Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Eco PTT 2
Eco PTT 2
Uploaded by
angelinstanley2003Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Employment and Unemployment & Social DevelopmentDocument12 pagesEmployment and Unemployment & Social DevelopmentS Sohaib HGNo ratings yet
- Preventing Absenteeism at Work: Understand and beat this widespread phenomenonFrom EverandPreventing Absenteeism at Work: Understand and beat this widespread phenomenonNo ratings yet
- Eco PPT 1Document13 pagesEco PPT 1angelinstanley2003No ratings yet
- Group 8 - Macroeconomic Instability UnemploymentDocument40 pagesGroup 8 - Macroeconomic Instability Unemployment2021-110735No ratings yet
- Course Title: Principles of Economics Course Code: Eco 205W Topic: UnemploymentDocument7 pagesCourse Title: Principles of Economics Course Code: Eco 205W Topic: UnemploymentHoripriya Das ArpitaNo ratings yet
- Group 8 - Macroeconomic Instability UnemploymentDocument40 pagesGroup 8 - Macroeconomic Instability Unemployment2021-110735No ratings yet
- Lesson Proper For Week 13Document4 pagesLesson Proper For Week 13Sh1njo SantosNo ratings yet
- What Is UnemploymentDocument5 pagesWhat Is Unemploymentmagudamach97No ratings yet
- NSTPDocument41 pagesNSTPhiraethaileeNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Unemployment PEC100110 Principles of Economics UNILAKDocument10 pagesUnit 9 Unemployment PEC100110 Principles of Economics UNILAKalexisNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: Lecturer: Mr. AllicockDocument73 pagesMacroeconomics: Lecturer: Mr. AllicockPrecious MarksNo ratings yet
- Speech UnemplymentDocument12 pagesSpeech UnemplymentRimy KaedeNo ratings yet
- Types of UnemploymentDocument22 pagesTypes of UnemploymentKusantha Rohan WickremasingheNo ratings yet
- Ch3. UnemploymentDocument22 pagesCh3. UnemploymentDang Linh NhiNo ratings yet
- On UnemploymentDocument16 pagesOn UnemploymentIndra PrakashNo ratings yet
- Marxist Theory of UnemploymentDocument5 pagesMarxist Theory of UnemploymentSON OF WRATH HOLLOW POLNo ratings yet
- Causes of Frictional UnemploymentDocument3 pagesCauses of Frictional UnemploymentErin SuryandariNo ratings yet
- Finals NSTP2 LessonDocument58 pagesFinals NSTP2 LessonCLARK KENTH C. AGULONo ratings yet
- AhmadDocument3 pagesAhmadSHAMSUDEEN ABDULRAZAQNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Introduction To EconomicsDocument30 pages1.0 Introduction To Economicsraosamhith1No ratings yet
- UnemploymentDocument3 pagesUnemploymentKatherine Asis NatinoNo ratings yet
- Impact of Unemployment in India: Group MembersDocument17 pagesImpact of Unemployment in India: Group Membersrajesh8811No ratings yet
- Unemployment NotesDocument9 pagesUnemployment Notesdc1901020No ratings yet
- LunemploymentDocument27 pagesLunemploymentmayadaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Unemployment On EconomyDocument19 pagesEffects of Unemployment On EconomyJeet SummerNo ratings yet
- Employment, Migration, and UrbanizationDocument14 pagesEmployment, Migration, and UrbanizationAlzen Marie DelvoNo ratings yet
- Week 13 NSTP 2Document12 pagesWeek 13 NSTP 2Christian SupanNo ratings yet
- Notes Ch. Employment XII-Economics-1Document14 pagesNotes Ch. Employment XII-Economics-1abhayshukla3225No ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document3 pagesLecture 5Jenica SaludesNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Part 2Document2 pagesModule 1 - Part 2Janel Yuka AokiNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document2 pagesTopic 4Patricia PaminsaranNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Monitoring Jobs and InflationDocument5 pagesMacroeconomics Monitoring Jobs and InflationJoe100% (1)
