Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous
Uploaded by
saqlain18148Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pharm Drug ListDocument17 pagesPharm Drug Listanon_523534678No ratings yet
- Harrison TablesDocument163 pagesHarrison Tablesfrancieudo1No ratings yet
- Nursing Updates On AntidotesDocument1 pageNursing Updates On Antidotesseigelystic100% (15)
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.DDocument28 pagesReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.Dmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Antidotes Mechanism of ActionDocument10 pagesAntidotes Mechanism of Actionﻧﻮﺭﻭﻝ ﻋﻠﻴﻨﺎ ﺣﺎﺝ يهيNo ratings yet
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFDocument21 pagesReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFAndres F. TorresNo ratings yet
- Toxicology and AntidoteDocument6 pagesToxicology and AntidoteVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs - Med WardDocument1 pageCommon Drugs - Med WardRohannah D. MalawadNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument3 pagesDrugsxsuilujxNo ratings yet
- Master Pharm Drug ListDocument1 pageMaster Pharm Drug ListMichelle StramNo ratings yet
- General Principles and Management of PoisonsDocument5 pagesGeneral Principles and Management of PoisonsOkpetah Chioma christabelNo ratings yet
- Cology 3Document6 pagesCology 3arsalankhan8626No ratings yet
- 100 DrugsDocument3 pages100 Drugsp0theads015No ratings yet
- Antidotes To Commn MedicationDocument1 pageAntidotes To Commn Medicationjosephabram051590No ratings yet
- Drugs AntidotesDocument2 pagesDrugs AntidotesThierd Cañete IIINo ratings yet
- Drugs and AntidotesDocument1 pageDrugs and AntidotesKandice ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Toxicology: Saba SaeedDocument34 pagesToxicology: Saba SaeedMudassir FarooqNo ratings yet
- A-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicDocument28 pagesA-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicMahmoud Ahmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Drugs in FADocument10 pagesDrugs in FAAmanda MurphyNo ratings yet
- Drug AntidoteDocument1 pageDrug AntidoteJc JemzNo ratings yet
- Drugs and AntidotesDocument1 pageDrugs and AntidoteskiranbhandarkarNo ratings yet
- AgentDocument1 pageAgentcfournier1982No ratings yet
- Pharm C Exam 10 Drug ListDocument2 pagesPharm C Exam 10 Drug ListVokdadaNo ratings yet
- NSG AntidotesDocument1 pageNSG Antidotesshopguru101100% (1)
- Poison & Antidote Chart IWK Regional Poison Cen PDFDocument1 pagePoison & Antidote Chart IWK Regional Poison Cen PDFdeeptiNo ratings yet
- Brand NameDocument3 pagesBrand NameBia PayawalNo ratings yet
- Unit 07: Drugs Acting On The Immune System Anti-Inflammatory, Antiarthritis, and Related AgentsDocument14 pagesUnit 07: Drugs Acting On The Immune System Anti-Inflammatory, Antiarthritis, and Related AgentsDental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- AntidotesDocument5 pagesAntidotesAdaweya Arnaiz Ebrahim100% (2)
- Antidote Indication Mode of ActionDocument5 pagesAntidote Indication Mode of ActionRegalado AguhayonNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs AntidotesDocument3 pagesCommon Drugs AntidotesJhix JadraqueNo ratings yet
- NLE Poisons and AntidotesDocument2 pagesNLE Poisons and AntidotesGodfrey Franco100% (1)
- The Effect of Drugs in The Oral Cavity - A Review: Trophimus Gnanabagyan JayakaranDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Drugs in The Oral Cavity - A Review: Trophimus Gnanabagyan JayakaranHartotok VipnetNo ratings yet
- Drug Use and Dosing in Chronic Kidney Disease: Yahaya Hassan,, Rowa'J Al-Ramahi,, Noorizan Abd Aziz,, Rozina GhazaliDocument6 pagesDrug Use and Dosing in Chronic Kidney Disease: Yahaya Hassan,, Rowa'J Al-Ramahi,, Noorizan Abd Aziz,, Rozina GhazaliSoraya DiliwiyaniNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Pharmacology SkinDocument31 pagesDermatology Pharmacology SkinEuro UndisaNo ratings yet
