Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Econ Progresss
Econ Progresss
Uploaded by
tonggennnCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Time Series Analysis - Univariate and Multivariate Methods by William Wei PDFDocument634 pagesTime Series Analysis - Univariate and Multivariate Methods by William Wei PDFAnuj Sachdev100% (3)
- Economic Theory and Operations Analysis-1Document7 pagesEconomic Theory and Operations Analysis-1roasted friesNo ratings yet
- CT6 Statistical Methods PDFDocument6 pagesCT6 Statistical Methods PDFVignesh Srinivasan0% (2)
- Process Analysis by Statistical Methods D. HimmelblauDocument474 pagesProcess Analysis by Statistical Methods D. HimmelblauSofia Mac Rodri100% (4)
- Machine Learning Assignment Report - CarsDocument42 pagesMachine Learning Assignment Report - Carssurajramkumar100% (4)
- CustomerChurn AssignmentDocument15 pagesCustomerChurn AssignmentMalavika R Kumar100% (3)
- Multivariable Model - Building: A Pragmatic Approach to Regression Anaylsis based on Fractional Polynomials for Modelling Continuous VariablesFrom EverandMultivariable Model - Building: A Pragmatic Approach to Regression Anaylsis based on Fractional Polynomials for Modelling Continuous VariablesNo ratings yet
- Top 12 Questions PG StatsDocument2 pagesTop 12 Questions PG StatsRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- FULL Download Ebook PDF Introduction To Probability Models 12th Edition PDF EbookDocument47 pagesFULL Download Ebook PDF Introduction To Probability Models 12th Edition PDF Ebookfaith.bratcher185100% (33)
- Course OutlineDocument2 pagesCourse Outlineasu manNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University Islamabad (Department of Business Administration)Document5 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University Islamabad (Department of Business Administration)Noo UllahNo ratings yet
- CT4 Models PDFDocument6 pagesCT4 Models PDFVignesh Srinivasan0% (1)
- Question Bank RMDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank RMharshaNo ratings yet
- AICM 702 - Research Statistical MethodsDocument156 pagesAICM 702 - Research Statistical MethodsCar Sebial VelascoNo ratings yet
- A1388404476 - 64039 - 23 - 2023 - Machine Learning IIDocument10 pagesA1388404476 - 64039 - 23 - 2023 - Machine Learning IIraj241299No ratings yet
- Modern Industrial Statistics: with applications in R, MINITAB and JMPFrom EverandModern Industrial Statistics: with applications in R, MINITAB and JMPNo ratings yet
- 1011MPFM EconometricsDocument3 pages1011MPFM EconometricseXcuvatorNo ratings yet
- PGDBA SyllabusDocument5 pagesPGDBA Syllabusarpan singhNo ratings yet
- 311 LO Part IIDocument3 pages311 LO Part IIu20417242No ratings yet
- Time Series Course OutlineDocument4 pagesTime Series Course OutlineAba MachaNo ratings yet
- F23 Final Exam ReviewDocument12 pagesF23 Final Exam ReviewBrandi Burchell-LeedomNo ratings yet
- Discrete-Event System Simulation: Fourth EditionDocument9 pagesDiscrete-Event System Simulation: Fourth EditionFaizan RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Bmat202l Probability-And-Statistics TH 1.0 65 Bmat202lDocument3 pagesBmat202l Probability-And-Statistics TH 1.0 65 Bmat202lManav IsraniNo ratings yet
- Gis 2012 Paper Alina PettiferDocument8 pagesGis 2012 Paper Alina PettiferGABRIEL LUQUENo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistical Techniques For Analytics (Course Handout, 2018H2)Document6 pagesAdvanced Statistical Techniques For Analytics (Course Handout, 2018H2)mugenishereNo ratings yet
- SMS - QBDocument5 pagesSMS - QBAtul Dhar dubeyNo ratings yet
- Time Series - SASDocument9 pagesTime Series - SASManoj Kumar ManishNo ratings yet
- Statistical ForecastingDocument328 pagesStatistical ForecastingRakyNo ratings yet
- Categorical Data Analysis With SAS and SPSS ApplicationsDocument576 pagesCategorical Data Analysis With SAS and SPSS Applicationsyas100% (1)
