Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 viewsBEE Bits
BEE Bits
Uploaded by
singamgiridharreddy13691Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Circuit TheoryDocument33 pagesCircuit Theoryavi713331No ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Question BankDocument33 pagesCircuit Theory Question BankGayathri RSNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Question BankDocument33 pagesCircuit Theory Question Bankaishuvc1822No ratings yet
- Ee6201 Circuit Question BankDocument33 pagesEe6201 Circuit Question BankBanu ChandarNo ratings yet
- BEE Orals 22-23Document8 pagesBEE Orals 22-23rohan prakashNo ratings yet
- Basics of Power SystemsDocument63 pagesBasics of Power SystemsAravind BalaNo ratings yet
- Pee Unit 1 NotesDocument9 pagesPee Unit 1 NotesGopi chand GamerNo ratings yet
- Ecs 2Document30 pagesEcs 2vedanth patilNo ratings yet
- Circuit Elements: Voltage & Current Sources Electrical Resistance (Ohm's Law) Kirchhoff's LawsDocument26 pagesCircuit Elements: Voltage & Current Sources Electrical Resistance (Ohm's Law) Kirchhoff's Lawsgulzar ahmadNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit1 (BEEE)Document48 pagesNotes Unit1 (BEEE)Vedashree ShetyeNo ratings yet
- NA Unit-1Document99 pagesNA Unit-1phani5016No ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Question Bank, 2 Marks With AnswersDocument0 pagesCircuit Theory Question Bank, 2 Marks With Answersaishuvc1822No ratings yet
- Phy Pract Viva QNDocument19 pagesPhy Pract Viva QNkunala523No ratings yet
- Cie-Part B QBDocument4 pagesCie-Part B QBMURUGAN SUBRAMANIANNo ratings yet
- Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesElectrical Engineeringmaruder.sllayerNo ratings yet
- BEEM 2marks PDFDocument40 pagesBEEM 2marks PDFPragna Sidhireddy100% (1)
- Circuit Theory Question Bank - CIT EditionDocument33 pagesCircuit Theory Question Bank - CIT EditionMichael FosterNo ratings yet
- Lesson: ElectricityDocument13 pagesLesson: Electricitybudesasaiaw.v.re32.90No ratings yet
- NUMERICAL - Electricity & Its Effects For (Class X)Document6 pagesNUMERICAL - Electricity & Its Effects For (Class X)Gayathiri SureshNo ratings yet
- EE-1151 CT SubmittedDocument26 pagesEE-1151 CT Submittedbala_c84111No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Direct Current Circuits1Document8 pagesLesson 5 Direct Current Circuits1AjzNo ratings yet
- Physics Project 12Document16 pagesPhysics Project 12Ashmi LoukyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit Analysis: Part-ADocument10 pagesBasic Circuit Analysis: Part-AmanoprabhaNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument107 pagesElectric CircuitsKristine Cris VenusNo ratings yet
- Physics year projectDocument8 pagesPhysics year projectdivyasriravi287No ratings yet
- General Electrial McqsDocument48 pagesGeneral Electrial Mcqszain zafar100% (1)
- MC Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pagesMC Electrical CircuitsMelvin Garcia QuirosNo ratings yet
- Current and ResistanceDocument42 pagesCurrent and ResistancehelsaNo ratings yet
- Network AnalysisDocument20 pagesNetwork AnalysisRamesh DongaraNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Class 12 Viva Questions With Answers - 2Document5 pagesPhysics Practical Class 12 Viva Questions With Answers - 2dick kumarNo ratings yet
- Important Viva QuestionsDocument19 pagesImportant Viva QuestionsAtul TripathiNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument8 pagesSample QuestionsSong BrokerNo ratings yet
- AC and DC CircuitsDocument87 pagesAC and DC Circuitsjan paul OmandapNo ratings yet
- Is Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityDocument3 pagesIs Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityAshok Pradhan100% (1)
- Physics PresentationDocument24 pagesPhysics PresentationGrace jereNo ratings yet
- Study MaterialsDocument47 pagesStudy MaterialsGURU DAKKUNo ratings yet
- Tema 2 FizikaDocument6 pagesTema 2 Fizika4p4xvyqtfqNo ratings yet
