Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Smacna Hvac Duct Construction Standards
Smacna Hvac Duct Construction Standards
Uploaded by
MEP EngineeringCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Seismic Restraint Manual 2008 LatestDocument202 pagesSeismic Restraint Manual 2008 LatestHassaan HameedNo ratings yet
- CAT Service Manuals TL642 TL943Document197 pagesCAT Service Manuals TL642 TL943Shivanan Singh100% (7)
- SMACNA Duct Construction Standards - 3rd Edition - 2005Document396 pagesSMACNA Duct Construction Standards - 3rd Edition - 2005Eric E' Sandoval A100% (7)
- Tl642 Cat Services Manual TelehandlerDocument197 pagesTl642 Cat Services Manual TelehandlerRoxana Elizabeth Valencia NavarrteNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE Temperature Tables For All US CitiesDocument12 pagesASHRAE Temperature Tables For All US Citiespuneetmathur8247100% (3)
- Gradall 534D-9 PartsDocument710 pagesGradall 534D-9 PartsAlejandro Bonilla100% (4)
- Tl1055 Service ManualDocument178 pagesTl1055 Service ManualJose Cruz Martinez Medina100% (1)
- Service Manual TL642 TL943 PDFDocument196 pagesService Manual TL642 TL943 PDFGeorge Guerrero100% (3)
- Specification For Phenolic Duct Works SystemsDocument2 pagesSpecification For Phenolic Duct Works Systemspsn_kylm100% (1)
- 2019 ASHRAE Handbook HVAC Applications SI Swimming PoolDocument8 pages2019 ASHRAE Handbook HVAC Applications SI Swimming PoolTsz Ho LAI100% (1)
- Smacna Duct ConstructionDocument23 pagesSmacna Duct ConstructionKaustubh Bidkar100% (2)
- RTS Example Montreal ASHRAE Chapter 6oct2003Document26 pagesRTS Example Montreal ASHRAE Chapter 6oct2003Sid KherNo ratings yet
- SMACNA Round Industrial Duct Construction Standards - Chapter 2 Industrial Duct ApplicationsDocument2 pagesSMACNA Round Industrial Duct Construction Standards - Chapter 2 Industrial Duct ApplicationsMinh Tran50% (2)
- ASHRAE Fundamentals Handbook (2009)Document2 pagesASHRAE Fundamentals Handbook (2009)Luís Fernando Ferreira Silva50% (2)
- Part 1. Load Estimating - Chapter 4. Solar Heat Gain Thru GlassDocument3 pagesPart 1. Load Estimating - Chapter 4. Solar Heat Gain Thru Glasskiran raghukiranNo ratings yet
- Smacna Industrial Rounded Duct Construction Tabla ContenidosDocument4 pagesSmacna Industrial Rounded Duct Construction Tabla Contenidosedgar_glezav0% (3)
- VRV Xpress Manual V612 Tcm135-168625Document82 pagesVRV Xpress Manual V612 Tcm135-168625Cărunta-Crista Sergiu83% (6)
- York Fan Coil UnitDocument16 pagesYork Fan Coil Unitjaja100% (3)
- 1922Document301 pages1922Rafael Leonardo GomezNo ratings yet
- Servicio tl642cDocument206 pagesServicio tl642cpablo100% (4)
- Caterpillar JLG Parts ManualDocument320 pagesCaterpillar JLG Parts ManualJuan Esteban Sloboda Aranguren100% (1)
- HAP Thermal Load Cal - FormulaDocument19 pagesHAP Thermal Load Cal - Formulamajortay100% (1)
- ASHRAE Article - Boiler Ventilation PDFDocument8 pagesASHRAE Article - Boiler Ventilation PDFrfriosEPNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE Journal - VAV System Duct Main DesignDocument5 pagesASHRAE Journal - VAV System Duct Main DesignJhoNo ratings yet
- Carrier 23XL Product Data 1996Document48 pagesCarrier 23XL Product Data 1996DaveEger100% (1)
- ASHRAE Commercial Duct CalculationsDocument4 pagesASHRAE Commercial Duct CalculationsNirmal KvNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Ventilation ExistinghomesDocument35 pagesEvaluating Ventilation ExistinghomesKatamba RogersNo ratings yet
- Heat Gain From Electrical and Control Equipment in Industrial Plants, Part II, ASHRAE Research Project RP-1395Document4 pagesHeat Gain From Electrical and Control Equipment in Industrial Plants, Part II, ASHRAE Research Project RP-1395Michael LagundinoNo ratings yet
- Duct DesignDocument32 pagesDuct DesignsupportLSMNo ratings yet
- Ductwork Leakage Testing: A Practical Guide ToDocument17 pagesDuctwork Leakage Testing: A Practical Guide ToGoyal SanjaiNo ratings yet
- Ashrae Pocket Guide I P PDFDocument36 pagesAshrae Pocket Guide I P PDFMUKESH DAYMANo ratings yet