- Handout 1 - Measuring Employment and UnemploymentDocument2 pagesHandout 1 - Measuring Employment and UnemploymentJntNo ratings yet
- Horipriya Das ArpitaDocument7 pagesHoripriya Das ArpitaHoripriya Das ArpitaNo ratings yet
- UnemploymentDocument14 pagesUnemploymentkunalkhalkhoNo ratings yet
- UnemploymentDocument1 pageUnemploymentMatus MirekNo ratings yet
- Unemployment PPT AarDocument16 pagesUnemployment PPT AarAAR11No ratings yet
- MacroDocument6 pagesMacroSherona ReidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document36 pagesChapter 5getayetemesgen99No ratings yet
- Why Is Employment So ImportantDocument13 pagesWhy Is Employment So ImportantMANDULA VARALAKSHMINo ratings yet
- 11 Economics Notes Ch15Document5 pages11 Economics Notes Ch15HackerzillaNo ratings yet
- BBF1201 - Chapter 4Document15 pagesBBF1201 - Chapter 4keemeNo ratings yet
- Unemployment NDocument10 pagesUnemployment NDj I amNo ratings yet
- Introduction To UnemploymentDocument3 pagesIntroduction To UnemploymentNozeelia BlairNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: Business Cycle and UnemploymentDocument16 pagesMacroeconomics: Business Cycle and UnemploymentAnisur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Course of The ActionDocument2 pagesCourse of The ActionHilma KamoorNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 25 Dec 2022Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 25 Dec 2022Archita VermaNo ratings yet
- Unemployment in IndiaDocument4 pagesUnemployment in IndiarakeshNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 7 UnemploymentDocument13 pagesTOPIC 7 UnemploymentPeter KimaniNo ratings yet
- Topic D) UnemploymentDocument8 pagesTopic D) UnemploymentRachel HiiNo ratings yet
- InnovationDocument3 pagesInnovationGrace haleblianNo ratings yet
- Seasonal UnemploymentDocument1 pageSeasonal UnemploymentOana PuiuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 UnemploymentDocument31 pagesLecture 3 Unemploymentephraim chisangaNo ratings yet
- The Problem of Unemployment, Poverty and Inequality: Module - 2Document15 pagesThe Problem of Unemployment, Poverty and Inequality: Module - 2Double A CreationNo ratings yet
- UNEMPLOYMENTDocument7 pagesUNEMPLOYMENTGodfrey RushabureNo ratings yet
- Economics Unit 5Document73 pagesEconomics Unit 5Aishvariya SNo ratings yet
- Vaishnavi UnemploymentDocument19 pagesVaishnavi UnemploymentVaishnavi AnthatiNo ratings yet
- Class 12 EMPLOYMENTDocument5 pagesClass 12 EMPLOYMENTAryan ph vlogsNo ratings yet
- Part-1 - Prices and Unemployment-02Document8 pagesPart-1 - Prices and Unemployment-02Manish NepaliNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgements:: "No Report Is Ever A Work of Only One Person and This One Is No Exception"Document26 pagesAcknowledgements:: "No Report Is Ever A Work of Only One Person and This One Is No Exception"lubnaarainNo ratings yet
Eco PTT 2
Eco PTT 2
Uploaded by
angelinstanley2003Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Eco PTT 2
Eco PTT 2
Uploaded by
angelinstanley2003Copyright:
Available Formats
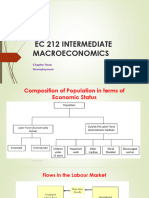
Unemployment
Unemployment occurs when someone is willing and able to work but does not
have a paid job. The unemployment rate is the percentage of people in the
labour force who are unemployed. Consequently, measuring the
unemployment rate requires identifying who is in the labour force.
Natural rate of unemployment
The natural unemployment rate is the minimum unemployment rate
resulting from real or voluntary economic forces.
It represents the number of people unemployed due to the structure of
the labor force, such as those replaced by technology or those who lack
the skills to get hired.
