Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NHADEN Reflection
NHADEN Reflection
Uploaded by
Ellixander LanuzoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The German Law of Contract.Document1,034 pagesThe German Law of Contract.Алексей Агеев92% (13)
- Gender Equality Thesis Queen AngDocument52 pagesGender Equality Thesis Queen AngQueen Ang72% (25)
- Til 1755-R3 Lci Water - Cooled Bus LeaksDocument8 pagesTil 1755-R3 Lci Water - Cooled Bus LeaksMichael SanchezNo ratings yet
- Iloilo City Gender Code: RO 2006-087Document23 pagesIloilo City Gender Code: RO 2006-087Iloilo City Council100% (1)
- Torts: Mbe Practice QuestionsDocument16 pagesTorts: Mbe Practice Questionsnkolder84No ratings yet
- Gender&Youth AssignmentDocument9 pagesGender&Youth Assignmentbereket woldemedhinNo ratings yet
- Women, Development, and Gender Inequality: Published Online: 09 June 2016Document9 pagesWomen, Development, and Gender Inequality: Published Online: 09 June 2016ReynNo ratings yet
- Rotc Finals Exam ReviewerDocument387 pagesRotc Finals Exam ReviewerLorielle OlivaNo ratings yet
- Gen - Soc End Term Lesson 1 and 2Document23 pagesGen - Soc End Term Lesson 1 and 2Dianne ShakiraNo ratings yet
- International InstrumentsDocument4 pagesInternational InstrumentsTitus MasilaNo ratings yet
- GAD AwarenessDocument10 pagesGAD AwarenessKyla Alap-apNo ratings yet
- Module 8Document8 pagesModule 8Winnie ToribioNo ratings yet
- Gender and Development: Internationa L MandatesDocument88 pagesGender and Development: Internationa L MandatesIrene AnastasiaNo ratings yet
- Gender and DevelopmentDocument9 pagesGender and DevelopmentmiaallysabretanaNo ratings yet
- Pa 201Document11 pagesPa 201Sarah Mae PelaezNo ratings yet
- Gender Equality Policy GuidelinesDocument27 pagesGender Equality Policy GuidelinesRAHUL LALJIBHAI PANCHOLI-IBNo ratings yet
- Human Rights Approach: Republic of The Philippines Commission On Higher Education Samar College, Inc. Catbalogan CityDocument5 pagesHuman Rights Approach: Republic of The Philippines Commission On Higher Education Samar College, Inc. Catbalogan CityKJ PacamparaNo ratings yet
- Group 5Document20 pagesGroup 5James bryan TayuponNo ratings yet
- EDUC 110 CHAP 5 8 The Te WPS OfficeDocument18 pagesEDUC 110 CHAP 5 8 The Te WPS OfficeDumapias RobraceNo ratings yet
- Achieving The Sustainable Development Goals in Africa: Call For A Paradigm ShiftDocument3 pagesAchieving The Sustainable Development Goals in Africa: Call For A Paradigm ShiftKobutungi ClaireNo ratings yet
- Women and Sustainable Development Goals: Delhi. E Mail-Contact: 09711440385 (Corresponding Author)Document7 pagesWomen and Sustainable Development Goals: Delhi. E Mail-Contact: 09711440385 (Corresponding Author)Danah Angelica SambranaNo ratings yet
- Beijing Platform For Action: Philippine Comission For WomenDocument21 pagesBeijing Platform For Action: Philippine Comission For WomenMark PorcadillaNo ratings yet
- Rich HensonDocument3 pagesRich HensonJerwin CanterasNo ratings yet
- Laws, Policies & Programs For Philippine WomenDocument38 pagesLaws, Policies & Programs For Philippine WomenAngel Marie Rule100% (1)
- Educ 110 ReportDocument4 pagesEduc 110 ReportJosephine Claire UgalinoNo ratings yet
- MALUYA, Gwyneth ASSIGNMENT#1Document5 pagesMALUYA, Gwyneth ASSIGNMENT#1Maluya GwynethNo ratings yet
- Pelaez ReportDocument3 pagesPelaez ReportSarah Mae PelaezNo ratings yet
- Psir Model Answers For Previous Year Questions Paper-IiDocument64 pagesPsir Model Answers For Previous Year Questions Paper-IiBbudyNo ratings yet
- Basic Research ProposalDocument17 pagesBasic Research ProposalDENNIS RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- SDG EssayDocument4 pagesSDG Essayagracecastaneros09No ratings yet
- Human Rights and DevelopmentDocument1 pageHuman Rights and DevelopmentDianne MendozaNo ratings yet
