Professional Documents
Culture Documents
9618 MJ 12 Q4b
9618 MJ 12 Q4b
Uploaded by
Riaz KhanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
9618 MJ 12 Q4b
9618 MJ 12 Q4b
Uploaded by
Riaz KhanCopyright:
Available Formats
8
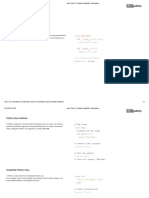
(b) Some bit manipulation instructions are shown in the table:
Instruction
Explanation
Opcode Operand
AND #n Bitwise AND operation of the contents of ACC with the operand
AND <address> Bitwise AND operation of the contents of ACC with the contents of <address>
XOR #n Bitwise XOR operation of the contents of ACC with the operand
XOR <address> Bitwise XOR operation of the contents of ACC with the contents of <address>
OR #n Bitwise OR operation of the contents of ACC with the operand
OR <address> Bitwise OR operation of the contents of ACC with the contents of <address>
<address> can be an absolute address or a symbolic address
# denotes a denary number, e.g. #123
The contents of the memory address 300 are shown:
Bit Number 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
300 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
(i) The contents of memory address 300 represent an unsigned binary integer.
Write the denary value of the unsigned binary integer in memory address 300.
..................................................................................................................................... [1]
(ii) An assembly language program needs to test if bit number 2 in memory address 300
is a 1.
Complete the assembly language instruction to perform this test.
......................... #4
[1]
(iii) An assembly language program needs to set bit numbers 4, 5, 6 and 7 to 0, but keep
bits 0 to 3 with their existing values.
Write the assembly language instruction to perform this action.
...........................................................................................................................................
..................................................................................................................................... [2]
© UCLES 2021 9618/12/M/J/21
You might also like
- Cambridge IGCSE: Computer Science 0478/12Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Computer Science 0478/12waihon.pang2011100% (2)
- Assembly Programming:Simple, Short, And Straightforward Way Of Learning Assembly LanguageFrom EverandAssembly Programming:Simple, Short, And Straightforward Way Of Learning Assembly LanguageRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Lenguaje Ensamblador. Problemas: Capítulo 1Document8 pagesLenguaje Ensamblador. Problemas: Capítulo 1Jorge ArmasNo ratings yet
- Chapter6 AnsDocument8 pagesChapter6 Ansdaria77No ratings yet
- Computer Laboratory Manual1Document58 pagesComputer Laboratory Manual1Sreekanth PagadapalliNo ratings yet
- 4th and 5th Chapter TestDocument14 pages4th and 5th Chapter TestKleanthis KokkinosNo ratings yet
- 2210 w16 QP 12Document6 pages2210 w16 QP 12TrynosNo ratings yet
- Half p2 Cs GcseDocument10 pagesHalf p2 Cs GcsealexanderjimjohnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Assembly Language-PPandMS-2018Document7 pagesChapter 6 Assembly Language-PPandMS-2018Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-3 Test (Hodder)Document8 pagesChapter 1-3 Test (Hodder)AbdulBasitBilalSheikhNo ratings yet
- Information Representation TestDocument8 pagesInformation Representation Testbilal.jamalNo ratings yet
- 2 1 Tick (3) One Box To Show Which Term Is An Example of A Verification CheckDocument103 pages2 1 Tick (3) One Box To Show Which Term Is An Example of A Verification CheckZane sohNo ratings yet
- PEQs 231 AlgorithmsDocument281 pagesPEQs 231 Algorithmsharoon.sham13No ratings yet
- 1 1 1-Binary-SystemsDocument12 pages1 1 1-Binary-SystemsinternationalmakkhayarNo ratings yet
- Computer Science 3Document123 pagesComputer Science 3Muhtasim Ibne kamalNo ratings yet
- Processor Fundamentals QuestionsDocument15 pagesProcessor Fundamentals QuestionsLisaNo ratings yet
- Binary & Coding - QP-1Document12 pagesBinary & Coding - QP-1tobleroneNo ratings yet
- G12 - RevisionDocument4 pagesG12 - RevisionMs. SewdineNo ratings yet
