Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Https App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 704sap 2
Https App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 704sap 2
Uploaded by
adarsh.singh.jprCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- H7 Mini Test 3Document2 pagesH7 Mini Test 3Ramadhan ShaffiNo ratings yet
- PromoDocument7 pagesPromoGujarati GamersNo ratings yet
- Solution 1203600Document11 pagesSolution 1203600arb88279No ratings yet
- 3rdgrading Lesson 1Document18 pages3rdgrading Lesson 1Atheena LunaNo ratings yet
- 8L3 Solving Congruent TrianglesDocument4 pages8L3 Solving Congruent TrianglesJewel SantosNo ratings yet
- Maths Sa1 Sp2Document15 pagesMaths Sa1 Sp2Shivam PandeyNo ratings yet
- Https - App - Oswaalbooks.com - Download - Sample-Qp - Subsolution - 888self Ass Paper - 2 (Sol)Document2 pagesHttps - App - Oswaalbooks.com - Download - Sample-Qp - Subsolution - 888self Ass Paper - 2 (Sol)anmolsinghji141No ratings yet
- Day 2 Lesson 4Document28 pagesDay 2 Lesson 4Ezrine UmaniNo ratings yet
- Isucceed Sample Question Paper 16 Maths 9Document4 pagesIsucceed Sample Question Paper 16 Maths 9Yuvraj KatiyarNo ratings yet
- SUSTECH MathDocument24 pagesSUSTECH Matht0xic.369xNo ratings yet
- SOLUTION SET Math IIIDocument4 pagesSOLUTION SET Math IIIMichael ManuelNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument10 pagesVector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDFSupriya Santre100% (1)
- Vector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDF 1Document10 pagesVector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDF 1nazeeraNo ratings yet
- Grade 10Document9 pagesGrade 10Iya Sicat PatanoNo ratings yet
- Quants: Topics Questions ExplanationDocument20 pagesQuants: Topics Questions ExplanationNikhilaNo ratings yet
- H7 Mini Test 3 AnsDocument2 pagesH7 Mini Test 3 AnsRamadhan ShaffiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Test Review: Geometry CP NameDocument6 pagesChapter 4 Test Review: Geometry CP NameFiona IsbellNo ratings yet
- Properties of Parallelograms Special ParallelogramsDocument16 pagesProperties of Parallelograms Special Parallelogramsjeehan dolorosaNo ratings yet
- Math Reviewer 2 Answers KeyDocument9 pagesMath Reviewer 2 Answers KeyEstepanie Gopet100% (1)
- XII Mathematics 2024 Final Paper SolutionsDocument12 pagesXII Mathematics 2024 Final Paper Solutionswebsite040306No ratings yet
- Rev 1 105 Items Answer KeyDocument5 pagesRev 1 105 Items Answer KeyAinah JovenNo ratings yet
- Top Questions CalculusDocument171 pagesTop Questions CalculusMehul TotalaNo ratings yet
- FinalExam Spring2022 With Answer KeyDocument5 pagesFinalExam Spring2022 With Answer KeyQuangAnh VuNo ratings yet
- Algebra - PDF Version 1 PDFDocument66 pagesAlgebra - PDF Version 1 PDFবাংলার মিল্টনNo ratings yet
- Topper 110 2 3 Maths Solution Up202308291227 1693292242 2785Document19 pagesTopper 110 2 3 Maths Solution Up202308291227 1693292242 2785abhimanyou076No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 TestDocument6 pagesChapter 3 TestJose SegalesNo ratings yet
- Murray Klamkin Problems 1nbsped 091955816x CompressDocument1 pageMurray Klamkin Problems 1nbsped 091955816x CompressRaju RajNo ratings yet
- ps42 n3cs19 SDocument2 pagesps42 n3cs19 Sapi-234377298No ratings yet
- Imo Level1 Solution Class 8 Set 1Document4 pagesImo Level1 Solution Class 8 Set 1chirag birlaNo ratings yet
- E2Qdif CDocument2 pagesE2Qdif CLucas ShazNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Mathematics: Project Katuparan (Document3 pagesAnswer Key: Mathematics: Project Katuparan (Fudge FajardoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 108.5 - Law of Sines and CosinesDocument3 pagesWorksheet 108.5 - Law of Sines and CosinesEditha CuencoNo ratings yet
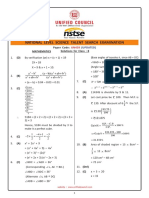
- Unified Council: National Level Science Talent Search ExaminationDocument6 pagesUnified Council: National Level Science Talent Search ExaminationpriyaamirthaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2020 Paper: Date of Exam: 7 January 2020 (Shift 2) Time: 2:30 P.M. To 5:30 P.M. Subject: MathematicsDocument13 pagesJEE Main 2020 Paper: Date of Exam: 7 January 2020 (Shift 2) Time: 2:30 P.M. To 5:30 P.M. Subject: Mathematicskruthika karraNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer 3 Math Major AnsKey SolnDocument12 pagesLET Reviewer 3 Math Major AnsKey SolnJhon Rey Leonardo LedamaNo ratings yet