Natural unemployment is commonplace in the labor market as workers
flow to and from jobs or companies.
Unemployment is not considered natural if it is cyclical, institutional, or
policy-based unemployment.
Because of natural unemployment, 100% full employment is
unattainable in an economy
Frictional unemployment
Frictional unemployment occurs in a growing, stable economy. Workers moving
from job to job and new workers entering the workforce contribute to frictional
unemployment. Frictional unemployment is also caused by those deciding to
prioritize taking care of their family, returning to school, or finding purpose in
life.
Wait unemployment
One kind of frictional unemployment is called wait unemployment: it refers to
the effects of the existence of some sectors where employed workers are paid
more than the market-clearing equilibrium wage
You might also like
- Employment and Unemployment & Social DevelopmentDocument12 pagesEmployment and Unemployment & Social DevelopmentS Sohaib HGNo ratings yet
- Preventing Absenteeism at Work: Understand and beat this widespread phenomenonFrom EverandPreventing Absenteeism at Work: Understand and beat this widespread phenomenonNo ratings yet
- Eco PPT 1Document13 pagesEco PPT 1angelinstanley2003No ratings yet
- Group 8 - Macroeconomic Instability UnemploymentDocument40 pagesGroup 8 - Macroeconomic Instability Unemployment2021-110735No ratings yet
- Course Title: Principles of Economics Course Code: Eco 205W Topic: UnemploymentDocument7 pagesCourse Title: Principles of Economics Course Code: Eco 205W Topic: UnemploymentHoripriya Das ArpitaNo ratings yet
- Group 8 - Macroeconomic Instability UnemploymentDocument40 pagesGroup 8 - Macroeconomic Instability Unemployment2021-110735No ratings yet
- Lesson Proper For Week 13Document4 pagesLesson Proper For Week 13Sh1njo SantosNo ratings yet
- What Is UnemploymentDocument5 pagesWhat Is Unemploymentmagudamach97No ratings yet
- NSTPDocument41 pagesNSTPhiraethaileeNo ratings yet
- Unit 9 Unemployment PEC100110 Principles of Economics UNILAKDocument10 pagesUnit 9 Unemployment PEC100110 Principles of Economics UNILAKalexisNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: Lecturer: Mr. AllicockDocument73 pagesMacroeconomics: Lecturer: Mr. AllicockPrecious MarksNo ratings yet
- Speech UnemplymentDocument12 pagesSpeech UnemplymentRimy KaedeNo ratings yet
- Types of UnemploymentDocument22 pagesTypes of UnemploymentKusantha Rohan WickremasingheNo ratings yet
- Ch3. UnemploymentDocument22 pagesCh3. UnemploymentDang Linh NhiNo ratings yet
- On UnemploymentDocument16 pagesOn UnemploymentIndra PrakashNo ratings yet
- Marxist Theory of UnemploymentDocument5 pagesMarxist Theory of UnemploymentSON OF WRATH HOLLOW POLNo ratings yet
- Causes of Frictional UnemploymentDocument3 pagesCauses of Frictional UnemploymentErin SuryandariNo ratings yet
- Finals NSTP2 LessonDocument58 pagesFinals NSTP2 LessonCLARK KENTH C. AGULONo ratings yet
- AhmadDocument3 pagesAhmadSHAMSUDEEN ABDULRAZAQNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Introduction To EconomicsDocument30 pages1.0 Introduction To Economicsraosamhith1No ratings yet
- UnemploymentDocument3 pagesUnemploymentKatherine Asis NatinoNo ratings yet
- Impact of Unemployment in India: Group MembersDocument17 pagesImpact of Unemployment in India: Group Membersrajesh8811No ratings yet
- Unemployment NotesDocument9 pagesUnemployment Notesdc1901020No ratings yet
- LunemploymentDocument27 pagesLunemploymentmayadaNo ratings yet
- Effects of Unemployment On EconomyDocument19 pagesEffects of Unemployment On EconomyJeet SummerNo ratings yet
