Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 7-31 Energy Transfer
Grade 7-31 Energy Transfer
Uploaded by
وسلاتي مريمCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Demo - COT1Document5 pagesDemo - COT1joana mariel c. magadia100% (2)
- TataAIA PAR Product Bonus History FY23Document4 pagesTataAIA PAR Product Bonus History FY23Arpit ShahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science IVDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Science IVPrecilla Ugarte Halago100% (10)
- Buttross Susan Understanding ADHD PDFDocument141 pagesButtross Susan Understanding ADHD PDFRuth Gasparini67% (3)
- Unit 4: Heat EnergyDocument15 pagesUnit 4: Heat EnergyMahamud elmogeNo ratings yet
- 5 Lesson Plan On HeatDocument4 pages5 Lesson Plan On HeatJustine Collamar GanabNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science IVDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in Science IVMaria Allen Ann CasilihanNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 6: How Heat Transfer and Energy Transformation Makes Heat Engine WorkDocument11 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 6: How Heat Transfer and Energy Transformation Makes Heat Engine WorkEECezar JeicyyuiNo ratings yet
- Text Reading - Temperature and Heat WorksheetDocument4 pagesText Reading - Temperature and Heat WorksheetScot BelfordNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Physics With No AnswerDocument11 pagesModule 6 Physics With No AnswerHannah CagatanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021Document20 pagesThermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021anembam putobungbongNo ratings yet
- Q4-Science-9-Week 6Document4 pagesQ4-Science-9-Week 6Jovel TabiosNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 NoteDocument5 pagesScience Form 1 NoteDaniel ChanNo ratings yet
- Final Notes CH 1 G-8Document8 pagesFinal Notes CH 1 G-8voiditycypherNo ratings yet
- 6th STD Science 2nd Term Notes QuestionsDocument29 pages6th STD Science 2nd Term Notes QuestionsAamir KhanNo ratings yet
- Heat Chapter-10: Answer To The Short QuestionsDocument18 pagesHeat Chapter-10: Answer To The Short QuestionsG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Temperature and HeatDocument5 pagesTemperature and HeatHari Krishna KommiNo ratings yet
- G-8 Physics Unit 4 Note - 07-08-13796168803685 - Gobe - 3Document9 pagesG-8 Physics Unit 4 Note - 07-08-13796168803685 - Gobe - 3AbebechNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 HeatDocument6 pagesChapter 7 HeatShyeshaNo ratings yet
- Heat Chapter NotesDocument9 pagesHeat Chapter NotesMaanya KumarNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q4 Module 5 WK 5 v.01 CC Released 29may2021Document22 pagesScience 9 Q4 Module 5 WK 5 v.01 CC Released 29may2021Jecka FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 50Document52 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 50JOVELYN Y. ALFORQUENo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HeatDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Heatsahoobijayalaxmi13No ratings yet
- Textual EvaluationDocument22 pagesTextual EvaluationVikas BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection RadiationDocument26 pagesConduction Convection Radiationnavketsharma6280100% (1)
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Energy and Technology DawiliDocument5 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Energy and Technology DawiliSydsyd DawiliNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document22 pagesModule 5euhanalmendras1No ratings yet
- Si UnitsDocument92 pagesSi UnitsRAVI2296No ratings yet
- Phy Ch5Document7 pagesPhy Ch5vivanhirani11No ratings yet
- Sci-9-Q4-Module-7-Week 7Document17 pagesSci-9-Q4-Module-7-Week 7shimuraririkkuNo ratings yet
- Science: Self Learning Kit inDocument18 pagesScience: Self Learning Kit inJOHN MAYKALE FARRALESNo ratings yet
- sw8 chp06Document22 pagessw8 chp06api-115560904No ratings yet
