Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Alternating Currents - Revision Practice Sheet - Safal 2.0
Alternating Currents - Revision Practice Sheet - Safal 2.0
Uploaded by
dhruvapocof1Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alternating Currents - Revision Practice Sheet - Safal 2.0
Alternating Currents - Revision Practice Sheet - Safal 2.0
Uploaded by
dhruvapocof1Copyright:
Available Formats
1
Safal 2.0
Alternating Currents
Revision Practice Sheet
1. The ratio of the mean value over half cycle to the 6. A constant current of 3A exists in a resistor.
r.m.s. value of an A.C. is The r.m.s current is
(1) 2 : (2) 12 2 : (1) 3A (2)
3
A
(3) 2: (4) 2 :1 2
3
(3) 3 2 A (4) A
2. The peak value of an alternating e.m.f. given by 2
E = E0 cos t is 10 volt and its frequency is 50 Hz.
1 7. An alternating voltage is given by V = 10 cos 314 t.
At a time t = s the instantaneous value of the
600 1
At t = s, the instantaneous value of voltage is
e.m.f. is 300
(1) 10 V
(1) 10 volt (2) 5 3 volt
(2) 8 V
(3) 5 volt (4) 1 volt
(3) 5 V
(4) 1 V
3. The frequency of an alternating voltage is
50 cycles/sec and its amplitude is 120 V. Then the
8. The mean value of current for half cycle for a current
r.m.s. value of voltage is
variation shown by the graph is
(1) 101.3 V (2) 84.8 V
(3) 70.7 V (4) 56.5 V
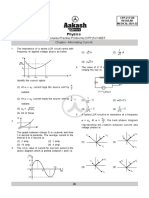
4. Find the average value of current shown graphically
from t = 0 to t = 2 s
𝑖0
(1) (2) i0
2
𝑖0 𝑖0
(3) (4)
√3 3
(1) 3 A (2) 5 A 9. The peak value of an alternating e.m.f.
(3) 10 A (4) 4 A E = E0 sin t is 10 volt and its frequency is 50 Hz. At
1
a time t = , the instantaneous value of the e.m.f.
5. If the instantaneous current in a circuit is given by 600 s
i = 10 cos ( t – ) ampere, the r.m.s. value of the is
current is (1) 1 volt
(1) 10 A (2) 7 A (2) 5√3 volt
(3) 14 A (4) Zero (3) 5 volt
(4) 10 volt
2
10. If I = 2t, then the R.M.S. value of current between 1
16. A coil having an inductance of H and resistance of
zero to 2 second is
2 4 300 ohm is connected to a 200 V, 200 Hz ac source.
(1) √ (2)
3 √3 The phase angle between voltage and current is
5 3 4
(3) √ (4) Zero (1) tan–1 (2) tan–1
3 4 3
4 5
11. The r.m.s. value of current for (3) tan–1 (4) tan–1
5 4
I = 3 sin t + 4 cos t is
(1) 5A (2) 5√2 A 17. A resistance of 20 is connected to a source of an
5 7
(3) A (4) A alternating potential V = 220 sin(100 t). The time
√2 √2
taken by the current to change from its peak value to
rms value, is
12. A resistance of 20 is connected to a source of
(1) 0.2s (2) 0.25 s
alternating current rated 110 V, 50 Hz. Then the time –3
(3) 2.5 × 10 s (4) 2.5 ×10–6s
taken by the current to change from Its maximum
value to the r.m.s value
18. An a.c. voltage is applied to a pure inductor L, drives
(1) 2.5 × 10–3 sec
a current in the inductor. The current in the inductor
(2) 2.5 × 10–2 sec
would be
(3) 5 × 10–3 sec
(4) 25 × 10–3 sec
(1) Ahead of the voltage by
2
13. The frequency of an alternating current is 50 Hz, then
(2) Lagging the voltage by
the time taken by it in reaching from zero to peak 2
value is
(3) Ahead of the voltage by
(1) 5 ms (2) 10 ms 4
(3) 20 ms (4) 50 ms 3
(4) Lagging the voltage by
2
14. An alternating voltage v =200 2 sin 100t is
connected to 1 µF capacitor through an ac ammeter. 19. In a series circuit the AC voltages across resistance R,
The reading of the ammeter shall be inductance L and capacitance C are 5 V, 10V and
(1) 10 mA (2) 20 mA 10 V respectively. The ac voltage applied to the
(3) 40 mA (4) 80 mA circuit will be
(1) 25 V (2) 20 V
15. In the case of an inductor (3) 10 V (4) 5 V
(1) Voltage lags the current by
2 20. In an A.C. circuit, the current is i = 5 sin (100t –/2 )
amp and the A.C. potential is V = 200 sin (100 t) volt.