- Drug of Choice List PDFDocument2 pagesDrug of Choice List PDFHeceas Heceas0% (1)
- FPGEE Drug ListDocument9 pagesFPGEE Drug Listrahima67No ratings yet
- 2 Pharmacology of ChemotherapeuticsDocument34 pages2 Pharmacology of ChemotherapeuticsTilaye GebruNo ratings yet
- Amphotericin B (Conventional) (Amphotericin B Deoxycholate) Dosing, Indications, Interactions, Adverse Effects, and MoreDocument1 pageAmphotericin B (Conventional) (Amphotericin B Deoxycholate) Dosing, Indications, Interactions, Adverse Effects, and MoreMohammed Taha sharjeelNo ratings yet
- Antidotes To Common Medications: Medication AntidoteDocument1 pageAntidotes To Common Medications: Medication AntidoteshangguanlongkuiNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Nervous System: A: Direct ActingDocument13 pagesAdrenergic Nervous System: A: Direct ActingmlinaballerinaNo ratings yet
- AntidotesDocument34 pagesAntidotesDivithNo ratings yet
- AntidoteDocument3 pagesAntidoteAnkush BhushanNo ratings yet
- CHOLINERGICDocument15 pagesCHOLINERGICAnita AkbarNo ratings yet
- Assignment in PharmacologyDocument4 pagesAssignment in PharmacologyGracian Vel AsocsomNo ratings yet
- Antidotes & Mechanism of ActionDocument10 pagesAntidotes & Mechanism of ActionMatsrial50% (2)
- Pharmacology MneumonicDocument40 pagesPharmacology MneumonicNikunjNo ratings yet
- Common Medications UsedDocument3 pagesCommon Medications UsedRay Michael CasupananNo ratings yet
- Drug Lists 300Document36 pagesDrug Lists 300Sammy SaloomNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Phar681 Drug List FALL 2013: Pharmacokinetics Cholinergic AntagonistsDocument10 pagesPharmacology Phar681 Drug List FALL 2013: Pharmacokinetics Cholinergic AntagonistsWilliam JonesNo ratings yet
- Gluteraldehyde, Peracetic Acid Alcohol, Iodophors QAC (Quarternary Ammonium Compounds)Document3 pagesGluteraldehyde, Peracetic Acid Alcohol, Iodophors QAC (Quarternary Ammonium Compounds)applesncoreNo ratings yet
- 120 Common MedicationsDocument5 pages120 Common MedicationsllanosarmidaNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Antidotes: Substance AntidoteDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and Antidotes: Substance AntidoteJo Ellie MarfilNo ratings yet
- List of AntibioticsDocument10 pagesList of AntibioticsAia JavierNo ratings yet
- Over 13 Years of Age Are As Follows:: Cytochrome P-450 Enzyme InteractionDocument2 pagesOver 13 Years of Age Are As Follows:: Cytochrome P-450 Enzyme InteractionMbali MabuzaNo ratings yet
- Gpat 1 ST LecDocument11 pagesGpat 1 ST LecSita mahalakshmi VakkapatlaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Made EasyDocument11 pagesPharma Made EasyLory Lyn100% (1)
- MedicineDocument3 pagesMedicineIntanNurjannahNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide Made Simple For Pharmacy Technicians 3rd Edition: 3rd EditionFrom EverandRevision Guide Made Simple For Pharmacy Technicians 3rd Edition: 3rd EditionNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide Made Simple For Pharmacy Technicians - PTCB: 4th EditionFrom EverandRevision Guide Made Simple For Pharmacy Technicians - PTCB: 4th EditionNo ratings yet
- Spire Internship ProgramDocument10 pagesSpire Internship Programsaqlain18148No ratings yet
- IMG Friendly Programs - Sheet1Document5 pagesIMG Friendly Programs - Sheet1saqlain18148No ratings yet
- DermaDocument7 pagesDermasaqlain18148No ratings yet
- Rare 01 QuestionaireDocument2 pagesRare 01 Questionairesaqlain18148No ratings yet
- Lecture 16 AntimycobacterialsDocument43 pagesLecture 16 Antimycobacterialssaqlain18148No ratings yet
Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous
Uploaded by
saqlain18148Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Miscellaneous
Miscellaneous
Uploaded by
saqlain18148Copyright:
Available Formats
Q.
At times, a patient may require administration of multiple drugs for any
disease due to which drug interactions may occur. What are different types of
Pharmacokinetic drug-drug interactions? Give examples.
