Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Class 6 Pathology
Class 6 Pathology
Uploaded by
Mostafizur Rahman0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesNeoplasm refers to abnormal cell growth and can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Benign tumors are self-limited and do not invade other tissues, while malignant tumors are characterized by uncontrolled growth and invasion. Oncology is the study of tumors. Tumors are classified based on their tissue of origin and behavior. The key differences between benign and malignant tumors are size, growth rate, invasion of surrounding tissues, spread to distant sites, and whether they recur after removal.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentNeoplasm refers to abnormal cell growth and can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Benign tumors are self-limited and do not invade other tissues, while malignant tumors are characterized by uncontrolled growth and invasion. Oncology is the study of tumors. Tumors are classified based on their tissue of origin and behavior. The key differences between benign and malignant tumors are size, growth rate, invasion of surrounding tissues, spread to distant sites, and whether they recur after removal.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views4 pagesClass 6 Pathology
Class 6 Pathology
Uploaded by
Mostafizur RahmanNeoplasm refers to abnormal cell growth and can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Benign tumors are self-limited and do not invade other tissues, while malignant tumors are characterized by uncontrolled growth and invasion. Oncology is the study of tumors. Tumors are classified based on their tissue of origin and behavior. The key differences between benign and malignant tumors are size, growth rate, invasion of surrounding tissues, spread to distant sites, and whether they recur after removal.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 4
Neoplasm
What is Neoplasm?
Neoplasm comes from the word neoplasia that means new growth.
The term neoplasia refers to a mass that has developed due to
abnormal cell or tissue growth.
Neoplasm can be define as a new growth of tissue characterized by
progressive, uncontrolled proliferation of cells. generally word
neoplasm is known as tumour.
Oncology : Oncology is the study of tumour or neoplasm. Greek
“oncos” means tumour.
Classification:
Histogenetic:
1. Tumour of epithelial tissue origin.
2. Tumour of connective tissue origin.
Behavioural Type:
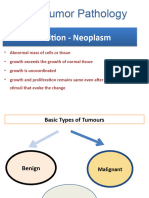
1.BenignTumour: They do not invade surrounding or remote tissue.
2.Malignent tumour: Always invade the surrounding or remote
tissue.Generally word these are known as cancer.
3.Latent Cancer: Cell of these neoplasm shows features of malignant
tumour but clinically silent. e.g. prostate cancer of elderly man.
Benign Tumour: Benign neoplasm are those neoplasm which do not
invade surrounding or remote tissue. Generally the suffix “oma”
denotes benign neoplasm; e.g. adenoma means benign tumour of
epithelial cell.
Characteristics of benign tumour:
1. Generally small in size.
2. Within a capsule.
3. No local invasion.
4. Slow Growth.
5. No variation of tumour cell morphology.
6. Tumour cells are similar to the cells of tissue origin.
7. Nucleus is similar in size and nucleus cytoplasm ratio is normal(1:4
to 1:6)
8. No spreadign to remote tissue.
9. Generally no recurrence after complete removal.
10. Generally not fatal.
Malignant Tumour: Malignant neoplasm are those neoplasm which
invade surrounding or remote tissues. In common word malignent
tumour are known as cancer. Suffix “carcinoma” “Sarcoma” “blastoma”
denotes malignant tumour. E.g. adenocarcinoma means malignant
tumour of epithelial cell.
sarcoma: Generally malignant tumour of soft tissue are expressed by
sarcoma.
Carcinoma: Generally malignant tumour of epithelium tissue are
expressed by carcinoma.
Characteristics of malignant tumour:
1. Generally large in size.
2. Local invasion is one of the main characteristics.
3. Rapid growth.
4. Neoplasms cells are not similar to the cell of tissue origin.
5. Variation in tumour cell morphology.
6. Nucleus size is variate.
7. Nucleus and cytoplasm ratio is abnormal.(May be 1:1).
8. Generally spread to remote tissue.
9. Recurrence after complete removal can be found.
10. Almost fatal.
Different between benign and malignanttumour:
Benign neoplasm Malignant neoplasm
Generally small Generally Large
Slow Growth Rapid Growth
Possess a capsule No capsule.
