Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cambridge International Examinations: Mathematics 9709/32 March 2017
Cambridge International Examinations: Mathematics 9709/32 March 2017
Uploaded by
rogchen666Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- HESI A2 Math Practice Tests: HESI A2 Nursing Entrance Exam Math Study GuideFrom EverandHESI A2 Math Practice Tests: HESI A2 Nursing Entrance Exam Math Study GuideNo ratings yet
- 9709 s17 Ms 32 PDFDocument12 pages9709 s17 Ms 32 PDFFortiter FysproNo ratings yet
- Exam Paper 9709Document9 pagesExam Paper 9709MayaNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 12Document8 pages9709 w16 Ms 12yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- 9709 s17 Ms 33 PDFDocument9 pages9709 s17 Ms 33 PDFFortiter FysproNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Mathematics 9709/12 March 2017Document13 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Mathematics 9709/12 March 2017mengleeNo ratings yet
- 9709 s17 Ms 13Document14 pages9709 s17 Ms 13Fortiter FysproNo ratings yet
- MARK SCHEME For The November 2004 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument7 pagesMARK SCHEME For The November 2004 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International Examinationsdkorean493No ratings yet
- 9709 m17 Ms 62Document9 pages9709 m17 Ms 62jenNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument14 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelLOKE CHENG LEONGNo ratings yet
- June 2008 MS - P3Document7 pagesJune 2008 MS - P3leaowa.mNo ratings yet
- June 2016 (v2) MS - P1 CIE Maths A-LevelDocument8 pagesJune 2016 (v2) MS - P1 CIE Maths A-LevelSnookayNo ratings yet
- 9709 s10 Ms 31Document6 pages9709 s10 Ms 31Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- 2017 Specimen Markscheme 1Document14 pages2017 Specimen Markscheme 1Bassem Khalid YasseenNo ratings yet
- June 2010 (v1) MS - P3 CIE Maths A-LevelDocument6 pagesJune 2010 (v1) MS - P3 CIE Maths A-LevelZi QianNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 32Document9 pages9709 w16 Ms 32yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 22Document7 pages9709 w16 Ms 22yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- 9709 s10 Ms 22Document5 pages9709 s10 Ms 22Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/32 October/November 2017Document9 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/32 October/November 2017Abu Anas ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 33Document6 pages9709 w16 Ms 33yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The March 2016 SeriesDocument7 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The March 2016 SerieswircexdjNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument5 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International ExaminationsHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 SeriesDocument7 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 SeriesHadi Santoso SSi MSi MMNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument8 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelBassem Khalid YasseenNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Additional Mathematics 0606/22 October/November 2020Document8 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Additional Mathematics 0606/22 October/November 2020May OsmanNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument7 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersMuhammad InamNo ratings yet
- Published Mark Scheme Notes: © UCLES 2017 Page 2 of 9Document8 pagesPublished Mark Scheme Notes: © UCLES 2017 Page 2 of 9Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- 9709 s10 Ms 21Document5 pages9709 s10 Ms 21Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- 9709 s11 Ms 22Document5 pages9709 s11 Ms 22Diksha KoossoolNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument10 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International ExaminationswircexdjNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2007 Question PaperDocument6 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2007 Question PaperKelvin SerimweNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/42 March 2018Document9 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/42 March 2018rogchen666No ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The March 2016 SeriesDocument6 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The March 2016 Seriesjoelk.brown15No ratings yet
- 9709 w17 Ms 13 PDFDocument15 pages9709 w17 Ms 13 PDFErkhes BarsboldNo ratings yet
- Marking SchemeDocument8 pagesMarking SchemePranav PurawooNo ratings yet
- A Level 2020 Paper 2 MSDocument21 pagesA Level 2020 Paper 2 MSRiley CollinsNo ratings yet
- 9709 w15 Ms 12 PDFDocument7 pages9709 w15 Ms 12 PDFyuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- 9709 w08 Ms 3Document8 pages9709 w08 Ms 3Str33tRulerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Additional Mathematics 0606/22 May/June 2022Document14 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Additional Mathematics 0606/22 May/June 2022Aurpa RahmanNo ratings yet