- ICSE-X Mathematics 23-24 SQP SolutionDocument14 pagesICSE-X Mathematics 23-24 SQP SolutionkillerninjaredNo ratings yet
- Https App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 471sap 3Document6 pagesHttps App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 471sap 3hritamgemsNo ratings yet
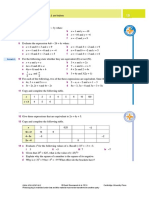
- 7 A B C D e F 8 A B C D e F 9 A B C D e F G H 10 A B C D 11: Chapter 1 Algebraic Techniques 2 and IndicesDocument2 pages7 A B C D e F 8 A B C D e F 9 A B C D e F G H 10 A B C D 11: Chapter 1 Algebraic Techniques 2 and IndicessNo ratings yet
- State Math Contest 2015-Junior Exam SolutionsDocument16 pagesState Math Contest 2015-Junior Exam SolutionsDgjjkNo ratings yet
- Isometries: 1.1 Transformations of The PlaneDocument38 pagesIsometries: 1.1 Transformations of The PlaneAbebaw MebiratuNo ratings yet
- chapter2 答案Document3 pageschapter2 答案lilyq zNo ratings yet
- Polygons TasksDocument16 pagesPolygons TasksнуркызNo ratings yet
- Math III SolutionSet PDFDocument4 pagesMath III SolutionSet PDFqwertyNo ratings yet
- KCB S.6TEST2 2020mathDocument4 pagesKCB S.6TEST2 2020mathTRIPPLE KAYZ UGNo ratings yet
- Math Pre BoardDocument5 pagesMath Pre BoardAnne KathrineNo ratings yet
- 02 DPPnurturestudentDocument2 pages02 DPPnurturestudentReevu ThapaNo ratings yet
- Basic Mathematics-02-Solved ExampleDocument8 pagesBasic Mathematics-02-Solved ExampleRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2004 Year 9 Maths Yearly & SolutionsDocument6 pagesJames Ruse 2004 Year 9 Maths Yearly & SolutionsKaushik SarkarNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDFDocument9 pagesVector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDFkavinkumareceNo ratings yet
- Part B Unit 1 PDFDocument102 pagesPart B Unit 1 PDFLolu PandeyNo ratings yet
- Xii Math Mock Question Paper Mid Term ExamDocument13 pagesXii Math Mock Question Paper Mid Term Examlove.mansijhaNo ratings yet
- Ahsme 1961Document5 pagesAhsme 1961vidyakumari808940No ratings yet
- X Maths 2023 Sample Paper SolutionsDocument10 pagesX Maths 2023 Sample Paper SolutionsKanchan AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Maths Paper 10THDocument4 pagesMaths Paper 10THSara Aamir ToorNo ratings yet
- PPSC Mock Test 2 Akhtar AbbasDocument4 pagesPPSC Mock Test 2 Akhtar AbbasUmair AliNo ratings yet
- Solution-1337554 240504 204019Document8 pagesSolution-1337554 240504 204019rkumarirani6No ratings yet
- QuadrilateralsDocument24 pagesQuadrilateralsHenry LavitoriaNo ratings yet
- 2014-2015 Midterm ExamDocument2 pages2014-2015 Midterm ExamCHANDNI VERMANo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- The Chinese Cultural Revolution: A Historiographical StudyDocument18 pagesThe Chinese Cultural Revolution: A Historiographical StudyjohndeereNo ratings yet
- John Robinson ResumeDocument2 pagesJohn Robinson Resumeapi-508032756No ratings yet
- The Mystic Will - Based Upon A Study of The Philosophy of Jacob Boehme (PDFDrive)Document296 pagesThe Mystic Will - Based Upon A Study of The Philosophy of Jacob Boehme (PDFDrive)Beni ValdesNo ratings yet
- Compound SentencesDocument3 pagesCompound SentencesNoha Bayoumy0% (1)
- Language and Sex (Sociolinguistics)Document13 pagesLanguage and Sex (Sociolinguistics)Yusrilsyah LimbanadiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Rubric in Stylistic Analysis of TextDocument2 pagesAssessment Rubric in Stylistic Analysis of TextAira Mae67% (3)
- Directory of School and Community LeadersDocument6 pagesDirectory of School and Community LeadersWinston CelestialNo ratings yet
- Medical-for-Coaches-Asst-Coaches-ChaperonesDocument1 pageMedical-for-Coaches-Asst-Coaches-ChaperonesLeah CarnateNo ratings yet
- Character Certificate For Army RecruitmentDocument11 pagesCharacter Certificate For Army Recruitmentkijni2024No ratings yet
- Airworthiness Notice No. 1101: Appendix 2Document3 pagesAirworthiness Notice No. 1101: Appendix 2fareezNo ratings yet
- Read and Write Numbers From 0 To 10 in Symbols and in Words LPDocument4 pagesRead and Write Numbers From 0 To 10 in Symbols and in Words LPJohn Ericson Mabunga100% (1)
- 朱一清的琵琶独奏曲《彼岸民谣》创作特征初探 鲁立怡Document33 pages朱一清的琵琶独奏曲《彼岸民谣》创作特征初探 鲁立怡still451No ratings yet
