Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 16 Hearing Sense
Lesson 16 Hearing Sense
Uploaded by
musmanshahid660 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesLesson 16 hearing sense
Original Title
Lesson 16 hearing sense
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentLesson 16 hearing sense
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesLesson 16 Hearing Sense
Lesson 16 Hearing Sense
Uploaded by
musmanshahid66Lesson 16 hearing sense
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Introduction to Psychology 114
PSY101
Lecture no: 16
HEARING (AUDITION) AND BALANCE
Hearing or audition is the sense of sound perception and results from tiny hair fibers in
the inner ear detecting the motion of a membrane which vibrates in response to changes
in the pressure exerted by atmospheric particles within (at best) a range of 20 to 20000
Hz. Sound can also be detected as vibrations conducted through the body by tactician.
Lower and higher frequencies than can be heard are detected this way only. The main
features regarding ear are:
• Ear is regarded as the organ of hearing.
• Like our other senses, our hearing or audition, is highly adaptive
• Sense of motion and balance is regarded as the main and important function of
the ear
• Organisms have the ability to hear a wide range of sounds with different
frequencies (ranging from higher to very low faint voice)__ but more importantly
we can easily detect different voices of people whom we know or met
• For this, the important question is how we do it? How the transformation of sound
waves into neural messages takes place?
Some Interesting Facts About Hearing:
• Animals have the capability of hearing more sounds than humans
• Dolphins have the best sense of hearing among all animals
• When people go up high in the mountains, the changes in pressure cause the ear to
pop
• Babies can get ear aches because of the milk deposit in the eustachian tube, which
helps the bacteria to grow there and may cause problems later in life
• Children can hear more noises than adults, as their ears are more sensitive than
that of adults
• Ear aches result when too much fluid causes pressure in the eardrum__ often
occur due to allergies, virus or some sort of infection
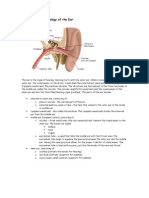
THE HUMAN EAR: ANATOMY/ STRUCTURE:
The primary apparatus of hearing i.e., the ear is divided into three parts
I. The outer ear
II. The middle ear
III. The inner ear
©Copyright Virtual University of Pakistan 114
Introduction to Psychology 115
PSY101
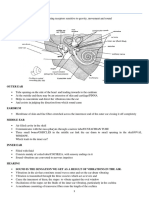
THE OUTER EAR
• The outer ear serves the function of collecting the sound waves from the
environment to the internal portions of the ear. It is shaped like a reverse megaphone
• It also plays an important role in locating the sound direction from which it
originates
Auditory Canal:
• When sound waves originate from the vibrating object, they then pass through the
auditory canal, which is a tube like passage through which the sound travels to the
inner part of the ear or “ the eardrum”.
Eardrum:
• The part of the ear that starts vibrating when sound waves strike/ hit it.
• Its intensity of vibration is dependent on how intense the sound waves are___ the more
intense the sound, the more intensely it vibrates.
• These vibrations are then transmitted to the “ middle ear”.
Middle Ear
• A tiny chamber between the eardrum and cochlea containing three bones---- the
hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup, which transmit vibrations to the oval window.
• These three bones have only one function, i.e. to convey/ transmit the message to the
inner ear.
• These bones are also effective in the sense that they strengthen
the stimulus (vibration) so that it can be easily heard.