- Syl5213 08Document11 pagesSyl5213 08stephen_debique9455No ratings yet
- Operation ResearchsDocument5 pagesOperation ResearchsHassan Funsho AkandeNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation by Simulation and Analysis with Applications to Computer NetworksFrom EverandPerformance Evaluation by Simulation and Analysis with Applications to Computer NetworksNo ratings yet
- Bourne, DavidW. A. - Strauss, Steven - Mathematical Modeling of Pharmacokinetic Data (2018, CRC Press - Routledge)Document153 pagesBourne, DavidW. A. - Strauss, Steven - Mathematical Modeling of Pharmacokinetic Data (2018, CRC Press - Routledge)GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Ebook Ebook PDF Introductory Econometrics For Finance 4Th Edition All Chapter PDF Docx KindleDocument41 pagesEbook Ebook PDF Introductory Econometrics For Finance 4Th Edition All Chapter PDF Docx Kindlevicki.lusk103100% (30)
- Full Download Ebook PDF Introductory Econometrics For Finance 4th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook PDF Introductory Econometrics For Finance 4th Edition PDFtimothy.mees274100% (44)
- (Routledge Advances in Risk Management) Kin Keung Lai, Jerome Yen, Shifei Zhou, Hao Wang - Volatility Surface and Term Structure - High-Profit Options Trading Strategies-Routledge (2013)Document98 pages(Routledge Advances in Risk Management) Kin Keung Lai, Jerome Yen, Shifei Zhou, Hao Wang - Volatility Surface and Term Structure - High-Profit Options Trading Strategies-Routledge (2013)Yuming MaNo ratings yet
- Analytics 02011 Learning Path - Curriculum (6632)Document22 pagesAnalytics 02011 Learning Path - Curriculum (6632)Sheetal JNo ratings yet
- Fnal+Report Advance+StatisticsDocument44 pagesFnal+Report Advance+StatisticsPranav Viswanathan100% (1)
- STAT 221 Mid Term (2) MidtermDocument4 pagesSTAT 221 Mid Term (2) MidtermDiane BangtuanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum-PGP in Big Data Analytics and OptimizationDocument16 pagesCurriculum-PGP in Big Data Analytics and Optimizationjprakash0205No ratings yet
- Course Outline EconometricsDocument2 pagesCourse Outline Econometricshaile ethioNo ratings yet
- DML 2Document117 pagesDML 2Rodrigo TavaresNo ratings yet
- Log-Linear Modeling: Concepts, Interpretation, and ApplicationFrom EverandLog-Linear Modeling: Concepts, Interpretation, and ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Subject CT4 Models Core Technical Syllabus: The Faculty of Actuaries and Institute of ActuariesDocument8 pagesSubject CT4 Models Core Technical Syllabus: The Faculty of Actuaries and Institute of ActuariesgeekeizNo ratings yet
- Core Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesCore Learning Objectivesbriella120899No ratings yet
- Statistics For Engineers (MAT2001) - SyllabusDocument3 pagesStatistics For Engineers (MAT2001) - Syllabusmanjeet kumarNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Engineers (MAT2001) - SyllabusDocument3 pagesStatistics For Engineers (MAT2001) - SyllabusDiyali67% (3)
- Short Book ReviewsDocument29 pagesShort Book Reviewsjavad shateryanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Models in Marketing ResearchDocument222 pagesQuantitative Models in Marketing ResearchArijit DasNo ratings yet
- ANR 312 2021 Biostat and Research Course OutlineDocument5 pagesANR 312 2021 Biostat and Research Course OutlineChileshe SimonNo ratings yet
- RM AssignmentDocument6 pagesRM AssignmentManu Sehgal100% (1)
- It6006 Da Iq Nov - Dec 2018 RejinpaulDocument1 pageIt6006 Da Iq Nov - Dec 2018 RejinpaulVanathi AnandavelNo ratings yet
- CQEDocument1 pageCQENour Gamal MomtazNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research and Statistics QP CODE: 1773 Question BankDocument11 pagesNursing Research and Statistics QP CODE: 1773 Question BankSanal c SabuNo ratings yet