- ESM DUCT CALCULATOR Rev2Document1 pageESM DUCT CALCULATOR Rev2qwerty_conanNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE HVAC 2001 Fundamentals HandbookDocument6 pagesASHRAE HVAC 2001 Fundamentals HandbookJosé A. Ramírez100% (1)
- Round Industrial Duct Construction Standards: Sheet Metal and Air Conditioning Contractors' National Association, IncDocument19 pagesRound Industrial Duct Construction Standards: Sheet Metal and Air Conditioning Contractors' National Association, IncNathanNo ratings yet
- Ashrae: Laboratory Design GuideDocument12 pagesAshrae: Laboratory Design GuideAlex PullaNo ratings yet
- Comfort and Critical Outdoor Design ConditionsDocument6 pagesComfort and Critical Outdoor Design ConditionshueyliewNo ratings yet
- 2005 Smacna Shop Standards For Rectangular Duct ConstructionDocument6 pages2005 Smacna Shop Standards For Rectangular Duct ConstructionAshiq IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Titus Engineering Guidelines Grilles and Diffusers Engineering Data B13269Document34 pagesTitus Engineering Guidelines Grilles and Diffusers Engineering Data B13269Renan GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Construction Standards: Accepted Industry Practices For Sheet Metal LaggingDocument13 pagesConstruction Standards: Accepted Industry Practices For Sheet Metal LaggingTeoxNo ratings yet
- VRF Installation Quick GuideDocument84 pagesVRF Installation Quick GuideErwin MaldoNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE CH 12 (Hydronic Heating and Cooling System Design)Document18 pagesASHRAE CH 12 (Hydronic Heating and Cooling System Design)RIYANTO BEBETNo ratings yet
- Aeroflex Main New Catalog PDFDocument32 pagesAeroflex Main New Catalog PDFnaren233No ratings yet
- Dynair Ecology UnitDocument12 pagesDynair Ecology Unitrid100% (1)
- Smacna Duct LeakageDocument3 pagesSmacna Duct Leakageanton7786No ratings yet
- Ashrae Duct PDFDocument3 pagesAshrae Duct PDFAnonymous XhkjXCxxsTNo ratings yet
- HVAC - How To Size and Design (CED Engineering) (Static Loss, Etc)Document91 pagesHVAC - How To Size and Design (CED Engineering) (Static Loss, Etc)Zulfadzli RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Duct & FittingsDocument26 pagesRectangular Duct & Fittingsmakmak90% (1)
- Duct Construction ChartDocument23 pagesDuct Construction ChartMattNo ratings yet
- AL HVAC Contractor Comprehensive Tutorial 10Document278 pagesAL HVAC Contractor Comprehensive Tutorial 10William Worrell100% (1)
- HVAC Duct Construction StandardsDocument308 pagesHVAC Duct Construction StandardsGuilherme Valadares100% (1)
- Smacna Fire Smoke Combined Dampers 1Document64 pagesSmacna Fire Smoke Combined Dampers 1Santiago J. ramos jr100% (5)
- Ductwork Leakage & Leak Testing JournalDocument9 pagesDuctwork Leakage & Leak Testing JournalAlex ChinNo ratings yet
- Duct Fittings LossesDocument42 pagesDuct Fittings LossesmostafaabdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Air Distribution SystemDocument21 pagesAir Distribution SystemRohit JainNo ratings yet
- Ventilation For Commercial Cooking Operations: ANSI/ASHRAE Addendum C To ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 154-2016Document5 pagesVentilation For Commercial Cooking Operations: ANSI/ASHRAE Addendum C To ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 154-2016mahboobNo ratings yet
- HVAC - Duct ConstructionDocument75 pagesHVAC - Duct ConstructionGaapchu100% (2)
- VRF Test MethodDocument6 pagesVRF Test Methodprado01No ratings yet
- Cargador TELEHANDLER PDFDocument454 pagesCargador TELEHANDLER PDFFersigal GalsiferNo ratings yet
- Telehandler TL642C - TL943C (Thg00150&after - Thl00150&after - Thh00150&after - Sxh00150&after) PDFDocument446 pagesTelehandler TL642C - TL943C (Thg00150&after - Thl00150&after - Thh00150&after - Sxh00150&after) PDFChristian Andy H. ChavezNo ratings yet
- Ee 6 FinalsDocument3 pagesEe 6 FinalsSantos, Jewella C.No ratings yet
- 12h Parking BrakeDocument4 pages12h Parking Brakeaniri100% (1)
- 25 - Quinte Series EnglishDocument14 pages25 - Quinte Series EnglishJajang NurwandiNo ratings yet
- Hospital Electrical Design BookletDocument52 pagesHospital Electrical Design Bookletssubup100% (3)