- Computer Organisation PYQ 2010 TO 2022 3RD SEM CSE ITDocument52 pagesComputer Organisation PYQ 2010 TO 2022 3RD SEM CSE ITKAJI AZAD ALINo ratings yet
- Edexcel Computer Science IGCSE Revision PaperDocument15 pagesEdexcel Computer Science IGCSE Revision PapersivaNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Computer Architecture - Jan 2003 (PAST PAPER)Document3 pagesFundamentals of Computer Architecture - Jan 2003 (PAST PAPER)BIG MNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityprajapatidhnjNo ratings yet
- Revision Questions For Chapter 1: Register To Register Transfer Load Accumulator From MemoryDocument2 pagesRevision Questions For Chapter 1: Register To Register Transfer Load Accumulator From MemoryWilliam manzhi KajjubiNo ratings yet
- Mock 2022Document9 pagesMock 2022Muhammad Ahsan SaleemNo ratings yet
- MIPS Assembly Language Programming: Computer Organization and AssemblyDocument33 pagesMIPS Assembly Language Programming: Computer Organization and AssemblySardar IrfanullahNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument14 pagesGujarat Technological University220170107139No ratings yet
- hw6 CircuitsDocument4 pageshw6 Circuitsayylmao kekNo ratings yet
- CsDocument20 pagesCsRAGHU RAM SAKAMURINo ratings yet
- Non-Restoring Division. (8) : A B+ C G HDocument2 pagesNon-Restoring Division. (8) : A B+ C G HNehaNo ratings yet
- Images675874 2023 Specimen Paper 1b PDFDocument12 pagesImages675874 2023 Specimen Paper 1b PDF2025svyasNo ratings yet
- CS Q (C)Document10 pagesCS Q (C)internationalmakkhayarNo ratings yet
- Comsci 1 NewDocument16 pagesComsci 1 NewpetriNo ratings yet
- Holiday Work f3Document7 pagesHoliday Work f3dhrisha05No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityprajapatidhnjNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 HomeworkDocument3 pagesGrade 9 Homeworkkeech.No ratings yet
- CS2203 - Computer Organization - MTE1 PaperDocument2 pagesCS2203 - Computer Organization - MTE1 PaperUshashi NandiNo ratings yet
- Base64 Encoding Torn ApartDocument15 pagesBase64 Encoding Torn ApartSahil QaiserNo ratings yet
- 02.machine Structure - Machine Language - Assembly LanguageDocument13 pages02.machine Structure - Machine Language - Assembly LanguagemingmangNo ratings yet
- CAO Set 8Document8 pagesCAO Set 8Vilayat AliNo ratings yet
- Bachelor in Computer Applications Term-End F.xamination June, 2OO7Document4 pagesBachelor in Computer Applications Term-End F.xamination June, 2OO7Yaśodānandan DāsNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Computer Science 0478/12Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Computer Science 0478/12Walter white heisenbergNo ratings yet
- CS 2110 Homework 5 Intro To AssemblyDocument15 pagesCS 2110 Homework 5 Intro To AssemblyKlutch BoyNo ratings yet
- Digital Homework 202883836281Document13 pagesDigital Homework 202883836281depressedtortNo ratings yet
- Lab 2Document12 pagesLab 2DavidNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Computer Systems Architecture: Page 1 of 9 Examination - January Semester 2018Document9 pagesIntroduction To Computer Systems Architecture: Page 1 of 9 Examination - January Semester 2018Benjamin TangNo ratings yet
- Draw The Instruction Word Format and Indicate The Number of Bits in Each PartDocument12 pagesDraw The Instruction Word Format and Indicate The Number of Bits in Each PartYogendra KshetriNo ratings yet
- ICT121 - JULY - 2017 - Exam PaperDocument8 pagesICT121 - JULY - 2017 - Exam PaperBenjamin TangNo ratings yet
- Question Bank For DecoDocument2 pagesQuestion Bank For Decotheamg7272No ratings yet
- B2 Ece2003 50333 50077 50428Document2 pagesB2 Ece2003 50333 50077 50428NanduNo ratings yet
- Number SystemDocument2 pagesNumber SystemTravellerNo ratings yet
- GTU CO PaperDocument2 pagesGTU CO PaperVishal TailorNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2: Fundamental of C' LanguageDocument28 pagesChapter-2: Fundamental of C' LanguageISHITA BASU ROYNo ratings yet
- Cambridge O Level: Computer Science 2210/11Document12 pagesCambridge O Level: Computer Science 2210/11syafiynuralif2912No ratings yet
- DPPL Sessional-II SolutionDocument3 pagesDPPL Sessional-II Solutionhimanshu.m.singh132No ratings yet