- 9280 Mathematics (Us) : MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SeriesDocument6 pages9280 Mathematics (Us) : MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SeriesKelvin SerimweNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 11Document6 pages9709 w16 Ms 11yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2012 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument7 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2012 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersHaiqa NasrNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Additional Mathematics 4037/22 May/June 2022Document14 pagesCambridge O Level: Additional Mathematics 4037/22 May/June 2022Kwaku Ofosu AsareNo ratings yet
- 9709 w12 Ms 33Document7 pages9709 w12 Ms 33Nicholas TehNo ratings yet
- 0606 m17 Ms 22Document8 pages0606 m17 Ms 22StanleyNo ratings yet
- 9709 s17 Ms 43 PDFDocument12 pages9709 s17 Ms 43 PDFFortiter FysproNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/31 May/June 2018Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/31 May/June 2018osama ansariNo ratings yet
- 9709 w03 MsDocument33 pages9709 w03 Msmichael hengNo ratings yet
- A Level Maths November 2012 Mark Scheme 12Document7 pagesA Level Maths November 2012 Mark Scheme 12Kelvin MuzaNo ratings yet
- 9709 w11 Ms 32Document7 pages9709 w11 Ms 32Helen B. EvansNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument6 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersJia SyuenNo ratings yet
- 9709 w09 Ms 32Document7 pages9709 w09 Ms 32Alex Antia0% (1)
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2009 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument8 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2009 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersSeleine ChongNo ratings yet
- Aqa 83651 MS Nov21Document27 pagesAqa 83651 MS Nov21sammitsui0804No ratings yet
- 9709 w14 Ms 61Document6 pages9709 w14 Ms 61MuhammadIbrahimNo ratings yet
- 9709 w17 Ms 11Document14 pages9709 w17 Ms 11charlene junusNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Additional Mathematics 0606/12 October/November 2020Document9 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Additional Mathematics 0606/12 October/November 2020May OsmanNo ratings yet
- 9709 w18 Ms 32Document19 pages9709 w18 Ms 32John KagandaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Ab Review Limits and Derivatives Answer Key1Document4 pagesCalculus Ab Review Limits and Derivatives Answer Key1rogchen666No ratings yet
- Calculus Ab Review Limits and DerivativesDocument4 pagesCalculus Ab Review Limits and Derivativesrogchen666No ratings yet
- Calculus Ab Review Transcendentals Diffeqs and VolumeareaDocument4 pagesCalculus Ab Review Transcendentals Diffeqs and Volumearearogchen666No ratings yet
- Calculus Ab Review Transcendentals Diffeqs and Volumearea Answer Key1Document4 pagesCalculus Ab Review Transcendentals Diffeqs and Volumearea Answer Key1rogchen666No ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/42 March 2019Document13 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/42 March 2019rogchen666No ratings yet
- SL Paper1Document15 pagesSL Paper1rogchen666No ratings yet
- SL Paper1Document31 pagesSL Paper1rogchen666No ratings yet
- (Maa 3.1-3.3) 3d Geometry - Triangles - SolutionsDocument15 pages(Maa 3.1-3.3) 3d Geometry - Triangles - Solutionsrogchen666No ratings yet
- (Maa 3.7) Trigonometric Functions - SolutionsDocument12 pages(Maa 3.7) Trigonometric Functions - Solutionsrogchen666No ratings yet
- (Maa 3.5) Sin, Cos, Tan On The Unit Circle - Identities - SolutionsDocument6 pages(Maa 3.5) Sin, Cos, Tan On The Unit Circle - Identities - Solutionsrogchen666No ratings yet
- AP宏观2016选择题Document12 pagesAP宏观2016选择题rogchen666No ratings yet
- AP 宏观2018选择题Document11 pagesAP 宏观2018选择题rogchen666No ratings yet
- Physics HL Review (In The Works)Document76 pagesPhysics HL Review (In The Works)rogchen666No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme 0620 - s09 - Ms - 1Document5 pagesMark Scheme 0620 - s09 - Ms - 1inaNo ratings yet
- 3247 First Language Urdu: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SeriesDocument5 pages3247 First Language Urdu: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 Seriesmstudy123456No ratings yet
- 5054 s13 Ms 22Document7 pages5054 s13 Ms 22Saaif ZareerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge o Level Results Statistics November 2023Document2 pagesCambridge o Level Results Statistics November 2023Zain NadeemNo ratings yet
- 4024 w12 Ms 12 PDFDocument5 pages4024 w12 Ms 12 PDFMustafa IqbalNo ratings yet
- TarcDocument4 pagesTarcmothicyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/34 May/June 2020Document9 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/34 May/June 2020Arthur WirjoNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document69 pagesPaper 2maryam yahyaiNo ratings yet
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT) - IGCSE Past PapersDocument1 pageInformation and Communication Technology (ICT) - IGCSE Past PapersAhmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- S3 (Exp)Document4 pagesS3 (Exp)adarashintaaqylaNo ratings yet
- Time TableDocument17 pagesTime TableBin SaadunNo ratings yet
- Copylist 2089 of K LelveDocument6 pagesCopylist 2089 of K LelveLEARNING COASTERNo ratings yet
- 0580 w18 Ms 41 PDFDocument8 pages0580 w18 Ms 41 PDFHilmar AlfianNo ratings yet