- Employment, Migration, and UrbanizationDocument14 pagesEmployment, Migration, and UrbanizationAlzen Marie DelvoNo ratings yet
- Week 13 NSTP 2Document12 pagesWeek 13 NSTP 2Christian SupanNo ratings yet
- Notes Ch. Employment XII-Economics-1Document14 pagesNotes Ch. Employment XII-Economics-1abhayshukla3225No ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document3 pagesLecture 5Jenica SaludesNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Part 2Document2 pagesModule 1 - Part 2Janel Yuka AokiNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document2 pagesTopic 4Patricia PaminsaranNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Monitoring Jobs and InflationDocument5 pagesMacroeconomics Monitoring Jobs and InflationJoe100% (1)
- Handout 1 - Measuring Employment and UnemploymentDocument2 pagesHandout 1 - Measuring Employment and UnemploymentJntNo ratings yet
- Horipriya Das ArpitaDocument7 pagesHoripriya Das ArpitaHoripriya Das ArpitaNo ratings yet
- UnemploymentDocument14 pagesUnemploymentkunalkhalkhoNo ratings yet
- UnemploymentDocument1 pageUnemploymentMatus MirekNo ratings yet
- Unemployment PPT AarDocument16 pagesUnemployment PPT AarAAR11No ratings yet
- MacroDocument6 pagesMacroSherona ReidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document36 pagesChapter 5getayetemesgen99No ratings yet
- Why Is Employment So ImportantDocument13 pagesWhy Is Employment So ImportantMANDULA VARALAKSHMINo ratings yet
- 11 Economics Notes Ch15Document5 pages11 Economics Notes Ch15HackerzillaNo ratings yet
- BBF1201 - Chapter 4Document15 pagesBBF1201 - Chapter 4keemeNo ratings yet
- Unemployment NDocument10 pagesUnemployment NDj I amNo ratings yet
- Introduction To UnemploymentDocument3 pagesIntroduction To UnemploymentNozeelia BlairNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics: Business Cycle and UnemploymentDocument16 pagesMacroeconomics: Business Cycle and UnemploymentAnisur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Course of The ActionDocument2 pagesCourse of The ActionHilma KamoorNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 25 Dec 2022Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 25 Dec 2022Archita VermaNo ratings yet
- Unemployment in IndiaDocument4 pagesUnemployment in IndiarakeshNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 7 UnemploymentDocument13 pagesTOPIC 7 UnemploymentPeter KimaniNo ratings yet
- Topic D) UnemploymentDocument8 pagesTopic D) UnemploymentRachel HiiNo ratings yet
- InnovationDocument3 pagesInnovationGrace haleblianNo ratings yet
- Seasonal UnemploymentDocument1 pageSeasonal UnemploymentOana PuiuNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 UnemploymentDocument31 pagesLecture 3 Unemploymentephraim chisangaNo ratings yet
- The Problem of Unemployment, Poverty and Inequality: Module - 2Document15 pagesThe Problem of Unemployment, Poverty and Inequality: Module - 2Double A CreationNo ratings yet
- UNEMPLOYMENTDocument7 pagesUNEMPLOYMENTGodfrey RushabureNo ratings yet
- Economics Unit 5Document73 pagesEconomics Unit 5Aishvariya SNo ratings yet
- Vaishnavi UnemploymentDocument19 pagesVaishnavi UnemploymentVaishnavi AnthatiNo ratings yet
- Class 12 EMPLOYMENTDocument5 pagesClass 12 EMPLOYMENTAryan ph vlogsNo ratings yet
- Part-1 - Prices and Unemployment-02Document8 pagesPart-1 - Prices and Unemployment-02Manish NepaliNo ratings yet
- Acknowledgements:: "No Report Is Ever A Work of Only One Person and This One Is No Exception"Document26 pagesAcknowledgements:: "No Report Is Ever A Work of Only One Person and This One Is No Exception"lubnaarainNo ratings yet