- Subject: Science Class - VII Chapter - 4 Heat (Module) : Question - AnswerDocument3 pagesSubject: Science Class - VII Chapter - 4 Heat (Module) : Question - AnswerAzib KhanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer LessonDocument15 pagesHeat Transfer Lessonapi-252516966100% (1)
- Conduction: Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument10 pagesConduction: Transfer of Thermal Energyanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Good Afternoon!Document79 pagesGood Afternoon!Perlita CarpenteroNo ratings yet
- 6 - Q4 ScienceDocument14 pages6 - Q4 Sciencemaximo meridaNo ratings yet
- 7 Heat SolutionsDocument7 pages7 Heat Solutionssmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Science Le - Thirdquarter - HeattransferDocument4 pagesScience Le - Thirdquarter - HeattransferFatima Abacan Reyes100% (3)
- Science 6 Q3 W4 LAS 2Document2 pagesScience 6 Q3 W4 LAS 2Ellen Jenneth PudaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Energy Transfer (Student Guide)Document11 pagesModule 4 - Energy Transfer (Student Guide)greggcllam619076No ratings yet
- Module 5 Physics With No AnswerDocument8 pagesModule 5 Physics With No AnswerHannah CagatanNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Teacher Made Module Quarter 4 Week 6Document2 pagesScience 9 Teacher Made Module Quarter 4 Week 6Ricky Peñaroyo VentozaNo ratings yet
- Notes Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument12 pagesNotes Transfer of Thermal Energymahrosh mamoon100% (2)
- Heat and Work NotesDocument5 pagesHeat and Work Notesdavid rentoriaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Chapter 6 NotesDocument54 pagesGrade 7 Science Chapter 6 Notesapi-238589602No ratings yet
- Thermo m3Document8 pagesThermo m3Marlyn AngelesNo ratings yet
- CLASS VII Physics HeatQADocument6 pagesCLASS VII Physics HeatQAtojendra laltenNo ratings yet
- Heat NotesDocument28 pagesHeat NotesRoyal PrasNo ratings yet
- How Hurricanes Pick Up EnergyDocument23 pagesHow Hurricanes Pick Up EnergyAhanaNo ratings yet
- Grade VII-Physics - L 1 Heat NotesDocument7 pagesGrade VII-Physics - L 1 Heat NotesDEBENDRA NATH CHOUDHURYNo ratings yet
- EHM Lesson 5 FT PDFDocument14 pagesEHM Lesson 5 FT PDFMuhammed NazardeenNo ratings yet
- Group 12 - Group Work 6 - Heat TransferDocument4 pagesGroup 12 - Group Work 6 - Heat TransferMiah MuthmainnahNo ratings yet
- Modules: Quarter 4 - Weeks 5 - 8Document44 pagesModules: Quarter 4 - Weeks 5 - 8rebadullafrancheskaNo ratings yet
- Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument24 pagesLaws of ThermodynamicsMYBNG SHPPRNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Temperature: Activity 1Document7 pagesLesson 1: Temperature: Activity 1Jonathan Jay-r RestOr100% (1)
- Science 7 - Q3 - Episode 6 - SLMDocument5 pagesScience 7 - Q3 - Episode 6 - SLMCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- 7e LP - ConductionDocument13 pages7e LP - ConductionKresha LluismaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan No 1Document4 pagesLesson Plan No 1hafeez ahmed0% (1)
- Science 8 Module 5Document8 pagesScience 8 Module 5Kristel TelmoNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Q4 Module5 6Document17 pagesGrade 9 Q4 Module5 6rinalynparasNo ratings yet
- G7 Lesson 2Document2 pagesG7 Lesson 2وسلاتي مريمNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education ChemistryDocument8 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education Chemistryوسلاتي مريمNo ratings yet
- 0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesDocument2 pages0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 Seriesوسلاتي مريمNo ratings yet
- PSD Gr7 Gr8 Science Review EnergyDocument36 pagesPSD Gr7 Gr8 Science Review Energyوسلاتي مريمNo ratings yet
- Energy Transfer WorksheetDocument2 pagesEnergy Transfer Worksheetوسلاتي مريمNo ratings yet
- Warehouse & Storage Techniques - Lecture 3Document29 pagesWarehouse & Storage Techniques - Lecture 3Muhammad AhsanNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 and Disinfectants and Sanitizers in Food PremisesDocument5 pagesCOVID-19 and Disinfectants and Sanitizers in Food Premisesnur atiqah sobriNo ratings yet
- Pressure Conversion ChartDocument1 pagePressure Conversion Chartamarkore3486No ratings yet