- WCF-SERIES-Top Suspension Manual PDFDocument36 pagesWCF-SERIES-Top Suspension Manual PDFYiannis ToufexisNo ratings yet
- Retrofit Kits Technical BrochureDocument10 pagesRetrofit Kits Technical BrochureISHAN VERMANo ratings yet
- ESP Price List 01 May 2024Document121 pagesESP Price List 01 May 2024Devender KumarNo ratings yet
- Viii. Troubleshooting Circulation Pump - Service Index UC/06, UC/11 & UC/12 Parts ChangesDocument4 pagesViii. Troubleshooting Circulation Pump - Service Index UC/06, UC/11 & UC/12 Parts ChangesnilsNo ratings yet
- Firealrm, Detection&Tele 3Document23 pagesFirealrm, Detection&Tele 3Kumar DigvijayNo ratings yet
- Common Service Panel SLDDocument1 pageCommon Service Panel SLDVikasNehraNo ratings yet
- JVC Av-2115ee Chassis CGDocument150 pagesJVC Av-2115ee Chassis CGDarwin Yasmani Martinez ColqueNo ratings yet
- Leviton Highbay Occupancy SensorDocument4 pagesLeviton Highbay Occupancy SensorMohammed YasarNo ratings yet
- Goodwinch Limited: Importers, Exporters, Wholesale Distributors and Retailers of Winches and AccessoriesDocument5 pagesGoodwinch Limited: Importers, Exporters, Wholesale Distributors and Retailers of Winches and AccessoriesPzan PeacemakerNo ratings yet
- KAP 12-24 KV 300 ENACC MVACC DS ENDocument1 pageKAP 12-24 KV 300 ENACC MVACC DS ENMd Imran pashaNo ratings yet
- Floor Plan of Kitchen & Dinning Room: D. Dry StorageDocument1 pageFloor Plan of Kitchen & Dinning Room: D. Dry StoragedejomarlubNo ratings yet
- GamLaser EX5Document4 pagesGamLaser EX5AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Pec Yellow + Zabala Sure 13 PagesDocument13 pagesPec Yellow + Zabala Sure 13 PagesTeddy GutayNo ratings yet
- Pasolink Maintenance Qref v2.0Document40 pagesPasolink Maintenance Qref v2.0pankajengNo ratings yet
- 938K Eletrico Serie AltaDocument39 pages938K Eletrico Serie AltaEmanoel FelipeNo ratings yet
- DUNGS GW 150 A6 (Pressure Switch Aux Boiler)Document6 pagesDUNGS GW 150 A6 (Pressure Switch Aux Boiler)mt.sasongkoNo ratings yet
- Twin Leaf Boring Bars - Sigma Toolings, Fine Boring Tools, Cutting Tools ManufacturerDocument3 pagesTwin Leaf Boring Bars - Sigma Toolings, Fine Boring Tools, Cutting Tools ManufacturerSigma ToolingsNo ratings yet
- Surface PlateDocument3 pagesSurface PlateSaket OraonNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 2N59-1R-200-45Document5 pagesDatasheet 2N59-1R-200-45Bennie ManionNo ratings yet
- Instructions Manual KF8000E KF10000E Multilingual 070207Document56 pagesInstructions Manual KF8000E KF10000E Multilingual 070207Hoff Beer100% (2)
- Nd3361 Hgs620 Termadv Jun12Document10 pagesNd3361 Hgs620 Termadv Jun12Mohamed RafihNo ratings yet
- EE110 Obias Gilbert LM2 3-1Document1 pageEE110 Obias Gilbert LM2 3-1Gilbert ObiasNo ratings yet
- 2017 Trijicon CatalogDocument87 pages2017 Trijicon CatalogАлександр100% (1)
- Registration of Electrical ContractorsDocument69 pagesRegistration of Electrical ContractorsKevin NdetiNo ratings yet
- Legend DSLNGDocument13 pagesLegend DSLNGTim DuncanNo ratings yet
- Q-Free Quartz Sensor: Product SheetDocument2 pagesQ-Free Quartz Sensor: Product SheetRobert CalcanNo ratings yet
Smacna Hvac Duct Construction Standards
Smacna Hvac Duct Construction Standards
Uploaded by
MEP EngineeringOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Smacna Hvac Duct Construction Standards
Smacna Hvac Duct Construction Standards
Uploaded by
MEP EngineeringCopyright:
Available Formats
>
CHAPTER 3 ROUND. OVAL. AND FLEXIBLE DUCT
ROUND DUCT CONSTRUCTION STANDARDS .................................................................... 3.7
. . . . .MITERED
. . . . . . . . . . .ELBOWS
. . . . . . . . . . .TABLE
. . . . . . . . 3-1
..... 3.1
COMMENTARY.........................................................................................................................3.2
ROUND DUCT GAGE UNREINFORCED POSITIVE PRESSURE TABLE 3.2A .....................3.3
ROUND DUCT GAGE NEGATIVE PRESSURE TABLE 3.28 .................................................. 3.5
ALUMINUM ROUND DUCT GAGE SCHEDULE TABLE 3-3 .................................................. 3.7
.
