Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 viewsIntroduction To Psychology
Introduction To Psychology
Uploaded by
dwenkirby97The developing fetus goes through three stages - germinal, embryonic, and fetal. The brain develops first followed by the heart. By birth, the brain has over 100 billion cells. Prenatal development is influenced by both nature and nurture factors like the mother's health, diet, and environment. Personality and cognitive traits begin developing before birth through temperament. At birth, hearing is well developed while vision continues improving through infancy. Early cognitive development in infants involves visual preference and looking patterns. Musical training in childhood can structurally change the brain by thickening areas related to music skills.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- SAS - Session 8 - PSY079 - Intro To PsychologyDocument9 pagesSAS - Session 8 - PSY079 - Intro To PsychologyLordelee Mae N PamaylaonNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument29 pagesPrenatal DevelopmentReymart MancaoNo ratings yet
- Psychology 1000 Notes (Chapters 9-17)Document6 pagesPsychology 1000 Notes (Chapters 9-17)Ninth ExplorerNo ratings yet
- Brain Development The Critical 1000 DaysDocument9 pagesBrain Development The Critical 1000 DaysVillaver, Danessa Rose D.No ratings yet
- Gen Psych Chapter 5Document27 pagesGen Psych Chapter 5piper8757No ratings yet
- Unit-II-BIOLOGICAL-DEVELOPMENTS 20240303 183620 0000Document94 pagesUnit-II-BIOLOGICAL-DEVELOPMENTS 20240303 183620 0000Charm MarceloNo ratings yet
- Biological DevelopmentDocument48 pagesBiological DevelopmentDaph P. EchaneNo ratings yet
- Psychology Canadian 2Nd Edition Feist Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument48 pagesPsychology Canadian 2Nd Edition Feist Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFdiemdac39kgkw100% (12)
- Psychology Canadian 2nd Edition Feist Solutions ManualDocument27 pagesPsychology Canadian 2nd Edition Feist Solutions Manualrowanariel26r2100% (31)
- AP Psych Chapter 4 Study GuideDocument21 pagesAP Psych Chapter 4 Study Guidejimmysmyname123No ratings yet
- Early DevelopmentDocument11 pagesEarly DevelopmentMar sianNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Brain Development Through Lifespan 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: Brain Development Through Lifespan 1James McCrearyNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document18 pagesModule 3Pldtangge hilNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Development and Birth: The Development of Children (5 Ed.) Cole, Cole & LightfootDocument44 pagesPrenatal Development and Birth: The Development of Children (5 Ed.) Cole, Cole & LightfootWafiy AkmalNo ratings yet
- Il,.m F) x57 !8uqz.Document5 pagesIl,.m F) x57 !8uqz.Charles JoseNo ratings yet
- P103 Class NotesDocument16 pagesP103 Class NotesArice DulagNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Development of The Learners at Various StagesDocument25 pagesModule 6 - Development of The Learners at Various StagesRachelle DalingNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Life SpanDocument18 pagesWeek 4 Life SpanabextekNo ratings yet
- Developmental PsychologyDocument9 pagesDevelopmental PsychologyLoekieNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Psychology 2Document5 pagesReviewer in Psychology 2Sean GozarNo ratings yet
- Takshila - Magazine VOL 1.4Document41 pagesTakshila - Magazine VOL 1.4kzaiusa6978No ratings yet
- Hayat Ataya 1Document2 pagesHayat Ataya 1hanaNo ratings yet
- Unit2 HumanGrowth&DevtDocument4 pagesUnit2 HumanGrowth&DevtMay Anne BañagaNo ratings yet
- Development of The Learners at The Various StagesDocument21 pagesDevelopment of The Learners at The Various StagesMay ann AntonioNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry: Human Development Throughout The Life CycleDocument64 pagesPsychiatry: Human Development Throughout The Life CycleIan Russ BautistaNo ratings yet