(2) Voltage leads the current by Then the power consumption is
2
(1) 20 watts
(3) Voltage leads the current by (2) 40 watts
3
(3) 1000 watts
(4) Voltage leads the current by (4) 0 watt
4
3
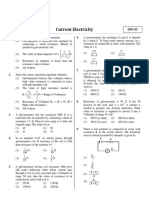
21. In the circuit shown below, what will be the readings 25. In L–C–R series A.C. circuit, the phase angle between
of the voltmeter and ammeter? current and voltage is
(1) Any angle between 0 and
2
(2)
2
(3)
(4) Any angle between and
(1) 800 V, 2A (2) 300 V, 2A 2
(3) 220 V, 2.2 A (4) 100 V, 2A
26. An alternating current of frequency f is flowing
22. In an LCR circuit, the capacitance is made one-fourth, through a resistance R and inductance L connected in
when in resonance. Then what should be change in series. The impedance of the circuit is
inductance, so that the circuit remains in resonance? (1) R + L
(1) 4 times (2) 1/4 times (2) r + 2 fL
(3) 8 times (4) 2 times
(3) R 2 + 4 2 f 2 L2
23. In an A.C. circuit, a resistance R is connected in series (4) R 2 + L2
with an inductance L. If phase angle between voltage
and current be 45°, the value of inductive reactance 27. The average power dissipation in a pure series circuit
will be containing resistance R and inductance L when A.C.
R R current I is passing through it is
(1) (2)
4 2 1 2 1 2
(1) LI (2) LI
(3) R (4) None of these 2 4
(3) Zero (4) RI2
24. The average power dissipation in a pure capacitor in
AC circuit is
1
(1) CV2 (2) CV2
2
(3) 2CV2 (4) Zero
4
Answer Key
1. (2) 15. (2)
2. (2) 16. (2)
3. (2) 17. (3)
4. (2) 18. (2)
5. (2) 19. (4)
6. (1) 20. (4)
7. (3) 21. (3)
8. (1) 22. (1)
9. (3) 23. (3)
10. (2) 24. (4)
11. (3) 25. (1)
12. (1) 26. (3)
13. (1) 27. (4)
14. (2)
PW Web/App - https://smart.link/7wwosivoicgd4
Library- https://smart.link/sdfez8ejd80if
You might also like
- Neet 2022 Abroad Paper (Solved)Document36 pagesNeet 2022 Abroad Paper (Solved)NinaNo ratings yet
- Manual de Servicio Monitor LCD Dell E190SfDocument59 pagesManual de Servicio Monitor LCD Dell E190SfAntonio Chavez100% (1)
- File 2 10Document8 pagesFile 2 10camelod555No ratings yet
- Alternating Current DPPsDocument2 pagesAlternating Current DPPsMayur BelsareNo ratings yet
- Neet Booster Test Series (NBTS) For Neet-2021 Test - 8: PhysicsDocument15 pagesNeet Booster Test Series (NBTS) For Neet-2021 Test - 8: PhysicsupsahuNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - Live Session: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718Document3 pagesCurrent Electricity - Live Session: Contact Number: 9667591930 / 8527521718demoNo ratings yet
- Week End Test - 8 (2 Year) : Green Park International Senior Secondary School, NamakkalDocument8 pagesWeek End Test - 8 (2 Year) : Green Park International Senior Secondary School, Namakkals.hiruthivNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current DPP 02 Manish Raj Sir Neet Crash Course RelaunchDocument2 pagesAlternating Current DPP 02 Manish Raj Sir Neet Crash Course Relaunchabu326274No ratings yet
- Target DPP Test: Ω Hz Hz Hz 500 HzDocument6 pagesTarget DPP Test: Ω Hz Hz Hz 500 HzBidyut Bikash BaruahNo ratings yet
- 65c246cf784c52001843f8bd - ## - Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Assignment 01 Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)Document11 pages65c246cf784c52001843f8bd - ## - Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Assignment 01 Yakeen 2.0 2024 (Legend)singhsneha29369No ratings yet