- NUMERICALS On Electricity-10Document5 pagesNUMERICALS On Electricity-10Tanmay PandeyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 12 AnswersDocument12 pagesAssignment 12 AnswersNanda KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Circuit Analysis Techniques: "The Algebraic Sum of All Currents Entering and Exiting A Node Must Equal Zero"Document32 pagesUnit-I Circuit Analysis Techniques: "The Algebraic Sum of All Currents Entering and Exiting A Node Must Equal Zero"Suresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Join @cbse10bystudentshelper On TelegramDocument26 pagesOhm's Law: Join @cbse10bystudentshelper On TelegramValerie CoxNo ratings yet
- Circuit TheoryDocument13 pagesCircuit TheoryMANIKANDAN MNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument9 pagesElectricitymohametabdirahman334No ratings yet
- Unit 9 NotesDocument17 pagesUnit 9 Notesyooh9814No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument12 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsAnandhi SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (ECE)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank (ECE)Manav JainNo ratings yet
- Bee MidtermsDocument103 pagesBee MidtermsROSABELLE CABADINNo ratings yet
- Electrical Interview QuestionsDocument43 pagesElectrical Interview QuestionsIsabella Swan100% (1)
- First-Order Circuits: Presented By: Gabriel BacaniDocument8 pagesFirst-Order Circuits: Presented By: Gabriel Bacanikhrid3No ratings yet
- Cns-Ee1 PDFDocument9 pagesCns-Ee1 PDFLanbert FranciscoNo ratings yet
- ECE131 Unit 1 Lecture 2Document35 pagesECE131 Unit 1 Lecture 2Vijay ReddyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On Unit IDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank On Unit IanupamNo ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument6 pagesCapacitorPramod BokdeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Interview QuestionsDocument43 pagesElectrical Interview QuestionsAbbas JaveedNo ratings yet
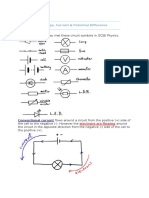
- Electricity: Circuit Symbols - You Met These Circuit Symbols in GCSE PhysicsDocument22 pagesElectricity: Circuit Symbols - You Met These Circuit Symbols in GCSE PhysicsBaberBegNo ratings yet
- Phy Assinment 2Document5 pagesPhy Assinment 2umarirfan208No ratings yet
- Common Course BrainStorming Questions FinallDocument107 pagesCommon Course BrainStorming Questions Finallassefag92No ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Title and SummaryDocument1 pageTitle and Summarysingamgiridharreddy13691No ratings yet
- StudentsDocument3 pagesStudentssingamgiridharreddy13691No ratings yet
- Preprocessor DirectivesDocument7 pagesPreprocessor Directivessingamgiridharreddy13691No ratings yet
- RecursionsDocument8 pagesRecursionssingamgiridharreddy13691No ratings yet
BEE Bits
BEE Bits
Uploaded by
singamgiridharreddy136910 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesOriginal Title
BEE Bits (1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesBEE Bits
BEE Bits
Uploaded by
singamgiridharreddy13691Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
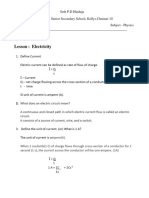
1) The unit of resistance is in ohms.
2) The unit of inductance is in Henries
3) The unit of capacitance is in farads
4) The resister is a element which dissipates the energy in the form of heat.
5) Inductor is a element which stores the energy in the form of magnetic field/current.
6) capacitor is a element which stores the energy in the form of electric field/voltage.
7) According to ohms law applied voltage is directly proportional to current and current
inversely proportional to resistance.
8) Superposition theorem is applicable for linear circuits only.
9) Time constant of series RL circuits is (L/R)
10) Time constant for series RC circuits is RC.
11) As per the Thevenin’s equivalent circuit diagram, the voltage source is connected in
series with the internal resistance.
12) As per the Nortons equivalent circuit diagram, the current source is connected in
parallel with the internal resistance.
13) Resister does not store any energy.
14) Inductor does not allow sudden change in current.
15) Capacitor does not allow sudden change in voltage.
16) A element which deliver electrical energy is called active element.
