Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy Class Test - AAMIR-Sir
Anatomy Class Test - AAMIR-Sir
Uploaded by
krishnavy2000Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 39: Plant Responses To Internal and External SignalsDocument11 pagesChapter 39: Plant Responses To Internal and External Signalskuitang100% (2)
- Practice Test 11 - BotanyDocument7 pagesPractice Test 11 - BotanyLoma somNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants - ELP-4Document2 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants - ELP-410ayushranjannNo ratings yet
- DPP - Extra - Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesDPP - Extra - Anatomy of Flowering Plantsgk7936No ratings yet
- 5 6206059040699580929Document3 pages5 6206059040699580929Arunima halderNo ratings yet
- PDF ZoologeDocument3 pagesPDF ZoologeShruti YadavNo ratings yet
- NEET Test Series 5Document24 pagesNEET Test Series 5Willis ChekovNo ratings yet
- 0) LT PACE-5 - PAPER With Key - 23.07.2023 - 1290861 - 2023 - 07 - 24 - 11 - 37Document24 pages0) LT PACE-5 - PAPER With Key - 23.07.2023 - 1290861 - 2023 - 07 - 24 - 11 - 37vulurakashsharma2005No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants DPP 01of Lecture 2 Arjuna NEET 2024Document3 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants DPP 01of Lecture 2 Arjuna NEET 2024z5476259No ratings yet
- Yakeen NEET (2024) Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesYakeen NEET (2024) Morphology of Flowering Plantsmedical ChyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02) - (Yakeen 2.0 2023 PW Stars)Document3 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02) - (Yakeen 2.0 2023 PW Stars)kalarimanohar05No ratings yet
- Biology Day-12Document1 pageBiology Day-12anvith srinivasNo ratings yet
- 64d733f4ca588200185c827c ## Morphology of Flowering Plants DPP 01Document3 pages64d733f4ca588200185c827c ## Morphology of Flowering Plants DPP 01athena20777No ratings yet
- Jb5-Anatomy of Flowering Plant (Final)Document8 pagesJb5-Anatomy of Flowering Plant (Final)anvith srinivasNo ratings yet
- 01 Animal Tissue DPPDocument16 pages01 Animal Tissue DPPRuchi DandaleNo ratings yet
- M CAPS 13 (RM) Botany (PMTcorner - In)Document3 pagesM CAPS 13 (RM) Botany (PMTcorner - In)Sonu RajNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom - 1Document4 pagesAnimal Kingdom - 1gk7936No ratings yet
- 2003 PDFDocument4 pages2003 PDFjp techNo ratings yet
- 2002 PDFDocument4 pages2002 PDFjp techNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Practice - NEET - EnglishDocument18 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Practice - NEET - EnglishEducation PointNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom1Document10 pagesAnimal Kingdom1kevxin.johnNo ratings yet
- Kinematics IIDocument3 pagesKinematics IINeetaiimsjipmer Ipe720/720No ratings yet
- Bot Test & Discussion-03 (Code-A)Document4 pagesBot Test & Discussion-03 (Code-A)pal018488No ratings yet
- Uits 2Document45 pagesUits 2Firoj AhmedNo ratings yet
- NEET Test Series 45Document34 pagesNEET Test Series 45anitalakshmi32No ratings yet
- SR Elite, Aiims S60, MPL & LTC Neet Grand Test - 1 Paper (29-05-2022)Document28 pagesSR Elite, Aiims S60, MPL & LTC Neet Grand Test - 1 Paper (29-05-2022)srsoumyaranjantareiNo ratings yet
- Tula Drina Nia IaDocument9 pagesTula Drina Nia IaHarsh SaravatNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 01 BotanyDocument3 pagesPractice Test 01 Botanybhupendranaik330No ratings yet
- Classroom Contact Programme: Pre Medical: Leader Course Pre Medical 2021Document1 pageClassroom Contact Programme: Pre Medical: Leader Course Pre Medical 2021Rakshadharan K PNo ratings yet
- Alternate: AlstoniaDocument4 pagesAlternate: AlstoniaArunima halderNo ratings yet
- NCERT Line Wise MCQs On FrogDocument5 pagesNCERT Line Wise MCQs On FrogThorat's Baarbeque MisalNo ratings yet
- NEET Test Series 2Document24 pagesNEET Test Series 2bal_thakreNo ratings yet
- XI - CBSE - Worksheet - 3 - Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument3 pagesXI - CBSE - Worksheet - 3 - Anatomy of Flowering PlantsRajasekar Karuppannan100% (1)