- The InfantDocument13 pagesThe InfantMark Jhon PausanosNo ratings yet
- Module 11 Balasbas Cyrel Andrie V.Document13 pagesModule 11 Balasbas Cyrel Andrie V.Mary Angeline De LeonNo ratings yet
- Educ 1 - 4Document71 pagesEduc 1 - 4Rolando T. Jaravata Jr.No ratings yet
- I. Biological Beginnings: The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument7 pagesI. Biological Beginnings: The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principlesrizzamae belenNo ratings yet
- Child AdoDocument25 pagesChild AdoJochelle Mae SucuanoNo ratings yet
- 9 Developmental Lecture NotesDocument33 pages9 Developmental Lecture NotesReseNo ratings yet
- Malingin Ronibe Educ101 PortfolioDocument16 pagesMalingin Ronibe Educ101 PortfolioRonibe B MalinginNo ratings yet
- Prenat DevelDocument3 pagesPrenat DevelenergygapNo ratings yet
- Human Development - Chapter 3Document100 pagesHuman Development - Chapter 3Ashley AgustinNo ratings yet
- Developmental PsychologyDocument10 pagesDevelopmental PsychologyDeniNo ratings yet
- Cephalocaudal and Proximodistal PatternsDocument9 pagesCephalocaudal and Proximodistal PatternsDan Gela Mæ MaYoNo ratings yet
- BPY 1063 Human Growth and Development: W2: Development From Conception To BirthDocument31 pagesBPY 1063 Human Growth and Development: W2: Development From Conception To BirthnayanaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Physical, Cognitive, and Socio-Emotional Development of Prenatal PeriosDocument24 pagesSynthesis of Physical, Cognitive, and Socio-Emotional Development of Prenatal PeriosJefte CasullaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document140 pagesChapter 10John David CrossNo ratings yet
- Development of The Learners at The Various StagesDocument32 pagesDevelopment of The Learners at The Various StagesMelanie SerquiñaNo ratings yet
- Development TestDocument18 pagesDevelopment TesthypsdreamerNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Perinatal NotesDocument4 pagesWeek 1 Perinatal Notesm.alkhosoussyNo ratings yet
- Written Report PsychDocument17 pagesWritten Report PsychShanaia BualNo ratings yet
- Educ 101.module 12Document10 pagesEduc 101.module 12Avigale VelascoNo ratings yet
- Earlybrain PDFDocument21 pagesEarlybrain PDFMaría Regina Castro CataldiNo ratings yet
- Dev Psy 28feb2018Document21 pagesDev Psy 28feb2018Bryan AppleNo ratings yet
- Developing Through The Life Span: Learning ObjectivesDocument18 pagesDeveloping Through The Life Span: Learning ObjectivesHayaton IRNo ratings yet
- Developing Through The Life SpanDocument11 pagesDeveloping Through The Life SpanMa. Nenita L. MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Developmental PsychologyDocument14 pagesDevelopmental PsychologyHayley Van SchoorNo ratings yet
- HUMAN DEvelopmentDocument27 pagesHUMAN DEvelopmentReshia Mae Lagrosa NamiaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Development and Developmental TasksDocument6 pagesStages of Development and Developmental TasksJeyd Montefalco100% (1)
- Mind in The MakingDocument6 pagesMind in The Makingjayson virtucioNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument20 pagesPrenatal DevelopmentVictoria AntonetteNo ratings yet
- Psychology Canadian 2nd Edition Feist Solutions Manual instant download all chapterDocument50 pagesPsychology Canadian 2nd Edition Feist Solutions Manual instant download all chapterkrifijilie100% (5)
- Prenatal Development Final RevisedDocument3 pagesPrenatal Development Final Revisedapi-251842259No ratings yet
- Notes Introduction To Developmental PsychologyDocument9 pagesNotes Introduction To Developmental Psychologyshokor khanNo ratings yet
- Sychological DevelopmentDocument4 pagesSychological DevelopmentChristine Ann GamboaNo ratings yet
- PRE-NATAL - Development of The Learners at Various StagesDocument119 pagesPRE-NATAL - Development of The Learners at Various Stageskristinegaleon89No ratings yet
- Psych Term 3Document69 pagesPsych Term 3annistafford04No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Microbial Growth Module BSED-ScienceDocument16 pagesCHAPTER 5 Microbial Growth Module BSED-ScienceXy-Za OlivaNo ratings yet