- All India Test Series Full Syllabus Test-07 - NEET - 04-05-2023 - QuestionsDocument17 pagesAll India Test Series Full Syllabus Test-07 - NEET - 04-05-2023 - QuestionsMusical MaanishNo ratings yet
- PRACTICE SHEET - 15 (Physics)Document4 pagesPRACTICE SHEET - 15 (Physics)ABD 17No ratings yet
- Parishram 2024: Alternating CurrentDocument2 pagesParishram 2024: Alternating Currentabhyanandk42No ratings yet
- FT09 - OYM - Code J (03-07-2022)Document17 pagesFT09 - OYM - Code J (03-07-2022)World WarriorNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current 2024Document8 pagesAlternating Current 2024Shoaib FaruqiNo ratings yet
- AIATS-2022 (CF+OYM) Test-03 - Code-A - 09.01.2022Document24 pagesAIATS-2022 (CF+OYM) Test-03 - Code-A - 09.01.2022Nainaa AryaNo ratings yet
- 0102 Physics Paper With Answer MorningDocument5 pages0102 Physics Paper With Answer Morningspicypip123No ratings yet
- Term Test-03 (OYM) @DefeatNEETDocument21 pagesTerm Test-03 (OYM) @DefeatNEETlakshyakhokhar78No ratings yet
- XII-Physics Chapter Test-17-Current ElectricityDocument5 pagesXII-Physics Chapter Test-17-Current ElectricityIshanNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02)Document4 pagesCurrent Electricity - DPP 01 (Of Lec 02)ABIR ROYNo ratings yet
- Neet Paper 2021: Section - A (Physics) AnsDocument21 pagesNeet Paper 2021: Section - A (Physics) AnsMission NEET 2022No ratings yet
- NEET UG 2024 Sample Paper 01Document20 pagesNEET UG 2024 Sample Paper 01VARSHAN GAMINGNo ratings yet
- February 1 - MorningDocument12 pagesFebruary 1 - Morningadhyayan.learning.2021No ratings yet
- Space For Rough Work: EnglishDocument20 pagesSpace For Rough Work: EnglishIt's Actually SimpleNo ratings yet
- Objective Questions: Section (A) : Average, Peak and RMS Values and RMS ValuesDocument8 pagesObjective Questions: Section (A) : Average, Peak and RMS Values and RMS Valuesaabha esqueNo ratings yet
- Narayana Medical Academy: PhysicsDocument9 pagesNarayana Medical Academy: PhysicsNagendra BharadwazNo ratings yet
- ALTERNATING CURRENTS (Ansset)Document12 pagesALTERNATING CURRENTS (Ansset)vishwanath c kNo ratings yet
- 66334b69f003b1001860e146 - ## - NEET Replica Test - 02 Test PaperDocument21 pages66334b69f003b1001860e146 - ## - NEET Replica Test - 02 Test Paperslapkingbadshah19No ratings yet
- Sample 02 - Class12Document21 pagesSample 02 - Class12vasudevanrv9405No ratings yet
- AITS Full Syllabus Test 02 Dropper NEET Evening 26 04 2023 QuestionsDocument29 pagesAITS Full Syllabus Test 02 Dropper NEET Evening 26 04 2023 Questionsbishnuprasadmohapatra01No ratings yet
- Test Series: Test - 14: PhysicsDocument23 pagesTest Series: Test - 14: PhysicsRajkumar JainNo ratings yet
- Cls Jeead-18-19 Xii Phy Target-5 Set-2 Chapter-3Document84 pagesCls Jeead-18-19 Xii Phy Target-5 Set-2 Chapter-3Samir Rai100% (1)
- (@NEETpassionate) Aakash CPP - 7Document30 pages(@NEETpassionate) Aakash CPP - 7akashchandakash6355No ratings yet
- SemiconductorDocument4 pagesSemiconductorriyasharma270406No ratings yet
- Neet Paper 2021: ε 1 2 ε E 1 2 ε E AdDocument19 pagesNeet Paper 2021: ε 1 2 ε E 1 2 ε E AdShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- 643f6d50677f39001865b126 - ## - AITS Part Test-10 - Dropper NEET - Morning - 19-04-2023 - QuestionsDocument26 pages643f6d50677f39001865b126 - ## - AITS Part Test-10 - Dropper NEET - Morning - 19-04-2023 - Questionsvision xeroxNo ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument8 pagesCurrent Electricityhj48khy8jjNo ratings yet