- Class IX-X - 2023-24Document2 pagesClass IX-X - 2023-24SneaXNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Information TechnologyDocument15 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Information TechnologyAse AqeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument24 pagesCambridge International ExaminationsArun Kumar AruchamyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/62 May/June 2020Document7 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/62 May/June 2020Hin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- 2025 Specimen Paper 2 Mark SchemeDocument10 pages2025 Specimen Paper 2 Mark SchemeSonia KhurramNo ratings yet
- Non-Teaching Staff Positions Advert Nov. 2023Document2 pagesNon-Teaching Staff Positions Advert Nov. 2023Isamah ChukwunaluNo ratings yet
- 4024 s18 GT PDFDocument1 page4024 s18 GT PDFShameer KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/43 October/November 2017Document7 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/43 October/November 2017junjia.fang666No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/11 May/June 2020Document3 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/11 May/June 2020Hin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: English As A Second Language 0510/22 March 2019Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: English As A Second Language 0510/22 March 2019lylyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Global Perspectives 0457/32 May/June 2017Document18 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Global Perspectives 0457/32 May/June 2017spotifysubs250No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Cambridge International Mathematics 0607/42 October/November 2020Document9 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Cambridge International Mathematics 0607/42 October/November 2020nathan.kimNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Global Perspectives 0457/32 March 2017Document17 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Global Perspectives 0457/32 March 2017Nadeesha PereraNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 May 2005Document7 pagesPaper 2 May 2005MSHNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Physics 5054/22Document11 pagesCambridge O Level: Physics 5054/22Lapu LapuNo ratings yet
- 0457 Specimen Paper Answers Paper 1 (For Examination From 2025)Document25 pages0457 Specimen Paper Answers Paper 1 (For Examination From 2025)Akshaj Gupta100% (2)
- Marathi 3218Document11 pagesMarathi 3218Nuvishta RammaNo ratings yet
Cambridge International Examinations: Mathematics 9709/32 March 2017
Cambridge International Examinations: Mathematics 9709/32 March 2017
Uploaded by
rogchen666Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge International Examinations: Mathematics 9709/32 March 2017
Cambridge International Examinations: Mathematics 9709/32 March 2017
Uploaded by
rogchen666Copyright:
Available Formats
Cambridge International Examinations
Cambridge International Advanced Level
MATHEMATICS 9709/32
Paper 3 Pure Mathematics March 2017
MARK SCHEME
Maximum Mark: 75
Published
This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates, to indicate the requirements of the
examination. It shows the basis on which Examiners were instructed to award marks. It does not indicate the
details of the discussions that took place at an Examiners’ meeting before marking began, which would have
considered the acceptability of alternative answers.
Mark schemes should be read in conjunction with the question paper and the Principal Examiner Report for
Teachers.
Cambridge will not enter into discussions about these mark schemes.
Cambridge is publishing the mark schemes for the March 2017 series for most Cambridge IGCSE®,
Cambridge International A and AS Level components and some Cambridge O Level components.
® IGCSE is a registered trademark.
This document consists of 11 printed pages.
© UCLES 2017 [Turn over
9709/32 Cambridge International A Level – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Mark Scheme Notes
Marks are of the following three types:
M Method mark, awarded for a valid method applied to the problem. Method marks are not lost
for numerical errors, algebraic slips or errors in units. However, it is not usually sufficient for a
candidate just to indicate an intention of using some method or just to quote a formula; the
formula or idea must be applied to the specific problem in hand, e.g. by substituting the
relevant quantities into the formula. Correct application of a formula without the formula being
quoted obviously earns the M mark and in some cases an M mark can be implied from a
correct answer.
A Accuracy mark, awarded for a correct answer or intermediate step correctly obtained.
Accuracy marks cannot be given unless the associated method mark is earned (or implied).
B Mark for a correct result or statement independent of method marks.
• When a part of a question has two or more “method” steps, the M marks are generally
independent unless the scheme specifically says otherwise; and similarly when there are several
B marks allocated. The notation DM or DB (or dep*) is used to indicate that a particular M or B
mark is dependent on an earlier M or B (asterisked) mark in the scheme. When two or more
steps are run together by the candidate, the earlier marks are implied and full credit is given.
