Professional Documents
Culture Documents
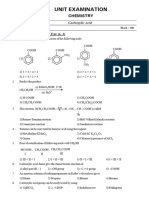
Alcohol, Phenol, & Ether - DPP 01 - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024
Alcohol, Phenol, & Ether - DPP 01 - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024
Uploaded by
chitranshpriyanshu80Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Alcohol, Phenol, & Ether - DPP 01 - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024
Alcohol, Phenol, & Ether - DPP 01 - Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024
Uploaded by
chitranshpriyanshu80Copyright:
Available Formats
1
Lakshya JEE 2.0 2024
Alcohol, Phenol & Ether DPP-01
1. Match the columns - 3. Mechanism of acid catalysed hydration reaction
Column-I Column-II involves -
A. OH P. Quinol (a) Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by
electrophilic attack of H3O+.
(b) Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
(c) Deprotonation to form alcohol.
B. OH Q. Phenol (1) (a) and (b) (2) (a) and (c)
OH
(3) (a), (b) and (c) (4) (b) and (c)
4. Read the following statements and choose the correct
C. OH R. Catechol option-
(a) Ethanol on dehydration at 443K gives ethene.
(b) Ethanol on dehydration at 413K gives diethyl
OH
OH ether.
D. S. Resorcinol
(c) The dehydration of 2º and 3º alcohols to give
corresponding ethers is unsuccessful as
elimination competes over substitution.
(d) 1º alcohol > 2º alcohol > 3º alcohol ( Ease of
OH dehydration)
2. Match the columns - (1) TTFF (2) TFTF
Column-I Column-II (3) TTTF (4) FTTF
A. P. No-reaction
O 5. Which of the following statements are correct
regarding dehydration of alcohols.
⎯⎯⎯
H 3O
→ I. Conc. H2SO4 or Con. H3PO4 or An. ZnCl2 or
B. CH3 Q. CH3 Al2O3 can be used as dehydrating alcohol.
| |
CH3 − C − O − CH − CH3 CH3 − C − OH II. The mechanism involves : Protonation →
| | | Formation of carbocation → Deprotonation
CH3 CH3 CH3 III. Primary alcohols are easiest to dehydrate.
IV. Formation of carbocation is rds step.
⎯⎯⎯
H 3O
→ is one of
the product (1) I, II, III (2) II and IV
(3) I, II, IV (4) I, II, III and IV
C. CH3 R. OH 6. Which of the following statements are correct?
O C CH3 (a) In phenols, the —OH group is attached to sp2
CH3
hybridised carbon of an aromatic ring.
⎯⎯⎯
H 3O
→ is one of the (b) The carbon – oxygen bond length (136 pm) in
product of the phenol is slightly more than that in methanol.
reaction (c) Partial double bond character in C–O bond of
D. CH3 S. CH3 − CH − OH phenol is due to the conjugation of unshared
O CH |
CH3 CH3 electron pair of oxygen with the aromatic ring.
H 3O (d) –OH group in phenol show +M-effect.
⎯⎯⎯→ is one of the
(1) (a), (b) and (v) (2) (a), (b) and (c)
product of the
reaction (3) (a), (c) and (d) (4) (a) and (d)
2
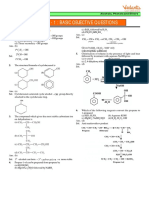
7. Which of the following reactions will yield phenol? 11. An alcohol (A) on treatment with conc. H2SO4 gave
Cl an alkene (B). The compound (B), on reacting with
Br2 water and subsequent dehydrobromination with
(a) ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯
(i)fusion with NaOH at 300 atm
⎯→ NaNH2 produced a compound (C). The compound
+
(ii)H 2O/H (C) with dil. H2SO4 in presence of HgSO4 gave a
NH2 compound 'D'. The compound D can also be obtained
by oxidation of A by acidified KMnO4 or from dry
heating of calcium acetate. Calculate molecular
(b) ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯→
(i)NaNO2 /HCl
(ii)H O(Warming) weight of 'C'.
2
12. Complete the following reactions by writing
(c) ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯(i)Oleum
(ii) NaOH,( Heating )
→ appropriate reactant or major product.
(iii)H + H2SO4
Cl ‘A’
4 13 K
(a) CH3CH2OH
(i)NaOH( aq.)298K/1atm
(d) ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯ → H2SO4
(ii)HCl ‘B’
4 43 K
(1) (a), (b) and (c) (2) (a) and (c) CH3
(3) (a), (c) and (d) (4) (b), (c) and (d) (b) CH3–Cl + CH3–C–ONa
8. Which of the following would not produce phenol as
final product -
CH3
CH3
(1) Acidification of sodium benzene sulphonate.
(2) Hydrolysis of benzene diazonium chloride. (c) CH3–C–Cl + CH3 –ONa
(3) Oxidation of toluene by hot alkaline KMnO4.
CH3
(4) Dow process.