.
SEAMS-ROUND DUCT AND F l n l N G S FIGURE 3-1 .......................... ............................. 3.8
TRANSVERSE JOINTS-ROUND DUCT FIGURE 3-2 .............................................................3.9
ROUND DUCT ELBOWS FIGURE 3-3 ................................................................................. 3.10
90 DEGREES TEES AND LATERALS FIGURE 3-4 ............................................................... 3.11
CONICAL TEES FIGURE 3-5 .................................................................................................. 3.12
FLAT OVAL DUCT CONSTRUCTION STANDARDS ..............................................................3.13
COMMENTARY ........................................................................................................................
3.13
FLAT OVAL DUCT CONSTRUCTION TABLE 3-4 ..................................................................3.13
FLAT OVAL DUCTS FIGURE 3-6 ......................................................................................... 3.14
FLEXIBLE DUCT INSTALLATION STANDARDS .................................................................. 3.15
TYPES OF FLEXIBLE DUCT FIGURE 3-7 ........................................................................... 3.16
SPECIFICATION FOR JOINING AND ATTACHING FLEXIBLE DUCT ................................. 3.17
SPECIFICATION FOR SUPPORTING FLEXIBLE DUCT ..................................................... 3.19
FLEXIBLE DUCT SUPPORTS FIGURE 3-9 ........................................................................ 3.20
FLEXIBLE DUCT SUPPORTS FIGURE 3-10 ........................................................................ 3.21
COMMENTARY...................................................................................................................... 3.22
UNDERGROUND DUCT CONSTRUCTION STANDARDS .................................................... 3.23
TYPICAL UNDERSLAB DUCT FIGURE 3-11 ......................................................................... 3.24
ANCHORS FOR DUCT ENCASEMENT FIGURE 3-12 ..........................................................3.25
COMMENTARY........................................................................................................................3.26
CHAPTER 4 HANGERS AND SUPPORTS
4.1 HANGING AND SUPPORTING SYSTEMS .............................................................................. 4.1
4.2 COMMENTARY .........................................................................................................................
4.1
HANGER ATACHMENTS TO STRUCTURES FIGURE 4-1 ................................................4.3
UPPER ATTACHMENT DEVICES-TYPICAL FIGURE 4-2 ......................................................4.4
UPPER ATTACHMENTS-TYPICAL FIGURE 4-3 ................................................................... 4.5
RECTANGULAR DUCT HANGERS MINIMUM SIZE TABLE 4-1 ............................................ 4.6
MINIMUM HANGER SIZES FOR ROUND DUCT TABLE 4.2 ................................................. 4.8
LOWER HANGER ATTACHMENTS FIGURE 4-4 ....................................................................4.9
ALLOWABLE LOADS FOR TRAPEZE BARS TABLE 4-3 ....................................................... 4.10
TRAPEZE LOAD DIAGRAM FIGURE 4-5 .............................................................................. 4.12
LARGE DUCT SUPPORT FIGURE 4-6 ................................................................................. 4.13
RISER SUPP.QRTS-FROM FLOOR FIGURE 4-7 ................:............................................... 4.14
SUPPORTS FROM WALL FIGURE 4-8 AND TABLE 4-4 ..................................................... 4.16
RISER SUPPORT-FROM FLOOR FIGURE 4-9 ................................................................... 4.18
HVAC UNIT SUSPENSION FIGURE 4-10 .............................................................................. 4.19
CHAPTER 5 EXTERIOR COMPONENTS
5.1 INTRODUCTION .................................................................................................................... 5.1