- Animal Tissue - 3: Location FunctionDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissue - 3: Location FunctionKb AshishNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument3 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsFarahan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plant - DPP 02 (Of Lecture 04) - Yakeen NEET 2024Document3 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plant - DPP 02 (Of Lecture 04) - Yakeen NEET 2024Himanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Target DPP Test: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Document5 pagesTarget DPP Test: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Deep SapuiNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plant - DPP 03 (Extra DPP) - Yakeen NEET 2024Document4 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plant - DPP 03 (Extra DPP) - Yakeen NEET 2024Himanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Dropper Test Paper: Biology Nugas Classes By: G.K. Nugas 'Main Market, Sector-13, HUDA, Hisar / Mob. 8529147033Document7 pagesDropper Test Paper: Biology Nugas Classes By: G.K. Nugas 'Main Market, Sector-13, HUDA, Hisar / Mob. 8529147033UV JANGRANo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals DPP 07 (Of Lec 11) Yakeen 2.0 2023 VP Stars-2Document3 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals DPP 07 (Of Lec 11) Yakeen 2.0 2023 VP Stars-2suryawanshiashish549No ratings yet
- M-Caps-01 - (Cf+oym) - Botany - 2Document2 pagesM-Caps-01 - (Cf+oym) - Botany - 2Rahul0% (2)
- XII - CBSE - Worksheet - Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Answer KeyDocument1 pageXII - CBSE - Worksheet - Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Answer KeyKishor KumarNo ratings yet
- SR Elite, Aiims S60, Neet MPL & Ic - LTC Neet Grand Test - 4 Paper (24-04-18) PDFDocument32 pagesSR Elite, Aiims S60, Neet MPL & Ic - LTC Neet Grand Test - 4 Paper (24-04-18) PDFGanesa Sri Vel100% (1)
- 2000 PDFDocument3 pages2000 PDFjp techNo ratings yet
- Balanoglossus Pila Octopus Saccoglossus: Subject: ZoologyDocument1 pageBalanoglossus Pila Octopus Saccoglossus: Subject: ZoologyDaksh SinghNo ratings yet
- JR Aiims S60 Neet Weekend Test - 11 Paper (19-09-2022)Document20 pagesJR Aiims S60 Neet Weekend Test - 11 Paper (19-09-2022)rashmipoorvi shettyNo ratings yet
- IPL Test-4 Paper-SplitDocument1 pageIPL Test-4 Paper-Splitkksah0200No ratings yet
- Incoming JR Aiims S60 & Neet MPL (Batch-1&2) NWT - 13 Paper (29-08-2021)Document18 pagesIncoming JR Aiims S60 & Neet MPL (Batch-1&2) NWT - 13 Paper (29-08-2021)Mission NEET 2022No ratings yet
- 64d5e4ae9baa3b0018ef584e ## Plant Kingdom DPP 05 of Lec 06 YakeenDocument3 pages64d5e4ae9baa3b0018ef584e ## Plant Kingdom DPP 05 of Lec 06 Yakeenathena20777No ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants &animal Tissues-Q.pDocument8 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants &animal Tissues-Q.pchp8615742No ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of Life DPP 02 (Of Lec 06)Document3 pagesCell The Unit of Life DPP 02 (Of Lec 06)sairajkhedkar69No ratings yet
- Tissue - NSEJS-Primo Race.Document5 pagesTissue - NSEJS-Primo Race.Kanchan Shirbhate0% (1)
- AITS - 02 - Botany Practice SheetDocument4 pagesAITS - 02 - Botany Practice Sheetanvitabhardwaj24No ratings yet
- Test-01 - 11th Full SyllabusDocument5 pagesTest-01 - 11th Full SyllabusShaina Hayat KhanNo ratings yet
- SR Elite (Ser - 2) Neet Module Test - 2 Paper (25-10-2022)Document20 pagesSR Elite (Ser - 2) Neet Module Test - 2 Paper (25-10-2022)scisyhp007No ratings yet
- Test - 01 - Cell Unit of Life - Biology - 01-11-2023 - TestDocument4 pagesTest - 01 - Cell Unit of Life - Biology - 01-11-2023 - TestHarsh BadoniyaNo ratings yet
- 2001 PDFDocument4 pages2001 PDFjp techNo ratings yet
- Interactions Between Non-Pathogenic Soil Microorganisms And PlantsFrom EverandInteractions Between Non-Pathogenic Soil Microorganisms And PlantsNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - The Story!!!!Document2 pagesPhotosynthesis - The Story!!!!Alladin P. PolintanNo ratings yet
- Resistance Breeding To IMI and SU Herbicides in SunflowerDocument6 pagesResistance Breeding To IMI and SU Herbicides in SunflowerIoana MarișNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth 2Document2 pagesPlant Growth 2Asnani AsudinNo ratings yet
- 69018Document76 pages69018TANNo ratings yet