- What Are The Characteristics of A Teacher Who Can Established A WellDocument6 pagesWhat Are The Characteristics of A Teacher Who Can Established A WellVhiy Dizon BantingNo ratings yet
- Tewwg Essay GuidelinesDocument5 pagesTewwg Essay Guidelinesapi-253342683No ratings yet
- You Successfully Passed A Job Interview. You Are Expected To Start On November 15, ButDocument9 pagesYou Successfully Passed A Job Interview. You Are Expected To Start On November 15, ButGeorgie StephenNo ratings yet
- Cambridge English: First Practice Test ADocument3 pagesCambridge English: First Practice Test AJuan NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Sign Language and Common Gesture Using CNNDocument7 pagesSign Language and Common Gesture Using CNNVelumani s0% (1)
- Ipcr Part 3 4 NTP 2019Document3 pagesIpcr Part 3 4 NTP 2019Lavandera Lpt Vargas JoannaNo ratings yet
- Problems of AJK Learners of English LanguageDocument14 pagesProblems of AJK Learners of English LanguageAsad Mehmood67% (3)
- The First Presbyterian Church in The City of New York Welcomes Rev. Dr. Greg Stovell, Pastor/Head of StaffDocument3 pagesThe First Presbyterian Church in The City of New York Welcomes Rev. Dr. Greg Stovell, Pastor/Head of StaffPR.comNo ratings yet
- Individualism vs. CollectivismDocument4 pagesIndividualism vs. CollectivismNGITPANo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Topic 3Document14 pagesLesson 2 Topic 3Vincent Efraim G. TabatNo ratings yet
- Score Sheet in Thesis/Capstone Oral Defense: AMA UniversityDocument1 pageScore Sheet in Thesis/Capstone Oral Defense: AMA UniversityRafael Aquino100% (1)
- Summer Life Skills - Week 2 Day 33Document14 pagesSummer Life Skills - Week 2 Day 33dg94k72k4vNo ratings yet
- Entertainment: Listening WS: Student's DetailsDocument3 pagesEntertainment: Listening WS: Student's DetailsDino CatNo ratings yet
- Development and Validation of A Customized CompetencyDocument14 pagesDevelopment and Validation of A Customized CompetencyxiaoyuNo ratings yet
- SAP BW-IP Training Integrated Planning - Basic ConceptDocument11 pagesSAP BW-IP Training Integrated Planning - Basic ConceptDurgesh SinghNo ratings yet
- KTEA 3 Parent Report - 54433345 - 1712666972404Document9 pagesKTEA 3 Parent Report - 54433345 - 1712666972404p0074790No ratings yet
- My Hopes and Dreams For My FamilyDocument1 pageMy Hopes and Dreams For My FamilyThez BritanicoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Regulation of Human Phospholipase DDocument10 pagesStructure and Regulation of Human Phospholipase Dxtang2No ratings yet
Https App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 704sap 2
Https App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 704sap 2
Uploaded by
adarsh.singh.jprOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Https App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 704sap 2
Https App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 704sap 2
Uploaded by
adarsh.singh.jprCopyright:
Available Formats
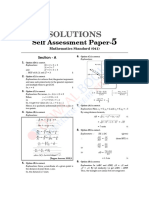
SOLUTIONS
Self Assessment Paper-2
MATHEMATICS (041)
Section-A 8. Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: x2 + x = 1 is not linear as highest power
1. Option (B) is correct. is 2. Also, it is an equation in one variable.
Explanation: According to graph ‘Bear 415’ is nearest Thus, it is not a linear equation in two variables.
to a paved road as compared to other Bear’s.
9. Option (A) is correct.
2. Option (C) is correct.
Explanation: Original height of sapling = 0.25 m
10. Option (B) is correct.
Explanation: In || gm ABCD
Average growth rate per year = 0.27 m
AB = CD
∴ Height of Red maple tree after t years,
(opposite sides of a || gm are equal)
h = 0.25 + 0.27t.
So, 2y – 3 = 5
3. Option (B) is correct. 2y = 5 + 3
Explanation: As we can see from figure given below, y=4
the distance between the two intersecting lines
Increases as they travel beyond the point. 11. Option (B) is correct.
Explanation: Let the radius of a cone
r = 4x
A D
and slant height
P l = 7x
CSA = 792 cm2
C B prl = 792
4. Option (C) is correct. 22
or, × 4 x × 7 x = 792
Explanation: Let the angle be x, then 7
792 × 7
1 x2 = =9
By given condition, x = (90° –x) 22 × 4 × 7
5
or, x = 3 cm
or, 5x = 90° – x \ radius = 4 × 3
or, x = 15° = 12 cm
5. Option (B) is correct. 12. Option (B) is correct.
Explanation: According to quadrilateral’s property 13. Option (A) is correct.