• The symbol implies that the A or B mark indicated is allowed for work correctly following on
from previously incorrect results. Otherwise, A or B marks are given for correct work only. A and
B marks are not given for fortuitously “correct” answers or results obtained from incorrect
working.
• Note: B2 or A2 means that the candidate can earn 2 or 0.
B2/1/0 means that the candidate can earn anything from 0 to 2.
The marks indicated in the scheme may not be subdivided. If there is genuine doubt whether a
candidate has earned a mark, allow the candidate the benefit of the doubt. Unless otherwise
indicated, marks once gained cannot subsequently be lost, e.g. wrong working following a correct
form of answer is ignored.
• Wrong or missing units in an answer should not lead to the loss of a mark unless the scheme
specifically indicates otherwise.
• For a numerical answer, allow the A or B mark if a value is obtained which is correct to 3 s.f., or
which would be correct to 3 s.f. if rounded (1 d.p. in the case of an angle). As stated above, an A
or B mark is not given if a correct numerical answer arises fortuitously from incorrect working. For
Mechanics questions, allow A or B marks for correct answers which arise from taking g equal to
9.8 or 9.81 instead of 10.
© UCLES 2017 Page 2 of 11
9709/32 Cambridge International A Level – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
The following abbreviations may be used in a mark scheme or used on the scripts:
AEF/OE Any Equivalent Form (of answer is equally acceptable) / Or Equivalent
AG Answer Given on the question paper (so extra checking is needed to ensure that the
detailed working leading to the result is valid)
CAO Correct Answer Only (emphasising that no “follow through” from a previous error is
allowed)
CWO Correct Working Only – often written by a ‘fortuitous’ answer
ISW Ignore Subsequent Working
SOI Seen or implied
SR Special Ruling (detailing the mark to be given for a specific wrong solution, or a case
where some standard marking practice is to be varied in the light of a particular
circumstance)
Penalties
MR –1 A penalty of MR –1 is deducted from A or B marks when the data of a question or part
question are genuinely misread and the object and difficulty of the question remain
unaltered. In this case all A and B marks then become “follow through ” marks. MR is
not applied when the candidate misreads his own figures – this is regarded as an error in
accuracy. An MR –2 penalty may be applied in particular cases if agreed at the
coordination meeting.
PA –1 This is deducted from A or B marks in the case of premature approximation. The PA –1
penalty is usually discussed at the meeting.
© UCLES 2017 Page 3 of 11
9709/32 Cambridge International A Level – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
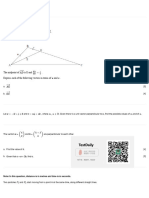
1 Remove logarithm and obtain 1 + 2 x = e 2 B1
Use correct method to solve an equation of the form 2 x = a , where a > 0 M1
Obtain answer x = 2.676 A1
Total: 3
Question Answer Marks
2 EITHER:
State or imply non-modular inequality ( x − 4) 2 < (2(3x + 1)) 2 , or corresponding (B1
quadratic equation, or pair of linear equations x − 4 = ±2(3x + 1)
Make reasonable solution attempt at a 3-term quadratic, or solve two linear M1
equations for x
Obtain critical values x = − 65 and x = 2 A1
7
State final answer x < − 65 , x > 2 A1)
7
OR:
Obtain critical value x = − 65 from a graphical method, or by inspection, or by (B1
solving a linear equation or inequality
Obtain critical value x = 2
similarly B2
7
State final answer x < − 65 , x > 2 B1)
7
Total: 4
Question Answer Marks
3(i) Sketch a relevant graph, e.g. y = e
− 12 x B1
Sketch a second relevant graph, e.g. y = 4 − x 2 , and justify the given statement B1
Total: 2
3(ii) Calculate the value of a relevant expression or values of a pair of expressions at M1
x = – 1 and x = – 1.5
complete the argument correctly with correct calculated values A1
Total: 2
© UCLES 2017 Page 4 of 11
9709/32 Cambridge International A Level – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
3(iii) Use the iterative formula correctly at least once M1
Obtain final answer – 1.41 A1
Show sufficient iterations to 4 d.p. to justify – 1.41 to 2 d.p., or show there is a sign A1
change in the interval ( – 1.415, – 1.405)
Total: 3
Question Answer Marks
4(i) State R = 17 B1
Use trig formula to find α M1
Obtain α = 61.93° with no errors seen A1
Total: 3
4(ii) Evaluate cos −1 (4 / 17) to at least 1d.p. (76.39° to 2 d.p.) B1
Use a correct method to find a value of x in the interval 0° < x < 180° M1
Obtain answer, e.g. x = 7.2° A1
Obtain second answer, e.g. x = 110.8°and no others A1
[Ignore answers outside the given interval.]