- Common Farm Equipment Tle AgricultureDocument11 pagesCommon Farm Equipment Tle AgricultureJyrah DuronNo ratings yet
- Symptoms and DiseasesDocument8 pagesSymptoms and Diseaseschristy maeNo ratings yet
- Leaves: Parts of A LeafDocument17 pagesLeaves: Parts of A LeafLuisa ValenciaNo ratings yet
- A Revised Survey of The Forest Types of PDFDocument609 pagesA Revised Survey of The Forest Types of PDFGaurang TawdeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 6Document6 pagesLesson Plan in Science 6MonNo ratings yet
- Report Week 5 (5.5.23)Document5 pagesReport Week 5 (5.5.23)NUR DALILAH HUSNINA MOHD ZULFAKAR SHAHNo ratings yet
- Loyola International Schools Qatar Academic Session:2023-2024 Science PT 2 Exam Revision WorksheetDocument3 pagesLoyola International Schools Qatar Academic Session:2023-2024 Science PT 2 Exam Revision WorksheetchikenbiriyanieaterNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2004 Biology QuestionsDocument7 pagesKcse 2004 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Seed MaterialDocument69 pagesSeed Materialvishal patelNo ratings yet
- Coromandel - 1Document4 pagesCoromandel - 1Anirban BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 7.medicinal Plants at EPTRIDocument5 pages7.medicinal Plants at EPTRIRaja Vamsi MavuduruNo ratings yet
- Aspidistra Production and Use: Robert H. StampsDocument9 pagesAspidistra Production and Use: Robert H. Stampsw pNo ratings yet
- Sex DeterminationDocument11 pagesSex DeterminationJulio SubagioNo ratings yet
- Fi To HormonDocument118 pagesFi To HormonRizha Darraa DJuantie100% (1)
- CaptionDocument4 pagesCaptionRizqika Khoerul F.No ratings yet
- Kil New Chinese Herbs ListDocument18 pagesKil New Chinese Herbs Listnataarajan praveen100% (1)
- Elementary Algebra For College Students 9th Edition Angel Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesElementary Algebra For College Students 9th Edition Angel Solutions ManualMrTaylorPowellcdpf100% (53)
- Boletin HeliconiasDocument16 pagesBoletin HeliconiasCarlos MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Document3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 4MacellyBudiongan100% (1)
- Plants For Sensory GardenDocument14 pagesPlants For Sensory GardenMuthuselvam sakthivelNo ratings yet
- The Plant BodyDocument2 pagesThe Plant BodyIJ SeducoNo ratings yet
- EggplantDocument8 pagesEggplantJean SuarezNo ratings yet
- Cell and Developmental Biology: Practical 4: Tissue CultureDocument10 pagesCell and Developmental Biology: Practical 4: Tissue CultureJoanne Ch'ngNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis QuizDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis QuizAssignment JamNo ratings yet
- Plas Moly SisDocument1 pagePlas Moly SisRaymund BondeNo ratings yet
Anatomy Class Test - AAMIR-Sir
Anatomy Class Test - AAMIR-Sir
Uploaded by
krishnavy2000Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Anatomy Class Test - AAMIR-Sir
Anatomy Class Test - AAMIR-Sir
Uploaded by
krishnavy2000Copyright:
Available Formats
SUBJECT : BOTANY
SECTION-A 3. Absence of phloem parenchyma and presence of
Attempt All 35 questions water containing cavities are characteristic
feature of
1.
(1) Monocotyledon stem
(2) Dicotyledon root
(3) Dicotyledon stem
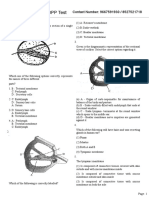
Which of the following is correct for given (4) Monocotyledon root
diagramatic sketch ? 4.
(1) found in stems of grasses
(2) presence of intra-fascicular cambium
(3) found in stems of sun-flower
(4) presence of secondary xylem and
secondary phloem
2. Tissue which are commonly found in the fruit
wall of nuts, pulp of fruits like guava, pear and What type of vascular bundles are A, B and C?
sapota; seed coats of legumes and leaves of tea,
is (1) Radial, close collateral conjoint, open
collateral conjoint
(1) Collenchyma (2) Sclerenchyma
(2) Close collateral conjoint, open collateral
(3) Parenchyma (4) Aerenchyma conjoint, Radial
(3) Open collateral conjoint, close collateral
conjoint, Radial
(4) Bicollateral, Concentric, Radial
Practice Test - All 1103CJA100122013
Space for Rough Work Page 1/11
5. Which of the following characteristics is correct 9. Which type of meristem regenerate parts
about monocot leaf ? removed by the grazing herbivores?