OCH3
9. Statement-I : With HI, anisole gives methyl phenyl
oxonium ion is formed as intermediate.
Statement-II : The attack of I– on methyl phenyl (d) A + B ⎯⎯
→ + NaX
( Alkyl halide )
oxonium ion produces methanol and phenyl iodide.
(1) Statement-I is correct, statement-II is also correct. OH
(2) Statement-I is correct, statement-II is
incorrect. (e) ⎯⎯⎯
NaOH
→ A ⎯⎯⎯
CH3Cl
→B
(3) Statement-I is incorrect, statement-II is correct.
(4) Both statements-I and II are incorrect. (f) CH3 − O − CH3 ⎯⎯⎯
HBr
→ A ⎯⎯⎯
HBr
→B
alcohol
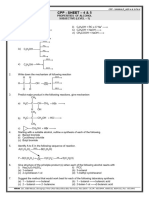
10. At 413 K, ethanol is dehydrated to produce
ethoxyethane. (g) CH3 − O − CH2 − CH3 ⎯⎯
HI
→
CH3 − CH2 − OH ⎯⎯⎯→
H2SO4
C2H5OC2H5 CH3
413K HI
Read the statements given below, and choose the (h) CH3–O–C–CH3
option containing correct statements. CH3
I. Such reaction is suitable for preparation of OCH3
ethers having primary alkyl groups only.
II. The mechanism involves following sequence-
Protonation of alcohol → Attack of another (i) ⎯⎯⎯
HBr
→
alcohol molecule on protonated alcohol →
OCH3
Deprotonation
III. At 443K, the same reaction would produce
ethene as major product. (j) ⎯⎯⎯⎯⎯ Br2
Ethanoic Acid
→
(1) I, II (2) II, III
(3) I, III (4) I, II, and III
3
Note: Kindly find the Video Solution of DPPs Questions in the DPPs Section.
Answer Key
1. (A-Q) ; (B-R) ; (C-S) ; (D-P)
2. (A-P) ; (B-Q, S) ; (C-P, Q) ; (D-R, S)
3. (3)
4. (3)
5. (3)
6. (3)
7. (1)
8. (1,3)
9. (2)
10. (4)
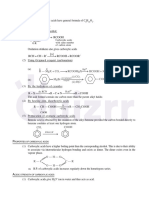
11. (40)
CH3
12. (a) A CH3–CH2–O–CH2–CH3 (b) CH3–C–O–CH3
B CH2=CH2 CH3
CH2
(c) (d) A CH3–X X Cl, Br, I
CH3–C–CH3 ONa
B
ONa OCH3
(e) A B (f) A CH3–OH
B CH3–Br
CH3
(g) CH3 − I + CH3 − CH2 − OH (h) CH3–OH + CH3–C– I
CH3
OH OCH3 OCH3
Br
(i) + CH3Br (j)
Br Minor
Major
PW Web/App - https://smart.link/7wwosivoicgd4
Library- https://smart.link/sdfez8ejd80if
You might also like
- Chapter 10-Structure and Synthesis of AlcoholsDocument22 pagesChapter 10-Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols張湧浩No ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols & EthersDocument12 pagesAlcohols, Phenols & EtherssiddharthchillapwarNo ratings yet
- Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution-03-Assignments (New)Document18 pagesElectrophilic Aromatic Substitution-03-Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Alcohal, Phenol and EtherDocument13 pagesAlcohal, Phenol and EtherVishal TiwariNo ratings yet
- Anjaam Practice Sheet-3 PDFDocument4 pagesAnjaam Practice Sheet-3 PDFtemp93630No ratings yet
- 01 Aory)Document34 pages01 Aory)3107aloksinghNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon Pages Containing HWDocument23 pagesHydrocarbon Pages Containing HWashishkumarberia016No ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and EthersDocument13 pagesChemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and EthersSURENDRA MOHNOTNo ratings yet
- 10 Hydrocarbons: AssignmentDocument6 pages10 Hydrocarbons: AssignmentalarmbarbarNo ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument14 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenesshreyansh tanwarNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Ethers and Phenol-03 - Assignments (New)Document26 pagesAlcohols Ethers and Phenol-03 - Assignments (New)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument18 pagesAlcohols Phenols and EthersFurious AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Deeper Neet DCT - ChemistryDocument8 pagesDeeper Neet DCT - Chemistryhbhaiya643No ratings yet
- Alcohols, Phenols Ethers: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument30 pagesAlcohols, Phenols Ethers: Multiple Choice QuestionsUrja MoonNo ratings yet
- Organic - Structural IsomerismDocument5 pagesOrganic - Structural Isomerismankit.shrivastavaNo ratings yet
- P Block LRNDocument8 pagesP Block LRNNeeharika ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Work Book - P - VDocument29 pagesWork Book - P - VAshwani Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- DGT Alcohols Phenols and EthersDocument69 pagesDGT Alcohols Phenols and Ethersjayashree krishnaNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IIDocument8 pagesOrganic Chemistry IIRoberto SIlvaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 1683183099Document27 pagesExercise 1 1683183099shivam126921No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument14 pagesHaloalkanes and HaloarenesKalpesh BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic AcidDocument6 pagesCarboxylic Acidhareharanbt22No ratings yet