[Treat answers in radians as a misread.]
Total: 4
Question Answer Marks
5 Use product rule M1
Obtain correct derivative in any form A1
Equate derivative to zero, use Pythagoras and obtain a quadratic equation in tan x M1
Obtain tan 2 x − a tan x + 1 = 0 , or equivalent A1
Use the condition for a quadratic to have only one root M1
Obtain answer a = 2 A1
Obtain answer x = 14 π A1
Total: 7
© UCLES 2017 Page 5 of 11
9709/32 Cambridge International A Level – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
6(i) Verify that the point with position vector i + 2 j − 3k lies in the plane B1
EITHER:
Find a second point on l and substitute its coordinates in the equation of p (M1
Verify that the second point, e.g. (3, 1, – 2), lies in the plane A1)
OR:
Expand scalar product of a normal to p and the direction vector of l (M1
Verify scalar product is zero A1)
Total: 3
© UCLES 2017 Page 6 of 11
9709/32 Cambridge International A Level – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
6(ii) EITHER:
Use scalar product to obtain a relevant equation in a , b and c, e.g. 2a − b + c = 0 (B1
Obtain a second relevant equation, e.g. 3a + b − 5c = 0 , and solve for one ratio M1
e.g. a : b
Obtain a : b : c = 4 : 13 : 5 , or equivalent A1
Substitute (3, – 1, 2) and the values of a, b and c in the general equation and find d M1
Obtain answer 4 x + 13 y + 5 z = 9 , or equivalent A1)
OR1:
Attempt to calculate vector product of relevant vectors, e.g. (M1
(2i − j + k ) × (3i + j − 5k )
Obtain two correct components A1
Obtain correct answer, e.g. 4i + 13j + 5k A1
Substitute (3, – 1, 2) in 4 x + 13 y + 5 z = d , or equivalent, and find d M1
Obtain answer 4 x + 13 y + 5 z = 9 , or equivalent A1)
OR2:
Using the relevant point and relevant vectors form a 2-parameter equation for the (M1
plane
State a correct equation, e.g. r = 3i − j + 2k + λ (2i − j + k ) + µ (3i + j − 5k ) A1
State three correct equations in x, y, z, λ and µ A1
Eliminate λ and µ M1
Obtain answer 4 x + 13 y + 5 z = 9 , or equivalent A1)
OR3:
Using the relevant point and relevant vectors form a determinant equation for the (M1
plane
x − 3 y +1 z − 2 A1
State a correct equation, e.g. 2 −1 1 =0
3 1 −5
Attempt to expand the determinant M1
Obtain or imply two correct cofactors A1
© UCLES 2017 Page 7 of 11
9709/32 Cambridge International A Level – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
Obtain answer 4 x + 13 y + 5 z = 9 , or equivalent A1)
Total: 5
© UCLES 2017 Page 8 of 11
9709/32 Cambridge International A Level – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
7(i) dV dh B1
State or imply =2
dt dt
dV B1
State or imply = 1 − 0.2 h
dt
Obtain the given answer correctly B1
Total: 3
7(ii) 1 B1
State or imply du = − dh , or equivalent
2 h
Substitute for h and dh throughout M1
5
20(5 − u ) A1
Obtain T = ∫
3
u
du , or equivalent
Integrate and obtain terms 100ln u − 20u , or equivalent A1
Substitute limits u = 3 and u = 5 correctly M1
Obtain answer 11.1, with no errors seen A1
Total: 6
© UCLES 2017 Page 9 of 11
9709/32 Cambridge International A Level – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
8(i) Substitute z = −1 + i and attempt expansions of the z 2 and z 4 terms M1
Use i 2 = −1 at least once M1
Complete the verification correctly A1
Total: 3
8(ii) State second root z = −1 − i B1
Carry out a complete method for finding a quadratic factor with zeros M1
−1 + i and − 1 − i
Obtain z 2 + 2 z + 2 , or equivalent A1
Attempt division of p(z) by z 2 + 2 z + 2 and reach a partial quotient z 2 + kz M1
Obtain quadratic factor z 2 − 2 z + 5 A1
Solve 3-term quadratic and use i 2 = −1 M1
Obtain roots 1 + 2i and 1 – 2i A1
Total: 7
Question Answer Marks
9(i) A Bx + C B1
State or imply the form +
2 + x 4 + x2
Use a relevant method to determine a constant M1
Obtain one of the values A = – 2, B = 1, C = 4 A1
Obtain a second value A1
Obtain the third value A1
Total: 5
© UCLES 2017 Page 10 of 11
9709/32 Cambridge International A Level – Mark Scheme March 2017
PUBLISHED
Question Answer Marks
9(ii) Use correct method to obtain the first two terms of the expansion of (1 + 12 x ) −1 , M1
(2 + x) −1 , (1 + 14 x 2 ) −1 or (4 + x 2 ) −1
Obtain correct unsimplified expansions up to the term in x 2 of each partial fraction A1 + A1
Multiply out up to the term in x 2 by Bx + C , where BC ≠ 0 M1
Obtain final answer 3
x − 12 x 2 A1
4
[Symbolic binomial coefficients, e.g. −1 C 2 , are not sufficient for the first M1. The
f.t. is on A, B, C.]