Sum of opposite angles = 180°. Explanation: ∠BDA = ∠BCA = 40°
6. Option (D) is correct. (Angles in the same segment)
Explanation: Now, since AD || BC,
∠DBC = ∠BDA
1 1 1 3 8 3 8
(Alternate interior angles)
9 8 3 8 3 8 3 8 9 8
∴ ∠DBC = 40°
3 2 4 3 2 2 14. Option (D) is correct.
7. Option (B) is correct. Explanation: ∠COF = 2x
3 (vertically opposite angles)
Explanation: Degree of x + 5 = 3
\ 3x + 2x + 5x = 180° (straight line angle)
Degree of 4 – x5 = 5
or, 10x = 180° Þ x =18°
Now, (x3 + 5)(4 – x5) = 4x3 – x8 + 20 – 5x5
= –x8 – 5x5 + 4x3 + 20 15. Option (A) is correct.
Degree of (x + 5)(4 – x5) = 8
3 1 2
Explanation: Volume of right circular cone = pr h
3
2 Oswaal CBSE Sample Question Papers, MATHEMATICS, Class-IX
1 22
= × × ( 6 )2 × 7 Answering Tip
3 7
1 22 Understand the concepts of both the theorems
= × × 36 × 7
3 7 and do adequate practice to solve problems
= 264 cm3 based on them.
16. Option (C) is correct. 22. A dot in the map is for representational purpose. [1]
17. Option (B) is correct. Dot is used only to show the location of the city, not
its area.
18. Option (A) is correct.
∴ Savita is wrong. [1]
19. Option (A) is correct.
Explanation: In case of Assertion (A): 23.
Y
Let x = a and y = –a
x + y = a + (–a) Þ a – a = 0
\ Assertion is true.
\ In case of Reason (R):
Number of
Any pair (x, y) satisfies ax + by + c = 0 then (x, y) is
students
the solution.
\ Reason is true.
Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) is the correct
explanation of (A).
20. Option (D) is correct.
4 3
Explanation: Volume of sphere = pr [2]
3 X
4 3 Marks
πr1 27
Ratio of Volume = 3 =
24. Sanya can find mid-points of the sides of the
4 3 8
πr2
3 triangular region and create a smaller triangular
r13 27 r1 3 region by connecting them, In this way, the
⇒ 3
= \ = =3:2 triangular region can be divided into four triangles
r2 8 r2 2
of equal area. [2]
4 πr12 32 9
Ratio of surface Area = = = OR
4 πr22 22 4 No, it is not possible as there can be three cases. [½]
=9:4 When all the points are collinear, the resulting figure
is a line.
\ Assertion is false but Reason is true as volume of
When three points are collinear out of four, the
4
sphere = pr 3 and Surface area = 4pr2 resulting figure is a triangle.
3
When no three points out of four are collinear, the
Hence, Assertion (A) is false but Reason (R) is true. resulting figure is a quadrilateral. [1½]
25. 8a3 + 8b3 = (2a)3 + (2b)3
Section-B
= (2a + 2b)[(2a)2 + (2b)2 – (2a) × (2b)][1]
21. Given, (x – 2) is a factor of f(x). [ a3 + b3 = (a + b)(a2 + b2 – ab)]
\ f(2) = 0 [1] = 2(a + b) × 4(a2 + b2 – ab)
Þ (2)2 + k(2) + 2k = 0 = 8(a + b)(a2 + b2 – ab) [1]
Þ 4 + 2k + 2k = 0
OR
Þ 4 + 4k = 0
Þ k =–1 [1] 8x3 – (2x – y)3 = (2x)3 – (2x – y)3
[CBSE Marking Scheme, 2016] = [2x – (2x – y)][(2x)2 + (2x – y)2
+ 2x(2x – y)]
[Since, (a3 – b3) = (a – b)(a2 + b2 + ab)]
Commonly Made Error = y[4x2 + 4x2 + y2 – 4xy + 4x2 – 2xy]
Sometimes students are confused between = y[12x2 + y2 – 6xy] [2]
Remainder Theorem and Factor Theorem. [CBSE Marking Scheme, 2015]
Solutions 3
Section-C As, Area reserved under Zone 1 = Area reserved
under zone 2 + 3
26. Irrational numbers are non-terminating with more
But it doesn’t means that the area reserved under
number of decimals so precision on measuring
Zone 2 and 3 are equal and their sum is equal to the
scale can be more. But they are non-terminating, so
area of zone 1. [2]
fixing their exact location on a measuring scale is not
possible. [3] 30. Sides of triangle a = 15 cm, b = 15 cm, c = 15 cm.
a + b + c 15 + 15 + 15
27. p(x) = x3 + x2 – x – 1 s= =
2 2
Let x = 1,
45
then p (1) = 13 + 12 – 1 – 1 =
2
=1+1–1–1 = 22.5 cm
=0 [1]
Now take x = –1 Area = s( s − a )( s − b )( s − c )
then, p(–1) = (–1)3 + (–1)2 – (–1) – 1 = 22.5( 22.5 − 15)( 22.5 − 15)( 22.5 − 15)
= –1 + 1 + 1 – 1 = 22.5 × 7.5 × 7.5 × 7.5
= 0. [1]
= 225 3 sq. cm.