- Origin and Development of Organ Systems NotesDocument4 pagesOrigin and Development of Organ Systems NotesimnasNo ratings yet
- Nature Nurture Debate On Human Sexual OrientationDocument58 pagesNature Nurture Debate On Human Sexual OrientationKevin Brewer100% (3)
- Clinical Case 47 - InfertilityDocument5 pagesClinical Case 47 - Infertilityselina kalenderNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Sci QRTR 2 Module 5 Perpetuation of Life Student Edition Grade 11 DescartesDocument46 pagesEarth and Life Sci QRTR 2 Module 5 Perpetuation of Life Student Edition Grade 11 Descartesmelvin madronal100% (1)
- Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Animals PDFDocument7 pagesAsexual and Sexual Reproduction in Animals PDFZakir100% (1)
- The Theories of Organic EvolutionDocument2 pagesThe Theories of Organic EvolutionMary Rose Bobis VicenteNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Seeds: New Phytologist June 2010Document16 pagesThe Evolution of Seeds: New Phytologist June 2010Rudolf KiraljNo ratings yet
- Biology WAEC Likely Questions PDF DownloadDocument6 pagesBiology WAEC Likely Questions PDF DownloadCharles Obaleagbon100% (1)
- Grades Blastomere Size Fragmentation 4 3 2 1Document4 pagesGrades Blastomere Size Fragmentation 4 3 2 1easa_tNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3. Photoperiodism and EmbryogenesisDocument7 pagesWorksheet 3. Photoperiodism and EmbryogenesisSukmagita RahajengNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction For Grade 11 Worksheet 2Document8 pagesPlant Reproduction For Grade 11 Worksheet 2KISHANo ratings yet
- Asexual Vs Sexual ReproductionDocument9 pagesAsexual Vs Sexual ReproductionEdenNo ratings yet
- A Guide For AdolescentsDocument68 pagesA Guide For AdolescentsJaseme OtoyoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet. 4. Asexual ReproductionDocument3 pagesWorksheet. 4. Asexual ReproductionLeonita SwandjajaNo ratings yet
- ANAT2341 Student 2015 Quiz QuestionsDocument12 pagesANAT2341 Student 2015 Quiz QuestionsHassan ContehNo ratings yet
- How Does Protococcus ReproduceDocument2 pagesHow Does Protococcus ReproduceJohn Vincent Gomez100% (1)
- 964 QP 2 STPM Biology 2012 Section BDocument2 pages964 QP 2 STPM Biology 2012 Section BSeanNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction Vs Asexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesSexual Reproduction Vs Asexual ReproductionIsabel HontiverosNo ratings yet
- Perkecambahan Dan Pertumbuhan Palem Jepang (Actinophloeus Macarthurii Becc.) Akibat Perendaman Biji Dalam LumpurDocument7 pagesPerkecambahan Dan Pertumbuhan Palem Jepang (Actinophloeus Macarthurii Becc.) Akibat Perendaman Biji Dalam LumpurNurma YahyaNo ratings yet
- Asexual and Sexual Reproduction QuizDocument2 pagesAsexual and Sexual Reproduction QuizShannen Abegail FernandezNo ratings yet
- JNL College (Pallavi For Botany B.SC Part I) Topic-MarseliaDocument13 pagesJNL College (Pallavi For Botany B.SC Part I) Topic-MarseliaNguyễn HươngNo ratings yet
- 1-Embryonic-Stem-Cells 1ST LECDocument31 pages1-Embryonic-Stem-Cells 1ST LECrihamazim2018No ratings yet
- Animations CompleteDocument18 pagesAnimations CompleteStruggl EarthNo ratings yet
- 2 - Gametogenesis and Female CyclesDocument31 pages2 - Gametogenesis and Female CyclesMax DanhNo ratings yet
- 39740-PDF Notes Grade - 3 Science Lesson 1 Living and Non-Living ThingsDocument14 pages39740-PDF Notes Grade - 3 Science Lesson 1 Living and Non-Living ThingsNishant JasaniNo ratings yet
- Arun Muthivel Vs Union of India and OrsDocument11 pagesArun Muthivel Vs Union of India and OrsAkhil BenNo ratings yet
- General Characters of Rhodophyceae & Life Cycle of PolysiphoniaDocument49 pagesGeneral Characters of Rhodophyceae & Life Cycle of PolysiphoniaSona PectusNo ratings yet