- 09 Rey TyDocument27 pages09 Rey TyJoanne Mae VillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document3 pagesChapter 5Paulo Justin Tabangcora OropillaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5. Maam B. FINAL DRAFTDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 5. Maam B. FINAL DRAFTMariza GiraoNo ratings yet
- GROUP 4 ProfEd 312Document25 pagesGROUP 4 ProfEd 312Rochelle UrbodaNo ratings yet
- Civic GENDER AND DEVELOPMENTDocument13 pagesCivic GENDER AND DEVELOPMENTGustaval VulcanNo ratings yet
- Slot-Tb2 Digital Assignment-3 Gender Inequality: Introduction To Innovative Project (Phy1901)Document13 pagesSlot-Tb2 Digital Assignment-3 Gender Inequality: Introduction To Innovative Project (Phy1901)AnirudhPavanNo ratings yet
- ProfEd 602 Reporting WPS OfficeDocument38 pagesProfEd 602 Reporting WPS OfficeLilyNo ratings yet
- STS Gender EqualityDocument2 pagesSTS Gender EqualityEJ PalomariaNo ratings yet
- Global Issues That Concern Schools and SocietyDocument4 pagesGlobal Issues That Concern Schools and Societycelestine samuya50% (4)
- Colouring the Future: Why the United Nations plan to end poverty and wars is workingFrom EverandColouring the Future: Why the United Nations plan to end poverty and wars is workingNo ratings yet
- Ldp616 Gender Issues in Development Exam RevsDocument56 pagesLdp616 Gender Issues in Development Exam Revsdmugalloy100% (1)
- Gender EqualityDocument3 pagesGender EqualityRamakant PatilNo ratings yet
- Gender Discrimination in India: Dr.E.Raju, M.A., M.Phil., PH.D., Post Doctoral FellowDocument11 pagesGender Discrimination in India: Dr.E.Raju, M.A., M.Phil., PH.D., Post Doctoral FellowRaja RajhansNo ratings yet
- Combating Gender Based ViolenceDocument32 pagesCombating Gender Based Violencemary engNo ratings yet
- Group 1: Abigail D. Monis Paul Jenrae Samson Mikaella JarabaDocument15 pagesGroup 1: Abigail D. Monis Paul Jenrae Samson Mikaella JarabaAbigail MonisNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 3 Complete Chapters 7 10Document31 pagesProf Ed 3 Complete Chapters 7 10Melay AlmoradoNo ratings yet
- SDGsDocument9 pagesSDGsoluwatimileyinjoshua88No ratings yet
- Policy BriefDocument6 pagesPolicy BriefJust BNo ratings yet
- National Gender Policy 2015Document57 pagesNational Gender Policy 2015mvulamacfieldNo ratings yet
- Act 1Document2 pagesAct 1Gripthru ShotsNo ratings yet
- Are Men Different To Women (Sem 1Document9 pagesAre Men Different To Women (Sem 1Kyle Christian Manuel MorilloNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development GoalsDocument7 pagesSustainable Development GoalsYugenNo ratings yet
- Gender EqualityDocument3 pagesGender EqualityShoto TodorokiNo ratings yet
- Gender EqualityDocument5 pagesGender EqualityFadi FreeNo ratings yet
- What Is Gender and Why Does It Matter?Document13 pagesWhat Is Gender and Why Does It Matter?Jaymark AmarilleNo ratings yet
- Global Issues That Concern Schools and SocietyDocument23 pagesGlobal Issues That Concern Schools and SocietyMary Grace Apinado100% (1)
- SDGDocument7 pagesSDGsheena baquirelNo ratings yet
- Gender Equality: Importance of Gender EgualityDocument3 pagesGender Equality: Importance of Gender EgualityDD ENTERTAINNo ratings yet
- Gender DRR Information Booklet EngDocument25 pagesGender DRR Information Booklet EngNune HarutyunyanNo ratings yet
- Beijin Declaration and Platform For Action of 1995Document6 pagesBeijin Declaration and Platform For Action of 1995VanshikNo ratings yet
- Gender Perspective in Business RKB Law College AssamDocument9 pagesGender Perspective in Business RKB Law College AssamSAYANTAN ROYNo ratings yet
- Gender EqualityDocument16 pagesGender EqualityJapheth David (diplomat)No ratings yet
- Discusssion ForumDocument2 pagesDiscusssion ForumEllixander LanuzoNo ratings yet