Hence, value of x = 1, –1. [1]
Thus, area of tile = 225 3 sq. cm. [2]
28. (i) Here, two ordered pairs are equal.
\ a – 3 = 4; a + b = 6
31.
P C
a = 4 + 3; 7 + b = – 6 D
(substituting value of ‘a’)
a = 7; b = –6 – 7
b = –13 [2]
O X d
Hence a = 7 and b = –13
(ii) Clearly point (7, –13) lies in IV quadrant. [1] N
c
OR
Here, A(–2, 9) can also be expressed as (1 + x, y2) a b
A
Þ (–2, 9) = (1 + x, y2) where y > 0 M B
\ 1 + x = –2, y2 = 9 [1] According to figure
x = – 3, y = 9 MX is normal and OM is incident ray.
∴ ∠AMX = 90°
y = 3 ( y > 0)
(Q Incident ray makes a right angle with normal)
Now, P(y, x) = (3, –3), it lies in IV quadrant [1]
OM is bisector
S(2x, –3y) = [2 × (–3), (–3 × 3)]
∴ ∠a = 45° ...(i) [1]
= (–6, –9), it lies in III quadrant [1]
Similarly ∠d = 45°
29. l = 25 cm, r = 7 cm ( YN is normal and PN is bisector) ...(ii) [1]
l = h2 + r2
2
Adding eqs. (i) and (ii)
or, h2 = l2 – r2 ∠a + ∠d = 90° [1]
h2 = (25)2 – (7)2
or,
Section-D
or, h = 24 cm
32. a – b = 0
Area required = C.S.A. of cone [1]
2 x −1 2−x
= prl or, − x +1 = 0 [1]
2x −2 2
22
= × 7 × 25 or, 2 x – 1 – (x – 2) – 2 – x – (x + 1) = 0
7
= 550 cm2 [1] or, 2x–1–x+2 – 2–x–x–1 = 0 [1]
or, 21 – 2 – 2x – 1 = 0
Area required to make 10 such caps
or, 2– 2x –1 = 21
= 10 × 550 = 5500 cm2 [1] ⇒ -2x – 1 = 1 [1]
2
= 0.55 m . or, -2x = 2
or, x = –1 [2]
OR
No, we don’t have enough information regarding [CBSE Marking Scheme, 2015]
area under zone 1,2 and 3. [1] OR
4 Oswaal CBSE Sample Question Papers, MATHEMATICS, Class-IX
5 +1 100 = OM2 + 36
x =
5 −1 OM = 100 − 36 = 64
5 + 1
2 OM = 8 cm
6 + 2 5 3 + 5 [1]
x2 = = =
(i) If PQ and RS lie on same side of centre O.
5 − 1 6−2 5 3− 5
5 −1
y=
5 +1
2
5 − 1 6−2 5 3− 5
y2 = = 6 + 2 5 = 3 + 5 [1]
5 + 1
3+ 5 3− 5
Distance between PQ and RS
\ x2 + y2 = + [1]
3− 5 3+ 5 = LM = OM – OL
(3 + 5 ) + (3 − 5 )
2 2
x2 + y2 = [1]
=8–6
\
(3 − 5 ) (3 + 5 ) = 2 cm [1]
9+5+6 5 +9+5−6 5
(ii) If PQ and RS lie on opposite sides of centre O
=
9−5 R M S
28
=
4
O
\ x2 + y2 = 7 [1]
[CBSE Marking Scheme, 2016] P L Q
Distance between PQ and RS [1]
Commonly Made Error
= LM = OL + OM
Few students make calculation mistake while = 6 + 8 cm
rationalizing terms.
= 14 cm [1]
34. Let f = m(n – p2) + n(p2 – m2) + p(m2 – n2)
2
Answering Tip \
f(m = n) = n(n2 – p2) + n(p2 – n2) + p(n2 – n2)
= n(n2 – p2) – n(n2 – p2) + 0
Double check the steps while working with
=0
rational numbers.
So, m – n is a factor of f.
Similarly, f(n = p) = 0 & f(p = m)= 0
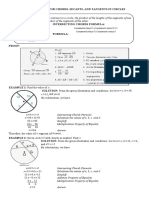
33. Given, OP = OR = 10 cm (Radii of same circle)
\ (m – n), (n – p) and (p – m) are factors of f.