- 0610 s21 QP 31 PDFDocument20 pages0610 s21 QP 31 PDFAarush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology - From A Cell To An Organism (Genetics Evolution)Document225 pagesDevelopmental Biology - From A Cell To An Organism (Genetics Evolution)ekamutiaraNo ratings yet
Introduction To Psychology
Introduction To Psychology
Uploaded by
dwenkirby970 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesThe developing fetus goes through three stages - germinal, embryonic, and fetal. The brain develops first followed by the heart. By birth, the brain has over 100 billion cells. Prenatal development is influenced by both nature and nurture factors like the mother's health, diet, and environment. Personality and cognitive traits begin developing before birth through temperament. At birth, hearing is well developed while vision continues improving through infancy. Early cognitive development in infants involves visual preference and looking patterns. Musical training in childhood can structurally change the brain by thickening areas related to music skills.
Original Description:
Original Title
INTRODUCTION-TO-PSYCHOLOGY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe developing fetus goes through three stages - germinal, embryonic, and fetal. The brain develops first followed by the heart. By birth, the brain has over 100 billion cells. Prenatal development is influenced by both nature and nurture factors like the mother's health, diet, and environment. Personality and cognitive traits begin developing before birth through temperament. At birth, hearing is well developed while vision continues improving through infancy. Early cognitive development in infants involves visual preference and looking patterns. Musical training in childhood can structurally change the brain by thickening areas related to music skills.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views3 pagesIntroduction To Psychology
Introduction To Psychology
Uploaded by
dwenkirby97The developing fetus goes through three stages - germinal, embryonic, and fetal. The brain develops first followed by the heart. By birth, the brain has over 100 billion cells. Prenatal development is influenced by both nature and nurture factors like the mother's health, diet, and environment. Personality and cognitive traits begin developing before birth through temperament. At birth, hearing is well developed while vision continues improving through infancy. Early cognitive development in infants involves visual preference and looking patterns. Musical training in childhood can structurally change the brain by thickening areas related to music skills.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
INTRODUCTION TO PSYCHOLOGY - By this time, all the major organs have
(MIDTERMS) already begun to form.
- Between 8 and 12 weeks into
Chapter 5: Human development development, the heartbeat can be
detected with a stethoscope.
THE DEVELOPING FETUS
The brain is the first major organ to form.
The heart develops about a week later. Brain and Sensory Development before Birth
A little more than 8 months later, when we are the brain is the first major organ to develop, and
born, the brain has more than 100 billion cells. it is still growing rapidly at birth.
Personality and cognitive traits are already By the time an infant is born, its head has grown
being shaped before we are born. to 25% of its adult weight, whereas its body is
only 5% of its adult weight.
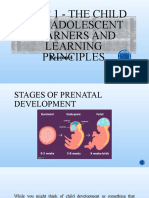
Stages of Prenatal Development From months 3 through 5 of pregnancy, neurons
Life before birth is commonly divided into three move from one part of the brain to their more
distinct stages: germinal, embryonic, and fetal. permanent home in a process known as neural
migration.
1. Germinal stage After conception, the neurons connecting the
- begins at conception, lasts for 2 weeks. ear to the brain are complete around 18 weeks,
- At conception, the fertilized egg is a single- and the fetus begins to respond to sound
celled zygote which starts dividing rapidly around 26 weeks
around 36 hours after conception.