(1) Having reticulate venation (1) Apical meristem
(2) Absence of bulliform cells (2) Intercalary meristem
(3) Mesophyll not differentiated into palisade (3) Vascular cambium
and spongy tissues (4) Cork cambium
(4) Well differentiated mesophyll cells are 10. Arrangement of xylem in stem is :-
present
(1) Endarch
6. The dicot root is identified from the monocot
root by the presence of (2) Exarch
(1) Exarch xylem (3) Mesarch
(2) 2-4 xylem bundles (4) Both (1) and (2)
(3) > 6 xylem bundles 11. The epidermal hairs of the stem are called :-
(4) Large and well developed pith (1) Root hairs
7. The length of different internodes in a culm of (2) Trichomes
sugarcane is variable because of :- (3) Trichoblasts
(1) Size of leaf lamina at the node below each (4) None of the above
internode
12. Casparian strips occur in
(2) Intercalary meristem
(1) Epidermis (2) Pericycle
(3) SAM
(3) Cortex (4) Endodermis
(4) Position of axillary bud
13. Trichomes, hairs, stomata, etc. are included
8. Innumerable scattered vascular bundles, lack of under :-
cambium and lack of well demarcated pith is
(1) Ground tissue system
found in stem of :-
(2) Vascular tissue system
(1) Sugarcane
(3) Epidermal tissue system
(2) Sunflower
(4) None of these
(3) Pea
(4) Tomato
Practice Test - All 1103CJA100122013
Page 2/11 Space for Rough Work
14. The growth of the root and stem in length with 19. In Dorsi-ventral Leaf .. …
the help of apical meristem is called : (1) Dorsal Surface is adaxial and Ventral is
(1) Primary growth Abaxial
(2) Primary and secondary growth (2) Dorsal Surface is Abaxial and Ventral is
(3) Secondary growth Adaxial
(4) Reproductive growth (3) The abaxial epidermis generally bears more
stomata than the adaxial epidermis
15. Which of the following is responsible for leaf
rolling and unrolling in monocot : (4) Option 2 and 3 both are correct.
(1) Bundle sheath 20. Given below is the diagram of transverse section
of dorsiventral leaf. Identify the parts labelled A,
(2) Bulliform cell B, C and D and select the right option about
(3) Spongy tissue then:-
(4) Palisade tissue
16. Leaf mesophyll is a part of:-
(1) Epidermal tissue system
(2) Ground tissue system
(3) Vascular tissue system
(4) Conducting tissue system
17. Which is the outer most layer in dicot root?
(1) Epidermis (2) Cortex
(3) Pericycle (4) Plerome
18. In dorsiventral leaf, the location of palisade
tissue and phloem respectively is :-
(1) Adaxial and abaxial
(2) Abaxial and adaxial
(3) Adaxial and adaxial
(4) Abaxial and abaxial (1) 1 (2) 2 (3) 3 (4) 4
Practice Test - All 1103CJA100122013
Space for Rough Work Page 3/11
21. Fill in the blanks and select the correct option 23. Given diagram represents primary wall
for (A) & (B). In stem the type of primary xylem thickenings at corners. Which of the following
is called _____(A)_____ while in roots the material is not found in primary wall
arrangement of primary xlem is called thickenings?
____B____.
(1) Pectin (2) Cellulose
(1) A (2) B (3) C (4) D (3) Hemicellulose (4) Lignin
22. Assertion : Usually polyarch condition is found 24. Identify the given transverse sections of plant
in monocot root. part and suggest the nature of xylem and order of
Reason : Usually 2-4 xylem bundles are present development of xylem in vascular bundles of the
in the dicot root. respective sections :-
(1) Both Assertion & Reason are True & the
Reason is a correct explanation of the
Assertion.
(2) Both Assertion & Reason are True but
Reason is not a correct explanation of the
Assertion. Transverse Transverse
section-A section-B
(3) Assertion is True but the Reason is False. Nature Order of Nature Order of
(4) Both Assertion & Reason are False. of Develop- of Develop-
xylem ment xylem ment
Monocot Centri Dicot Centri
(1) Exarch Exarch
Root petal Root petal
Dicot Centri Monocot Centri
(2) Exarch Exarch
stem petal stem petal
Dicot Centri Monocot Centri
(3) Endarch Endarch
stem fugal stem fugal
Monocot Centri Dicot Centri
(4) Endarch Endarch
stem fugal stem fugal
Practice Test - All 1103CJA100122013
Page 4/11 Space for Rough Work
25. In a dicot root, the pericycle gives rise to 30. Which of the following is wrong for dorsiventral
(1) Lateral roots leaf ?
(2) Cork cambium (1) Spongy tissue is situated towards abaxial
surface
(3) A portion of vascular cambium
(2) Cuticle on upper surface is thick
(4) All of the above
(3) Palisade tissue is situated towards abaxial
26. A leaf which possesses stomata exclusively on surface
its upper side is
(4) Present at right angle to stem
(1) Oat (2) Oat
31. Which of the following statements are correct for
(3) Lotus (4) cactus the given diagram ?