[5]
PQ = 16 cm
[CBSE Marking Scheme, 2015]
RS = 12 cm
Draw OL ⊥ PQ and OM ⊥ RS [1] 35. BC = AC (Given)
Since, perpendicular from the centre to the chord ∴ ∠CBA = ∠BAC = a°
bisects the chord. (Angles opposite to equal sides are equal). [1]
1 So, ∠BAD = a° + x° ...(i) [1]
\ PL = LQ = PQ = 8 cm
2 In ∆ ABD,
1 ∠ABC + ∠ADB + ∠BAD = 180°
RM = MS = RS = 6 cm
2 ∴ a° +x° +(a° +x°) = 180° [1]
In right triangle OLP, Now,
OP2 = OL2 + PL2 2a° + 2x° = 180°
2(a° + x°) = 180°
(By Pythagoras theorem)
a° + x° = 90° [1]
2
100 = OL + 64 ∴ ∠BAD = 90° [from (i)] [1]
OL = 100 − 64 = 36 [1]
OL = 6 cm Section-E
In right triangle OMR, 36. (i) Let contribution given by Sita = ` x
And, contribution done by Gita =` y
OR2 = OM2 + RM2
∴ Linear equation = x + y = 200. [1]
(By Pythagoras theorem)
Solutions 5
(ii) If x = ` 76, then 76 + y = 200 [1] (iii) Budget in the year 2008-09 = 9060 million
y = 200 – 76 Budget in the year 2009 – 10 = 9160 million
y = ` 124 [1] Difference = 9160 – 9060
OR = 100 million [1]
If x = y, then x + x = 200 [1]
Perimeter 20
2x = 200 38. (i) Required semi perimeter = =
2 2
x = 100 [1] = 10 m [1]
Thus, each contributed ` 100.
(ii) Since, semi perimeter, s = 10 m
(iii) Since x = –5
⇒ x + 5 = 0 [½] \ Area = s( s − a )( s − b )( s − c ) [2]
Thus, standard form of x = –5 is = 10(10 − 8 )(10 − 8 )(10 − 4 )
1. x + 0.y + 5 = 0. [½] = 10( 2 )( 2 )( 6 )
37. (i) According to graph, = 4 15 cm 2
In year 2007-08 the budget was minimum. [1]
OR
(ii) Bar graph is a pictorial representation of data. Let x cm be the length of equal sides of the
[½]
isosceles triangle.
It can be vertical or horizontal. [½]
So, x + x + 4 = 20 [1]
Heights of the bar depend on the values of the
2x + 4 = 20
variable. [½]
2x = 20 – 4
There is gap in between consecutive rectangles.
2x = 16
[½]
x = 8 cm [1]
OR
Ladli scheme was launched by the government. (iii) Heron’s formula is used to calculate area of
[1] triangle. [1]
In year 2010-11 the budget was maximum. [1]
You might also like
- H7 Mini Test 3Document2 pagesH7 Mini Test 3Ramadhan ShaffiNo ratings yet
- PromoDocument7 pagesPromoGujarati GamersNo ratings yet
- Solution 1203600Document11 pagesSolution 1203600arb88279No ratings yet
- 3rdgrading Lesson 1Document18 pages3rdgrading Lesson 1Atheena LunaNo ratings yet
- 8L3 Solving Congruent TrianglesDocument4 pages8L3 Solving Congruent TrianglesJewel SantosNo ratings yet
- Maths Sa1 Sp2Document15 pagesMaths Sa1 Sp2Shivam PandeyNo ratings yet
- Https - App - Oswaalbooks.com - Download - Sample-Qp - Subsolution - 888self Ass Paper - 2 (Sol)Document2 pagesHttps - App - Oswaalbooks.com - Download - Sample-Qp - Subsolution - 888self Ass Paper - 2 (Sol)anmolsinghji141No ratings yet
- Day 2 Lesson 4Document28 pagesDay 2 Lesson 4Ezrine UmaniNo ratings yet
- Isucceed Sample Question Paper 16 Maths 9Document4 pagesIsucceed Sample Question Paper 16 Maths 9Yuvraj KatiyarNo ratings yet
- SUSTECH MathDocument24 pagesSUSTECH Matht0xic.369xNo ratings yet
- SOLUTION SET Math IIIDocument4 pagesSOLUTION SET Math IIIMichael ManuelNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument10 pagesVector Calculus - GATE Study Material in PDFSupriya Santre100% (1)
- Vector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDF 1Document10 pagesVector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDF 1nazeeraNo ratings yet
- Grade 10Document9 pagesGrade 10Iya Sicat PatanoNo ratings yet
- Quants: Topics Questions ExplanationDocument20 pagesQuants: Topics Questions ExplanationNikhilaNo ratings yet
- H7 Mini Test 3 AnsDocument2 pagesH7 Mini Test 3 AnsRamadhan ShaffiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Test Review: Geometry CP NameDocument6 pagesChapter 4 Test Review: Geometry CP NameFiona IsbellNo ratings yet
- Properties of Parallelograms Special ParallelogramsDocument16 pagesProperties of Parallelograms Special Parallelogramsjeehan dolorosaNo ratings yet
- Math Reviewer 2 Answers KeyDocument9 pagesMath Reviewer 2 Answers KeyEstepanie Gopet100% (1)
- XII Mathematics 2024 Final Paper SolutionsDocument12 pagesXII Mathematics 2024 Final Paper Solutionswebsite040306No ratings yet
- Rev 1 105 Items Answer KeyDocument5 pagesRev 1 105 Items Answer KeyAinah JovenNo ratings yet