- PT 2 TAX LAW Gen Math Piecewise Function Repaired RepairedDocument4 pagesPT 2 TAX LAW Gen Math Piecewise Function Repaired RepairedEllixander LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Croatia Gec11Document6 pagesCroatia Gec11Ellixander LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Green Red and White Modern Christmas Party A4 DocumentDocument1 pageGreen Red and White Modern Christmas Party A4 DocumentEllixander LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Elec 1 Assessment 2Document1 pageElec 1 Assessment 2Ellixander LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Measurement LevelsDocument67 pagesMeasurement LevelsEllixander LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Chattisgarh Stamp ActDocument31 pagesChattisgarh Stamp ActASHUTOSH MISHRANo ratings yet
- Rc2172017a0009 - Cbi Fir Against NDTVDocument88 pagesRc2172017a0009 - Cbi Fir Against NDTVPGurus100% (9)
- 10 - Đề Thi Tham Khảo Ts10 - 2020Document4 pages10 - Đề Thi Tham Khảo Ts10 - 2020Duyen MyNo ratings yet
- AHHHHDocument2 pagesAHHHHerscholaraccNo ratings yet
- Bhanwar Singh v. Puran AIR 2008 SC 1490Document8 pagesBhanwar Singh v. Puran AIR 2008 SC 1490bobby1993 DunnaNo ratings yet
- Magnaye Isaiah. AsynchronousDocument2 pagesMagnaye Isaiah. AsynchronousAyen Rodriguez MagnayeNo ratings yet
- PGL - 500B Euro - AQUANTUS KAMA - 16 NOV 2023-VF2Document9 pagesPGL - 500B Euro - AQUANTUS KAMA - 16 NOV 2023-VF2Pablo ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Ticket Trogir Zagreb 3020784371Document2 pagesTicket Trogir Zagreb 3020784371AnaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 PDFDocument85 pagesCH 2 PDFSajidNo ratings yet
- Lazatin v. Desierto (As Ombudsman) and Sandiganbayan (Case Brief)Document3 pagesLazatin v. Desierto (As Ombudsman) and Sandiganbayan (Case Brief)nikkisalsNo ratings yet
- FASH257 Midterm 3Document4 pagesFASH257 Midterm 3Cj DatoyNo ratings yet
- Criminal Complaint in Fond Du Lac Verizon Store CrashDocument5 pagesCriminal Complaint in Fond Du Lac Verizon Store CrashFOX 11 NewsNo ratings yet
- Bhel EvaDocument3 pagesBhel Eva9377027588No ratings yet
- The Decay of The American Dream - Tennessee Williams and - em - The GDocument8 pagesThe Decay of The American Dream - Tennessee Williams and - em - The GRamesh KumarNo ratings yet
- CIR vs. Metro StarDocument1 pageCIR vs. Metro StarRodney SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Activity Example 1040 TaxDocument2 pagesActivity Example 1040 TaxKevin ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Control Interno - Marco Integrado: Resumen EjecutivoDocument3 pagesControl Interno - Marco Integrado: Resumen EjecutivoLisardo LunaNo ratings yet
- 2) Allied Banking Corp. vs. Lim Sio Wan, 549 SCRA 504 (2008)Document2 pages2) Allied Banking Corp. vs. Lim Sio Wan, 549 SCRA 504 (2008)Zyrene CabaldoNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Beginners Guide To ArabicDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Word - Beginners Guide To ArabicMustakeem Rafik SatyaNo ratings yet
- Les Pronoms Relatifs Qui - Que WorksheetDocument3 pagesLes Pronoms Relatifs Qui - Que WorksheetІнна РибакNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Celebrity Cinta Laura KiehlDocument2 pagesAn Analysis of Celebrity Cinta Laura Kiehlnur auliaNo ratings yet
- America The Story of Us Episode 5civil War WorksheetDocument1 pageAmerica The Story of Us Episode 5civil War WorksheetHugh Fox IIINo ratings yet
- 2020 Hispanic Market ReportDocument22 pages2020 Hispanic Market ReportErick IsaacNo ratings yet
- 02 - LTCCDocument20 pages02 - LTCCfaye margNo ratings yet
- UK Visas & Immigration: Personal InformationDocument9 pagesUK Visas & Immigration: Personal Informationbera academyNo ratings yet
- GST 212Document34 pagesGST 212muhammadkhalidgiwaNo ratings yet
- Caricatures in The American Colonial PeriodDocument27 pagesCaricatures in The American Colonial PeriodKyla Yssabelle DolorNo ratings yet
NHADEN Reflection
NHADEN Reflection
Uploaded by
Ellixander LanuzoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NHADEN Reflection
NHADEN Reflection
Uploaded by
Ellixander LanuzoCopyright:
Available Formats
NHADEN D.