LOUVERS AND SCREENS FIGURE 5-1 ................................................................................5.2
LOUVER FREE AREA CALCULATION FIGURE 5-2 ............................................................... 5.4
5.2 ROOFTOP EQUIPMENT INSTALLATION .......................... .
. ............................................. 5.5
5.3 COMMENTARY ......................................................................................................................... 5.5
ROOFTOP DUCT INSTALLATION FIGURE 5-3 ...................................................................... 5.6
EQUIPMENT AND DUCT SUPPORT FLASHING FIGURE 5-4 ............................................... 5.7
HVAC DUCT CONSTRUCTION STANDARDS METAL AND FLEXIBLE ix
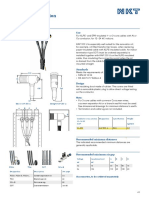
2.2 VOLUME DAMPERS Modified versions can be constructed for tight shut off.
2.3 NOTES FOR FIGURES 2-12 AND 2-13 OBD (opposed blade damper) devices installed with
grilles anddiffusers shouldnot be reliedon to take more
than 114 to 112 closure without noise.
1. Unless otherwise permitted, dampers shall be
provided with the general configuration, materials,
andapplication limits indicated in Figures2-14 and Single-blade or opposed-blade dampers are preferred
2- 15 and in related notes. over splitters.
2. Damper hardware must be durable and installed Oriticeplatesorperforatedmetalwithrequiredpressure-
properly. dropcharacteristics may be used in lieuofdampers to set
up permanent loss in duct runs.
3. Dampers must be stable underoperatingconditions.
Round and rectangular damper blades must be Multiblade damper styles are normally parallel blade
stiffened by formingorothermethod ifrequired for fortwo positionoperation; opposed blade formodulating
position.
the duty.
Dampcrs with bladc lengths over 48" (1219 mm) arc
4. All single bladedampersmusthavealockir~gdevice
normally sectioned horizontally.
to hold the dampers in a fixed position without
vibration.
Motor operators for dampers should develop sufficient
5. Damper component penetration of ducts must be torque to operate properly. l'he motor supplier should
closed, in keeping with the sealing classification select operatorscarefully. In certaincases, afire damper
applicable for the pressure class. End bearings or may be used for flow rate control. If it serves a dual
other seals are required on 3" w.g. (750 Pa) static function, its operation as a fire damper must not be
pressure class. impaired. The installation must not develop noise or
vibration.
6. Theinstallationofadamperinalinedductmustnot
damage the liner or cause liner erosion. Volume control devices that are capable of throttling
flowoverwide pressure differentials withoutgenerating
noise are normally special procurement items. Low-
2.4 COMMENTARY
pressure drop dampers should not be used for wide-
pressure differentials.
Designers must show all required air volume control
devices on the contract drawings. Nothing in this
Consult duct design texts and manufacturer's data for
document implies an obligation to provide volume
loss coefficients.
control devices that are not on the contract drawings.
The ASHRAE Syslerns Hondbook chapter on testing, The designer must carefully evaluate pressure change in
adjusting, and balancing defines ducts as follows: a dkcts and provide pressure relief measures where
necessary. System status changes, as in smoke control
mainductservesthesyste~'smajororentire fluid flow;
mode or energy conservation use, impose different
a submain serves two or more branch mains; a branch
requirements for normally open, normally closed, and
main serves two or yore terminals; a branch serves a
modulathg dampers.
single terminal."lllustrating dampers on contract
drawings relieves contractors from interpreting damper
requirements.
Thedamperdesigns illustrated in Figures2-14 and2-15
are for reducedvolumecontrol, not for positive shut off.