- John The Baptists DietDocument2 pagesJohn The Baptists DietAnida Maria Moraes GomesNo ratings yet
- Examen Selectividad Pau Madrid Ingles 2011 JunioDocument6 pagesExamen Selectividad Pau Madrid Ingles 2011 Juniold250% (1)
- Susan Sugarman - Freud's Interpretation of Dreams - A Reappraisal-Cambridge University Press (2022)Document195 pagesSusan Sugarman - Freud's Interpretation of Dreams - A Reappraisal-Cambridge University Press (2022)Rodolfo Ferronatto De SouzaNo ratings yet
- RPZ Testing Form 215bDocument2 pagesRPZ Testing Form 215bSam ChoiNo ratings yet
- Diah Mustika HW, SPS, Kic Intensive Care Unit of Emergency Department Naval Hospital DR Ramelan, SurabayaDocument33 pagesDiah Mustika HW, SPS, Kic Intensive Care Unit of Emergency Department Naval Hospital DR Ramelan, SurabayaNabilaNo ratings yet
- Project List Export 10-10-2023Document12 pagesProject List Export 10-10-2023Muhammad AzharuddinNo ratings yet
- EMP For The PPG For TA To Afghanistan - AILA Project (Clean Version)Document30 pagesEMP For The PPG For TA To Afghanistan - AILA Project (Clean Version)Ahmad BelalNo ratings yet
- Mounted On Rails or Rubber Tyres and Is Able To Straddle Several Rows of ContainersDocument2 pagesMounted On Rails or Rubber Tyres and Is Able To Straddle Several Rows of ContainersIcha AfNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument69 pagesPlantsAkshay JainNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationErika Mae MananganNo ratings yet
- File 274804260391Document22 pagesFile 274804260391Nemanja NikolicNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Study GuideDocument24 pagesBiotechnology Study GuideÖzlem ErdemNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Reaction - KLP 5Document23 pagesCarbohydrates Reaction - KLP 5Putri SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Construction MaterialsDocument20 pagesLecture 1 - Construction MaterialspuskarNo ratings yet
- (Ebook PDF) Introduction To Food Science and Food Systems 2nd Edition Rick Parker - Ebook PDF All ChapterDocument69 pages(Ebook PDF) Introduction To Food Science and Food Systems 2nd Edition Rick Parker - Ebook PDF All Chapterfaishdarron100% (7)
- Lost Foam Casting (LFC)Document26 pagesLost Foam Casting (LFC)Gurudutta Mishra100% (3)
- 2.fluid and Electrolyte Management of The Surgical PatientDocument18 pages2.fluid and Electrolyte Management of The Surgical Patientjqmrtc8cfgNo ratings yet
- Garments Workers in BangladeshDocument4 pagesGarments Workers in BangladeshtasnianasirNo ratings yet
- Kiln Inlet Analyzer.: CalibrationDocument3 pagesKiln Inlet Analyzer.: CalibrationZakariya ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY CAKE BATIK Proximate AnalysisDocument25 pagesCASE STUDY CAKE BATIK Proximate AnalysisNur Azhani100% (1)
- Technical Data Sheet: Tire Lube and SealDocument1 pageTechnical Data Sheet: Tire Lube and SealDon HowardNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Nursing Informatics, Quality and SafetyDocument36 pagesEvidence-Based Nursing Informatics, Quality and Safetymagdaashaaban100% (1)
- G2C & B2C Services: Telecentre Entrepreneur CourseDocument6 pagesG2C & B2C Services: Telecentre Entrepreneur CourseKarthik VanamNo ratings yet
- QC ProcedureDocument6 pagesQC ProcedureEkyharyans100% (1)
- Effects of Experimental Parameters On NF3 Decomposition Fraction in An Oxygen-Based 2004Document7 pagesEffects of Experimental Parameters On NF3 Decomposition Fraction in An Oxygen-Based 2004Регина ШаяхметоваNo ratings yet
Grade 7-31 Energy Transfer
Grade 7-31 Energy Transfer
Uploaded by
وسلاتي مريمOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 7-31 Energy Transfer
Grade 7-31 Energy Transfer
Uploaded by
وسلاتي مريمCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade: 7
Subject: Natural Science
Dates: 31/08/2020- 04/09/2020
Lesson & Topic: Lesson 1: Heat transfer
Heating as a transfer of energy
Instructions:
Good day learners I trust that you are in good health. Please read the content
on pages 147-162 of your Platinum Science textbook and watch the video.