[In the case of an attempt to expand x(6 − x)(2 + x) −1 (4 + x 2 ) −1 , give M1A1A1 for
the expansions, M1 for multiplying out fully, and A1 for the final answer.]
Total: 5
Question Answer Marks
10(i) ln x B1
State or imply derivative is 2
x
State or imply gradient of the normal at x = e is − 12 e , or equivalent B1
Carry out a complete method for finding the x-coordinate of Q M1
2 A1
Obtain answer x = e + , or exact equivalent
e
Total: 4
10(ii) Justify the given statement by integration or by differentiation B1
Total: 1
10(iii) ln x M1*
Integrate by parts and reach ax(ln x)2 + b x. ∫ x
dx
Complete the integration and obtain x(ln x) 2 − 2 x ln x + 2 x , or equivalent A1
Use limits x = 1 and x = e correctly, having integrated twice DM1
Obtain exact value e – 2 A1
1 B1
Use x- coordinate of Q found in part (i) and obtain final answer e − 2 +
e
Total: 5
© UCLES 2017 Page 11 of 11
You might also like
- HESI A2 Math Practice Tests: HESI A2 Nursing Entrance Exam Math Study GuideFrom EverandHESI A2 Math Practice Tests: HESI A2 Nursing Entrance Exam Math Study GuideNo ratings yet
- 9709 s17 Ms 32 PDFDocument12 pages9709 s17 Ms 32 PDFFortiter FysproNo ratings yet
- Exam Paper 9709Document9 pagesExam Paper 9709MayaNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 12Document8 pages9709 w16 Ms 12yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- 9709 s17 Ms 33 PDFDocument9 pages9709 s17 Ms 33 PDFFortiter FysproNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Mathematics 9709/12 March 2017Document13 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Mathematics 9709/12 March 2017mengleeNo ratings yet
- 9709 s17 Ms 13Document14 pages9709 s17 Ms 13Fortiter FysproNo ratings yet
- MARK SCHEME For The November 2004 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument7 pagesMARK SCHEME For The November 2004 Question Paper: University of Cambridge International Examinationsdkorean493No ratings yet
- 9709 m17 Ms 62Document9 pages9709 m17 Ms 62jenNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument14 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelLOKE CHENG LEONGNo ratings yet
- June 2008 MS - P3Document7 pagesJune 2008 MS - P3leaowa.mNo ratings yet
- June 2016 (v2) MS - P1 CIE Maths A-LevelDocument8 pagesJune 2016 (v2) MS - P1 CIE Maths A-LevelSnookayNo ratings yet
- 9709 s10 Ms 31Document6 pages9709 s10 Ms 31Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- 2017 Specimen Markscheme 1Document14 pages2017 Specimen Markscheme 1Bassem Khalid YasseenNo ratings yet
- June 2010 (v1) MS - P3 CIE Maths A-LevelDocument6 pagesJune 2010 (v1) MS - P3 CIE Maths A-LevelZi QianNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 32Document9 pages9709 w16 Ms 32yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 22Document7 pages9709 w16 Ms 22yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- 9709 s10 Ms 22Document5 pages9709 s10 Ms 22Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/32 October/November 2017Document9 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/32 October/November 2017Abu Anas ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 33Document6 pages9709 w16 Ms 33yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The March 2016 SeriesDocument7 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The March 2016 SerieswircexdjNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument5 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International ExaminationsHubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 SeriesDocument7 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2014 SeriesHadi Santoso SSi MSi MMNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument8 pagesCambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelBassem Khalid YasseenNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Additional Mathematics 0606/22 October/November 2020Document8 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Additional Mathematics 0606/22 October/November 2020May OsmanNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument7 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2010 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersMuhammad InamNo ratings yet
- Published Mark Scheme Notes: © UCLES 2017 Page 2 of 9Document8 pagesPublished Mark Scheme Notes: © UCLES 2017 Page 2 of 9Ahmed AliNo ratings yet
- 9709 s10 Ms 21Document5 pages9709 s10 Ms 21Hubbak KhanNo ratings yet