-
HVAC Duct Construction Standards Metal and Flexible Second Edition 2.15
You might also like
- Seismic Restraint Manual 2008 LatestDocument202 pagesSeismic Restraint Manual 2008 LatestHassaan HameedNo ratings yet
- CAT Service Manuals TL642 TL943Document197 pagesCAT Service Manuals TL642 TL943Shivanan Singh100% (7)
- SMACNA Duct Construction Standards - 3rd Edition - 2005Document396 pagesSMACNA Duct Construction Standards - 3rd Edition - 2005Eric E' Sandoval A100% (7)
- Tl642 Cat Services Manual TelehandlerDocument197 pagesTl642 Cat Services Manual TelehandlerRoxana Elizabeth Valencia NavarrteNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE Temperature Tables For All US CitiesDocument12 pagesASHRAE Temperature Tables For All US Citiespuneetmathur8247100% (3)
- Gradall 534D-9 PartsDocument710 pagesGradall 534D-9 PartsAlejandro Bonilla100% (4)
- Tl1055 Service ManualDocument178 pagesTl1055 Service ManualJose Cruz Martinez Medina100% (1)
- Service Manual TL642 TL943 PDFDocument196 pagesService Manual TL642 TL943 PDFGeorge Guerrero100% (3)
- Specification For Phenolic Duct Works SystemsDocument2 pagesSpecification For Phenolic Duct Works Systemspsn_kylm100% (1)
- 2019 ASHRAE Handbook HVAC Applications SI Swimming PoolDocument8 pages2019 ASHRAE Handbook HVAC Applications SI Swimming PoolTsz Ho LAI100% (1)
- Smacna Duct ConstructionDocument23 pagesSmacna Duct ConstructionKaustubh Bidkar100% (2)
- RTS Example Montreal ASHRAE Chapter 6oct2003Document26 pagesRTS Example Montreal ASHRAE Chapter 6oct2003Sid KherNo ratings yet
- SMACNA Round Industrial Duct Construction Standards - Chapter 2 Industrial Duct ApplicationsDocument2 pagesSMACNA Round Industrial Duct Construction Standards - Chapter 2 Industrial Duct ApplicationsMinh Tran50% (2)
- ASHRAE Fundamentals Handbook (2009)Document2 pagesASHRAE Fundamentals Handbook (2009)Luís Fernando Ferreira Silva50% (2)
- Part 1. Load Estimating - Chapter 4. Solar Heat Gain Thru GlassDocument3 pagesPart 1. Load Estimating - Chapter 4. Solar Heat Gain Thru Glasskiran raghukiranNo ratings yet
- Smacna Industrial Rounded Duct Construction Tabla ContenidosDocument4 pagesSmacna Industrial Rounded Duct Construction Tabla Contenidosedgar_glezav0% (3)
- VRV Xpress Manual V612 Tcm135-168625Document82 pagesVRV Xpress Manual V612 Tcm135-168625Cărunta-Crista Sergiu83% (6)
- York Fan Coil UnitDocument16 pagesYork Fan Coil Unitjaja100% (3)
- 1922Document301 pages1922Rafael Leonardo GomezNo ratings yet
- Servicio tl642cDocument206 pagesServicio tl642cpablo100% (4)
- Caterpillar JLG Parts ManualDocument320 pagesCaterpillar JLG Parts ManualJuan Esteban Sloboda Aranguren100% (1)
- HAP Thermal Load Cal - FormulaDocument19 pagesHAP Thermal Load Cal - Formulamajortay100% (1)
- ASHRAE Article - Boiler Ventilation PDFDocument8 pagesASHRAE Article - Boiler Ventilation PDFrfriosEPNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE Journal - VAV System Duct Main DesignDocument5 pagesASHRAE Journal - VAV System Duct Main DesignJhoNo ratings yet
- Carrier 23XL Product Data 1996Document48 pagesCarrier 23XL Product Data 1996DaveEger100% (1)
- ASHRAE Commercial Duct CalculationsDocument4 pagesASHRAE Commercial Duct CalculationsNirmal KvNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Ventilation ExistinghomesDocument35 pagesEvaluating Ventilation ExistinghomesKatamba RogersNo ratings yet
- Heat Gain From Electrical and Control Equipment in Industrial Plants, Part II, ASHRAE Research Project RP-1395Document4 pagesHeat Gain From Electrical and Control Equipment in Industrial Plants, Part II, ASHRAE Research Project RP-1395Michael LagundinoNo ratings yet
- Duct DesignDocument32 pagesDuct DesignsupportLSMNo ratings yet