- By day 7, the multi-celled organism—now Nature and Nurture Influences on Fetal Development
called a blastocyst—travels down the To a fetus, the mother’s womb is its only
mother’s fallopian tube and attaches to the “environment.” Thus, what a pregnant mother
uterine wall. eats, drinks, smokes, feels, and experiences play
- This process is far from risk-free: Between an important role in fetal development.
30% and 50% of blastocysts do not implant Prenatal programming is the process by which
properly, and the pregnancy ends without events in the womb alter the development of
the woman’s having known she was physical and psychological health.
pregnant. Teratogens - Substances from the external
- Genetically, sex is determined at environment impact fetal and infant
conception; girls have two X chromosomes development.
(XX) and boys an X and a Y (XY).
Both schizophrenia and antisocial personality
disorder are more likely to occur if the mother is
2. Embryonic stage
malnourished during pregnancy (Neugebauer,
- begins at about 2 weeks after conception. Hoek, & Susser, 1999; Wahlbeck et al., 2001).
- lasts 8 weeks after conception Similarly, if pregnant women smoke, the risk of
- marked by the formation of the major the child developing bipolar disorder later in life
organs: the nervous system, heart, eyes, doubles (Talati et al., 2013).
ears, arms, legs, teeth, palate, and external fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) - A
genitalia. consequence of prenatal alcohol exposure that
- the central nervous system (brain and causes multiple problems, notably brain
spinal cord) takes the longest amount of damage.
time to develop. The most serious effect of prenatal alcohol
- Most major abnormalities occur only in exposure is fetal alcohol spectrum disorder
the early stages of development, when (FASD), which causes damage to the brain and
exposure to environmental hazards, such as central nervous system; intellectual disability;
drugs or illness, can cause serious defects. low birth weight; physical abnormalities in the
face, head, heart, and joints; and behavioral
problems (Burd et al., 2007; May & Gossage, 2001;
3. Fetal Stage Medina & Krahe, 2008; Moore et al., 2007; Sen &
- the formation of bone cells at 8 weeks Swaminathan, 2007; Uylings, 2006).
after conception.
Recent evidence points to musical training
Prenatal Personality Development enhancing neural activity in the hippocampus,
Temperament- The biologically based tendency
to behave in particular ways from very early in
life (begins before birth).
Personality- The unique and relatively enduring
set of behaviors, feelings, thoughts, and motives
that characterize an individual.
personality develops out of temperament
differences.
THE DEVELOPING INFANT AND CHILD
Hearing is almost fully developed at birth.
Visual sharpness, or acuity, continues to
improve during infancy; newborns do not see
colors very well and are best able to see black
and-white edges and patterns.
Unused synapses are left to die. Neural Pruning
is nature’s way of making the brain function
more efficiently.
Neglect exists when caregivers fail to provide
basic sensory experience and stimulation to a
child during key periods of development (Perry,
2002).
Early Cognitive Development
Infants look at things longer when they are
interested in them, and such looking can
indicate preference.
Researchers who study infants have come to
rely on visual preference as their primary means
of studying infant thought and attention
(Richards, Reynolds, & Courage, 2010).
Musical Training Changes the Brain
Musical training appears to shape the structure
of the brain.
People who have had intensive musical training
have a thicker corpus callosum and more brain
growth in regions associated with music-related
skills than do non-musicians, and the difference
is even greater if they started their training
before age 7.
A thicker corpus callosum makes for greater
communication between the two sides of the
brain.
Musicians have larger cerebellums (an area
involved in motor coordination) than do non-
musicians (Hutchinson et al.,2003).
which is the brain region most involved in
learning and memory (Herdener et al., 2010).