- Be Summer 2021Document2 pagesBe Summer 2021Chandresh KanzariyaNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9608/12Document16 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science 9608/12Daniel HakimNo ratings yet
- 2 B C D e Data Rep Comp Jan 2023Document4 pages2 B C D e Data Rep Comp Jan 2023alanchenyinNo ratings yet
- 2 Assembly 1Document54 pages2 Assembly 1Eduardo Garcia BreijoNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document4 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.krithikgokul selvamNo ratings yet
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 6No ratings yet
- Sel Pp-MsDocument1 pageSel Pp-MsRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- © Cambridge International Examinations 2015Document1 page© Cambridge International Examinations 2015Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- 7.4. External Hardware DevicesDocument10 pages7.4. External Hardware DevicesRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Information Technology 9626/04Document8 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Information Technology 9626/04Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Published Answer Marks One Mark For Each Point (Max Three) - 3Document1 pagePublished Answer Marks One Mark For Each Point (Max Three) - 3Riaz Khan100% (1)
- 2210/22/M/J/15 © Ucles 2015Document1 page2210/22/M/J/15 © Ucles 2015Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- 1.1 PMT Data Representation1Document14 pages1.1 PMT Data Representation1Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Information Technology 9626/13 October/November 2021Document11 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Information Technology 9626/13 October/November 2021Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- 9.4. The Transmission Control Protocol - Internet Protocol (TCP IP)Document13 pages9.4. The Transmission Control Protocol - Internet Protocol (TCP IP)Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- 2 0Document1 page2 0Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Information Technology 9626/12 October/November 2021Document11 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Information Technology 9626/12 October/November 2021Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Learn Python 3 - Python - Code Challenges (Optional) Cheatsheet - CodecademyDocument12 pagesLearn Python 3 - Python - Code Challenges (Optional) Cheatsheet - CodecademyRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science For Examination From 2021Document28 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Computer Science For Examination From 2021Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Learn Python 3 - Modules Cheatsheet - CodecademyDocument4 pagesLearn Python 3 - Modules Cheatsheet - CodecademyRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- WB Chapter 8 ProgrammingDocument29 pagesWB Chapter 8 ProgrammingRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- WB Chapter 5 The Internet and Cyber Security-AnswersDocument7 pagesWB Chapter 5 The Internet and Cyber Security-AnswersRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Learn Python 3 - Lists Cheatsheet - CodecademyDocument9 pagesLearn Python 3 - Lists Cheatsheet - CodecademyRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Learn Python 3 - Loops Cheatsheet - CodecademyDocument5 pagesLearn Python 3 - Loops Cheatsheet - CodecademyRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Learn Python 3 - Classes Cheatsheet - CodecademyDocument6 pagesLearn Python 3 - Classes Cheatsheet - CodecademyRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- WB Chapter 7 Algorithm Design and Problem SolvingDocument21 pagesWB Chapter 7 Algorithm Design and Problem SolvingRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- WB Chapter 2 Data TransmissionDocument15 pagesWB Chapter 2 Data TransmissionRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- WB Chapter 1 Data RepresentationDocument21 pagesWB Chapter 1 Data RepresentationRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- 1 2 2-Security-AspectsDocument9 pages1 2 2-Security-AspectsRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- WB Chapter 6 Automated and Emerging TechnologiesDocument12 pagesWB Chapter 6 Automated and Emerging TechnologiesRiaz Khan100% (1)