BENITEZ 2ND YEAR / BEED2A
REFLECTION
Chapter 6: Global Gender Issues
The reading materials gave us an insight about the global gender issues we
faced today that could be traced back from ancient times. Unfair treatment of
individuals based on their gender is deeply rooted throughout the course of
human history. Gender-based injustices were linked to the uneven divisions of
power, opportunity, and rights among men and women. Nowadays, women
and some other marginalized groups still experience injustices but there are
laws created to provide for their protection.
Human rights refers to the rights to justice and fair treatment of an individual
regardless of his or her gender, educational attainment, and social status.
Human rights is fundamental and a necessity for it provides fairness and
equality in the society. Children and members of the LGBT community were
also a subjects of human rights. Women's struggle on having a fair treatment
and opportunities is traced back to the Spanish colonial era. Women also play
a vital role during the revolution to attain freedom against the Spaniards. They
have created organizations to help other women and aid the katipuneros and
also to spread awareness that women and men were equal. Several laws were
created to protect women and children against abuse. According to the
module there were three types of domestic abuse a women may experience
which is the physical, emotional or psychological and economic abuse.
Physical abuse refers to the infliction of pain and physical injury that may
become life-threatening. Emotional or psychological abuse involves threats,
manipulation and intimidation. Economic abuse is the deprivation of one's
right to financial independence. There are several more kinds of violence
against women and children such as rape, prostitution, sexual harassment,
human trafficking, female genital mutilation and forced marriage. To aid and
protect women and children against these abuses, eighteen laws together
with an article on the Philippine constitution were created by the Philippine
government.
The module provides information about the struggles faced by LGBT
community in the society. They also experience discrimination, harassment
and threats. There were 4 types of abuse and discrimination they faced that
highlight their struggles. These were named as homophobia, marginalization
and social exclusion, psychological distress and hate and crime violence.
Homophobia refers to the fear or agression against gay people.
Marginalization and social exclusion on LGBT may result in attempting
suicide,being ignored and isolated, dropping out of school, lack of family and
social support, leaving home and family, migration to other place to seek
better livelihood and acceptance, being unable to find regular jobs, and being
unable to access various social services. Psychological distress includes
experiencing casual homophobic comments, childhood sexual abuse,
harassment of neighbors, no protection against discrimination at work,
physical violence and discrimination, prejudice, rejection and verbal
harassment. Hate and crime violence or also known as biased-motivated
crimes occurs whenever a perpetrator targets a victim because of the groups
or communities they're involvedbor a part of. LGBT movement has always
been very supportive in making a change in the society. These movements
aim to give the LGBT organizations for their specific needs, including
psychosocial support, political representation, sexual health, representation in
sports events, religious and spiritual needs.
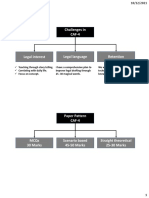
Chapter 7 INTERNATIONAL AND LOCAL POLICY RESPONSES ON
GENDER ISSUES
The module provides information on the International and local policy
responses on gender issues to spread awareness to students on this matter.
The UN general assembly in 2015 presented 17 SDGs ( Sustainable
development goal) that should be attained by 2030. Goal 1( no poverty)
aiming to end poverty in all forms and to provide both men and women an
equal rights to economic resources especially the poor and the vulnerable.
