A Linked List File Allocation MethodVinayak MahadevanNo ratings yet
- EGMO 2012-19 EN With Solutions PDFDocument151 pagesEGMO 2012-19 EN With Solutions PDFgarciacapitan100% (1)
- Villanuva, A, ElecsDocument25 pagesVillanuva, A, ElecsAaron VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- RNC6900 UMTS - Cell Dynamic Shutdown AligorithmDocument25 pagesRNC6900 UMTS - Cell Dynamic Shutdown AligorithmAmanANo ratings yet
- Capacitance ExDocument19 pagesCapacitance ExTejus VishwanathNo ratings yet
- Annex A - Scope of WorkDocument4 pagesAnnex A - Scope of Workمهيب سعيد الشميريNo ratings yet
- Network+ Guide To Networks 5 Edition: Introduction To TCP/IP ProtocolsDocument88 pagesNetwork+ Guide To Networks 5 Edition: Introduction To TCP/IP ProtocolsRyan OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Acción de La Estructura. Miller.Document12 pagesAcción de La Estructura. Miller.Pedro SosaNo ratings yet
- Branch and BoundDocument7 pagesBranch and BoundRidhima Amit KhamesraNo ratings yet
- Data LabDocument6 pagesData LabAnonymous Kmmc9rNo ratings yet
- Initial Draft - Jawi Coded Character Set For Information Interchange - V2Document15 pagesInitial Draft - Jawi Coded Character Set For Information Interchange - V2mohdzamrimurah_gmailNo ratings yet
- The Clinical Relevance of The Relation Between Maximum Flow Declination Rate and Sound Pressure Level in Predicting Vocal FatigueDocument10 pagesThe Clinical Relevance of The Relation Between Maximum Flow Declination Rate and Sound Pressure Level in Predicting Vocal FatigueChrisNo ratings yet
- CH 21 Hull Fundamentals 8 The DDocument23 pagesCH 21 Hull Fundamentals 8 The DjlosamNo ratings yet
- Full Download Teknologi Digital Immersive Pemanfaatan Untuk Kemajuan Bangsa Herman Tolle Fais Al Huda Online Full Chapter PDFDocument69 pagesFull Download Teknologi Digital Immersive Pemanfaatan Untuk Kemajuan Bangsa Herman Tolle Fais Al Huda Online Full Chapter PDFneapoleancochranvy7bvw0pf100% (9)
- Weight of CalculationDocument5 pagesWeight of Calculationlitaanggita fordesignNo ratings yet