You might also like
- SAS - Session 8 - PSY079 - Intro To PsychologyDocument9 pagesSAS - Session 8 - PSY079 - Intro To PsychologyLordelee Mae N PamaylaonNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument29 pagesPrenatal DevelopmentReymart MancaoNo ratings yet
- Psychology 1000 Notes (Chapters 9-17)Document6 pagesPsychology 1000 Notes (Chapters 9-17)Ninth ExplorerNo ratings yet
- Brain Development The Critical 1000 DaysDocument9 pagesBrain Development The Critical 1000 DaysVillaver, Danessa Rose D.No ratings yet
- Gen Psych Chapter 5Document27 pagesGen Psych Chapter 5piper8757No ratings yet
- Unit-II-BIOLOGICAL-DEVELOPMENTS 20240303 183620 0000Document94 pagesUnit-II-BIOLOGICAL-DEVELOPMENTS 20240303 183620 0000Charm MarceloNo ratings yet
- Biological DevelopmentDocument48 pagesBiological DevelopmentDaph P. EchaneNo ratings yet
- Psychology Canadian 2Nd Edition Feist Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument48 pagesPsychology Canadian 2Nd Edition Feist Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFdiemdac39kgkw100% (12)
- Psychology Canadian 2nd Edition Feist Solutions ManualDocument27 pagesPsychology Canadian 2nd Edition Feist Solutions Manualrowanariel26r2100% (31)
- AP Psych Chapter 4 Study GuideDocument21 pagesAP Psych Chapter 4 Study Guidejimmysmyname123No ratings yet
- Early DevelopmentDocument11 pagesEarly DevelopmentMar sianNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Brain Development Through Lifespan 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: Brain Development Through Lifespan 1James McCrearyNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document18 pagesModule 3Pldtangge hilNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Development and Birth: The Development of Children (5 Ed.) Cole, Cole & LightfootDocument44 pagesPrenatal Development and Birth: The Development of Children (5 Ed.) Cole, Cole & LightfootWafiy AkmalNo ratings yet
- Il,.m F) x57 !8uqz.Document5 pagesIl,.m F) x57 !8uqz.Charles JoseNo ratings yet
- P103 Class NotesDocument16 pagesP103 Class NotesArice DulagNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - Development of The Learners at Various StagesDocument25 pagesModule 6 - Development of The Learners at Various StagesRachelle DalingNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Life SpanDocument18 pagesWeek 4 Life SpanabextekNo ratings yet
- Developmental PsychologyDocument9 pagesDevelopmental PsychologyLoekieNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Psychology 2Document5 pagesReviewer in Psychology 2Sean GozarNo ratings yet
- Takshila - Magazine VOL 1.4Document41 pagesTakshila - Magazine VOL 1.4kzaiusa6978No ratings yet
- Hayat Ataya 1Document2 pagesHayat Ataya 1hanaNo ratings yet
- Unit2 HumanGrowth&DevtDocument4 pagesUnit2 HumanGrowth&DevtMay Anne BañagaNo ratings yet
- Development of The Learners at The Various StagesDocument21 pagesDevelopment of The Learners at The Various StagesMay ann AntonioNo ratings yet
- Psychiatry: Human Development Throughout The Life CycleDocument64 pagesPsychiatry: Human Development Throughout The Life CycleIan Russ BautistaNo ratings yet
- The InfantDocument13 pagesThe InfantMark Jhon PausanosNo ratings yet
- Module 11 Balasbas Cyrel Andrie V.Document13 pagesModule 11 Balasbas Cyrel Andrie V.Mary Angeline De LeonNo ratings yet
- Educ 1 - 4Document71 pagesEduc 1 - 4Rolando T. Jaravata Jr.No ratings yet
- I. Biological Beginnings: The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument7 pagesI. Biological Beginnings: The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principlesrizzamae belenNo ratings yet
- Child AdoDocument25 pagesChild AdoJochelle Mae SucuanoNo ratings yet
- 9 Developmental Lecture NotesDocument33 pages9 Developmental Lecture NotesReseNo ratings yet