27. A vascular bundle in which phloem is on both
the sides of the xylem and separated from it by
strips of cambium is said to be -
(1) Collateral, open
(2) Bicollateral, open
(3) Concentric
(i) Presence of root hairs
(4) Bicollateral, closed (ii) Collenchymatous hypodermis
28. Vascular bundles in monocotyledons are (iii) Endodermis rich in protein
considered closed because : (iv) Semi lunar patches of sclerenchyma in
pericycle
(1) Cambium is absent
(v) Vascular bundles are open
(2) There are no vessels with perforations (vi) Absence of pith
(3) Xylem is surrounded all around by phloem (1) (i) (iii) (vi) (2) (ii) (iv) (v)
(4) A bundle sheath surrounds each bundle. (3) (i) (iii) (iv) (vi) (4) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v)
29. Vascular bundles of roots are
(1) Conjoint
(2) Concentric
(3) Bicollateral
(4) Radial
Practice Test - All 1103CJA100122013
Space for Rough Work Page 5/11
32. Assertion : Both apical and intercalary 35. Identify the diagram:
meristems are primary meristems.
Reason : Both appear early in the life of a plant
and contribute to the formation of the primary
plant body.
(1) Both Assertion & Reason are True &
Reason is the correct explanation of the
Assertion. (1) A → is lumen
(2) Both Assertion & Reason are True but (2) B → is branched bordered pit
Reason is not the correct explanation of the
(3) A → is sieve plate
Assertion.
(4) B → is intercellular space
(3) Assertion is True but Reason is False.
36. Sclerenchymatous hypodermis, scattered
(4) Both Assertion & Reason are False.
vascular bundles surrounded by a
33. During the formation of leaves and elongation sclerenchymatous bundle sheath are feature of -
of stem, some cells left behind from shoot apex,
(1) Monocot root (2) Dicot stem
constitutes:
(3) Dicot root (4) Monocot stem
(1) Lateral meristem
37. Sclereids are present in all the given structures,
(2) Leaf
except
(3) Foliar buds
(1) Fruit pulp of guava
(4) Axillary bud
(2) Seed coat of legumes
34. Collenchymatous hypodermis occurs in :-
(3) Petiole of the leaves of most dicots
(1) Dicot stem
(4) Leaves of tea
(2) Monocot stem
38. How many of the following features are correct
(3) Dicot roots regarding bulliform cells of grass leaves?
(4) Monocot leaf (a) Large size
(b) Presence of chlorophyll
(c) Curl leaves inwards to minimise water loss
(d) Present on adaxial epidermis
(1) One (2) Two (3) Three (4) Four
Practice Test - All 1103CJA100122013
Page 6/11 Space for Rough Work
39. All of the following structures constitute stele, 42. Given below is the diagram of the transverse
except section of leaf. Identify the parts labelled A, B, C
(1) Pericycle (2) Endodermis and D and select the right option about them: -
(3) Pith (4) Vascular bundle
40. Monocot root differs from dicot root in having
(1) Open vascular bundles
(2) Scattered vascular bundles
(3) Radially arranged vascular bundles
(1) A – Adaxial epidermis, B – Spongy tissue,
(4) Well developed pith
C – Palisade, D – Abaxial Epidermis
41. This structure belongs to : (2) A – Abaxial epidermis, B – Palisade tissue,
C – Spongy tissue, D – Adaxial epidermis
(3) A – Adaxial epidermis, B – Palisade tissue,
C – Spongy tissue, D – Abaxial epidermis
(4) A – Abaxial epidermis, B – Spongy tissue,
C – Palisade tissue, D – Adaxial epidermis
43.
Identify the given diagramatic sketch and select
(1) Dicot root (2) Dicot stem the correct option in respect of diagramm ?
(3) Monocot root (4) Monocot stem (1) Hypostomatic leaf
(2) Amphistomatic leaf
(3) Found in banana plant
(4) Presence of bulliform cells towards abaxial
surface
Practice Test - All 1103CJA100122013
Space for Rough Work Page 7/11
44. Which of the following is observed in 46. Find out correct option for given figure ?
sunflower plant ?