- 9709 s11 Ms 22Document5 pages9709 s11 Ms 22Diksha KoossoolNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument10 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International ExaminationswircexdjNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2007 Question PaperDocument6 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2007 Question PaperKelvin SerimweNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/42 March 2018Document9 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/42 March 2018rogchen666No ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The March 2016 SeriesDocument6 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The March 2016 Seriesjoelk.brown15No ratings yet
- 9709 w17 Ms 13 PDFDocument15 pages9709 w17 Ms 13 PDFErkhes BarsboldNo ratings yet
- Marking SchemeDocument8 pagesMarking SchemePranav PurawooNo ratings yet
- A Level 2020 Paper 2 MSDocument21 pagesA Level 2020 Paper 2 MSRiley CollinsNo ratings yet
- 9709 w15 Ms 12 PDFDocument7 pages9709 w15 Ms 12 PDFyuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- 9709 w08 Ms 3Document8 pages9709 w08 Ms 3Str33tRulerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Additional Mathematics 0606/22 May/June 2022Document14 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Additional Mathematics 0606/22 May/June 2022Aurpa RahmanNo ratings yet
- 9280 Mathematics (Us) : MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SeriesDocument6 pages9280 Mathematics (Us) : MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SeriesKelvin SerimweNo ratings yet
- 9709 w16 Ms 11Document6 pages9709 w16 Ms 11yuke kristinaNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2012 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument7 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2012 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersHaiqa NasrNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Additional Mathematics 4037/22 May/June 2022Document14 pagesCambridge O Level: Additional Mathematics 4037/22 May/June 2022Kwaku Ofosu AsareNo ratings yet
- 9709 w12 Ms 33Document7 pages9709 w12 Ms 33Nicholas TehNo ratings yet
- 0606 m17 Ms 22Document8 pages0606 m17 Ms 22StanleyNo ratings yet
- 9709 s17 Ms 43 PDFDocument12 pages9709 s17 Ms 43 PDFFortiter FysproNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/31 May/June 2018Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/31 May/June 2018osama ansariNo ratings yet
- 9709 w03 MsDocument33 pages9709 w03 Msmichael hengNo ratings yet
- A Level Maths November 2012 Mark Scheme 12Document7 pagesA Level Maths November 2012 Mark Scheme 12Kelvin MuzaNo ratings yet
- 9709 w11 Ms 32Document7 pages9709 w11 Ms 32Helen B. EvansNo ratings yet
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument6 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2011 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersJia SyuenNo ratings yet
- 9709 w09 Ms 32Document7 pages9709 w09 Ms 32Alex Antia0% (1)
- 9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2009 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument8 pages9709 Mathematics: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2009 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersSeleine ChongNo ratings yet
- Aqa 83651 MS Nov21Document27 pagesAqa 83651 MS Nov21sammitsui0804No ratings yet
- 9709 w14 Ms 61Document6 pages9709 w14 Ms 61MuhammadIbrahimNo ratings yet
- 9709 w17 Ms 11Document14 pages9709 w17 Ms 11charlene junusNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Additional Mathematics 0606/12 October/November 2020Document9 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Additional Mathematics 0606/12 October/November 2020May OsmanNo ratings yet
- 9709 w18 Ms 32Document19 pages9709 w18 Ms 32John KagandaNo ratings yet
- Calculus Ab Review Limits and Derivatives Answer Key1Document4 pagesCalculus Ab Review Limits and Derivatives Answer Key1rogchen666No ratings yet
- Calculus Ab Review Limits and DerivativesDocument4 pagesCalculus Ab Review Limits and Derivativesrogchen666No ratings yet
- Calculus Ab Review Transcendentals Diffeqs and VolumeareaDocument4 pagesCalculus Ab Review Transcendentals Diffeqs and Volumearearogchen666No ratings yet
- Calculus Ab Review Transcendentals Diffeqs and Volumearea Answer Key1Document4 pagesCalculus Ab Review Transcendentals Diffeqs and Volumearea Answer Key1rogchen666No ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/42 March 2019Document13 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Mathematics 9709/42 March 2019rogchen666No ratings yet
- SL Paper1Document15 pagesSL Paper1rogchen666No ratings yet
- SL Paper1Document31 pagesSL Paper1rogchen666No ratings yet
- (Maa 3.1-3.3) 3d Geometry - Triangles - SolutionsDocument15 pages(Maa 3.1-3.3) 3d Geometry - Triangles - Solutionsrogchen666No ratings yet