- Malingin Ronibe Educ101 PortfolioDocument16 pagesMalingin Ronibe Educ101 PortfolioRonibe B MalinginNo ratings yet
- Prenat DevelDocument3 pagesPrenat DevelenergygapNo ratings yet
- Human Development - Chapter 3Document100 pagesHuman Development - Chapter 3Ashley AgustinNo ratings yet
- Developmental PsychologyDocument10 pagesDevelopmental PsychologyDeniNo ratings yet
- Cephalocaudal and Proximodistal PatternsDocument9 pagesCephalocaudal and Proximodistal PatternsDan Gela Mæ MaYoNo ratings yet
- BPY 1063 Human Growth and Development: W2: Development From Conception To BirthDocument31 pagesBPY 1063 Human Growth and Development: W2: Development From Conception To BirthnayanaNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Physical, Cognitive, and Socio-Emotional Development of Prenatal PeriosDocument24 pagesSynthesis of Physical, Cognitive, and Socio-Emotional Development of Prenatal PeriosJefte CasullaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10Document140 pagesChapter 10John David CrossNo ratings yet
- Development of The Learners at The Various StagesDocument32 pagesDevelopment of The Learners at The Various StagesMelanie SerquiñaNo ratings yet
- Development TestDocument18 pagesDevelopment TesthypsdreamerNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Perinatal NotesDocument4 pagesWeek 1 Perinatal Notesm.alkhosoussyNo ratings yet
- Written Report PsychDocument17 pagesWritten Report PsychShanaia BualNo ratings yet
- Educ 101.module 12Document10 pagesEduc 101.module 12Avigale VelascoNo ratings yet
- Earlybrain PDFDocument21 pagesEarlybrain PDFMaría Regina Castro CataldiNo ratings yet
- Dev Psy 28feb2018Document21 pagesDev Psy 28feb2018Bryan AppleNo ratings yet
- Developing Through The Life Span: Learning ObjectivesDocument18 pagesDeveloping Through The Life Span: Learning ObjectivesHayaton IRNo ratings yet
- Developing Through The Life SpanDocument11 pagesDeveloping Through The Life SpanMa. Nenita L. MagallanesNo ratings yet
- Developmental PsychologyDocument14 pagesDevelopmental PsychologyHayley Van SchoorNo ratings yet
- HUMAN DEvelopmentDocument27 pagesHUMAN DEvelopmentReshia Mae Lagrosa NamiaNo ratings yet
- Stages of Development and Developmental TasksDocument6 pagesStages of Development and Developmental TasksJeyd Montefalco100% (1)
- Mind in The MakingDocument6 pagesMind in The Makingjayson virtucioNo ratings yet
- Prenatal DevelopmentDocument20 pagesPrenatal DevelopmentVictoria AntonetteNo ratings yet
- Psychology Canadian 2nd Edition Feist Solutions Manual instant download all chapterDocument50 pagesPsychology Canadian 2nd Edition Feist Solutions Manual instant download all chapterkrifijilie100% (5)
- Prenatal Development Final RevisedDocument3 pagesPrenatal Development Final Revisedapi-251842259No ratings yet
- Notes Introduction To Developmental PsychologyDocument9 pagesNotes Introduction To Developmental Psychologyshokor khanNo ratings yet
- Sychological DevelopmentDocument4 pagesSychological DevelopmentChristine Ann GamboaNo ratings yet
- PRE-NATAL - Development of The Learners at Various StagesDocument119 pagesPRE-NATAL - Development of The Learners at Various Stageskristinegaleon89No ratings yet
- Psych Term 3Document69 pagesPsych Term 3annistafford04No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5 Microbial Growth Module BSED-ScienceDocument16 pagesCHAPTER 5 Microbial Growth Module BSED-ScienceXy-Za OlivaNo ratings yet
- Origin and Development of Organ Systems NotesDocument4 pagesOrigin and Development of Organ Systems NotesimnasNo ratings yet
- Nature Nurture Debate On Human Sexual OrientationDocument58 pagesNature Nurture Debate On Human Sexual OrientationKevin Brewer100% (3)