- 6436282bacd0d6001866219f - ## - AITS-08 - Paper-1 - Dropper NEET - 12-04-2023 - QuestionsDocument26 pages6436282bacd0d6001866219f - ## - AITS-08 - Paper-1 - Dropper NEET - 12-04-2023 - Questionsvision xeroxNo ratings yet
- Physics Curretn Electricity: Resolute Batch / Abhyas Sheet-14Document3 pagesPhysics Curretn Electricity: Resolute Batch / Abhyas Sheet-14Vedika GoyalNo ratings yet
- 1484 TestQuestionDocument31 pages1484 TestQuestionArsalan MuzamilNo ratings yet
- JEE Mains Mock Test 01 - Test Paper (Physics) - (Lakshya JEE 2023)Document10 pagesJEE Mains Mock Test 01 - Test Paper (Physics) - (Lakshya JEE 2023)Hacker KingNo ratings yet
- 07 - Alternating CurrentDocument15 pages07 - Alternating CurrentKindman KindmanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Wave - DPPsDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Wave - DPPseruditespartan108No ratings yet
- LAKSHYA JEE (2024) : Current ElectricityDocument3 pagesLAKSHYA JEE (2024) : Current Electricityrajeevverma7269No ratings yet
- Current ElectricityDocument8 pagesCurrent ElectricitysnehaganeshpatilNo ratings yet
- SHORT PRACTICE TEST SERIES - No-006 - NEET - 2022-08-21 - 2022 - QDocument8 pagesSHORT PRACTICE TEST SERIES - No-006 - NEET - 2022-08-21 - 2022 - QPLABAN DASNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits - DPP 01 - Sarthak MHT-CET Crash Course 2.0Document4 pagesAC Circuits - DPP 01 - Sarthak MHT-CET Crash Course 2.0Pratiksha DNo ratings yet
- Physics: Chapter - Alternating Current Chapterwise Practise Problems (CPP) For NEETDocument21 pagesPhysics: Chapter - Alternating Current Chapterwise Practise Problems (CPP) For NEETsoyel afridiNo ratings yet
- OYPP Med Test Paper 25-04-2022 With AnswerkeyDocument16 pagesOYPP Med Test Paper 25-04-2022 With AnswerkeySwarnika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity - DPP 05 (Of Lec 08)Document4 pagesCurrent Electricity - DPP 05 (Of Lec 08)ABIR ROYNo ratings yet
- Parishram 2024: Alternating CurrentDocument2 pagesParishram 2024: Alternating Currentabhyanandk42No ratings yet
- Alternating Current (AC) : - Aashik Jha IOMDocument12 pagesAlternating Current (AC) : - Aashik Jha IOMManish GuptaNo ratings yet
- NJ Physics NJ Physics: Mains Revision Test Physics Mechanics and HeatDocument6 pagesNJ Physics NJ Physics: Mains Revision Test Physics Mechanics and HeataNo ratings yet
- 1d.current Electricity Synopsis (51 55)Document5 pages1d.current Electricity Synopsis (51 55)h21891965No ratings yet
- Semiconductor - Practice Sheet & SolutionDocument6 pagesSemiconductor - Practice Sheet & Solutionjawiv91660No ratings yet
- Te 03 Code B Phase 1Document22 pagesTe 03 Code B Phase 128092008pragyana2382No ratings yet
- Upload 3'Document16 pagesUpload 3'k.prarthu0909No ratings yet
- Exercise 1Document25 pagesExercise 1kavita aggarwal100% (1)
- 03B. Alternating Current (154-166)Document13 pages03B. Alternating Current (154-166)Mupli RajeshNo ratings yet
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeFrom EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Tunnel Field-effect Transistors (TFET): Modelling and SimulationFrom EverandTunnel Field-effect Transistors (TFET): Modelling and SimulationNo ratings yet
- AREVA T&D - GE T&D - ALSTOM - GEC - Schneider T&D Protection RelaysDocument224 pagesAREVA T&D - GE T&D - ALSTOM - GEC - Schneider T&D Protection RelaysVijayNo ratings yet
- Sensors and Transducers Unit-IDocument60 pagesSensors and Transducers Unit-ITamilnesan P0% (1)