Goal 2 ( Zero Hunger) aims to give and ensure access to safe and sufficient
food all year round to all people including infants. Goal 3( Ensure healthy lives
and promote well being for all at all ages) aims to reduce the mortality rate of
newborns and children under 5 years of age. This also aims to reduce the
number of deaths by hazard, contamination and accidents. Goal 4 (Quality
education) aims to provide quality education be it primary, secondary or
technical and vocational to all genders. Goal 5 ( achieve gender equality and
empower all women and girls) aims to eliminate all forms of discrimination
against women and girls anywhere. This also aims to give women an equal
opportunities in leadership and economic resources. Goal 6 (Ensure access to
water and sanitation for all) aims to reduce water pollution due to bad
economics and poor infrastructures for a cleaner water supply. Goal 7 (Ensure
access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy) ensures
universal access to affordable, reliable and modern energy services. Goal
8(promote inclusive and sustainable economic growth, employment and
decent work for all) will allow people to have quality jobs that stimulate the
economy while not harming the environment. Goal 9 ( build resilient
infrastructure , promote sustainable industrialization and foster innovation)
aims to empower communities in many countries to growth in productivity
and income by investment in infrastructures. Goal 10(reduce inequality within
and among countries) aims to reduce the inequality by creating universal
policies in principle and aims to pay attention to the needs of the
disadvantaged and marginalized population. Goal 11( make cities
inclusive,safe, resilient and sustainable) promotes efficient urban planning
and management practices to deal with the challenges brought by
urbanization. Goal 12(ensure sustainable consumption and production
patterns) promotes efficient and sustainable consumption and production of
energy, infrastructures and providing access to basic needs of everyone. Goal
13 (take urgent action to combat climate change and its impact) aims to
strengthen the global response to the threat of climate change, every country
adopted the Paris Agreement at the COD 21 in Paris. The Paris Agreement is
apact among countries to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Goal 14
(conserve and sustainably use the oceans, seas and marine resources) aims
to reduce marine pollution of all kinds. Goal 15 (sustainably manage forests,
combat desertification, Halt and reverse land degradation, halt biodiversity
loss) aims to conserve and restore ecosystem and stop deforestation and
desertification. Goal 16( promote just, peaceful and inclusive societies) aims
to reduce all forms of violence and related death rates everywhere. Goal 17
(revitalize the global partnership for sustainable development) aims to
strengthen partnership between governments for a sustainable development.
Aside from UN' SDGs , there are several platforms promoting equality and
empowerment on women and they are as follows;
The convention on the elimination of all forms of discrimination against
women or CEDAW is an organization adopted by UN in 1979. The convention
defines what constitutes discrimination against women and sets up an
agenda for national action to end such discrimination. The Beijing platform for
action (BPfA) is a landmark document for advancing the rights of women and
gender equality worldwide agreed during the 4th world conference on women
in 1995. Nairobi forward-looking strategies for the advancement of women
marked the first introduction of lesbian rights in an official UN meeting and a
turning point on the issues of violence against women. The UN Women or the
United Nations entity for gender equality and the empowerment of women
also laid out 12 areas of concern that is also identified as critical areas for
women( this includes economy, health, education, empowerment etc.).
Women in Development (WID), Women and Development (WAD), and Gender
and Development (GAD) are theoretical approaches use to aim understanding
and addressing women's issues.
In the Philippines there are also a number of policy responses addressing
gender equality concerns. R.A 7192 also known as "Women in Development
and Nation Building Act" recognizes the role of women in nation building and
ensures the fundamental equality of men and women.
Executive order 348 institutionalized the integrate women's concerns in the
development process as part of the country's compliance with the UN-CEDAW
and the Forward Looking strategies for the advancement of women (FLS).
Executive order 273 or The Philippine plan for gender responsive development
for 1995-2025 were a series of initiatives meant to provide Filipino women a
more active and participatory role in the development process. The Magna
Carta of Women is a comprehensive human rights law that seeks to eliminate
discrimination against women by recognizing, protecting, fulfilling and
promoting the rights of Filipino women
The last part of the module tackled the gender analysis in cooperatives. The
lesson explains the gender analysis which is the foundation for gender
mainstreaming. Gender equality is attained when women and men, girls and
boys have equal rights. It does not mean that women and men become the
same but it means that both have an equal opportunity to participate in policy-
making, management and administration of the cooperative to attain their
goals. Cooperatives should address and aim to identify and overcome the
causes of gender gaps in groups or society that brings inequality. This is
crucial so that everyone could be aware of each gender's specific needs for
the sake of achieving the goal of the community.