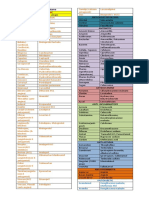
AFFECTING ABSORPTION
1. Antacids containing Ca or Al – tetracyclines.
2. Cholestyramine – digitalis & thyroxine.
3. Metoclopramide – cimetidine.
4. Liquid paraffin – Vit D.
5. Rate of absorption of paracetamol is reduced by anticholinergics & increased by
metoclopramide.
AFFECTING DISTRIBUTION
Drug displaces the other from plasma protein binding site.
1. Indomethacin, tolbutamide, sulfonamides displace warfarin.
2. Sulfonamides, salicylates displace tolbutamide.
3. Sulfonamide displace bilirubin.
AFFECTING METABOLISM
I. CYP450 family is the major metabolizing enzyme in phase I (oxidation process).
• Enzyme induction.
• Enzyme inhibition.
II. Xanthine oxidase inhibitor.
AFFECTING RENAL EXCRETION
1. Probenecid decreases tubular secretion of Penicillins, Dapsone
2. Aspirin increases toxicity of Methotrexate.
3. Sodium bicarbonate increases excretion of Aspirin & Barbiturates.
4. Ammonium chloride increases excretion of Amphetamine.
Q. A 28-year-old man working in a semi-conductor factory presented in OPD with
complaints of fatigue, nausea, conjunctivitis, skin irritation, and hair loss. On
examination, she has “milk and roses” complexion. What is your diagnosis and
how will you treat the patient?
Chronic Arsenic Poisoning. Chelator: Dimercaprol
Q. Define the following terms and give one example for each:
1. Antiseptic
Antimicrobial agents applied to living tissues to reduce possibility of infection.
E.g.; Alcohols (Ethanol and isopropyl alcohol), Povidone-iodine or Iodine tincture,
Chlorhexidine, Merbromin, Silver nitrate, Silver sulfadiazine, Potassium permanganate,
Hydrogen peroxide, Cetrimide, Benzalkonium chloride, Cetylpyridinium chloride, Dyes
(Gentian violet, brilliant green, Acriflavine), Boric acid, Acetic acid.
2. Astringents
Agents that precipitate surface proteins but don’t penetrate the cells; affecting
superficial layers only.
They toughen surface making it mechanically stronger and decrease exudation. E.g.;
Tannic acid and tannins, Ethanol, methanol, Mineral astringents (Al and Zn salts).
3. Demulcents
Agents that form soothing film over a mucous membrane, relieving minor pain and
inflammation of membrane. OR Mucoprotective agents. E.g.; Gum acacia, Gum
tragacanth, Glycyrrhiza, Methyl cellulose, Glycerin, Propylene glycol.
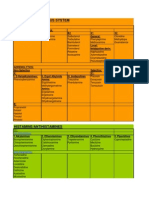
Q. Enlist the following:
1. Demelanizing agents
Hydroquinone, Mequinol, Monobenzone, Azelaic acid, Glycolic acid, Kojic acid, Lactic acid,
Tretinoin.
2. Trichogenic agents
Minoxidil, Bimatoprost, Finasteride.
3. Keratolytic agents
Salicylic acid, Urea, Propylene glycol, Podophyllum resin, Fluorouracil, Ingenol mebutate.
4. Anti-seborrheic agents
Selenium sulfide, Zinc pyrithione, Corticosteroids, Ketoconazole, Coal tar, Sulphur,