©Copyright Virtual University of Pakistan 115
You might also like
- Stock Watson 4E Exercisesolutions Chapter3 InstructorsDocument25 pagesStock Watson 4E Exercisesolutions Chapter3 InstructorsRodrigo PassosNo ratings yet
- The Customer Experience Book - How To Design, Measure and Improve Customer Experience in Your Business (PDFDrive)Document233 pagesThe Customer Experience Book - How To Design, Measure and Improve Customer Experience in Your Business (PDFDrive)Vera Pratiwi Goenfi100% (1)
- The Human EarDocument8 pagesThe Human EarSohid BacusNo ratings yet
- Lec 7b HearingDocument12 pagesLec 7b Hearingshahbaz40764No ratings yet
- Diagram of The Ear and Its FunctionsDocument14 pagesDiagram of The Ear and Its Functionsmcheche12No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Ear. AreteDocument12 pagesAnatomy of The Ear. AreteBrandon AreteNo ratings yet
- Physiology of EarDocument20 pagesPhysiology of EarChippy SinghNo ratings yet
- Bio ProjectDocument23 pagesBio Projectsoumya mazumdarNo ratings yet
- SENSORYDocument15 pagesSENSORYThe noble savageNo ratings yet
- The Ear - AnatomyDocument47 pagesThe Ear - Anatomymuhendaaron33No ratings yet
- Parts and Functions of The Ear: Fact FileDocument5 pagesParts and Functions of The Ear: Fact FileJyoti MeenaNo ratings yet
- Hearing SenseDocument13 pagesHearing SenseLuis NietoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document5 pagesChapter 6shiela sumalinogNo ratings yet
- Assessing Ears: Cos, Dimple J. Danao, Vina de Jesus, Manuela Marie BSN1-ADocument36 pagesAssessing Ears: Cos, Dimple J. Danao, Vina de Jesus, Manuela Marie BSN1-ADimple CosNo ratings yet
- 5 Assessing EarsDocument18 pages5 Assessing EarsAnecito BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Hearing Outline: - AnatomyDocument82 pagesHearing Outline: - AnatomyFadil BachmidNo ratings yet
- Biruk and Yasin Part 2Document21 pagesBiruk and Yasin Part 2Biruk YenewNo ratings yet
- The Human EarDocument13 pagesThe Human EarCalvo AdrianNo ratings yet
- Hearing: Neurophysiology For Medicine Auditory PhysiologyDocument11 pagesHearing: Neurophysiology For Medicine Auditory PhysiologyarthitbNo ratings yet
- O To SclerosisDocument44 pagesO To Sclerosismajhi.jhalak19No ratings yet
- The Ear: The Structure of The Ear PRESENTATION BY: Dr. Nicole LevyDocument31 pagesThe Ear: The Structure of The Ear PRESENTATION BY: Dr. Nicole LevynicoleNo ratings yet
- 33-3 The SensesDocument19 pages33-3 The Sensesnancie8No ratings yet
- Parts of The EarDocument5 pagesParts of The EarThons Nacu LisingNo ratings yet
- 1) Varaz Chaniago 2) Vicka Zahara Firdaus 3) Vina Nur Sholikhah 4) Zidan Abdul GaniDocument25 pages1) Varaz Chaniago 2) Vicka Zahara Firdaus 3) Vina Nur Sholikhah 4) Zidan Abdul GaniFikri RamaNo ratings yet
- Assessment of The Ear MEDSURGDocument18 pagesAssessment of The Ear MEDSURGzildjian joyNo ratings yet
- Aranilla - Laboratory No. 3Document4 pagesAranilla - Laboratory No. 3Mamamo157No ratings yet
- Esp EnglishDocument5 pagesEsp EnglishCahyaa NingsiihNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - BSci - BSN 1 F - Worksheet 7.5Document10 pagesGroup 2 - BSci - BSN 1 F - Worksheet 7.5Aiza CeciliaNo ratings yet
- Structure and Functions of The Ear Explicated With DiagramsDocument10 pagesStructure and Functions of The Ear Explicated With DiagramsemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesLesson PlanSharathNo ratings yet
- Other Sensory SystemsDocument95 pagesOther Sensory SystemsXi En LookNo ratings yet
- Jawaban Responsi PendengaranDocument3 pagesJawaban Responsi Pendengaranyasmin afifahNo ratings yet