You might also like
- The German Law of Contract.Document1,034 pagesThe German Law of Contract.Алексей Агеев92% (13)
- Gender Equality Thesis Queen AngDocument52 pagesGender Equality Thesis Queen AngQueen Ang72% (25)
- Til 1755-R3 Lci Water - Cooled Bus LeaksDocument8 pagesTil 1755-R3 Lci Water - Cooled Bus LeaksMichael SanchezNo ratings yet
- Iloilo City Gender Code: RO 2006-087Document23 pagesIloilo City Gender Code: RO 2006-087Iloilo City Council100% (1)
- Torts: Mbe Practice QuestionsDocument16 pagesTorts: Mbe Practice Questionsnkolder84No ratings yet
- Gender&Youth AssignmentDocument9 pagesGender&Youth Assignmentbereket woldemedhinNo ratings yet
- Women, Development, and Gender Inequality: Published Online: 09 June 2016Document9 pagesWomen, Development, and Gender Inequality: Published Online: 09 June 2016ReynNo ratings yet
- Rotc Finals Exam ReviewerDocument387 pagesRotc Finals Exam ReviewerLorielle OlivaNo ratings yet
- Gen - Soc End Term Lesson 1 and 2Document23 pagesGen - Soc End Term Lesson 1 and 2Dianne ShakiraNo ratings yet
- International InstrumentsDocument4 pagesInternational InstrumentsTitus MasilaNo ratings yet
- GAD AwarenessDocument10 pagesGAD AwarenessKyla Alap-apNo ratings yet
- Module 8Document8 pagesModule 8Winnie ToribioNo ratings yet
- Gender and Development: Internationa L MandatesDocument88 pagesGender and Development: Internationa L MandatesIrene AnastasiaNo ratings yet
- Gender and DevelopmentDocument9 pagesGender and DevelopmentmiaallysabretanaNo ratings yet
- Pa 201Document11 pagesPa 201Sarah Mae PelaezNo ratings yet
- Gender Equality Policy GuidelinesDocument27 pagesGender Equality Policy GuidelinesRAHUL LALJIBHAI PANCHOLI-IBNo ratings yet
- Human Rights Approach: Republic of The Philippines Commission On Higher Education Samar College, Inc. Catbalogan CityDocument5 pagesHuman Rights Approach: Republic of The Philippines Commission On Higher Education Samar College, Inc. Catbalogan CityKJ PacamparaNo ratings yet
- Group 5Document20 pagesGroup 5James bryan TayuponNo ratings yet
- EDUC 110 CHAP 5 8 The Te WPS OfficeDocument18 pagesEDUC 110 CHAP 5 8 The Te WPS OfficeDumapias RobraceNo ratings yet
- Achieving The Sustainable Development Goals in Africa: Call For A Paradigm ShiftDocument3 pagesAchieving The Sustainable Development Goals in Africa: Call For A Paradigm ShiftKobutungi ClaireNo ratings yet
- Women and Sustainable Development Goals: Delhi. E Mail-Contact: 09711440385 (Corresponding Author)Document7 pagesWomen and Sustainable Development Goals: Delhi. E Mail-Contact: 09711440385 (Corresponding Author)Danah Angelica SambranaNo ratings yet
- Beijing Platform For Action: Philippine Comission For WomenDocument21 pagesBeijing Platform For Action: Philippine Comission For WomenMark PorcadillaNo ratings yet
- Rich HensonDocument3 pagesRich HensonJerwin CanterasNo ratings yet
- Laws, Policies & Programs For Philippine WomenDocument38 pagesLaws, Policies & Programs For Philippine WomenAngel Marie Rule100% (1)
- Educ 110 ReportDocument4 pagesEduc 110 ReportJosephine Claire UgalinoNo ratings yet
- MALUYA, Gwyneth ASSIGNMENT#1Document5 pagesMALUYA, Gwyneth ASSIGNMENT#1Maluya GwynethNo ratings yet
- Pelaez ReportDocument3 pagesPelaez ReportSarah Mae PelaezNo ratings yet
- Psir Model Answers For Previous Year Questions Paper-IiDocument64 pagesPsir Model Answers For Previous Year Questions Paper-IiBbudyNo ratings yet
- Basic Research ProposalDocument17 pagesBasic Research ProposalDENNIS RAMIREZNo ratings yet
- SDG EssayDocument4 pagesSDG Essayagracecastaneros09No ratings yet
- Human Rights and DevelopmentDocument1 pageHuman Rights and DevelopmentDianne MendozaNo ratings yet