Answer the following activities:
Lesson & Topic: Lesson 1: Heat transfer
Heating as a transfer of energy
Activity 1: Find out what you know about energy and energy transfer.
Page 147
Activity 2: Describe examples in which heat energy is transferred
Page 149
Lesson & Topic: Lesson 2: Heat transfer
Conduction
Activity 3: Explain heat energy transfer by conduction
Page 151
Lesson & Topic: Lesson 3: Heat transfer
How to identify variables
Activity 5: Practise identify variables that affect results.
Page154
Lesson & Topic: Lesson 4: Heat transfer
Convection
Activity 8: Explain how convection occurs
Page 157
MEM0
Lesson & Topic: Lesson 1: Heat transfer
Heating as a transfer of energy
Activity 1: Find out what you know about energy and energy transfer.
Page 147
1. Energy is the ability to do work and energy transfer is the movement of
energy from one point to another.
2. The four systems are:
Mechanical systems
Electrical systems
Thermal systems
Biological systems
3. The Sun will fall under the thermal system.
4. Thermal energy is energy produced by heat. An example is when your
body is warmed by warm water in a bath.
5. B
6. It is cold in winter, so when you stand in direct sunlight you can be
warmed by the heat from the Sun.
Activity 2: Describe examples in which heat energy is transferred
Page 149
1. Figure 5: When sharpening a pencil, the friction between the pencil
sharpener and the pencil produces heat, which is transferred to both the
pencil and the sharpener.
Figure 6: A hair dryer produces warm air that is transferred to dry your
wet hair.
Figure 7: An iron has a hot base that transfers heat to iron the clothes.
Figure 8: When your lips touch a cup of hot chocolate, the heat from the
hot cup is transferred to warm your lips.
Figure 9: Burning wood in a fireplace produces heat, which is transferred
to warm the entire room.
2.
Medium required Example
Liquids Drinking hot chocolate
Gases Burning wood
Solids Using an iron
No medium None(There can be no heat transfer in a vacuum
Lesson & Topic: Lesson 2: Heat transfer
Conduction
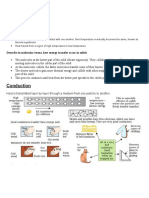
Activity 3: Explain heat energy transfer by conduction
Page 151
1. Heat transfer in each picture:
Figure 14: Heat is transferred from the iron to the clothing.
Figure 15: Heat is transferred from the mug of tea to the hands holding
the mug.
Figure 16: Heat is transferred from the hot tarmac to the feet of the
child.
2. The arrows on your diagrams must be correct.
Figure 14: Arrow from the iron to the clothing
Figure 15: Arrow from the cup to the hands
Figure 16: Arrows from the tar road to the feet
3. Answers may vary:
Burning a candle transfers heat from the flame to the room.
Computer heat sinks draw heat away from the heat-sensitive
computer components.
Bathwater transfers heat from the water to the person bathing.
4. Answers may vary:
Mining: Melting gold to make gold bars
Manufacturing industry: Glass production
Electricity generation: Cooling towers
Lesson & Topic: Lesson 3: Heat transfer
How to identify variables
Activity 5: Practise identify variables that affect results.
Page 159
1. The independent variables are the marshmallow and the peanut.
The dependent variable is the amount of energy produced (as indicated
by the temperature of the water).
The control variables are the amount of water in the test tubes, the time
taken and the type of test tube used.
2. The independent variables are the silver mat and the black mat.
The dependent variables are the hotness or coldness of the mats.
The control variables are the time taken, the material of the mats and the
exposure to the Sun.
Lesson & Topic: Lesson 4: Heat transfer
Convection
Activity 8: Explain how convection occurs
Page 157
1. Hot air rises therefore the heater is best positioned on the floor so that as
the warm air rises, the cooler air sinks down to be warmed by the heater
until the whole room is full of warm air. In summer, the air
conditioner is best positioned next to the ceiling, since the cool air
generated by the air conditioner sinks and the warm air rises (to be cooled
by the air conditioner) until the room is eventually filled with cool air.
2. Water expands as it gets warmer and it rises. The movement of water
creates currents that circulate the water around the fish tank. In this way,
all the water in the fish tank(not just the surface water)is kept warm.
3. The fireplace also uses the concept of convection, in that the warm or hot
air around the fire rises through the chimney and carries smoke with it.