- Top Questions CalculusDocument171 pagesTop Questions CalculusMehul TotalaNo ratings yet
- FinalExam Spring2022 With Answer KeyDocument5 pagesFinalExam Spring2022 With Answer KeyQuangAnh VuNo ratings yet
- Algebra - PDF Version 1 PDFDocument66 pagesAlgebra - PDF Version 1 PDFবাংলার মিল্টনNo ratings yet
- Topper 110 2 3 Maths Solution Up202308291227 1693292242 2785Document19 pagesTopper 110 2 3 Maths Solution Up202308291227 1693292242 2785abhimanyou076No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 TestDocument6 pagesChapter 3 TestJose SegalesNo ratings yet
- Murray Klamkin Problems 1nbsped 091955816x CompressDocument1 pageMurray Klamkin Problems 1nbsped 091955816x CompressRaju RajNo ratings yet
- ps42 n3cs19 SDocument2 pagesps42 n3cs19 Sapi-234377298No ratings yet
- Imo Level1 Solution Class 8 Set 1Document4 pagesImo Level1 Solution Class 8 Set 1chirag birlaNo ratings yet
- E2Qdif CDocument2 pagesE2Qdif CLucas ShazNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Mathematics: Project Katuparan (Document3 pagesAnswer Key: Mathematics: Project Katuparan (Fudge FajardoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 108.5 - Law of Sines and CosinesDocument3 pagesWorksheet 108.5 - Law of Sines and CosinesEditha CuencoNo ratings yet
- Unified Council: National Level Science Talent Search ExaminationDocument6 pagesUnified Council: National Level Science Talent Search ExaminationpriyaamirthaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2020 Paper: Date of Exam: 7 January 2020 (Shift 2) Time: 2:30 P.M. To 5:30 P.M. Subject: MathematicsDocument13 pagesJEE Main 2020 Paper: Date of Exam: 7 January 2020 (Shift 2) Time: 2:30 P.M. To 5:30 P.M. Subject: Mathematicskruthika karraNo ratings yet
- LET Reviewer 3 Math Major AnsKey SolnDocument12 pagesLET Reviewer 3 Math Major AnsKey SolnJhon Rey Leonardo LedamaNo ratings yet
- ICSE-X Mathematics 23-24 SQP SolutionDocument14 pagesICSE-X Mathematics 23-24 SQP SolutionkillerninjaredNo ratings yet
- Https App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 471sap 3Document6 pagesHttps App - Oswaalbooks.com Download Sample-Qp Subsolution 471sap 3hritamgemsNo ratings yet
- 7 A B C D e F 8 A B C D e F 9 A B C D e F G H 10 A B C D 11: Chapter 1 Algebraic Techniques 2 and IndicesDocument2 pages7 A B C D e F 8 A B C D e F 9 A B C D e F G H 10 A B C D 11: Chapter 1 Algebraic Techniques 2 and IndicessNo ratings yet
- State Math Contest 2015-Junior Exam SolutionsDocument16 pagesState Math Contest 2015-Junior Exam SolutionsDgjjkNo ratings yet
- Isometries: 1.1 Transformations of The PlaneDocument38 pagesIsometries: 1.1 Transformations of The PlaneAbebaw MebiratuNo ratings yet
- chapter2 答案Document3 pageschapter2 答案lilyq zNo ratings yet
- Polygons TasksDocument16 pagesPolygons TasksнуркызNo ratings yet
- Math III SolutionSet PDFDocument4 pagesMath III SolutionSet PDFqwertyNo ratings yet
- KCB S.6TEST2 2020mathDocument4 pagesKCB S.6TEST2 2020mathTRIPPLE KAYZ UGNo ratings yet
- Math Pre BoardDocument5 pagesMath Pre BoardAnne KathrineNo ratings yet
- 02 DPPnurturestudentDocument2 pages02 DPPnurturestudentReevu ThapaNo ratings yet
- Basic Mathematics-02-Solved ExampleDocument8 pagesBasic Mathematics-02-Solved ExampleRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- James Ruse 2004 Year 9 Maths Yearly & SolutionsDocument6 pagesJames Ruse 2004 Year 9 Maths Yearly & SolutionsKaushik SarkarNo ratings yet
- Vector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDFDocument9 pagesVector Calculus GATE Study Material in PDFkavinkumareceNo ratings yet
- Part B Unit 1 PDFDocument102 pagesPart B Unit 1 PDFLolu PandeyNo ratings yet
- Xii Math Mock Question Paper Mid Term ExamDocument13 pagesXii Math Mock Question Paper Mid Term Examlove.mansijhaNo ratings yet
- Ahsme 1961Document5 pagesAhsme 1961vidyakumari808940No ratings yet
- X Maths 2023 Sample Paper SolutionsDocument10 pagesX Maths 2023 Sample Paper SolutionsKanchan AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Maths Paper 10THDocument4 pagesMaths Paper 10THSara Aamir ToorNo ratings yet
- PPSC Mock Test 2 Akhtar AbbasDocument4 pagesPPSC Mock Test 2 Akhtar AbbasUmair AliNo ratings yet
- Solution-1337554 240504 204019Document8 pagesSolution-1337554 240504 204019rkumarirani6No ratings yet