- 09 Rey TyDocument27 pages09 Rey TyJoanne Mae VillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document3 pagesChapter 5Paulo Justin Tabangcora OropillaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 5. Maam B. FINAL DRAFTDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 5. Maam B. FINAL DRAFTMariza GiraoNo ratings yet
- GROUP 4 ProfEd 312Document25 pagesGROUP 4 ProfEd 312Rochelle UrbodaNo ratings yet
- Civic GENDER AND DEVELOPMENTDocument13 pagesCivic GENDER AND DEVELOPMENTGustaval VulcanNo ratings yet
- Slot-Tb2 Digital Assignment-3 Gender Inequality: Introduction To Innovative Project (Phy1901)Document13 pagesSlot-Tb2 Digital Assignment-3 Gender Inequality: Introduction To Innovative Project (Phy1901)AnirudhPavanNo ratings yet
- ProfEd 602 Reporting WPS OfficeDocument38 pagesProfEd 602 Reporting WPS OfficeLilyNo ratings yet
- STS Gender EqualityDocument2 pagesSTS Gender EqualityEJ PalomariaNo ratings yet
- Global Issues That Concern Schools and SocietyDocument4 pagesGlobal Issues That Concern Schools and Societycelestine samuya50% (4)
- Colouring the Future: Why the United Nations plan to end poverty and wars is workingFrom EverandColouring the Future: Why the United Nations plan to end poverty and wars is workingNo ratings yet
- Ldp616 Gender Issues in Development Exam RevsDocument56 pagesLdp616 Gender Issues in Development Exam Revsdmugalloy100% (1)
- Gender EqualityDocument3 pagesGender EqualityRamakant PatilNo ratings yet
- Gender Discrimination in India: Dr.E.Raju, M.A., M.Phil., PH.D., Post Doctoral FellowDocument11 pagesGender Discrimination in India: Dr.E.Raju, M.A., M.Phil., PH.D., Post Doctoral FellowRaja RajhansNo ratings yet
- Combating Gender Based ViolenceDocument32 pagesCombating Gender Based Violencemary engNo ratings yet
- Group 1: Abigail D. Monis Paul Jenrae Samson Mikaella JarabaDocument15 pagesGroup 1: Abigail D. Monis Paul Jenrae Samson Mikaella JarabaAbigail MonisNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 3 Complete Chapters 7 10Document31 pagesProf Ed 3 Complete Chapters 7 10Melay AlmoradoNo ratings yet
- SDGsDocument9 pagesSDGsoluwatimileyinjoshua88No ratings yet
- Policy BriefDocument6 pagesPolicy BriefJust BNo ratings yet
- National Gender Policy 2015Document57 pagesNational Gender Policy 2015mvulamacfieldNo ratings yet
- Act 1Document2 pagesAct 1Gripthru ShotsNo ratings yet
- Are Men Different To Women (Sem 1Document9 pagesAre Men Different To Women (Sem 1Kyle Christian Manuel MorilloNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Development GoalsDocument7 pagesSustainable Development GoalsYugenNo ratings yet
- Gender EqualityDocument3 pagesGender EqualityShoto TodorokiNo ratings yet
- Gender EqualityDocument5 pagesGender EqualityFadi FreeNo ratings yet
- What Is Gender and Why Does It Matter?Document13 pagesWhat Is Gender and Why Does It Matter?Jaymark AmarilleNo ratings yet
- Global Issues That Concern Schools and SocietyDocument23 pagesGlobal Issues That Concern Schools and SocietyMary Grace Apinado100% (1)
- SDGDocument7 pagesSDGsheena baquirelNo ratings yet
- Gender Equality: Importance of Gender EgualityDocument3 pagesGender Equality: Importance of Gender EgualityDD ENTERTAINNo ratings yet
- Gender DRR Information Booklet EngDocument25 pagesGender DRR Information Booklet EngNune HarutyunyanNo ratings yet
- Beijin Declaration and Platform For Action of 1995Document6 pagesBeijin Declaration and Platform For Action of 1995VanshikNo ratings yet
- Gender Perspective in Business RKB Law College AssamDocument9 pagesGender Perspective in Business RKB Law College AssamSAYANTAN ROYNo ratings yet
- Gender EqualityDocument16 pagesGender EqualityJapheth David (diplomat)No ratings yet
- Discusssion ForumDocument2 pagesDiscusssion ForumEllixander LanuzoNo ratings yet