Hence, we do not have smoke in the room. It is only when the wood is not
burning properly that you have smoke in the room. Another example is a
hot air balloon: The hot air inside the balloon causes it to rise because hot
air rises.
You might also like
- Demo - COT1Document5 pagesDemo - COT1joana mariel c. magadia100% (2)
- TataAIA PAR Product Bonus History FY23Document4 pagesTataAIA PAR Product Bonus History FY23Arpit ShahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science IVDocument4 pagesLesson Plan in Science IVPrecilla Ugarte Halago100% (10)
- Buttross Susan Understanding ADHD PDFDocument141 pagesButtross Susan Understanding ADHD PDFRuth Gasparini67% (3)
- Unit 4: Heat EnergyDocument15 pagesUnit 4: Heat EnergyMahamud elmogeNo ratings yet
- 5 Lesson Plan On HeatDocument4 pages5 Lesson Plan On HeatJustine Collamar GanabNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science IVDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in Science IVMaria Allen Ann CasilihanNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 6: How Heat Transfer and Energy Transformation Makes Heat Engine WorkDocument11 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 6: How Heat Transfer and Energy Transformation Makes Heat Engine WorkEECezar JeicyyuiNo ratings yet
- Text Reading - Temperature and Heat WorksheetDocument4 pagesText Reading - Temperature and Heat WorksheetScot BelfordNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Physics With No AnswerDocument11 pagesModule 6 Physics With No AnswerHannah CagatanNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021Document20 pagesThermodynamics Module 5: Assessment Task 5: Laguna University College of Education A.Y 2020-2021anembam putobungbongNo ratings yet
- Q4-Science-9-Week 6Document4 pagesQ4-Science-9-Week 6Jovel TabiosNo ratings yet
- Science Form 1 NoteDocument5 pagesScience Form 1 NoteDaniel ChanNo ratings yet
- Final Notes CH 1 G-8Document8 pagesFinal Notes CH 1 G-8voiditycypherNo ratings yet
- 6th STD Science 2nd Term Notes QuestionsDocument29 pages6th STD Science 2nd Term Notes QuestionsAamir KhanNo ratings yet
- Heat Chapter-10: Answer To The Short QuestionsDocument18 pagesHeat Chapter-10: Answer To The Short QuestionsG M Ali KawsarNo ratings yet
- Temperature and HeatDocument5 pagesTemperature and HeatHari Krishna KommiNo ratings yet
- G-8 Physics Unit 4 Note - 07-08-13796168803685 - Gobe - 3Document9 pagesG-8 Physics Unit 4 Note - 07-08-13796168803685 - Gobe - 3AbebechNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 HeatDocument6 pagesChapter 7 HeatShyeshaNo ratings yet
- Heat Chapter NotesDocument9 pagesHeat Chapter NotesMaanya KumarNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q4 Module 5 WK 5 v.01 CC Released 29may2021Document22 pagesScience 9 Q4 Module 5 WK 5 v.01 CC Released 29may2021Jecka FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lesson 50Document52 pagesChapter 2 Lesson 50JOVELYN Y. ALFORQUENo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 HeatDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Heatsahoobijayalaxmi13No ratings yet
- Textual EvaluationDocument22 pagesTextual EvaluationVikas BeniwalNo ratings yet
- Conduction Convection RadiationDocument26 pagesConduction Convection Radiationnavketsharma6280100% (1)
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Energy and Technology DawiliDocument5 pagesSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Energy and Technology DawiliSydsyd DawiliNo ratings yet
- Module 5Document22 pagesModule 5euhanalmendras1No ratings yet
- Si UnitsDocument92 pagesSi UnitsRAVI2296No ratings yet
- Phy Ch5Document7 pagesPhy Ch5vivanhirani11No ratings yet
- Sci-9-Q4-Module-7-Week 7Document17 pagesSci-9-Q4-Module-7-Week 7shimuraririkkuNo ratings yet
- Science: Self Learning Kit inDocument18 pagesScience: Self Learning Kit inJOHN MAYKALE FARRALESNo ratings yet