(1)
(1) A-Epidermis, B-Endodermis, C-Phloem, D-
(2) Xylem
(2) A-Endodermis, B-Epidermis, C-Xylem, D-
Phloem
(3) A-Epidermis, B-Cortex, C-Phloem, D-
Xylem
(3)
(4) A-Epidermis, B-Endodermis, C-Xylem, D-
Phloem
47. Match the following diagrams with the
statements given below :-
(4)
45. Identify the given diagram and select the correct
(i) Bicollateral vascular bundle
option :-
(ii) Conjoint, collateral and open vascular
bundle
(iii) Radial vascular bandle
(iv) Conjoint, collateral and closed vascular
bundle
(1) i-a, ii-b, iii-c, iv-d (2) i-d, ii-b, iii-c, iv-a
(1) Dicot root (2) Monocot root (3) i-d, ii-c, iii-a, iv-b (4) i-c, ii-b, iii-a, iv-d
(3) Monocot stem (4) Dicot stem
Practice Test - All 1103CJA100122013
Page 8/11 Space for Rough Work
48. Find out the correct sequence of labelling :- (2) A – Adaxial epidermis, B – Abaxial
epidermis, C – Xylem, D – Sub – stomatal
cavity, E – Stoma, F – Mesophyll, G –
Phloem
(3) A – Adaxial epidermis, B – Phloem,
C – Mesophyll, D – Sub – stomatal
cavity, E – Abaxial epidermis, F –
A B C
Xylem, G – Stoma
Subsidiary Epidermal Guard
(1) (4) A – Adaxial epidermis, B – Xylem,
cells cells cells
C – Stoma, D – Sub – stomatal cavity,
Subsidiary Epidermal
(2) Guard cells E – Abaxial epidermis, F – Phloem,
cells cells
G – Mesophyll
Epidermal Subsidiary
(3) Guard cells 50. Observe the given diagram carefully and how
cells cells
many statements are true about given diagram:
Subsidiary Epidermal
(4) Guard cells
cells cells
49. T.S. of monocot leaf is given below. Certain
parts are marked by alphabets (A G). Which of
the following options is correct for their
labelling? (a) The position of xylem in the vascular bundle
is adaxial
(b) The position of phloem in the vascular
bundle is abaxial
(c) Two distinct patches of parenchyma are
present above & below of the large vascular
bundle.
(d) The adaxially placed palisade parenchyma is
(1) A – Adaxial epidermis, B – Xylem, made up of elongated cells which are arranged
vertically and parallel to each other
C – Mesophyll, D – Sub – stomatal
cavity, E – Abaxial epidermis, F – (1) Two (2) Three (3) Four (4) One
Stoma, G – Phloem
Practice Test - All 1103CJA100122013
Space for Rough Work Page 9/11
You might also like
- Chapter 39: Plant Responses To Internal and External SignalsDocument11 pagesChapter 39: Plant Responses To Internal and External Signalskuitang100% (2)
- Practice Test 11 - BotanyDocument7 pagesPractice Test 11 - BotanyLoma somNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants - ELP-4Document2 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants - ELP-410ayushranjannNo ratings yet
- DPP - Extra - Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument8 pagesDPP - Extra - Anatomy of Flowering Plantsgk7936No ratings yet
- 5 6206059040699580929Document3 pages5 6206059040699580929Arunima halderNo ratings yet
- PDF ZoologeDocument3 pagesPDF ZoologeShruti YadavNo ratings yet
- NEET Test Series 5Document24 pagesNEET Test Series 5Willis ChekovNo ratings yet
- 0) LT PACE-5 - PAPER With Key - 23.07.2023 - 1290861 - 2023 - 07 - 24 - 11 - 37Document24 pages0) LT PACE-5 - PAPER With Key - 23.07.2023 - 1290861 - 2023 - 07 - 24 - 11 - 37vulurakashsharma2005No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants DPP 01of Lecture 2 Arjuna NEET 2024Document3 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants DPP 01of Lecture 2 Arjuna NEET 2024z5476259No ratings yet
- Yakeen NEET (2024) Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument5 pagesYakeen NEET (2024) Morphology of Flowering Plantsmedical ChyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Flowering Plants - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02) - (Yakeen 2.0 2023 PW Stars)Document3 pagesAnatomy of Flowering Plants - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02) - (Yakeen 2.0 2023 PW Stars)kalarimanohar05No ratings yet
- Biology Day-12Document1 pageBiology Day-12anvith srinivasNo ratings yet
- 64d733f4ca588200185c827c ## Morphology of Flowering Plants DPP 01Document3 pages64d733f4ca588200185c827c ## Morphology of Flowering Plants DPP 01athena20777No ratings yet
- Jb5-Anatomy of Flowering Plant (Final)Document8 pagesJb5-Anatomy of Flowering Plant (Final)anvith srinivasNo ratings yet
- 01 Animal Tissue DPPDocument16 pages01 Animal Tissue DPPRuchi DandaleNo ratings yet