- Econometric Analysis II (Theory and Lab) - Course OutlineDocument3 pagesEconometric Analysis II (Theory and Lab) - Course Outlineaayush.5.parasharNo ratings yet
- Bierens - Statistical Foundations of EconometricsDocument434 pagesBierens - Statistical Foundations of EconometricsMon DoremonNo ratings yet
- Wiley - Sensitivity Analysis in Practice - A Guide To Assessing Scientific Models Saltelli Et Al., 2004)Document232 pagesWiley - Sensitivity Analysis in Practice - A Guide To Assessing Scientific Models Saltelli Et Al., 2004)anon_648281803No ratings yet
- Homework Problems - Paired Samples T-TestDocument48 pagesHomework Problems - Paired Samples T-TestDevan BhallaNo ratings yet
- MMS 2022-24 QP Business StatisticsDocument5 pagesMMS 2022-24 QP Business StatisticsnimeshnarnaNo ratings yet
- Unit II Question Bank With Hints and AnswersDocument16 pagesUnit II Question Bank With Hints and Answersakshaya vijayNo ratings yet
- Residual AnalysisDocument6 pagesResidual AnalysisGagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Bias and Variance in Machine LearningDocument7 pagesBias and Variance in Machine LearningSHIKHA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 2023Document9 pagesAssignment 2 2023AbdAlrahman SiyamekNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentHabiba KausarNo ratings yet
- Measure of Relative PositionDocument24 pagesMeasure of Relative Positionkrystel basa100% (1)
- Key Concepts of Tests of Hypotheses On The Population Mean and Population ProportionDocument33 pagesKey Concepts of Tests of Hypotheses On The Population Mean and Population ProportionElisha Mae BuenaobraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial STA408 - EstimationDocument11 pagesTutorial STA408 - EstimationNoorNabilaNo ratings yet
- EnsembleDocument2 pagesEnsembleShivareddy GangamNo ratings yet
- SQC CH6Document63 pagesSQC CH6Khaled Toffaha0% (2)
- Research Methods in FinanceDocument97 pagesResearch Methods in FinancedirtyangelNo ratings yet
- Random Forest PDFDocument92 pagesRandom Forest PDFParimal ShivenduNo ratings yet
- Crystal Ball - Excell FunctionsDocument2 pagesCrystal Ball - Excell FunctionsVictor LuzardoNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument11 pagesOutputFARAH AMALIA PUTRI TITIANSYAHNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 Hypothesis TestingDocument49 pagesCHAPTER 10 Hypothesis TestingAyushi JangpangiNo ratings yet
- FIN236 Topic03Document48 pagesFIN236 Topic03Troy_ValiantNo ratings yet
- AS MCQ NewDocument13 pagesAS MCQ NewCHARAN GOPI KRISHNA Kondapalli100% (1)
- Stat Assignmet 2Document13 pagesStat Assignmet 2serachguruNo ratings yet
- Psych Stat Reviewer MidtermsDocument10 pagesPsych Stat Reviewer MidtermsROSEFEL GARNETT AGORNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 4th QuarterDocument13 pagesGrade 10 4th QuarterJaninne Villa Del ReyNo ratings yet
- Exam C FormulasDocument57 pagesExam C FormulasararararagiNo ratings yet
- Sessions 21-24 Factor Analysis - Ppt-RevDocument61 pagesSessions 21-24 Factor Analysis - Ppt-Revnandini swamiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document9 pagesAssignment 2Shreya SingiNo ratings yet
- Data Classification: Classes or Groups, With Each Class Represented A UniqueDocument12 pagesData Classification: Classes or Groups, With Each Class Represented A UniqueSaif RehmanNo ratings yet
- Investments 10Th Edition Bodie Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesInvestments 10Th Edition Bodie Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFWilliamCartersafg100% (11)
- Anderson 1997 Decision Support SystemsDocument18 pagesAnderson 1997 Decision Support SystemsIim MucharamNo ratings yet
Econ Progresss
Econ Progresss
Uploaded by
tonggennnOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Econ Progresss
Econ Progresss
Uploaded by
tonggennnCopyright:
Available Formats
Regression
Week 1 : Linear Regression
1. Simple linear regression recap