- sw8 chp06Document22 pagessw8 chp06api-115560904No ratings yet
- Subject: Science Class - VII Chapter - 4 Heat (Module) : Question - AnswerDocument3 pagesSubject: Science Class - VII Chapter - 4 Heat (Module) : Question - AnswerAzib KhanNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer LessonDocument15 pagesHeat Transfer Lessonapi-252516966100% (1)
- Conduction: Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument10 pagesConduction: Transfer of Thermal Energyanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Good Afternoon!Document79 pagesGood Afternoon!Perlita CarpenteroNo ratings yet
- 6 - Q4 ScienceDocument14 pages6 - Q4 Sciencemaximo meridaNo ratings yet
- 7 Heat SolutionsDocument7 pages7 Heat Solutionssmi_santhoshNo ratings yet
- Science Le - Thirdquarter - HeattransferDocument4 pagesScience Le - Thirdquarter - HeattransferFatima Abacan Reyes100% (3)
- Science 6 Q3 W4 LAS 2Document2 pagesScience 6 Q3 W4 LAS 2Ellen Jenneth PudaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 - Energy Transfer (Student Guide)Document11 pagesModule 4 - Energy Transfer (Student Guide)greggcllam619076No ratings yet
- Module 5 Physics With No AnswerDocument8 pagesModule 5 Physics With No AnswerHannah CagatanNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Teacher Made Module Quarter 4 Week 6Document2 pagesScience 9 Teacher Made Module Quarter 4 Week 6Ricky Peñaroyo VentozaNo ratings yet
- Notes Transfer of Thermal EnergyDocument12 pagesNotes Transfer of Thermal Energymahrosh mamoon100% (2)
- Heat and Work NotesDocument5 pagesHeat and Work Notesdavid rentoriaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Science Chapter 6 NotesDocument54 pagesGrade 7 Science Chapter 6 Notesapi-238589602No ratings yet
- Thermo m3Document8 pagesThermo m3Marlyn AngelesNo ratings yet
- CLASS VII Physics HeatQADocument6 pagesCLASS VII Physics HeatQAtojendra laltenNo ratings yet
- Heat NotesDocument28 pagesHeat NotesRoyal PrasNo ratings yet
- How Hurricanes Pick Up EnergyDocument23 pagesHow Hurricanes Pick Up EnergyAhanaNo ratings yet
- Grade VII-Physics - L 1 Heat NotesDocument7 pagesGrade VII-Physics - L 1 Heat NotesDEBENDRA NATH CHOUDHURYNo ratings yet
- EHM Lesson 5 FT PDFDocument14 pagesEHM Lesson 5 FT PDFMuhammed NazardeenNo ratings yet
- Group 12 - Group Work 6 - Heat TransferDocument4 pagesGroup 12 - Group Work 6 - Heat TransferMiah MuthmainnahNo ratings yet
- Modules: Quarter 4 - Weeks 5 - 8Document44 pagesModules: Quarter 4 - Weeks 5 - 8rebadullafrancheskaNo ratings yet
- Laws of ThermodynamicsDocument24 pagesLaws of ThermodynamicsMYBNG SHPPRNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Temperature: Activity 1Document7 pagesLesson 1: Temperature: Activity 1Jonathan Jay-r RestOr100% (1)
- Science 7 - Q3 - Episode 6 - SLMDocument5 pagesScience 7 - Q3 - Episode 6 - SLMCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- 7e LP - ConductionDocument13 pages7e LP - ConductionKresha LluismaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan No 1Document4 pagesLesson Plan No 1hafeez ahmed0% (1)
- Science 8 Module 5Document8 pagesScience 8 Module 5Kristel TelmoNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Q4 Module5 6Document17 pagesGrade 9 Q4 Module5 6rinalynparasNo ratings yet
- G7 Lesson 2Document2 pagesG7 Lesson 2وسلاتي مريمNo ratings yet
- University of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education ChemistryDocument8 pagesUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations International General Certificate of Secondary Education Chemistryوسلاتي مريمNo ratings yet
- 0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 SeriesDocument2 pages0620 Chemistry: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2013 Seriesوسلاتي مريمNo ratings yet
- PSD Gr7 Gr8 Science Review EnergyDocument36 pagesPSD Gr7 Gr8 Science Review Energyوسلاتي مريمNo ratings yet
- Energy Transfer WorksheetDocument2 pagesEnergy Transfer Worksheetوسلاتي مريمNo ratings yet