Resorcinol, Salicylic acid
Q. Enlist Ectoparasiticides.
1. Permethrin
2. Lindane (hexachlorocyclohexane)
3. Malathion
4. Ivermectin
5. Crotamiton
6. Sulfur
7. Benzyl alcohol
8. Spinosad
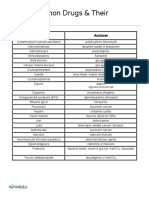
Q. Name the antidotes for overdosage of the following drugs:
DRUGS ANTIDOTES
Acetaminophen N-acetylcysteine
β-blockers Glucagon
Benzodiazepines Flumazenil
Heparin Protamine sulfate
Iron salts Deferoxamine, Deferasirox
Opioids Naloxone, Naltrexone
You might also like
- Top 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)From EverandTop 300 Drugs Pocket Reference Guide (2021 Edition)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Pharm Drug ListDocument17 pagesPharm Drug Listanon_523534678No ratings yet
- Harrison TablesDocument163 pagesHarrison Tablesfrancieudo1No ratings yet
- Nursing Updates On AntidotesDocument1 pageNursing Updates On Antidotesseigelystic100% (15)
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.DDocument28 pagesReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology: Terriann Crisp, PH.Dmus zaharaNo ratings yet
- Antidotes Mechanism of ActionDocument10 pagesAntidotes Mechanism of Actionﻧﻮﺭﻭﻝ ﻋﻠﻴﻨﺎ ﺣﺎﺝ يهيNo ratings yet
- Review Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFDocument21 pagesReview Handouts For Medical Pharmacology PDFAndres F. TorresNo ratings yet
- Toxicology and AntidoteDocument6 pagesToxicology and AntidoteVikash KushwahaNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs - Med WardDocument1 pageCommon Drugs - Med WardRohannah D. MalawadNo ratings yet
- DrugsDocument3 pagesDrugsxsuilujxNo ratings yet
- Master Pharm Drug ListDocument1 pageMaster Pharm Drug ListMichelle StramNo ratings yet
- General Principles and Management of PoisonsDocument5 pagesGeneral Principles and Management of PoisonsOkpetah Chioma christabelNo ratings yet
- Cology 3Document6 pagesCology 3arsalankhan8626No ratings yet
- 100 DrugsDocument3 pages100 Drugsp0theads015No ratings yet
- Antidotes To Commn MedicationDocument1 pageAntidotes To Commn Medicationjosephabram051590No ratings yet
- Drugs AntidotesDocument2 pagesDrugs AntidotesThierd Cañete IIINo ratings yet
- Drugs and AntidotesDocument1 pageDrugs and AntidotesKandice ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Toxicology: Saba SaeedDocument34 pagesToxicology: Saba SaeedMudassir FarooqNo ratings yet
- A-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicDocument28 pagesA-Autonomic Drugs: 1) CholinergicMahmoud Ahmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- Drugs in FADocument10 pagesDrugs in FAAmanda MurphyNo ratings yet
- Drug AntidoteDocument1 pageDrug AntidoteJc JemzNo ratings yet
- Drugs and AntidotesDocument1 pageDrugs and AntidoteskiranbhandarkarNo ratings yet
- AgentDocument1 pageAgentcfournier1982No ratings yet
- Pharm C Exam 10 Drug ListDocument2 pagesPharm C Exam 10 Drug ListVokdadaNo ratings yet
- NSG AntidotesDocument1 pageNSG Antidotesshopguru101100% (1)
- Poison & Antidote Chart IWK Regional Poison Cen PDFDocument1 pagePoison & Antidote Chart IWK Regional Poison Cen PDFdeeptiNo ratings yet
- Brand NameDocument3 pagesBrand NameBia PayawalNo ratings yet
- Unit 07: Drugs Acting On The Immune System Anti-Inflammatory, Antiarthritis, and Related AgentsDocument14 pagesUnit 07: Drugs Acting On The Immune System Anti-Inflammatory, Antiarthritis, and Related AgentsDental LecturesMMQNo ratings yet
- AntidotesDocument5 pagesAntidotesAdaweya Arnaiz Ebrahim100% (2)
- Antidote Indication Mode of ActionDocument5 pagesAntidote Indication Mode of ActionRegalado AguhayonNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs AntidotesDocument3 pagesCommon Drugs AntidotesJhix JadraqueNo ratings yet
- NLE Poisons and AntidotesDocument2 pagesNLE Poisons and AntidotesGodfrey Franco100% (1)
- The Effect of Drugs in The Oral Cavity - A Review: Trophimus Gnanabagyan JayakaranDocument8 pagesThe Effect of Drugs in The Oral Cavity - A Review: Trophimus Gnanabagyan JayakaranHartotok VipnetNo ratings yet