- The EarDocument103 pagesThe Eardharmendra kirarNo ratings yet
- Group 2: Amaliani Laraswati Dewi Andini Fifi Kurniawati Gita Rianti Nelly Marta Nadeak Nury Andriani Nur AnisahDocument15 pagesGroup 2: Amaliani Laraswati Dewi Andini Fifi Kurniawati Gita Rianti Nelly Marta Nadeak Nury Andriani Nur Anisahjihan salsabilaNo ratings yet
- Report 2 EMM352 - Muhammad Aiman Danial Bin YatimDocument3 pagesReport 2 EMM352 - Muhammad Aiman Danial Bin YatimAiman D.No ratings yet
- Sense of Hearing: Exercise 9Document4 pagesSense of Hearing: Exercise 9Stephen YorNo ratings yet
- Lect 7. EarDocument26 pagesLect 7. Earhla592071No ratings yet
- What Is Audition?Document70 pagesWhat Is Audition?LoraNo ratings yet
- Tugas Inggris KMB MGG 1-3Document6 pagesTugas Inggris KMB MGG 1-3Julia Wibawa HaryantoNo ratings yet
- Ears HomeworkDocument2 pagesEars HomeworkJonas Zacarias BalingbingNo ratings yet
- T3.9 The EarDocument3 pagesT3.9 The EarKudaNo ratings yet
- EbookDocument7 pagesEbookEusivia PasiNo ratings yet
- Auditory PhoneticsDocument12 pagesAuditory Phoneticsruth.pedrajitaNo ratings yet
- Pa Ears-Nose-MouthDocument108 pagesPa Ears-Nose-MouthDenniellePaulineKwonNo ratings yet
- 7 - Ear 1Document40 pages7 - Ear 1Touseeq ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EarDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EarrizzarNo ratings yet
- SAS - Session 7 - PSY079 - Intro To PsychologyDocument8 pagesSAS - Session 7 - PSY079 - Intro To PsychologyLordelee Mae N PamaylaonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The EarDocument196 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The EarChalsey Jene LorestoNo ratings yet
- Ossicles: The Malleus, The Incus, and The StapesDocument6 pagesOssicles: The Malleus, The Incus, and The StapesLili M.No ratings yet
- A. The External Ear, C. The Inner EarDocument3 pagesA. The External Ear, C. The Inner EarLili M.No ratings yet
- A Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsFrom EverandA Simple Guide to the Ear and Its Disorders, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 - EXPLAIN - ACTIVITY 2 - STEP 2 AND STEP 3 - MorenoDocument2 pagesLESSON 1 - EXPLAIN - ACTIVITY 2 - STEP 2 AND STEP 3 - MorenoAiza SaripNo ratings yet
- What Is Sound?Document8 pagesWhat Is Sound?Chrisshalyn Sy PinedaNo ratings yet
- April 29Document7 pagesApril 29api-292905822No ratings yet
- Anatomy of Human EarDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Human EarSharanz Twentyfour SevenNo ratings yet
- Human Senses and Human System : Auditory SenseDocument9 pagesHuman Senses and Human System : Auditory SenseJolly Ann PerdonNo ratings yet
- HearingDocument3 pagesHearingAnnabelle ArtiagaNo ratings yet
- VisionJ Hearing and Other SensesDocument13 pagesVisionJ Hearing and Other SensesbilcjesabellevivaNo ratings yet
- A Guide For Parents PDFDocument11 pagesA Guide For Parents PDFCierra JonesNo ratings yet
- How Sounds Travel To Our EarsDocument23 pagesHow Sounds Travel To Our Earslj8075702No ratings yet
- Assessing EarsDocument94 pagesAssessing EarscolendresjonnaNo ratings yet
- AICTE Model - Digital Electronics and Systems - Abhishek Bhatt - 17-01-2024Document539 pagesAICTE Model - Digital Electronics and Systems - Abhishek Bhatt - 17-01-2024matey.tushar5646No ratings yet
- NORFIELD - T-Do2014-Imperialism and Finance PDFDocument227 pagesNORFIELD - T-Do2014-Imperialism and Finance PDFLaercio Monteiro Jr.No ratings yet
- Cockateil Pairing DetailsDocument4 pagesCockateil Pairing DetailsWaseem UllahNo ratings yet