No local invasion. Local invasion present.
Similar to the cell of origin tissue. Not similar.
No variation of tumour cell Present variation of tumour cell
morphology. morphology.
Nucleus size is similar. Not similar
Nucleus cytoplasm ratio Nucleus cytoplasm ratio
normal(1:4 to 1:6) Increased(may be 1:1)
Generally no recurrent after May recurrent even after complete
complete removal. removal.
Metastasis absent. Must metastasis.
Usually not fatal. Fatal.
Metastasis:Metastasis means transport of malignant cells to remote
from its origin and invation of the tissue at transported site.
Carcinogen: Any kind of agent that can produce any type of tumour.
Such as: Radiation,Nicotine,papiloma virus etc.
Miasmatic bakground of tumour:
Homeopathic treatment:
You might also like
- NeoplasiaDocument150 pagesNeoplasiaDavon Richard Walter Van-VeenNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia (I) : Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-Sen UniversityDocument113 pagesNeoplasia (I) : Department of Pathology, Sun Yat-Sen UniversityleyreaNo ratings yet
- Pharma en OncologyDocument14 pagesPharma en Oncologyyaqoob008No ratings yet
- 2 - Fudamentals of Neoplasm 1 - 2022Document33 pages2 - Fudamentals of Neoplasm 1 - 2022noreentamer20No ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument31 pagesNeoplasiaAnin PrakashNo ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument16 pagesNeoplasiahassansjavaidNo ratings yet
- Oncology 1Document178 pagesOncology 1SUNIL KUMARNo ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument11 pagesNeoplasiaعبدالكريم الاسدNo ratings yet
- PathologyDocument15 pagesPathologySaba SaqerNo ratings yet
- Tumours and Their ManagemntDocument105 pagesTumours and Their ManagemntJoseph MuzabulaNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia IDocument37 pagesNeoplasia ISam JamesNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia ReviewDocument22 pagesNeoplasia ReviewLegnaNo ratings yet
- They Adhere To Any Part That They Seize In, Similar To A Crab's Behavior. Malignant, As AppliedDocument10 pagesThey Adhere To Any Part That They Seize In, Similar To A Crab's Behavior. Malignant, As AppliedbeylaNo ratings yet
- 3 - Fudamentals of Neoplasm 2022Document32 pages3 - Fudamentals of Neoplasm 2022noreentamer20No ratings yet
- 02.22.1 Neoplasia I Final PDFDocument79 pages02.22.1 Neoplasia I Final PDFSameeha AbbasNo ratings yet
- 2 NeoplasiaDocument48 pages2 Neoplasiayadetakebede53No ratings yet
- What Is NeoplasmsDocument38 pagesWhat Is NeoplasmsRashid HussainNo ratings yet
- 2011OncologyBasics Tutorial1 0Document12 pages2011OncologyBasics Tutorial1 0Vivek SinghNo ratings yet
- TumorsDocument10 pagesTumorsZain HadiNo ratings yet
- 4.nomenclature of NeoplasmDocument32 pages4.nomenclature of NeoplasmDipo Mas SuyudiNo ratings yet
- PBL 1 POD 2 (Malignant)Document3 pagesPBL 1 POD 2 (Malignant)xd7xopNo ratings yet
- 04 Basic Tumor Pathology1Document9 pages04 Basic Tumor Pathology1tharindu manjulaNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: Dr. Methaq Mueen Lec.2Document48 pagesNeoplasia: Dr. Methaq Mueen Lec.2bv2328002No ratings yet
- Pathology NeoplasiaDocument15 pagesPathology NeoplasiaLaiba WarisNo ratings yet
- CancerDocument18 pagesCancerIftikhar AhmedNo ratings yet
- NE0PLASIADocument28 pagesNE0PLASIADaniel SutantoNo ratings yet
- 212F - Oncology L1 - 2104Document25 pages212F - Oncology L1 - 2104Tyler LiuNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis and Classification of NeoplasiaDocument36 pagesPathogenesis and Classification of NeoplasiaCLEMENT0% (1)