- (Maa 3.7) Trigonometric Functions - SolutionsDocument12 pages(Maa 3.7) Trigonometric Functions - Solutionsrogchen666No ratings yet
- (Maa 3.5) Sin, Cos, Tan On The Unit Circle - Identities - SolutionsDocument6 pages(Maa 3.5) Sin, Cos, Tan On The Unit Circle - Identities - Solutionsrogchen666No ratings yet
- AP宏观2016选择题Document12 pagesAP宏观2016选择题rogchen666No ratings yet
- AP 宏观2018选择题Document11 pagesAP 宏观2018选择题rogchen666No ratings yet
- Physics HL Review (In The Works)Document76 pagesPhysics HL Review (In The Works)rogchen666No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme 0620 - s09 - Ms - 1Document5 pagesMark Scheme 0620 - s09 - Ms - 1inaNo ratings yet
- 3247 First Language Urdu: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SeriesDocument5 pages3247 First Language Urdu: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 Seriesmstudy123456No ratings yet
- 5054 s13 Ms 22Document7 pages5054 s13 Ms 22Saaif ZareerNo ratings yet
- Cambridge o Level Results Statistics November 2023Document2 pagesCambridge o Level Results Statistics November 2023Zain NadeemNo ratings yet
- 4024 w12 Ms 12 PDFDocument5 pages4024 w12 Ms 12 PDFMustafa IqbalNo ratings yet
- TarcDocument4 pagesTarcmothicyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/34 May/June 2020Document9 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/34 May/June 2020Arthur WirjoNo ratings yet
- Paper 2Document69 pagesPaper 2maryam yahyaiNo ratings yet
- Information and Communication Technology (ICT) - IGCSE Past PapersDocument1 pageInformation and Communication Technology (ICT) - IGCSE Past PapersAhmed MahmoudNo ratings yet
- S3 (Exp)Document4 pagesS3 (Exp)adarashintaaqylaNo ratings yet
- Time TableDocument17 pagesTime TableBin SaadunNo ratings yet
- Copylist 2089 of K LelveDocument6 pagesCopylist 2089 of K LelveLEARNING COASTERNo ratings yet
- 0580 w18 Ms 41 PDFDocument8 pages0580 w18 Ms 41 PDFHilmar AlfianNo ratings yet
- Class IX-X - 2023-24Document2 pagesClass IX-X - 2023-24SneaXNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Information TechnologyDocument15 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Information TechnologyAse AqeNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International ExaminationsDocument24 pagesCambridge International ExaminationsArun Kumar AruchamyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/62 May/June 2020Document7 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/62 May/June 2020Hin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- 2025 Specimen Paper 2 Mark SchemeDocument10 pages2025 Specimen Paper 2 Mark SchemeSonia KhurramNo ratings yet
- Non-Teaching Staff Positions Advert Nov. 2023Document2 pagesNon-Teaching Staff Positions Advert Nov. 2023Isamah ChukwunaluNo ratings yet
- 4024 s18 GT PDFDocument1 page4024 s18 GT PDFShameer KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/43 October/November 2017Document7 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Geography 0460/43 October/November 2017junjia.fang666No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/11 May/June 2020Document3 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Combined Science 0653/11 May/June 2020Hin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: English As A Second Language 0510/22 March 2019Document11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: English As A Second Language 0510/22 March 2019lylyNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Global Perspectives 0457/32 May/June 2017Document18 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Global Perspectives 0457/32 May/June 2017spotifysubs250No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Cambridge International Mathematics 0607/42 October/November 2020Document9 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Cambridge International Mathematics 0607/42 October/November 2020nathan.kimNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International Examinations: Global Perspectives 0457/32 March 2017Document17 pagesCambridge International Examinations: Global Perspectives 0457/32 March 2017Nadeesha PereraNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 May 2005Document7 pagesPaper 2 May 2005MSHNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Physics 5054/22Document11 pagesCambridge O Level: Physics 5054/22Lapu LapuNo ratings yet
- 0457 Specimen Paper Answers Paper 1 (For Examination From 2025)Document25 pages0457 Specimen Paper Answers Paper 1 (For Examination From 2025)Akshaj Gupta100% (2)
- Marathi 3218Document11 pagesMarathi 3218Nuvishta RammaNo ratings yet