- QZ EqDocument6 pagesQZ Eqgalati12345100% (1)
- A Practical Method For Calculation of Over-Excited Region in The Synchronous Generator Capability CurvesDocument6 pagesA Practical Method For Calculation of Over-Excited Region in The Synchronous Generator Capability CurvesRodNo ratings yet
- Q3 General Physics W456Document6 pagesQ3 General Physics W456Elia Saph MoonNo ratings yet
- Switches Pots: S1001 Mono Input ModuleDocument1 pageSwitches Pots: S1001 Mono Input ModuleChristian LesnesNo ratings yet
- Man 8037t PRGDocument286 pagesMan 8037t PRGalinger zanabriaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Introduction To Control Systems - Part2 - SlidesDocument24 pagesUnit 1 - Introduction To Control Systems - Part2 - SlidesSiphamandla CokaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - ElectrochemistryDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - ElectrochemistryMADHAVNo ratings yet
- Power Over Ethernet Injector: 12V: DescriptionDocument1 pagePower Over Ethernet Injector: 12V: DescriptionAakash MalviyaNo ratings yet
- Mastech MS2203 Manual PDFDocument35 pagesMastech MS2203 Manual PDFTeto ScheduleNo ratings yet
- E Installation of BatteryDocument16 pagesE Installation of BatteryPrashant KadamNo ratings yet
- Hyperloop One Letter Address 2159 Bay ST Los Angeles Ca 90021Document11 pagesHyperloop One Letter Address 2159 Bay ST Los Angeles Ca 90021api-646708752No ratings yet
- Unit - 4 - Power Electronics and Energy Storage in Smart GridDocument50 pagesUnit - 4 - Power Electronics and Energy Storage in Smart GridsujithNo ratings yet
- Z5 DC Compound Wound MotorDocument13 pagesZ5 DC Compound Wound MotorFitri VongolaNo ratings yet
- LOGO!Soft Comfort - Circuit Diagram2Document3 pagesLOGO!Soft Comfort - Circuit Diagram2Agustin CañeteNo ratings yet
- CiacisDocument8 pagesCiacisVladimir CedeñoNo ratings yet
- Kabeldon Cable Accessories 1-420 KV EnglishDocument6 pagesKabeldon Cable Accessories 1-420 KV EnglishAnonymous xBi2FsBxNo ratings yet
- Configured Digitally Programmable Potentiometer (DPP™) : Programmable Voltage ApplicationsDocument15 pagesConfigured Digitally Programmable Potentiometer (DPP™) : Programmable Voltage ApplicationsWisesaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Workshop: 1) Safety ClothesDocument12 pagesElectrical Workshop: 1) Safety Clothessohail arshadNo ratings yet
- Current & ResitanceDocument8 pagesCurrent & ResitanceElaine CalayagNo ratings yet
- Parts and Service Manual Supplement: Part No. 104980 Rev A November 2005Document39 pagesParts and Service Manual Supplement: Part No. 104980 Rev A November 2005Святослав ВороновNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EEN-112: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 05Document1 pageDepartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee Roorkee EEN-112: Electrical Science Tutorial Sheet - 05Kumar ShivamNo ratings yet
- BOQ No. 7-UG Water Tank and Pump RoomDocument24 pagesBOQ No. 7-UG Water Tank and Pump RoomUsman NadeemNo ratings yet
- Acc-E HFP A 1 07052015Document1 pageAcc-E HFP A 1 07052015ChaosNo ratings yet
- 680-198-01 MXP-539 16-Way Input 48-Way Output CardDocument10 pages680-198-01 MXP-539 16-Way Input 48-Way Output CardAdriano CostaNo ratings yet
- 2016 Ch2-MOS TransistorsDocument47 pages2016 Ch2-MOS Transistorsជើងកាង ភូមិ100% (1)
- GTP Ykp PDFDocument45 pagesGTP Ykp PDFSwarup NayakNo ratings yet