- PT 2 TAX LAW Gen Math Piecewise Function Repaired RepairedDocument4 pagesPT 2 TAX LAW Gen Math Piecewise Function Repaired RepairedEllixander LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Croatia Gec11Document6 pagesCroatia Gec11Ellixander LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Green Red and White Modern Christmas Party A4 DocumentDocument1 pageGreen Red and White Modern Christmas Party A4 DocumentEllixander LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Elec 1 Assessment 2Document1 pageElec 1 Assessment 2Ellixander LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Measurement LevelsDocument67 pagesMeasurement LevelsEllixander LanuzoNo ratings yet
- Chattisgarh Stamp ActDocument31 pagesChattisgarh Stamp ActASHUTOSH MISHRANo ratings yet
- Rc2172017a0009 - Cbi Fir Against NDTVDocument88 pagesRc2172017a0009 - Cbi Fir Against NDTVPGurus100% (9)
- 10 - Đề Thi Tham Khảo Ts10 - 2020Document4 pages10 - Đề Thi Tham Khảo Ts10 - 2020Duyen MyNo ratings yet
- AHHHHDocument2 pagesAHHHHerscholaraccNo ratings yet
- Bhanwar Singh v. Puran AIR 2008 SC 1490Document8 pagesBhanwar Singh v. Puran AIR 2008 SC 1490bobby1993 DunnaNo ratings yet
- Magnaye Isaiah. AsynchronousDocument2 pagesMagnaye Isaiah. AsynchronousAyen Rodriguez MagnayeNo ratings yet
- PGL - 500B Euro - AQUANTUS KAMA - 16 NOV 2023-VF2Document9 pagesPGL - 500B Euro - AQUANTUS KAMA - 16 NOV 2023-VF2Pablo ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Ticket Trogir Zagreb 3020784371Document2 pagesTicket Trogir Zagreb 3020784371AnaNo ratings yet
- CH 2 PDFDocument85 pagesCH 2 PDFSajidNo ratings yet
- Lazatin v. Desierto (As Ombudsman) and Sandiganbayan (Case Brief)Document3 pagesLazatin v. Desierto (As Ombudsman) and Sandiganbayan (Case Brief)nikkisalsNo ratings yet
- FASH257 Midterm 3Document4 pagesFASH257 Midterm 3Cj DatoyNo ratings yet
- Criminal Complaint in Fond Du Lac Verizon Store CrashDocument5 pagesCriminal Complaint in Fond Du Lac Verizon Store CrashFOX 11 NewsNo ratings yet
- Bhel EvaDocument3 pagesBhel Eva9377027588No ratings yet
- The Decay of The American Dream - Tennessee Williams and - em - The GDocument8 pagesThe Decay of The American Dream - Tennessee Williams and - em - The GRamesh KumarNo ratings yet
- CIR vs. Metro StarDocument1 pageCIR vs. Metro StarRodney SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Activity Example 1040 TaxDocument2 pagesActivity Example 1040 TaxKevin ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- Control Interno - Marco Integrado: Resumen EjecutivoDocument3 pagesControl Interno - Marco Integrado: Resumen EjecutivoLisardo LunaNo ratings yet
- 2) Allied Banking Corp. vs. Lim Sio Wan, 549 SCRA 504 (2008)Document2 pages2) Allied Banking Corp. vs. Lim Sio Wan, 549 SCRA 504 (2008)Zyrene CabaldoNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - Beginners Guide To ArabicDocument4 pagesMicrosoft Word - Beginners Guide To ArabicMustakeem Rafik SatyaNo ratings yet
- Les Pronoms Relatifs Qui - Que WorksheetDocument3 pagesLes Pronoms Relatifs Qui - Que WorksheetІнна РибакNo ratings yet
- An Analysis of Celebrity Cinta Laura KiehlDocument2 pagesAn Analysis of Celebrity Cinta Laura Kiehlnur auliaNo ratings yet
- America The Story of Us Episode 5civil War WorksheetDocument1 pageAmerica The Story of Us Episode 5civil War WorksheetHugh Fox IIINo ratings yet
- 2020 Hispanic Market ReportDocument22 pages2020 Hispanic Market ReportErick IsaacNo ratings yet
- 02 - LTCCDocument20 pages02 - LTCCfaye margNo ratings yet
- UK Visas & Immigration: Personal InformationDocument9 pagesUK Visas & Immigration: Personal Informationbera academyNo ratings yet
- GST 212Document34 pagesGST 212muhammadkhalidgiwaNo ratings yet
- Caricatures in The American Colonial PeriodDocument27 pagesCaricatures in The American Colonial PeriodKyla Yssabelle DolorNo ratings yet