- Warehouse & Storage Techniques - Lecture 3Document29 pagesWarehouse & Storage Techniques - Lecture 3Muhammad AhsanNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 and Disinfectants and Sanitizers in Food PremisesDocument5 pagesCOVID-19 and Disinfectants and Sanitizers in Food Premisesnur atiqah sobriNo ratings yet
- Pressure Conversion ChartDocument1 pagePressure Conversion Chartamarkore3486No ratings yet
- John The Baptists DietDocument2 pagesJohn The Baptists DietAnida Maria Moraes GomesNo ratings yet
- Examen Selectividad Pau Madrid Ingles 2011 JunioDocument6 pagesExamen Selectividad Pau Madrid Ingles 2011 Juniold250% (1)
- Susan Sugarman - Freud's Interpretation of Dreams - A Reappraisal-Cambridge University Press (2022)Document195 pagesSusan Sugarman - Freud's Interpretation of Dreams - A Reappraisal-Cambridge University Press (2022)Rodolfo Ferronatto De SouzaNo ratings yet
- RPZ Testing Form 215bDocument2 pagesRPZ Testing Form 215bSam ChoiNo ratings yet
- Diah Mustika HW, SPS, Kic Intensive Care Unit of Emergency Department Naval Hospital DR Ramelan, SurabayaDocument33 pagesDiah Mustika HW, SPS, Kic Intensive Care Unit of Emergency Department Naval Hospital DR Ramelan, SurabayaNabilaNo ratings yet
- Project List Export 10-10-2023Document12 pagesProject List Export 10-10-2023Muhammad AzharuddinNo ratings yet
- EMP For The PPG For TA To Afghanistan - AILA Project (Clean Version)Document30 pagesEMP For The PPG For TA To Afghanistan - AILA Project (Clean Version)Ahmad BelalNo ratings yet
- Mounted On Rails or Rubber Tyres and Is Able To Straddle Several Rows of ContainersDocument2 pagesMounted On Rails or Rubber Tyres and Is Able To Straddle Several Rows of ContainersIcha AfNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument69 pagesPlantsAkshay JainNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationErika Mae MananganNo ratings yet
- File 274804260391Document22 pagesFile 274804260391Nemanja NikolicNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Study GuideDocument24 pagesBiotechnology Study GuideÖzlem ErdemNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates Reaction - KLP 5Document23 pagesCarbohydrates Reaction - KLP 5Putri SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Construction MaterialsDocument20 pagesLecture 1 - Construction MaterialspuskarNo ratings yet
- (Ebook PDF) Introduction To Food Science and Food Systems 2nd Edition Rick Parker - Ebook PDF All ChapterDocument69 pages(Ebook PDF) Introduction To Food Science and Food Systems 2nd Edition Rick Parker - Ebook PDF All Chapterfaishdarron100% (7)
- Lost Foam Casting (LFC)Document26 pagesLost Foam Casting (LFC)Gurudutta Mishra100% (3)
- 2.fluid and Electrolyte Management of The Surgical PatientDocument18 pages2.fluid and Electrolyte Management of The Surgical Patientjqmrtc8cfgNo ratings yet
- Garments Workers in BangladeshDocument4 pagesGarments Workers in BangladeshtasnianasirNo ratings yet
- Kiln Inlet Analyzer.: CalibrationDocument3 pagesKiln Inlet Analyzer.: CalibrationZakariya ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY CAKE BATIK Proximate AnalysisDocument25 pagesCASE STUDY CAKE BATIK Proximate AnalysisNur Azhani100% (1)
- Technical Data Sheet: Tire Lube and SealDocument1 pageTechnical Data Sheet: Tire Lube and SealDon HowardNo ratings yet
- Evidence-Based Nursing Informatics, Quality and SafetyDocument36 pagesEvidence-Based Nursing Informatics, Quality and Safetymagdaashaaban100% (1)
- G2C & B2C Services: Telecentre Entrepreneur CourseDocument6 pagesG2C & B2C Services: Telecentre Entrepreneur CourseKarthik VanamNo ratings yet
- QC ProcedureDocument6 pagesQC ProcedureEkyharyans100% (1)
- Effects of Experimental Parameters On NF3 Decomposition Fraction in An Oxygen-Based 2004Document7 pagesEffects of Experimental Parameters On NF3 Decomposition Fraction in An Oxygen-Based 2004Регина ШаяхметоваNo ratings yet