- Neoplasia S. M Jawwad AliDocument25 pagesNeoplasia S. M Jawwad AliAnt EverafterNo ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument12 pagesNeoplasiaavidadarkestevillearnNo ratings yet
- Pharmacy 2 Pathology Lecture 10Document10 pagesPharmacy 2 Pathology Lecture 10Mohamad saeedNo ratings yet
- Slo Neoplsia Ca3Document13 pagesSlo Neoplsia Ca3perymeearumugamNo ratings yet
- L2-Principles of Surgical OncologyDocument25 pagesL2-Principles of Surgical OncologyTofeeq101 WaNo ratings yet
- Pathology AssignDocument5 pagesPathology AssignHidayaNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia IDocument47 pagesNeoplasia I7s49sv4rmzNo ratings yet
- Definitions of Benign Vs MalignantDocument4 pagesDefinitions of Benign Vs MalignantMitreswaran SelvakumaranNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia Summer 2020Document38 pagesNeoplasia Summer 2020Sharif HossainNo ratings yet
- Cars I No GenesisDocument30 pagesCars I No Genesiskes25251No ratings yet
- Medical-Surgical (Week 7) : (Sir Laingo-Octobe 07) JayloiseDocument6 pagesMedical-Surgical (Week 7) : (Sir Laingo-Octobe 07) Jayloisejeanylou chachi coronadoNo ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument48 pagesNeoplasiathomndumbaro401No ratings yet
- Name: Class: Department: Roll No.: Subject: Course Code: Cr. HR.: Submitted To: Date of Submission: TopicDocument8 pagesName: Class: Department: Roll No.: Subject: Course Code: Cr. HR.: Submitted To: Date of Submission: TopicAnoosha FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Benign Tumours Precancerous Conditions Malignant Tumours How Tumours and Cancers Are NamedDocument11 pagesBenign Tumours Precancerous Conditions Malignant Tumours How Tumours and Cancers Are Namedk_472894540No ratings yet
- Module 1: Pathophysiologic Concepts in Cellular AberrationsDocument9 pagesModule 1: Pathophysiologic Concepts in Cellular AberrationsJanelle Cabida SupnadNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: Dr. Dyah Marianingrum Mkes, SP - PADocument35 pagesNeoplasia: Dr. Dyah Marianingrum Mkes, SP - PANdari DyaekaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy (Lab Activity)Document3 pagesAnaphy (Lab Activity)Mvl KakashiNo ratings yet
- Non-Odontogenic Tumors of Epithelial Tissue Origin: Guided By-Presented byDocument93 pagesNon-Odontogenic Tumors of Epithelial Tissue Origin: Guided By-Presented byrajaniNo ratings yet
- OncologyDocument23 pagesOncologyEslam NassarNo ratings yet
- Translated MaxfaxDocument72 pagesTranslated Maxfaxtaaariii18No ratings yet
- Neoplasia Pathology IDocument38 pagesNeoplasia Pathology Isachin sharmaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Oncology NotesDocument58 pagesNursing Oncology Notesrachel lorenNo ratings yet
- PCM 332.1 (Pathology-Neoplasia)Document26 pagesPCM 332.1 (Pathology-Neoplasia)Nigel ZaraNo ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument7 pagesNeoplasiaJils SureshNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: NomenclatureDocument26 pagesNeoplasia: NomenclatureAbdul Samad NoonariNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: Introductory Surgery ClassDocument37 pagesNeoplasia: Introductory Surgery ClassPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Introductory To NeoplamsDocument4 pagesIntroductory To NeoplamsIoana GrayNo ratings yet
- OncologyDocument26 pagesOncologyPhilip Gene II MalacasNo ratings yet
- Robin's HistopathDocument6 pagesRobin's HistopathKennedy DelrosarioNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: Basic PathologyDocument12 pagesNeoplasia: Basic Pathologyandroid tricksNo ratings yet
- Cancers and Abnormal GrowthsDocument37 pagesCancers and Abnormal GrowthsNABAKOOZA ELIZABETHNo ratings yet