- M CAPS 13 (RM) Botany (PMTcorner - In)Document3 pagesM CAPS 13 (RM) Botany (PMTcorner - In)Sonu RajNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom - 1Document4 pagesAnimal Kingdom - 1gk7936No ratings yet
- 2003 PDFDocument4 pages2003 PDFjp techNo ratings yet
- 2002 PDFDocument4 pages2002 PDFjp techNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Practice - NEET - EnglishDocument18 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants - Practice - NEET - EnglishEducation PointNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom1Document10 pagesAnimal Kingdom1kevxin.johnNo ratings yet
- Kinematics IIDocument3 pagesKinematics IINeetaiimsjipmer Ipe720/720No ratings yet
- Bot Test & Discussion-03 (Code-A)Document4 pagesBot Test & Discussion-03 (Code-A)pal018488No ratings yet
- Uits 2Document45 pagesUits 2Firoj AhmedNo ratings yet
- NEET Test Series 45Document34 pagesNEET Test Series 45anitalakshmi32No ratings yet
- SR Elite, Aiims S60, MPL & LTC Neet Grand Test - 1 Paper (29-05-2022)Document28 pagesSR Elite, Aiims S60, MPL & LTC Neet Grand Test - 1 Paper (29-05-2022)srsoumyaranjantareiNo ratings yet
- Tula Drina Nia IaDocument9 pagesTula Drina Nia IaHarsh SaravatNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 01 BotanyDocument3 pagesPractice Test 01 Botanybhupendranaik330No ratings yet
- Classroom Contact Programme: Pre Medical: Leader Course Pre Medical 2021Document1 pageClassroom Contact Programme: Pre Medical: Leader Course Pre Medical 2021Rakshadharan K PNo ratings yet
- Alternate: AlstoniaDocument4 pagesAlternate: AlstoniaArunima halderNo ratings yet
- NCERT Line Wise MCQs On FrogDocument5 pagesNCERT Line Wise MCQs On FrogThorat's Baarbeque MisalNo ratings yet
- NEET Test Series 2Document24 pagesNEET Test Series 2bal_thakreNo ratings yet
- XI - CBSE - Worksheet - 3 - Anatomy of Flowering PlantsDocument3 pagesXI - CBSE - Worksheet - 3 - Anatomy of Flowering PlantsRajasekar Karuppannan100% (1)
- Animal Tissue - 3: Location FunctionDocument3 pagesAnimal Tissue - 3: Location FunctionKb AshishNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering PlantsDocument3 pagesMorphology of Flowering PlantsFarahan ShaikNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plant - DPP 02 (Of Lecture 04) - Yakeen NEET 2024Document3 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plant - DPP 02 (Of Lecture 04) - Yakeen NEET 2024Himanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Target DPP Test: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Document5 pagesTarget DPP Test: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Deep SapuiNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plant - DPP 03 (Extra DPP) - Yakeen NEET 2024Document4 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plant - DPP 03 (Extra DPP) - Yakeen NEET 2024Himanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Dropper Test Paper: Biology Nugas Classes By: G.K. Nugas 'Main Market, Sector-13, HUDA, Hisar / Mob. 8529147033Document7 pagesDropper Test Paper: Biology Nugas Classes By: G.K. Nugas 'Main Market, Sector-13, HUDA, Hisar / Mob. 8529147033UV JANGRANo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals DPP 07 (Of Lec 11) Yakeen 2.0 2023 VP Stars-2Document3 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals DPP 07 (Of Lec 11) Yakeen 2.0 2023 VP Stars-2suryawanshiashish549No ratings yet
- M-Caps-01 - (Cf+oym) - Botany - 2Document2 pagesM-Caps-01 - (Cf+oym) - Botany - 2Rahul0% (2)
- XII - CBSE - Worksheet - Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Answer KeyDocument1 pageXII - CBSE - Worksheet - Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Answer KeyKishor KumarNo ratings yet
- SR Elite, Aiims S60, Neet MPL & Ic - LTC Neet Grand Test - 4 Paper (24-04-18) PDFDocument32 pagesSR Elite, Aiims S60, Neet MPL & Ic - LTC Neet Grand Test - 4 Paper (24-04-18) PDFGanesa Sri Vel100% (1)
- 2000 PDFDocument3 pages2000 PDFjp techNo ratings yet
- Balanoglossus Pila Octopus Saccoglossus: Subject: ZoologyDocument1 pageBalanoglossus Pila Octopus Saccoglossus: Subject: ZoologyDaksh SinghNo ratings yet
- JR Aiims S60 Neet Weekend Test - 11 Paper (19-09-2022)Document20 pagesJR Aiims S60 Neet Weekend Test - 11 Paper (19-09-2022)rashmipoorvi shettyNo ratings yet
- IPL Test-4 Paper-SplitDocument1 pageIPL Test-4 Paper-Splitkksah0200No ratings yet
- Incoming JR Aiims S60 & Neet MPL (Batch-1&2) NWT - 13 Paper (29-08-2021)Document18 pagesIncoming JR Aiims S60 & Neet MPL (Batch-1&2) NWT - 13 Paper (29-08-2021)Mission NEET 2022No ratings yet