- Clinical Case 47 - InfertilityDocument5 pagesClinical Case 47 - Infertilityselina kalenderNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Sci QRTR 2 Module 5 Perpetuation of Life Student Edition Grade 11 DescartesDocument46 pagesEarth and Life Sci QRTR 2 Module 5 Perpetuation of Life Student Edition Grade 11 Descartesmelvin madronal100% (1)
- Asexual and Sexual Reproduction in Animals PDFDocument7 pagesAsexual and Sexual Reproduction in Animals PDFZakir100% (1)
- The Theories of Organic EvolutionDocument2 pagesThe Theories of Organic EvolutionMary Rose Bobis VicenteNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Seeds: New Phytologist June 2010Document16 pagesThe Evolution of Seeds: New Phytologist June 2010Rudolf KiraljNo ratings yet
- Biology WAEC Likely Questions PDF DownloadDocument6 pagesBiology WAEC Likely Questions PDF DownloadCharles Obaleagbon100% (1)
- Grades Blastomere Size Fragmentation 4 3 2 1Document4 pagesGrades Blastomere Size Fragmentation 4 3 2 1easa_tNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3. Photoperiodism and EmbryogenesisDocument7 pagesWorksheet 3. Photoperiodism and EmbryogenesisSukmagita RahajengNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction For Grade 11 Worksheet 2Document8 pagesPlant Reproduction For Grade 11 Worksheet 2KISHANo ratings yet
- Asexual Vs Sexual ReproductionDocument9 pagesAsexual Vs Sexual ReproductionEdenNo ratings yet
- A Guide For AdolescentsDocument68 pagesA Guide For AdolescentsJaseme OtoyoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet. 4. Asexual ReproductionDocument3 pagesWorksheet. 4. Asexual ReproductionLeonita SwandjajaNo ratings yet
- ANAT2341 Student 2015 Quiz QuestionsDocument12 pagesANAT2341 Student 2015 Quiz QuestionsHassan ContehNo ratings yet
- How Does Protococcus ReproduceDocument2 pagesHow Does Protococcus ReproduceJohn Vincent Gomez100% (1)
- 964 QP 2 STPM Biology 2012 Section BDocument2 pages964 QP 2 STPM Biology 2012 Section BSeanNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction Vs Asexual ReproductionDocument4 pagesSexual Reproduction Vs Asexual ReproductionIsabel HontiverosNo ratings yet
- Perkecambahan Dan Pertumbuhan Palem Jepang (Actinophloeus Macarthurii Becc.) Akibat Perendaman Biji Dalam LumpurDocument7 pagesPerkecambahan Dan Pertumbuhan Palem Jepang (Actinophloeus Macarthurii Becc.) Akibat Perendaman Biji Dalam LumpurNurma YahyaNo ratings yet
- Asexual and Sexual Reproduction QuizDocument2 pagesAsexual and Sexual Reproduction QuizShannen Abegail FernandezNo ratings yet
- JNL College (Pallavi For Botany B.SC Part I) Topic-MarseliaDocument13 pagesJNL College (Pallavi For Botany B.SC Part I) Topic-MarseliaNguyễn HươngNo ratings yet
- 1-Embryonic-Stem-Cells 1ST LECDocument31 pages1-Embryonic-Stem-Cells 1ST LECrihamazim2018No ratings yet
- Animations CompleteDocument18 pagesAnimations CompleteStruggl EarthNo ratings yet
- 2 - Gametogenesis and Female CyclesDocument31 pages2 - Gametogenesis and Female CyclesMax DanhNo ratings yet
- 39740-PDF Notes Grade - 3 Science Lesson 1 Living and Non-Living ThingsDocument14 pages39740-PDF Notes Grade - 3 Science Lesson 1 Living and Non-Living ThingsNishant JasaniNo ratings yet
- Arun Muthivel Vs Union of India and OrsDocument11 pagesArun Muthivel Vs Union of India and OrsAkhil BenNo ratings yet
- General Characters of Rhodophyceae & Life Cycle of PolysiphoniaDocument49 pagesGeneral Characters of Rhodophyceae & Life Cycle of PolysiphoniaSona PectusNo ratings yet
- 0610 s21 QP 31 PDFDocument20 pages0610 s21 QP 31 PDFAarush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology - From A Cell To An Organism (Genetics Evolution)Document225 pagesDevelopmental Biology - From A Cell To An Organism (Genetics Evolution)ekamutiaraNo ratings yet