- QuadrilateralsDocument24 pagesQuadrilateralsHenry LavitoriaNo ratings yet
- 2014-2015 Midterm ExamDocument2 pages2014-2015 Midterm ExamCHANDNI VERMANo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- The Chinese Cultural Revolution: A Historiographical StudyDocument18 pagesThe Chinese Cultural Revolution: A Historiographical StudyjohndeereNo ratings yet
- John Robinson ResumeDocument2 pagesJohn Robinson Resumeapi-508032756No ratings yet
- The Mystic Will - Based Upon A Study of The Philosophy of Jacob Boehme (PDFDrive)Document296 pagesThe Mystic Will - Based Upon A Study of The Philosophy of Jacob Boehme (PDFDrive)Beni ValdesNo ratings yet
- Compound SentencesDocument3 pagesCompound SentencesNoha Bayoumy0% (1)
- Language and Sex (Sociolinguistics)Document13 pagesLanguage and Sex (Sociolinguistics)Yusrilsyah LimbanadiNo ratings yet
- Assessment Rubric in Stylistic Analysis of TextDocument2 pagesAssessment Rubric in Stylistic Analysis of TextAira Mae67% (3)
- Directory of School and Community LeadersDocument6 pagesDirectory of School and Community LeadersWinston CelestialNo ratings yet
- Medical-for-Coaches-Asst-Coaches-ChaperonesDocument1 pageMedical-for-Coaches-Asst-Coaches-ChaperonesLeah CarnateNo ratings yet
- Character Certificate For Army RecruitmentDocument11 pagesCharacter Certificate For Army Recruitmentkijni2024No ratings yet
- Airworthiness Notice No. 1101: Appendix 2Document3 pagesAirworthiness Notice No. 1101: Appendix 2fareezNo ratings yet
- Read and Write Numbers From 0 To 10 in Symbols and in Words LPDocument4 pagesRead and Write Numbers From 0 To 10 in Symbols and in Words LPJohn Ericson Mabunga100% (1)
- 朱一清的琵琶独奏曲《彼岸民谣》创作特征初探 鲁立怡Document33 pages朱一清的琵琶独奏曲《彼岸民谣》创作特征初探 鲁立怡still451No ratings yet
- What Are The Characteristics of A Teacher Who Can Established A WellDocument6 pagesWhat Are The Characteristics of A Teacher Who Can Established A WellVhiy Dizon BantingNo ratings yet
- Tewwg Essay GuidelinesDocument5 pagesTewwg Essay Guidelinesapi-253342683No ratings yet
- You Successfully Passed A Job Interview. You Are Expected To Start On November 15, ButDocument9 pagesYou Successfully Passed A Job Interview. You Are Expected To Start On November 15, ButGeorgie StephenNo ratings yet
- Cambridge English: First Practice Test ADocument3 pagesCambridge English: First Practice Test AJuan NarvaezNo ratings yet
- Sign Language and Common Gesture Using CNNDocument7 pagesSign Language and Common Gesture Using CNNVelumani s0% (1)
- Ipcr Part 3 4 NTP 2019Document3 pagesIpcr Part 3 4 NTP 2019Lavandera Lpt Vargas JoannaNo ratings yet
- Problems of AJK Learners of English LanguageDocument14 pagesProblems of AJK Learners of English LanguageAsad Mehmood67% (3)
- The First Presbyterian Church in The City of New York Welcomes Rev. Dr. Greg Stovell, Pastor/Head of StaffDocument3 pagesThe First Presbyterian Church in The City of New York Welcomes Rev. Dr. Greg Stovell, Pastor/Head of StaffPR.comNo ratings yet
- Individualism vs. CollectivismDocument4 pagesIndividualism vs. CollectivismNGITPANo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Topic 3Document14 pagesLesson 2 Topic 3Vincent Efraim G. TabatNo ratings yet
- Score Sheet in Thesis/Capstone Oral Defense: AMA UniversityDocument1 pageScore Sheet in Thesis/Capstone Oral Defense: AMA UniversityRafael Aquino100% (1)
- Summer Life Skills - Week 2 Day 33Document14 pagesSummer Life Skills - Week 2 Day 33dg94k72k4vNo ratings yet
- Entertainment: Listening WS: Student's DetailsDocument3 pagesEntertainment: Listening WS: Student's DetailsDino CatNo ratings yet
- Development and Validation of A Customized CompetencyDocument14 pagesDevelopment and Validation of A Customized CompetencyxiaoyuNo ratings yet
- SAP BW-IP Training Integrated Planning - Basic ConceptDocument11 pagesSAP BW-IP Training Integrated Planning - Basic ConceptDurgesh SinghNo ratings yet
- KTEA 3 Parent Report - 54433345 - 1712666972404Document9 pagesKTEA 3 Parent Report - 54433345 - 1712666972404p0074790No ratings yet
- My Hopes and Dreams For My FamilyDocument1 pageMy Hopes and Dreams For My FamilyThez BritanicoNo ratings yet
- Structure and Regulation of Human Phospholipase DDocument10 pagesStructure and Regulation of Human Phospholipase Dxtang2No ratings yet