2. Goodness of fit
3. Assumptions in OLS
4. Hypothesis testing
5. Multiple linear regression
6. Model selection
Week 4 : Panel Data
1. Identify panel data and explain why it is useful
2. Explain the fixed effects model and estimate it in R
3. Explain the time fixed effects model and estimate it in R
4. Compare the output from different fixed effects models
5. Explain the random effects model
6. Estimate it in R and perform the Hausman test to select a
fixed or random effects model
Week 5 : Instrument Variable
1. Two stage least squares estimation
2. Demand for cigarettes
3. Poor instrument example
4. General IV regression
5. Model selection
6. Instrument selection
Week 6 : Limited Dependant Variable
1. Identify limited dependent variables and explain why they cannot be estimated using OLS
2. Explain the logit and probit models and estimate them in R
3. Interpret the results from logit and probit models
4. Discuss multinomial LDV models
5. Explain the Poisson model for count variables, estimate it in R and interpret the results
Time Series
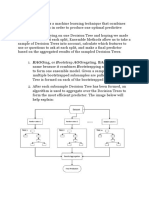
Week 7 : ARMA Models (Univariate Models)
1. Autocorrelation , Autocovariance, Stationary Process
2. White noise
3. Moving Average processes
4. Autoregressive processes
5. ARMA processes
6. Box-Jenkins methodology
7. Forecasting
8. Forecast Accuracy
Week 7 : VAR and Stationarity
1. VAR Models with two variables
2. Advantage and Disadvantage of VAR modelling
3. Inference and Selection in VARs
4. Lag Lengths Determination- Information Criteria
5. VAR Forecasting
6. Trends and Random Walk
7. AR(p) Models and Dickey- Fuller Test
Week 8 : Volatility Models
1. Discuss why financial time series don’t tend to have constant volatility
2. Various volatility models (Non-linear models, volatility models)
3. Autoregressive volatility models
4. ARCH model, ARCH effects, limitations
5. Unconditional Variance
6. GARCH model , GARCH as ARMA , example
7. Discuss asymmetric GARCH models
Data Science
Week 2 : Data Manipulation
1. Introduction to data science
2. Data transformation
o filter() to pick observations by their values
o arrange() to reorder rows
o select() to pick variables by their names
o mutate() to create new variables with functions of existing variables
o summarize() to collapse many values down to a single summary
3. Tidy data
o gather()
o spread()
o separate()
o unite()
Week 3 : Data Visualization
1. Data exploration VS data communication
2. Construction of a variety of plots in R (Scatterplot, Bar chart, Box plot)
3. Analysis of the output
4. Customisation of visualisations for clear communication
5. Data communication: Graphical excellence, Visual deception, Accessibility
6. Ethical use of data visualisations
Week 10 : Application and Ethics
1. Discuss the development of data science in the financial services , 4 example of data science in use
2. Discuss some case studies (BoE & FCA report on use of machine learning in financial services)
3. Consider the risks of data science, regulation.
4. Discuss ways to mitigate those risks, ethical use of data science
Tut Checklist:
[] Tut.1
[] Tut.2
[] Tut.3
[] Tut.4
[] Tut.5
[] Tut.6
[] Tut.7
[] Tut.8
[] Tut.9
[] Tut.10
Mock Exam :
[] Teacher provided
[] Mock 1
[] Mock 2
[] Mock 3
You might also like
- Time Series Analysis - Univariate and Multivariate Methods by William Wei PDFDocument634 pagesTime Series Analysis - Univariate and Multivariate Methods by William Wei PDFAnuj Sachdev100% (3)
- Economic Theory and Operations Analysis-1Document7 pagesEconomic Theory and Operations Analysis-1roasted friesNo ratings yet
- CT6 Statistical Methods PDFDocument6 pagesCT6 Statistical Methods PDFVignesh Srinivasan0% (2)
- Process Analysis by Statistical Methods D. HimmelblauDocument474 pagesProcess Analysis by Statistical Methods D. HimmelblauSofia Mac Rodri100% (4)