- State Centric Theories of International Relations Belong To The Past in Security StudiesDocument3 pagesState Centric Theories of International Relations Belong To The Past in Security StudiesshoufiiNo ratings yet
- Kreativitas Dan Inovasi Berpengaruh Terhadap Kewirausahaan Usaha KecilDocument17 pagesKreativitas Dan Inovasi Berpengaruh Terhadap Kewirausahaan Usaha Kecilapsari hasanNo ratings yet
- Manual enDocument216 pagesManual enmosquidoNo ratings yet
- VT572 Microwave Radar Motion Movement Sensor Detector Datasheet (Vutlan)Document16 pagesVT572 Microwave Radar Motion Movement Sensor Detector Datasheet (Vutlan)gm4984371No ratings yet
- FIP Corrosion Protection of Prestressing SteelsDocument79 pagesFIP Corrosion Protection of Prestressing SteelsRizwanNo ratings yet
- Hafs and Warsh (Part 2)Document4 pagesHafs and Warsh (Part 2)Asad HoseinyNo ratings yet
- 12 Architecture & Methodology ENDocument36 pages12 Architecture & Methodology ENYash BhatnagarNo ratings yet
- BC 367 Experiment 4 Kinetic Properties of Acid Phosphatase: Roh + Hpo Phosphatase + H ODocument8 pagesBC 367 Experiment 4 Kinetic Properties of Acid Phosphatase: Roh + Hpo Phosphatase + H OAliceKeikoNo ratings yet
- Historiography On The Origins of The Cold WarDocument4 pagesHistoriography On The Origins of The Cold Warapi-297872327100% (2)
- Integrated Door Motor Controller User Manual: Shenyang Bluelight Automatic Technology Co., LTDDocument56 pagesIntegrated Door Motor Controller User Manual: Shenyang Bluelight Automatic Technology Co., LTDJulio Cesar GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Rightpdf - Siemens Quotation SIQRMI231003001 REV03 Gradiant Pty LTD - WatermarkDocument14 pagesRightpdf - Siemens Quotation SIQRMI231003001 REV03 Gradiant Pty LTD - WatermarkNirmal KumarNo ratings yet
- Production of Xylitol From Corn Cob Hydrolysate - Mardawati - 2018 - IOP - Conf. - Ser. - Earth - Environ. - Sci. - 141 - 012019Document12 pagesProduction of Xylitol From Corn Cob Hydrolysate - Mardawati - 2018 - IOP - Conf. - Ser. - Earth - Environ. - Sci. - 141 - 012019RosalinaIlmiAmaliaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Introduction To JainismDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Introduction To JainismVertika guptaNo ratings yet
- Retreasure Pitch Deck - NSIA Prize For InnovationDocument16 pagesRetreasure Pitch Deck - NSIA Prize For InnovationRetreasure SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Test 11 Chap 1-5Document2 pagesChemistry Test 11 Chap 1-5Sabitra RudraNo ratings yet
- Testes Avaliação Inglês 6º AnoDocument43 pagesTestes Avaliação Inglês 6º AnoRui PauloNo ratings yet
- Part EM - Classical ElectrodynamicsDocument415 pagesPart EM - Classical Electrodynamicsapoorva singhNo ratings yet
- Engin EKER, MDDocument23 pagesEngin EKER, MDWorldEventsForumNo ratings yet
- Campbell Systematic Reviews - 2011 - Morton - Youth Empowerment Programs For Improving Self Efficacy and Self Esteem ofDocument81 pagesCampbell Systematic Reviews - 2011 - Morton - Youth Empowerment Programs For Improving Self Efficacy and Self Esteem ofAndra ComanNo ratings yet
- Plagiarism Check - Satya Dea PrawiraDocument3 pagesPlagiarism Check - Satya Dea PrawiraSatya Dea PrawiraNo ratings yet
- Implicit and Explicit InformationDocument3 pagesImplicit and Explicit InformationAbbas GholamiNo ratings yet
- Phyu Phyu Lwin CVDocument5 pagesPhyu Phyu Lwin CVphuy phyu100% (1)
- Reading 23 NovDocument5 pagesReading 23 NovAdhwa QurrotuainiNo ratings yet
- Coping Mechanisms of ScienceDocument26 pagesCoping Mechanisms of ScienceYouth ChoirNo ratings yet