17) A element which absorbs the electrical energy is called the passive element.
18) Practical voltage source consisting of voltage source connected in series with internal
resistance.
19) Practical current source consisting of current source connected in parallel with
internal resistance.
20) Nodal analysis is depending on KCL.
21) Mesh analysis is depending on KVL.
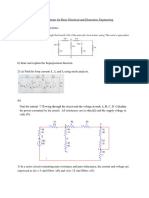
22) What is the equivalent resistance if two 10-ohm resistors are connected in series.
23) What is the equivalent resistance if two 10-ohm resistors are connected in parallel.
24) Define ohms law.
25) Define KCL.
26) Define KVL.
27) If 20V voltage source is connected across the the 100 Ohm resistor, then what is the
current in the circuit?
28) The frequency in dc circuits is zero.
29) The frequency in AC circuit is not equal to zero, Indian standard frequency is 50
Hertz.
30) Superposition theorem is not applicable for power.
You might also like
- Circuit TheoryDocument33 pagesCircuit Theoryavi713331No ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Question BankDocument33 pagesCircuit Theory Question BankGayathri RSNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Question BankDocument33 pagesCircuit Theory Question Bankaishuvc1822No ratings yet
- Ee6201 Circuit Question BankDocument33 pagesEe6201 Circuit Question BankBanu ChandarNo ratings yet
- BEE Orals 22-23Document8 pagesBEE Orals 22-23rohan prakashNo ratings yet
- Basics of Power SystemsDocument63 pagesBasics of Power SystemsAravind BalaNo ratings yet
- Pee Unit 1 NotesDocument9 pagesPee Unit 1 NotesGopi chand GamerNo ratings yet
- Ecs 2Document30 pagesEcs 2vedanth patilNo ratings yet
- Circuit Elements: Voltage & Current Sources Electrical Resistance (Ohm's Law) Kirchhoff's LawsDocument26 pagesCircuit Elements: Voltage & Current Sources Electrical Resistance (Ohm's Law) Kirchhoff's Lawsgulzar ahmadNo ratings yet
- Notes Unit1 (BEEE)Document48 pagesNotes Unit1 (BEEE)Vedashree ShetyeNo ratings yet
- NA Unit-1Document99 pagesNA Unit-1phani5016No ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Question Bank, 2 Marks With AnswersDocument0 pagesCircuit Theory Question Bank, 2 Marks With Answersaishuvc1822No ratings yet
- Phy Pract Viva QNDocument19 pagesPhy Pract Viva QNkunala523No ratings yet
- Cie-Part B QBDocument4 pagesCie-Part B QBMURUGAN SUBRAMANIANNo ratings yet
- Electrical EngineeringDocument3 pagesElectrical Engineeringmaruder.sllayerNo ratings yet
- BEEM 2marks PDFDocument40 pagesBEEM 2marks PDFPragna Sidhireddy100% (1)
- Circuit Theory Question Bank - CIT EditionDocument33 pagesCircuit Theory Question Bank - CIT EditionMichael FosterNo ratings yet
- Lesson: ElectricityDocument13 pagesLesson: Electricitybudesasaiaw.v.re32.90No ratings yet
- NUMERICAL - Electricity & Its Effects For (Class X)Document6 pagesNUMERICAL - Electricity & Its Effects For (Class X)Gayathiri SureshNo ratings yet
- EE-1151 CT SubmittedDocument26 pagesEE-1151 CT Submittedbala_c84111No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Direct Current Circuits1Document8 pagesLesson 5 Direct Current Circuits1AjzNo ratings yet
- Physics Project 12Document16 pagesPhysics Project 12Ashmi LoukyaNo ratings yet
- Basic Circuit Analysis: Part-ADocument10 pagesBasic Circuit Analysis: Part-AmanoprabhaNo ratings yet
- Electric CircuitsDocument107 pagesElectric CircuitsKristine Cris VenusNo ratings yet
- Physics year projectDocument8 pagesPhysics year projectdivyasriravi287No ratings yet
- General Electrial McqsDocument48 pagesGeneral Electrial Mcqszain zafar100% (1)
- MC Electrical CircuitsDocument8 pagesMC Electrical CircuitsMelvin Garcia QuirosNo ratings yet
- Current and ResistanceDocument42 pagesCurrent and ResistancehelsaNo ratings yet