- PDF File Neet - 2018 Question PaperDocument12 pagesPDF File Neet - 2018 Question PaperazimNo ratings yet
- Alchol, Ethor Phenol Ex-1Document12 pagesAlchol, Ethor Phenol Ex-1Subhangi MohantyNo ratings yet
- 07 IntegralsDocument27 pages07 IntegralsSubhangi MohantyNo ratings yet
- 29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument9 pages29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets Quizrrpowerranger34873No ratings yet
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - MCQSDocument3 pagesHaloalkanes and Haloarenes - MCQSDivyam GargNo ratings yet
- Aep 9Document3 pagesAep 9devkaushik0613No ratings yet
- Aldehyde KetoneDocument6 pagesAldehyde Ketone9125-N.S.SriHarshith Prasad XDNo ratings yet
- National Eligibility Cum Entrance Test Neet (Ug) ,: Phase-2 (CODE:BB-QQ-XX)Document19 pagesNational Eligibility Cum Entrance Test Neet (Ug) ,: Phase-2 (CODE:BB-QQ-XX)Vivek SinghNo ratings yet
- Ether (Theory) Module-4Document7 pagesEther (Theory) Module-4Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Aep-4 & 5Document9 pagesAep-4 & 5devkaushik0613No ratings yet
- Aep - CPP - 1Document9 pagesAep - CPP - 1ayesha sheikhNo ratings yet
- Alk Enes Al Kynes ExercisesDocument1 pageAlk Enes Al Kynes ExercisesAR LazagaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 9-AnswersDocument7 pagesTutorial Chapter 9-AnswersNKMS:)No ratings yet
- 29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument8 pages29 Carboxylic Acids Formula Sheets QuizrrArjunNo ratings yet
- This PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedDocument13 pagesThis PDF Is The Sample PDF Taken From Our Comprehensive Study Material For IIT-JEE Main & AdvancedGod is every whereNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument5 pagesChemKanu Raj AnandNo ratings yet
- Alcohol Jeemain - GuruDocument36 pagesAlcohol Jeemain - GuruSailost Jr.No ratings yet
- Chemistry - Aromatic HydrocarbonsDocument4 pagesChemistry - Aromatic Hydrocarbonswakeetha cNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDocument3 pagesChapter 10 Haloalkanes and HaloarenesAaryaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Ch-8.Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic AcidsDocument53 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Ch-8.Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acidskingoo0f1No ratings yet
- Leep511 PDFDocument14 pagesLeep511 PDFSubhabrata MabhaiNo ratings yet
- Aldehyde, Ketone & Carboxylic AcidDocument20 pagesAldehyde, Ketone & Carboxylic AcidRaj RastogiNo ratings yet
- Test - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - 28.8.2023Document3 pagesTest - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - 28.8.2023jayaprasanthsinghNo ratings yet
- Alcohol, Ether, Phenol - PrintDocument19 pagesAlcohol, Ether, Phenol - PrintShubham Raj100% (2)
- CLS Aipmt 19 20 XII Che Study Package 4 Level 1 Chapter 10Document36 pagesCLS Aipmt 19 20 XII Che Study Package 4 Level 1 Chapter 10Utkarsh KumarNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry IIDocument10 pagesOrganic Chemistry IIRoberto SIlvaNo ratings yet
- Oxygen Containing CompoundsDocument27 pagesOxygen Containing CompoundsSHIVI DwivediNo ratings yet
- CH 18Document32 pagesCH 18Dimas MitraNo ratings yet
- Previous HSE Questions and Answers For The Chapter "Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers"Document10 pagesPrevious HSE Questions and Answers For The Chapter "Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers"Adithya K SanjeevNo ratings yet
- Chem Sci Paper IIDocument7 pagesChem Sci Paper IIprivateinfNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons 1Document7 pagesHydrocarbons 1shalika42598No ratings yet
- Grade 10 Carbon and Its CompoundsDocument4 pagesGrade 10 Carbon and Its Compounds22550No ratings yet
- Bakliwal Tutorials: Organic Chemistry Assignment Topic: HydrocarbonsDocument17 pagesBakliwal Tutorials: Organic Chemistry Assignment Topic: HydrocarbonsJonathan ParkerNo ratings yet
- Reasoning Based Questions (6 Marks) Section-ADocument4 pagesReasoning Based Questions (6 Marks) Section-ARishi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Alcohols & Ethers TheoryDocument15 pagesAlcohols & Ethers TheorySaif KhanNo ratings yet