- Ductwork Leakage Testing: A Practical Guide ToDocument17 pagesDuctwork Leakage Testing: A Practical Guide ToGoyal SanjaiNo ratings yet
- Ashrae Pocket Guide I P PDFDocument36 pagesAshrae Pocket Guide I P PDFMUKESH DAYMANo ratings yet
- ESM DUCT CALCULATOR Rev2Document1 pageESM DUCT CALCULATOR Rev2qwerty_conanNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE HVAC 2001 Fundamentals HandbookDocument6 pagesASHRAE HVAC 2001 Fundamentals HandbookJosé A. Ramírez100% (1)
- Round Industrial Duct Construction Standards: Sheet Metal and Air Conditioning Contractors' National Association, IncDocument19 pagesRound Industrial Duct Construction Standards: Sheet Metal and Air Conditioning Contractors' National Association, IncNathanNo ratings yet
- Ashrae: Laboratory Design GuideDocument12 pagesAshrae: Laboratory Design GuideAlex PullaNo ratings yet
- Comfort and Critical Outdoor Design ConditionsDocument6 pagesComfort and Critical Outdoor Design ConditionshueyliewNo ratings yet
- 2005 Smacna Shop Standards For Rectangular Duct ConstructionDocument6 pages2005 Smacna Shop Standards For Rectangular Duct ConstructionAshiq IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Titus Engineering Guidelines Grilles and Diffusers Engineering Data B13269Document34 pagesTitus Engineering Guidelines Grilles and Diffusers Engineering Data B13269Renan GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Construction Standards: Accepted Industry Practices For Sheet Metal LaggingDocument13 pagesConstruction Standards: Accepted Industry Practices For Sheet Metal LaggingTeoxNo ratings yet
- VRF Installation Quick GuideDocument84 pagesVRF Installation Quick GuideErwin MaldoNo ratings yet
- ASHRAE CH 12 (Hydronic Heating and Cooling System Design)Document18 pagesASHRAE CH 12 (Hydronic Heating and Cooling System Design)RIYANTO BEBETNo ratings yet
- Aeroflex Main New Catalog PDFDocument32 pagesAeroflex Main New Catalog PDFnaren233No ratings yet
- Dynair Ecology UnitDocument12 pagesDynair Ecology Unitrid100% (1)
- Smacna Duct LeakageDocument3 pagesSmacna Duct Leakageanton7786No ratings yet
- Ashrae Duct PDFDocument3 pagesAshrae Duct PDFAnonymous XhkjXCxxsTNo ratings yet
- HVAC - How To Size and Design (CED Engineering) (Static Loss, Etc)Document91 pagesHVAC - How To Size and Design (CED Engineering) (Static Loss, Etc)Zulfadzli RidzuanNo ratings yet
- Rectangular Duct & FittingsDocument26 pagesRectangular Duct & Fittingsmakmak90% (1)
- Duct Construction ChartDocument23 pagesDuct Construction ChartMattNo ratings yet
- AL HVAC Contractor Comprehensive Tutorial 10Document278 pagesAL HVAC Contractor Comprehensive Tutorial 10William Worrell100% (1)
- HVAC Duct Construction StandardsDocument308 pagesHVAC Duct Construction StandardsGuilherme Valadares100% (1)
- Smacna Fire Smoke Combined Dampers 1Document64 pagesSmacna Fire Smoke Combined Dampers 1Santiago J. ramos jr100% (5)
- Ductwork Leakage & Leak Testing JournalDocument9 pagesDuctwork Leakage & Leak Testing JournalAlex ChinNo ratings yet
- Duct Fittings LossesDocument42 pagesDuct Fittings LossesmostafaabdelrazikNo ratings yet
- Air Distribution SystemDocument21 pagesAir Distribution SystemRohit JainNo ratings yet
- Ventilation For Commercial Cooking Operations: ANSI/ASHRAE Addendum C To ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 154-2016Document5 pagesVentilation For Commercial Cooking Operations: ANSI/ASHRAE Addendum C To ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 154-2016mahboobNo ratings yet
- HVAC - Duct ConstructionDocument75 pagesHVAC - Duct ConstructionGaapchu100% (2)
- VRF Test MethodDocument6 pagesVRF Test Methodprado01No ratings yet
- Cargador TELEHANDLER PDFDocument454 pagesCargador TELEHANDLER PDFFersigal GalsiferNo ratings yet