- Network AnalysisDocument20 pagesNetwork AnalysisRamesh DongaraNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Class 12 Viva Questions With Answers - 2Document5 pagesPhysics Practical Class 12 Viva Questions With Answers - 2dick kumarNo ratings yet
- Important Viva QuestionsDocument19 pagesImportant Viva QuestionsAtul TripathiNo ratings yet
- Sample QuestionsDocument8 pagesSample QuestionsSong BrokerNo ratings yet
- AC and DC CircuitsDocument87 pagesAC and DC Circuitsjan paul OmandapNo ratings yet
- Is Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityDocument3 pagesIs Electric Current A Scalar or Vector QuantityAshok Pradhan100% (1)
- Physics PresentationDocument24 pagesPhysics PresentationGrace jereNo ratings yet
- Study MaterialsDocument47 pagesStudy MaterialsGURU DAKKUNo ratings yet
- Tema 2 FizikaDocument6 pagesTema 2 Fizika4p4xvyqtfqNo ratings yet
- NUMERICALS On Electricity-10Document5 pagesNUMERICALS On Electricity-10Tanmay PandeyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 12 AnswersDocument12 pagesAssignment 12 AnswersNanda KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit-I Circuit Analysis Techniques: "The Algebraic Sum of All Currents Entering and Exiting A Node Must Equal Zero"Document32 pagesUnit-I Circuit Analysis Techniques: "The Algebraic Sum of All Currents Entering and Exiting A Node Must Equal Zero"Suresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Ohm's Law: Join @cbse10bystudentshelper On TelegramDocument26 pagesOhm's Law: Join @cbse10bystudentshelper On TelegramValerie CoxNo ratings yet
- Circuit TheoryDocument13 pagesCircuit TheoryMANIKANDAN MNo ratings yet
- ElectricityDocument9 pagesElectricitymohametabdirahman334No ratings yet
- Unit 9 NotesDocument17 pagesUnit 9 Notesyooh9814No ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument12 pagesElectronic Devices and CircuitsAnandhi SrinivasanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank (ECE)Document7 pagesQuestion Bank (ECE)Manav JainNo ratings yet
- Bee MidtermsDocument103 pagesBee MidtermsROSABELLE CABADINNo ratings yet
- Electrical Interview QuestionsDocument43 pagesElectrical Interview QuestionsIsabella Swan100% (1)
- First-Order Circuits: Presented By: Gabriel BacaniDocument8 pagesFirst-Order Circuits: Presented By: Gabriel Bacanikhrid3No ratings yet
- Cns-Ee1 PDFDocument9 pagesCns-Ee1 PDFLanbert FranciscoNo ratings yet
- ECE131 Unit 1 Lecture 2Document35 pagesECE131 Unit 1 Lecture 2Vijay ReddyNo ratings yet
- Question Bank On Unit IDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank On Unit IanupamNo ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument6 pagesCapacitorPramod BokdeNo ratings yet
- Electrical Interview QuestionsDocument43 pagesElectrical Interview QuestionsAbbas JaveedNo ratings yet
- Electricity: Circuit Symbols - You Met These Circuit Symbols in GCSE PhysicsDocument22 pagesElectricity: Circuit Symbols - You Met These Circuit Symbols in GCSE PhysicsBaberBegNo ratings yet
- Phy Assinment 2Document5 pagesPhy Assinment 2umarirfan208No ratings yet
- Common Course BrainStorming Questions FinallDocument107 pagesCommon Course BrainStorming Questions Finallassefag92No ratings yet
- Complete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsFrom EverandComplete Electronics Self-Teaching Guide with ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Title and SummaryDocument1 pageTitle and Summarysingamgiridharreddy13691No ratings yet
- StudentsDocument3 pagesStudentssingamgiridharreddy13691No ratings yet
- Preprocessor DirectivesDocument7 pagesPreprocessor Directivessingamgiridharreddy13691No ratings yet
- RecursionsDocument8 pagesRecursionssingamgiridharreddy13691No ratings yet