Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Instrumental Analysis Review
Instrumental Analysis Review
Uploaded by
scherrmantrigillolbmlf41040 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesThe document contains questions related to analytical chemistry techniques like UV spectroscopy, chromatography, and atomic spectroscopy. It includes 10 multiple choice questions testing knowledge of the basic principles and components of various instruments. It also lists short answer and long answer questions about additional topics such as qualitative vs. quantitative analysis, types of instrumental methods, atomic spectroscopy, Beer's and Lambert's laws, light sources, UV/visible spectrophotometer instrumentation, applications of UV spectroscopy, fluorescence principle and applications, advantages and disadvantages of FTIR with applications, GC instrumentation with column types, and two GC detectors.
Original Description:
ins
Original Title
Instrumental analysis review
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document contains questions related to analytical chemistry techniques like UV spectroscopy, chromatography, and atomic spectroscopy. It includes 10 multiple choice questions testing knowledge of the basic principles and components of various instruments. It also lists short answer and long answer questions about additional topics such as qualitative vs. quantitative analysis, types of instrumental methods, atomic spectroscopy, Beer's and Lambert's laws, light sources, UV/visible spectrophotometer instrumentation, applications of UV spectroscopy, fluorescence principle and applications, advantages and disadvantages of FTIR with applications, GC instrumentation with column types, and two GC detectors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesInstrumental Analysis Review
Instrumental Analysis Review
Uploaded by
scherrmantrigillolbmlf4104The document contains questions related to analytical chemistry techniques like UV spectroscopy, chromatography, and atomic spectroscopy. It includes 10 multiple choice questions testing knowledge of the basic principles and components of various instruments. It also lists short answer and long answer questions about additional topics such as qualitative vs. quantitative analysis, types of instrumental methods, atomic spectroscopy, Beer's and Lambert's laws, light sources, UV/visible spectrophotometer instrumentation, applications of UV spectroscopy, fluorescence principle and applications, advantages and disadvantages of FTIR with applications, GC instrumentation with column types, and two GC detectors.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
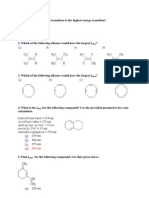
MCQ
1. UV SPECTROSCOPY working on which phenomenon?
a) Absorption b) Elution
c) A and B d) None of this
2. Ultra Violet spectroscopy wavelength is?
a) 200 nm to 300nm b) 200nm to 400nm
c) 400nm to 800 nm d) All of the above
3. Which radiation source has an electrode?
a) Tungsten lamp b) Hydrogen discharge lamp
c) Xenon Discharge Lamp d) Mercury lamp
4. Which type of vapor is stored in Mercury lamp?
a) Mercury vapor b) Hydrogen vapor
c) Xe d) Ozone
5. The device that converts light energy into an electrical signal is
a) Amplifier b) Detector
c) Sample cell d) Slit
6. The principal of IR spectroscopy?
a) Absorption b) Emissions
c) Adsorption d) None of these
7. The temperature in Incandescent lamp to produce IR radiation?
a) 1100 c b) 800 c
c) 300 d) 1400 c
8. Which technique is also known as color writing?
a) NMR b) Mass spectroscopy
c) Chromatography d) All of the above
9. Which compounds are held by the stationary phase?
a) Polar compound b) Nonpolar compound
c) A and B d) None of the above
10. What is the Analyte?
a) Substance for separation b) Substance for impurity
c) A and B d) None of the above
SHORT
1. Difference between qualitative and quantitative analysis.
2. Name different types of instrumental methods.
3. What is atomic spectroscopy?
4. Define Beer’s law and Lambert’s law.
5. Name different types of light sources in UV spectrophotometry.
LONG
1. With a neatly labeled diagram explain UV/Visible spectrophotometer
instrumentation.
2. What are the applications of UV spectroscopy?
3. Explain the principle of fluorescence.
4. What are the applications of fluorescence spectroscopy?
5. (a) What are the advantages and disadvantages of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
(FTIR)?
(b) What are its applications?
6. Explain GC instrumentation with a labeled diagram. Add a note on the
different types of GC columns.