- Machine Learning Assignment Report - CarsDocument42 pagesMachine Learning Assignment Report - Carssurajramkumar100% (4)
- CustomerChurn AssignmentDocument15 pagesCustomerChurn AssignmentMalavika R Kumar100% (3)
- Multivariable Model - Building: A Pragmatic Approach to Regression Anaylsis based on Fractional Polynomials for Modelling Continuous VariablesFrom EverandMultivariable Model - Building: A Pragmatic Approach to Regression Anaylsis based on Fractional Polynomials for Modelling Continuous VariablesNo ratings yet
- Top 12 Questions PG StatsDocument2 pagesTop 12 Questions PG StatsRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- FULL Download Ebook PDF Introduction To Probability Models 12th Edition PDF EbookDocument47 pagesFULL Download Ebook PDF Introduction To Probability Models 12th Edition PDF Ebookfaith.bratcher185100% (33)
- Course OutlineDocument2 pagesCourse Outlineasu manNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open University Islamabad (Department of Business Administration)Document5 pagesAllama Iqbal Open University Islamabad (Department of Business Administration)Noo UllahNo ratings yet
- CT4 Models PDFDocument6 pagesCT4 Models PDFVignesh Srinivasan0% (1)
- Question Bank RMDocument7 pagesQuestion Bank RMharshaNo ratings yet
- AICM 702 - Research Statistical MethodsDocument156 pagesAICM 702 - Research Statistical MethodsCar Sebial VelascoNo ratings yet
- A1388404476 - 64039 - 23 - 2023 - Machine Learning IIDocument10 pagesA1388404476 - 64039 - 23 - 2023 - Machine Learning IIraj241299No ratings yet
- Modern Industrial Statistics: with applications in R, MINITAB and JMPFrom EverandModern Industrial Statistics: with applications in R, MINITAB and JMPNo ratings yet
- 1011MPFM EconometricsDocument3 pages1011MPFM EconometricseXcuvatorNo ratings yet
- PGDBA SyllabusDocument5 pagesPGDBA Syllabusarpan singhNo ratings yet
- 311 LO Part IIDocument3 pages311 LO Part IIu20417242No ratings yet
- Time Series Course OutlineDocument4 pagesTime Series Course OutlineAba MachaNo ratings yet
- F23 Final Exam ReviewDocument12 pagesF23 Final Exam ReviewBrandi Burchell-LeedomNo ratings yet
- Discrete-Event System Simulation: Fourth EditionDocument9 pagesDiscrete-Event System Simulation: Fourth EditionFaizan RabbaniNo ratings yet
- Bmat202l Probability-And-Statistics TH 1.0 65 Bmat202lDocument3 pagesBmat202l Probability-And-Statistics TH 1.0 65 Bmat202lManav IsraniNo ratings yet
- Gis 2012 Paper Alina PettiferDocument8 pagesGis 2012 Paper Alina PettiferGABRIEL LUQUENo ratings yet
- Advanced Statistical Techniques For Analytics (Course Handout, 2018H2)Document6 pagesAdvanced Statistical Techniques For Analytics (Course Handout, 2018H2)mugenishereNo ratings yet
- SMS - QBDocument5 pagesSMS - QBAtul Dhar dubeyNo ratings yet
- Time Series - SASDocument9 pagesTime Series - SASManoj Kumar ManishNo ratings yet
- Statistical ForecastingDocument328 pagesStatistical ForecastingRakyNo ratings yet
- Categorical Data Analysis With SAS and SPSS ApplicationsDocument576 pagesCategorical Data Analysis With SAS and SPSS Applicationsyas100% (1)
- Syl5213 08Document11 pagesSyl5213 08stephen_debique9455No ratings yet
- Operation ResearchsDocument5 pagesOperation ResearchsHassan Funsho AkandeNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation by Simulation and Analysis with Applications to Computer NetworksFrom EverandPerformance Evaluation by Simulation and Analysis with Applications to Computer NetworksNo ratings yet
- Bourne, DavidW. A. - Strauss, Steven - Mathematical Modeling of Pharmacokinetic Data (2018, CRC Press - Routledge)Document153 pagesBourne, DavidW. A. - Strauss, Steven - Mathematical Modeling of Pharmacokinetic Data (2018, CRC Press - Routledge)GuillermoNo ratings yet
- Ebook Ebook PDF Introductory Econometrics For Finance 4Th Edition All Chapter PDF Docx KindleDocument41 pagesEbook Ebook PDF Introductory Econometrics For Finance 4Th Edition All Chapter PDF Docx Kindlevicki.lusk103100% (30)