- BCD-Error CorrectionDocument2 pagesBCD-Error CorrectionRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- BCD (Binary Coded Decimal)Document4 pagesBCD (Binary Coded Decimal)Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- 7 Transition Elements WSDocument73 pages7 Transition Elements WSRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Test IG Chapter 1Document4 pagesTest IG Chapter 1Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- 000 Python Basics ReferenceDocument12 pages000 Python Basics ReferenceRiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Three Schema Arch 1Document2 pagesThree Schema Arch 1Riaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Umesh MultithreadingDocument34 pagesUmesh MultithreadingEr Akhilesh SinghNo ratings yet
- Ajustar Boot Uefi LinuxDocument6 pagesAjustar Boot Uefi Linuxrobsonantunes21No ratings yet
- Microsoft Dynamics GP Performance White PaperDocument37 pagesMicrosoft Dynamics GP Performance White PaperMike ScottNo ratings yet
- HPE Flexible Slot Power SuppliesDocument3 pagesHPE Flexible Slot Power SuppliesReyes Saul Rodriguez EstradaNo ratings yet
- 18f4550 Timer0 ExampleDocument2 pages18f4550 Timer0 ExampleHumberto RoddhuerNo ratings yet
- OSY Lecture 2 Notes - MSBTE NEXT ICONDocument11 pagesOSY Lecture 2 Notes - MSBTE NEXT ICONBarik PradeepNo ratings yet
- Acer Altos W2000h-W370h F4 Ps v2.0Document2 pagesAcer Altos W2000h-W370h F4 Ps v2.0Ajay KrishnaNo ratings yet
- History of The MouseDocument12 pagesHistory of The MouseM_Salman_khanNo ratings yet
- DKA790GX Series: MS-7550 (V1.X) MainboardDocument116 pagesDKA790GX Series: MS-7550 (V1.X) MainboardPablo Antonio Ortega LuceroNo ratings yet
- Apple Macintosh 12-83Document18 pagesApple Macintosh 12-83heliosnineNo ratings yet
- Memory Reference Instructions ExecutionDocument13 pagesMemory Reference Instructions ExecutionAditya Singh100% (1)
- PC & Tech Authority - July 2018Document116 pagesPC & Tech Authority - July 2018Faik KurtishiNo ratings yet
- X0020Document32 pagesX0020cakristofNo ratings yet
- WiD Pricelist 2021Q4Document32 pagesWiD Pricelist 2021Q4Shashi Mae BonifacioNo ratings yet
- OSMAKDocument19 pagesOSMAKAlfredo TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Lan8710A/Lan8710Ai: Small Footprint Mii/Rmii 10/100 Ethernet Transceiver With HP Auto-Mdix and Flexpwr TechnologyDocument80 pagesLan8710A/Lan8710Ai: Small Footprint Mii/Rmii 10/100 Ethernet Transceiver With HP Auto-Mdix and Flexpwr TechnologyseborgNo ratings yet
- Vivobook 14 X413 (11th Gen Intel) - Tech Specs Laptops For Home ASUS IndiaDocument3 pagesVivobook 14 X413 (11th Gen Intel) - Tech Specs Laptops For Home ASUS IndiaSree HarshithNo ratings yet
- Geehy 32 Bit ARM Cortex MCU - 2023 07 13 090801Document4 pagesGeehy 32 Bit ARM Cortex MCU - 2023 07 13 090801palurdo2No ratings yet
- 1st Quarter - Periodical - Test-In - ICT 8 - 2023-2024Document3 pages1st Quarter - Periodical - Test-In - ICT 8 - 2023-2024analiza leah s nullenNo ratings yet
- Icts - Form No. Ims-2016-02-00 - 2020Document16 pagesIcts - Form No. Ims-2016-02-00 - 2020MIS MijerssNo ratings yet
- Comparc Cpo203Document39 pagesComparc Cpo203jerick_alviaNo ratings yet
- MSP 430Document32 pagesMSP 430Chahbaz AmanNo ratings yet
- LinuxLiteOs Manual InstallationDocument62 pagesLinuxLiteOs Manual Installationavion12No ratings yet
- Backup PS2 GamesDocument2 pagesBackup PS2 GamesBUFDHNo ratings yet
- My Book UserManualDocument90 pagesMy Book UserManualstfreidlinNo ratings yet
- DKP6008 Communication Protocol ReviewDocument2 pagesDKP6008 Communication Protocol ReviewВася Пупкин100% (1)
- 1999-07 The Computer Paper - BC EditionDocument138 pages1999-07 The Computer Paper - BC EditionthecomputerpaperNo ratings yet
- DP Monitor 14061 DriversDocument1,087 pagesDP Monitor 14061 Driversberto_716No ratings yet
- Computer 2.0 English (Computer Awareness Book by RBE)Document158 pagesComputer 2.0 English (Computer Awareness Book by RBE)shiva997738No ratings yet
- ReadmeDocument4 pagesReadmeJose Guillermo Morales BernalNo ratings yet