7. List and explain any 2 GC detectors.
You might also like
- Multiple Choice Questions For Fluorescence SpectrosDocument3 pagesMultiple Choice Questions For Fluorescence SpectrosArpit Bhargava83% (18)
- MCQ CharacterizationDocument18 pagesMCQ CharacterizationAmjed AL-KAHTEEB100% (3)
- Instrumental Analysis IIDocument2 pagesInstrumental Analysis IIzebasilt0% (1)
- FSC327 PossiblequesbyaviiDocument27 pagesFSC327 PossiblequesbyaviiAvinaash PraveenNo ratings yet
- Ima Question Bank NewDocument11 pagesIma Question Bank NewVIJAYANAND.N NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Ai Two MarkDocument25 pagesAi Two MarkmohanapriyaNo ratings yet
- Basics of Atomic Spectroscopy QADocument7 pagesBasics of Atomic Spectroscopy QASabera GogdaNo ratings yet
- Analytical Instruments BankDocument5 pagesAnalytical Instruments BankshishirNo ratings yet
- Assignment Instrumental Methods of Analysis CHE 432Document10 pagesAssignment Instrumental Methods of Analysis CHE 432Hager AhmedNo ratings yet
- Ir AssignmentDocument5 pagesIr AssignmentSUBHASISH DASHNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test (Electromagnetic Spectrum)Document2 pagesPre-Test (Electromagnetic Spectrum)Wayne David C. Padullon100% (3)
- UV-Vis QuestionsDocument3 pagesUV-Vis QuestionsManoj MathewsNo ratings yet
- UNIT V - Applied Optics - LASER Physics MCQDocument2 pagesUNIT V - Applied Optics - LASER Physics MCQsiva kesavNo ratings yet
- PDF اسئلة جزء د إكرامDocument11 pagesPDF اسئلة جزء د إكرامTarek EidNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 - MCQDocument7 pagesUnit 7 - MCQAbab CscdNo ratings yet
- AnalysisDocument14 pagesAnalysisBINDU100% (1)
- Instrumental Methods of Analysis MCQDocument86 pagesInstrumental Methods of Analysis MCQHITMAN100% (1)
- A. Absorption: B. Elution C. A and B D. None of ThisDocument7 pagesA. Absorption: B. Elution C. A and B D. None of ThisTRÂN NGUYỄN NGỌC BẢONo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument2 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsTajammal AminNo ratings yet
- Part 1: Choose The Best Answer From The Options Underneath EachDocument11 pagesPart 1: Choose The Best Answer From The Options Underneath EachGIRMA SELALE GELETANo ratings yet
- Physics: Unit - Iii Fibre Optics and Its Applications PART - A (2 Marks)Document3 pagesPhysics: Unit - Iii Fibre Optics and Its Applications PART - A (2 Marks)Preethi SharmiNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Final ExamDocument6 pagesInstrumentation Final ExamHabtamu Molla100% (2)
- Ai Interview QuestionsDocument31 pagesAi Interview QuestionsmohanapriyaNo ratings yet
- ITA Viva - Questions OnlyDocument4 pagesITA Viva - Questions OnlyManoj KhanalNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument2 pagesStructure of Atommirthika .RNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet (Atomic Spectroscopy - I) : School of Chemistry and Biochemistry, TIET, Patiala Applied Chemistry (UCB008)Document4 pagesTutorial Sheet (Atomic Spectroscopy - I) : School of Chemistry and Biochemistry, TIET, Patiala Applied Chemistry (UCB008)Yuvraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Instrumental Method For Environmental AnalysisDocument95 pagesInstrumental Method For Environmental AnalysisKaluNo ratings yet
- Solutions of The Tutorial Sheet: Atomic Spectroscopy - Part IDocument4 pagesSolutions of The Tutorial Sheet: Atomic Spectroscopy - Part ISanidhya VijayNo ratings yet
- INSTRUMENTAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK FOR B Tech BIOTECH PDFDocument3 pagesINSTRUMENTAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK FOR B Tech BIOTECH PDFFabian MataloNo ratings yet
- INSTRUMENTAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK FOR B.Tech BIOTECHDocument3 pagesINSTRUMENTAL METHODS OF ANALYSIS QUESTION BANK FOR B.Tech BIOTECHK.Selvaraj67% (3)
- Instrumental Methods of Analysis Question Bank For B Tech BiotechDocument3 pagesInstrumental Methods of Analysis Question Bank For B Tech BiotechJency BavithraNo ratings yet
- 2023 Exam PrepDocument3 pages2023 Exam PrepBaochen TianNo ratings yet
- Assignment QuestionsDocument1 pageAssignment QuestionsPavitra MurugesanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Introduction To PhotonicsDocument14 pagesUnit 3 Introduction To PhotonicsKapil TilwaniNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice: 20-1 Lamps and Lasers: Sources of LightDocument7 pagesMultiple-Choice: 20-1 Lamps and Lasers: Sources of LightBla NkNo ratings yet
- QuestionsDocument2 pagesQuestionsalina.tlekkabylova270202No ratings yet
- CHM 260 Lab Report Exp 3Document6 pagesCHM 260 Lab Report Exp 3Warina 01No ratings yet
- MCQ For Question PaperDocument11 pagesMCQ For Question PaperAjay Sharma Shankyan100% (2)
- Assignment 1 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1 1Bittu rajaNo ratings yet
- Compton Scattering Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesCompton Scattering Practice ProblemsJacob KeynesNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry Atomic Emission SpectrosDocument15 pagesFundamentals of Analytical Chemistry Atomic Emission SpectrosNandini KapoorNo ratings yet
- Unit - 2 MCQ'sDocument5 pagesUnit - 2 MCQ'srishavr2001No ratings yet
- 27 Aug 2011 Test Along With AnswersDocument4 pages27 Aug 2011 Test Along With AnswersdnagwaliorNo ratings yet
- Ami MCQDocument89 pagesAmi MCQRathinavel MAMCETNo ratings yet
- Xi Chem Chapt 2 Structure of Atom WorksheetDocument13 pagesXi Chem Chapt 2 Structure of Atom WorksheetNandini Classes,City Light ,Surat. Cell (9429090525No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and EMRDocument2 pagesAtomic Structure and EMRmusamugabazi68No ratings yet
- 000 - Problems1Document2 pages000 - Problems1Ijaz TalibNo ratings yet
- UNIT Topics QuestionsDocument5 pagesUNIT Topics QuestionsafiyatabssmNo ratings yet
- Medical Imaging Techniques Question BankDocument5 pagesMedical Imaging Techniques Question BankMATHANKUMAR.S86% (7)
- Core Biology NotesDocument7 pagesCore Biology NotesBeatriz SilvaNo ratings yet
- Guía de Estudio EspectrosDocument5 pagesGuía de Estudio EspectrosCésar CidNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 2 MCQ With AnswersDocument5 pagesChemistry Unit 2 MCQ With AnswersKaran VaswaniNo ratings yet
- Analytical Instruments QP PDFDocument10 pagesAnalytical Instruments QP PDFsenthilkumareceNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument39 pagesQuestion Bankamany mohamedNo ratings yet
- 04 Test Pharmaceutical ChemistryDocument115 pages04 Test Pharmaceutical ChemistryThuongNguyen1981No ratings yet
- Islamabad College For Boys, G-6/3, Islamabad Waves Optics (192) Semester 2 (BS/ADP-Math) Alternate To PracticalDocument4 pagesIslamabad College For Boys, G-6/3, Islamabad Waves Optics (192) Semester 2 (BS/ADP-Math) Alternate To PracticalAbdul JalilNo ratings yet
- BNBNDocument3 pagesBNBNwondimuNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Biological and Clinical Mass Spectrometry: An IntroductionFrom EverandQuantitative Biological and Clinical Mass Spectrometry: An IntroductionNo ratings yet
- Modern Vibrational Spectroscopy and Micro-Spectroscopy: Theory, Instrumentation and Biomedical ApplicationsFrom EverandModern Vibrational Spectroscopy and Micro-Spectroscopy: Theory, Instrumentation and Biomedical ApplicationsNo ratings yet