- Question:Discuss Various Malignancies of The Oral Region AnswersDocument6 pagesQuestion:Discuss Various Malignancies of The Oral Region AnswersMahdaba sheikh MohamudNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Managing and Coordinating Nursing Care Fifth EditionDocument7 pagesTest Bank For Managing and Coordinating Nursing Care Fifth Editionkelliejenkinsxzqnyeajkt100% (29)
- Hybridoma Technology and Its ApplicationDocument26 pagesHybridoma Technology and Its ApplicationAnonymous qxIMLafRNo ratings yet
- PenileDocument2 pagesPenileAREOLA Vera SophiaNo ratings yet
- NFL Jerseysj4kgegv PDFDocument60 pagesNFL Jerseysj4kgegv PDFhoeway88No ratings yet
- Hazard Classification of Household Chemical Products in Korea According To The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of ChemicalsDocument11 pagesHazard Classification of Household Chemical Products in Korea According To The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicalsjapra17No ratings yet
- Breast Cancer PP TDocument33 pagesBreast Cancer PP Tsupriyasalgare93No ratings yet
- Icam 1Document10 pagesIcam 1dusseldorf27No ratings yet
- Karsinoma NasofaringDocument28 pagesKarsinoma NasofaringTiara SafitriNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia Case Studies142654Document1 pageNeoplasia Case Studies142654Patrick Ngo'nga ChifwemaNo ratings yet
- NH Màn Hình 2023-02-17 Lúc 19.48.17Document46 pagesNH Màn Hình 2023-02-17 Lúc 19.48.17hoàng nguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and CancerDocument3 pagesThe Eukaryotic Cell Cycle and CancerKaren SinorNo ratings yet
- Article Breast Ultrasound - Why and When by Dr. HombalDocument2 pagesArticle Breast Ultrasound - Why and When by Dr. HombalDomica DavisNo ratings yet
- SBFR REPORT FORMAT NewDocument14 pagesSBFR REPORT FORMAT NewMiraf MesfinNo ratings yet
- Skin CancerDocument37 pagesSkin CancerSangita Sonwane100% (1)
- Breast Cancer Therapeutics and Biomarkers: Past, Present, and Future ApproachesDocument19 pagesBreast Cancer Therapeutics and Biomarkers: Past, Present, and Future ApproachesDavide RadiceNo ratings yet
- Chapter 77. Primary Care of Older AdultsDocument3 pagesChapter 77. Primary Care of Older AdultsAliNo ratings yet
- Idiom Collocation Phrasal VerbDocument35 pagesIdiom Collocation Phrasal VerbMai NgocNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2024Document10 pagesQuiz 2024bijay kumarNo ratings yet
- Prodige 23Document14 pagesProdige 23josebaNo ratings yet
- Hall 1 Hall 2 Hall 3 Hall 4 Hall 5 Hall 6 Hall 7Document4 pagesHall 1 Hall 2 Hall 3 Hall 4 Hall 5 Hall 6 Hall 7Adrián RattoNo ratings yet
- Surgical Pathologic Spread Patterns of Endometrial Cancer: A Group StudyDocument7 pagesSurgical Pathologic Spread Patterns of Endometrial Cancer: A Group StudyInsighte Behavioral CareNo ratings yet
- Survival With Cemiplimab in Recurrent Cervical CancerDocument12 pagesSurvival With Cemiplimab in Recurrent Cervical CancerKassem HijazyNo ratings yet
- HistopathologyDocument1 pageHistopathologyHershei Vonne BaccayNo ratings yet
- A Glimpse of HopeDocument2 pagesA Glimpse of HopeSwagatalokhi BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Medical PhysicistDocument11 pagesMedical Physicistniko.carson.9No ratings yet
- Case Presentation (Oncology)Document26 pagesCase Presentation (Oncology)Froilan FerrerNo ratings yet
- The Sun Daily-260621Document24 pagesThe Sun Daily-260621hanafi mamatNo ratings yet
- Essay 3. The CNN HeroesDocument3 pagesEssay 3. The CNN HeroesMARIA JOSE CARAVEO GUERRERONo ratings yet
- Rhabdomyosarcoma of The Vagina in An Adolescent GirDocument11 pagesRhabdomyosarcoma of The Vagina in An Adolescent GirPhn StanleyNo ratings yet