- Drug Use and Dosing in Chronic Kidney Disease: Yahaya Hassan,, Rowa'J Al-Ramahi,, Noorizan Abd Aziz,, Rozina GhazaliDocument6 pagesDrug Use and Dosing in Chronic Kidney Disease: Yahaya Hassan,, Rowa'J Al-Ramahi,, Noorizan Abd Aziz,, Rozina GhazaliSoraya DiliwiyaniNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Pharmacology SkinDocument31 pagesDermatology Pharmacology SkinEuro UndisaNo ratings yet
- Drug of Choice List PDFDocument2 pagesDrug of Choice List PDFHeceas Heceas0% (1)
- FPGEE Drug ListDocument9 pagesFPGEE Drug Listrahima67No ratings yet
- 2 Pharmacology of ChemotherapeuticsDocument34 pages2 Pharmacology of ChemotherapeuticsTilaye GebruNo ratings yet
- Amphotericin B (Conventional) (Amphotericin B Deoxycholate) Dosing, Indications, Interactions, Adverse Effects, and MoreDocument1 pageAmphotericin B (Conventional) (Amphotericin B Deoxycholate) Dosing, Indications, Interactions, Adverse Effects, and MoreMohammed Taha sharjeelNo ratings yet
- Antidotes To Common Medications: Medication AntidoteDocument1 pageAntidotes To Common Medications: Medication AntidoteshangguanlongkuiNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Nervous System: A: Direct ActingDocument13 pagesAdrenergic Nervous System: A: Direct ActingmlinaballerinaNo ratings yet
- AntidotesDocument34 pagesAntidotesDivithNo ratings yet
- AntidoteDocument3 pagesAntidoteAnkush BhushanNo ratings yet
- CHOLINERGICDocument15 pagesCHOLINERGICAnita AkbarNo ratings yet
- Assignment in PharmacologyDocument4 pagesAssignment in PharmacologyGracian Vel AsocsomNo ratings yet
- Antidotes & Mechanism of ActionDocument10 pagesAntidotes & Mechanism of ActionMatsrial50% (2)
- Pharmacology MneumonicDocument40 pagesPharmacology MneumonicNikunjNo ratings yet
- Common Medications UsedDocument3 pagesCommon Medications UsedRay Michael CasupananNo ratings yet
- Drug Lists 300Document36 pagesDrug Lists 300Sammy SaloomNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Phar681 Drug List FALL 2013: Pharmacokinetics Cholinergic AntagonistsDocument10 pagesPharmacology Phar681 Drug List FALL 2013: Pharmacokinetics Cholinergic AntagonistsWilliam JonesNo ratings yet
- Gluteraldehyde, Peracetic Acid Alcohol, Iodophors QAC (Quarternary Ammonium Compounds)Document3 pagesGluteraldehyde, Peracetic Acid Alcohol, Iodophors QAC (Quarternary Ammonium Compounds)applesncoreNo ratings yet
- 120 Common MedicationsDocument5 pages120 Common MedicationsllanosarmidaNo ratings yet
- Common Drugs and Antidotes: Substance AntidoteDocument2 pagesCommon Drugs and Antidotes: Substance AntidoteJo Ellie MarfilNo ratings yet
- List of AntibioticsDocument10 pagesList of AntibioticsAia JavierNo ratings yet
- Over 13 Years of Age Are As Follows:: Cytochrome P-450 Enzyme InteractionDocument2 pagesOver 13 Years of Age Are As Follows:: Cytochrome P-450 Enzyme InteractionMbali MabuzaNo ratings yet
- Gpat 1 ST LecDocument11 pagesGpat 1 ST LecSita mahalakshmi VakkapatlaNo ratings yet
- Pharma Made EasyDocument11 pagesPharma Made EasyLory Lyn100% (1)
- MedicineDocument3 pagesMedicineIntanNurjannahNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide Made Simple For Pharmacy Technicians 3rd Edition: 3rd EditionFrom EverandRevision Guide Made Simple For Pharmacy Technicians 3rd Edition: 3rd EditionNo ratings yet
- Revision Guide Made Simple For Pharmacy Technicians - PTCB: 4th EditionFrom EverandRevision Guide Made Simple For Pharmacy Technicians - PTCB: 4th EditionNo ratings yet
- Spire Internship ProgramDocument10 pagesSpire Internship Programsaqlain18148No ratings yet
- IMG Friendly Programs - Sheet1Document5 pagesIMG Friendly Programs - Sheet1saqlain18148No ratings yet
- DermaDocument7 pagesDermasaqlain18148No ratings yet
- Rare 01 QuestionaireDocument2 pagesRare 01 Questionairesaqlain18148No ratings yet
- Lecture 16 AntimycobacterialsDocument43 pagesLecture 16 Antimycobacterialssaqlain18148No ratings yet