- Telehandler TL642C - TL943C (Thg00150&after - Thl00150&after - Thh00150&after - Sxh00150&after) PDFDocument446 pagesTelehandler TL642C - TL943C (Thg00150&after - Thl00150&after - Thh00150&after - Sxh00150&after) PDFChristian Andy H. ChavezNo ratings yet
- Ee 6 FinalsDocument3 pagesEe 6 FinalsSantos, Jewella C.No ratings yet
- 12h Parking BrakeDocument4 pages12h Parking Brakeaniri100% (1)
- 25 - Quinte Series EnglishDocument14 pages25 - Quinte Series EnglishJajang NurwandiNo ratings yet
- Hospital Electrical Design BookletDocument52 pagesHospital Electrical Design Bookletssubup100% (3)
- WCF-SERIES-Top Suspension Manual PDFDocument36 pagesWCF-SERIES-Top Suspension Manual PDFYiannis ToufexisNo ratings yet
- Retrofit Kits Technical BrochureDocument10 pagesRetrofit Kits Technical BrochureISHAN VERMANo ratings yet
- ESP Price List 01 May 2024Document121 pagesESP Price List 01 May 2024Devender KumarNo ratings yet
- Viii. Troubleshooting Circulation Pump - Service Index UC/06, UC/11 & UC/12 Parts ChangesDocument4 pagesViii. Troubleshooting Circulation Pump - Service Index UC/06, UC/11 & UC/12 Parts ChangesnilsNo ratings yet
- Firealrm, Detection&Tele 3Document23 pagesFirealrm, Detection&Tele 3Kumar DigvijayNo ratings yet
- Common Service Panel SLDDocument1 pageCommon Service Panel SLDVikasNehraNo ratings yet
- JVC Av-2115ee Chassis CGDocument150 pagesJVC Av-2115ee Chassis CGDarwin Yasmani Martinez ColqueNo ratings yet
- Leviton Highbay Occupancy SensorDocument4 pagesLeviton Highbay Occupancy SensorMohammed YasarNo ratings yet
- Goodwinch Limited: Importers, Exporters, Wholesale Distributors and Retailers of Winches and AccessoriesDocument5 pagesGoodwinch Limited: Importers, Exporters, Wholesale Distributors and Retailers of Winches and AccessoriesPzan PeacemakerNo ratings yet
- KAP 12-24 KV 300 ENACC MVACC DS ENDocument1 pageKAP 12-24 KV 300 ENACC MVACC DS ENMd Imran pashaNo ratings yet
- Floor Plan of Kitchen & Dinning Room: D. Dry StorageDocument1 pageFloor Plan of Kitchen & Dinning Room: D. Dry StoragedejomarlubNo ratings yet
- GamLaser EX5Document4 pagesGamLaser EX5AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Pec Yellow + Zabala Sure 13 PagesDocument13 pagesPec Yellow + Zabala Sure 13 PagesTeddy GutayNo ratings yet
- Pasolink Maintenance Qref v2.0Document40 pagesPasolink Maintenance Qref v2.0pankajengNo ratings yet
- 938K Eletrico Serie AltaDocument39 pages938K Eletrico Serie AltaEmanoel FelipeNo ratings yet
- DUNGS GW 150 A6 (Pressure Switch Aux Boiler)Document6 pagesDUNGS GW 150 A6 (Pressure Switch Aux Boiler)mt.sasongkoNo ratings yet
- Twin Leaf Boring Bars - Sigma Toolings, Fine Boring Tools, Cutting Tools ManufacturerDocument3 pagesTwin Leaf Boring Bars - Sigma Toolings, Fine Boring Tools, Cutting Tools ManufacturerSigma ToolingsNo ratings yet
- Surface PlateDocument3 pagesSurface PlateSaket OraonNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 2N59-1R-200-45Document5 pagesDatasheet 2N59-1R-200-45Bennie ManionNo ratings yet
- Instructions Manual KF8000E KF10000E Multilingual 070207Document56 pagesInstructions Manual KF8000E KF10000E Multilingual 070207Hoff Beer100% (2)
- Nd3361 Hgs620 Termadv Jun12Document10 pagesNd3361 Hgs620 Termadv Jun12Mohamed RafihNo ratings yet
- EE110 Obias Gilbert LM2 3-1Document1 pageEE110 Obias Gilbert LM2 3-1Gilbert ObiasNo ratings yet
- 2017 Trijicon CatalogDocument87 pages2017 Trijicon CatalogАлександр100% (1)
- Registration of Electrical ContractorsDocument69 pagesRegistration of Electrical ContractorsKevin NdetiNo ratings yet
- Legend DSLNGDocument13 pagesLegend DSLNGTim DuncanNo ratings yet
- Q-Free Quartz Sensor: Product SheetDocument2 pagesQ-Free Quartz Sensor: Product SheetRobert CalcanNo ratings yet