- 64d5e4ae9baa3b0018ef584e ## Plant Kingdom DPP 05 of Lec 06 YakeenDocument3 pages64d5e4ae9baa3b0018ef584e ## Plant Kingdom DPP 05 of Lec 06 Yakeenathena20777No ratings yet
- Morphology of Flowering Plants &animal Tissues-Q.pDocument8 pagesMorphology of Flowering Plants &animal Tissues-Q.pchp8615742No ratings yet
- Cell The Unit of Life DPP 02 (Of Lec 06)Document3 pagesCell The Unit of Life DPP 02 (Of Lec 06)sairajkhedkar69No ratings yet
- Tissue - NSEJS-Primo Race.Document5 pagesTissue - NSEJS-Primo Race.Kanchan Shirbhate0% (1)
- AITS - 02 - Botany Practice SheetDocument4 pagesAITS - 02 - Botany Practice Sheetanvitabhardwaj24No ratings yet
- Test-01 - 11th Full SyllabusDocument5 pagesTest-01 - 11th Full SyllabusShaina Hayat KhanNo ratings yet
- SR Elite (Ser - 2) Neet Module Test - 2 Paper (25-10-2022)Document20 pagesSR Elite (Ser - 2) Neet Module Test - 2 Paper (25-10-2022)scisyhp007No ratings yet
- Test - 01 - Cell Unit of Life - Biology - 01-11-2023 - TestDocument4 pagesTest - 01 - Cell Unit of Life - Biology - 01-11-2023 - TestHarsh BadoniyaNo ratings yet
- 2001 PDFDocument4 pages2001 PDFjp techNo ratings yet
- Interactions Between Non-Pathogenic Soil Microorganisms And PlantsFrom EverandInteractions Between Non-Pathogenic Soil Microorganisms And PlantsNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - The Story!!!!Document2 pagesPhotosynthesis - The Story!!!!Alladin P. PolintanNo ratings yet
- Resistance Breeding To IMI and SU Herbicides in SunflowerDocument6 pagesResistance Breeding To IMI and SU Herbicides in SunflowerIoana MarișNo ratings yet
- Plant Growth 2Document2 pagesPlant Growth 2Asnani AsudinNo ratings yet
- 69018Document76 pages69018TANNo ratings yet
- Common Farm Equipment Tle AgricultureDocument11 pagesCommon Farm Equipment Tle AgricultureJyrah DuronNo ratings yet
- Symptoms and DiseasesDocument8 pagesSymptoms and Diseaseschristy maeNo ratings yet
- Leaves: Parts of A LeafDocument17 pagesLeaves: Parts of A LeafLuisa ValenciaNo ratings yet
- A Revised Survey of The Forest Types of PDFDocument609 pagesA Revised Survey of The Forest Types of PDFGaurang TawdeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 6Document6 pagesLesson Plan in Science 6MonNo ratings yet
- Report Week 5 (5.5.23)Document5 pagesReport Week 5 (5.5.23)NUR DALILAH HUSNINA MOHD ZULFAKAR SHAHNo ratings yet
- Loyola International Schools Qatar Academic Session:2023-2024 Science PT 2 Exam Revision WorksheetDocument3 pagesLoyola International Schools Qatar Academic Session:2023-2024 Science PT 2 Exam Revision WorksheetchikenbiriyanieaterNo ratings yet
- Kcse 2004 Biology QuestionsDocument7 pagesKcse 2004 Biology QuestionsUrex ZNo ratings yet
- Seed MaterialDocument69 pagesSeed Materialvishal patelNo ratings yet
- Coromandel - 1Document4 pagesCoromandel - 1Anirban BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- 7.medicinal Plants at EPTRIDocument5 pages7.medicinal Plants at EPTRIRaja Vamsi MavuduruNo ratings yet
- Aspidistra Production and Use: Robert H. StampsDocument9 pagesAspidistra Production and Use: Robert H. Stampsw pNo ratings yet
- Sex DeterminationDocument11 pagesSex DeterminationJulio SubagioNo ratings yet
- Fi To HormonDocument118 pagesFi To HormonRizha Darraa DJuantie100% (1)
- CaptionDocument4 pagesCaptionRizqika Khoerul F.No ratings yet
- Kil New Chinese Herbs ListDocument18 pagesKil New Chinese Herbs Listnataarajan praveen100% (1)
- Elementary Algebra For College Students 9th Edition Angel Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesElementary Algebra For College Students 9th Edition Angel Solutions ManualMrTaylorPowellcdpf100% (53)
- Boletin HeliconiasDocument16 pagesBoletin HeliconiasCarlos MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 4Document3 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 4MacellyBudiongan100% (1)
- Plants For Sensory GardenDocument14 pagesPlants For Sensory GardenMuthuselvam sakthivelNo ratings yet
- The Plant BodyDocument2 pagesThe Plant BodyIJ SeducoNo ratings yet
- EggplantDocument8 pagesEggplantJean SuarezNo ratings yet
- Cell and Developmental Biology: Practical 4: Tissue CultureDocument10 pagesCell and Developmental Biology: Practical 4: Tissue CultureJoanne Ch'ngNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis QuizDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis QuizAssignment JamNo ratings yet
- Plas Moly SisDocument1 pagePlas Moly SisRaymund BondeNo ratings yet