- Full Download Ebook PDF Introductory Econometrics For Finance 4th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesFull Download Ebook PDF Introductory Econometrics For Finance 4th Edition PDFtimothy.mees274100% (44)
- (Routledge Advances in Risk Management) Kin Keung Lai, Jerome Yen, Shifei Zhou, Hao Wang - Volatility Surface and Term Structure - High-Profit Options Trading Strategies-Routledge (2013)Document98 pages(Routledge Advances in Risk Management) Kin Keung Lai, Jerome Yen, Shifei Zhou, Hao Wang - Volatility Surface and Term Structure - High-Profit Options Trading Strategies-Routledge (2013)Yuming MaNo ratings yet
- Analytics 02011 Learning Path - Curriculum (6632)Document22 pagesAnalytics 02011 Learning Path - Curriculum (6632)Sheetal JNo ratings yet
- Fnal+Report Advance+StatisticsDocument44 pagesFnal+Report Advance+StatisticsPranav Viswanathan100% (1)
- STAT 221 Mid Term (2) MidtermDocument4 pagesSTAT 221 Mid Term (2) MidtermDiane BangtuanNo ratings yet
- Curriculum-PGP in Big Data Analytics and OptimizationDocument16 pagesCurriculum-PGP in Big Data Analytics and Optimizationjprakash0205No ratings yet
- Course Outline EconometricsDocument2 pagesCourse Outline Econometricshaile ethioNo ratings yet
- DML 2Document117 pagesDML 2Rodrigo TavaresNo ratings yet
- Log-Linear Modeling: Concepts, Interpretation, and ApplicationFrom EverandLog-Linear Modeling: Concepts, Interpretation, and ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Subject CT4 Models Core Technical Syllabus: The Faculty of Actuaries and Institute of ActuariesDocument8 pagesSubject CT4 Models Core Technical Syllabus: The Faculty of Actuaries and Institute of ActuariesgeekeizNo ratings yet
- Core Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesCore Learning Objectivesbriella120899No ratings yet
- Statistics For Engineers (MAT2001) - SyllabusDocument3 pagesStatistics For Engineers (MAT2001) - Syllabusmanjeet kumarNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Engineers (MAT2001) - SyllabusDocument3 pagesStatistics For Engineers (MAT2001) - SyllabusDiyali67% (3)
- Short Book ReviewsDocument29 pagesShort Book Reviewsjavad shateryanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Models in Marketing ResearchDocument222 pagesQuantitative Models in Marketing ResearchArijit DasNo ratings yet
- ANR 312 2021 Biostat and Research Course OutlineDocument5 pagesANR 312 2021 Biostat and Research Course OutlineChileshe SimonNo ratings yet
- RM AssignmentDocument6 pagesRM AssignmentManu Sehgal100% (1)
- It6006 Da Iq Nov - Dec 2018 RejinpaulDocument1 pageIt6006 Da Iq Nov - Dec 2018 RejinpaulVanathi AnandavelNo ratings yet
- CQEDocument1 pageCQENour Gamal MomtazNo ratings yet
- Nursing Research and Statistics QP CODE: 1773 Question BankDocument11 pagesNursing Research and Statistics QP CODE: 1773 Question BankSanal c SabuNo ratings yet
- Econometric Analysis II (Theory and Lab) - Course OutlineDocument3 pagesEconometric Analysis II (Theory and Lab) - Course Outlineaayush.5.parasharNo ratings yet
- Bierens - Statistical Foundations of EconometricsDocument434 pagesBierens - Statistical Foundations of EconometricsMon DoremonNo ratings yet
- Wiley - Sensitivity Analysis in Practice - A Guide To Assessing Scientific Models Saltelli Et Al., 2004)Document232 pagesWiley - Sensitivity Analysis in Practice - A Guide To Assessing Scientific Models Saltelli Et Al., 2004)anon_648281803No ratings yet
- Homework Problems - Paired Samples T-TestDocument48 pagesHomework Problems - Paired Samples T-TestDevan BhallaNo ratings yet
- MMS 2022-24 QP Business StatisticsDocument5 pagesMMS 2022-24 QP Business StatisticsnimeshnarnaNo ratings yet
- Unit II Question Bank With Hints and AnswersDocument16 pagesUnit II Question Bank With Hints and Answersakshaya vijayNo ratings yet
- Residual AnalysisDocument6 pagesResidual AnalysisGagandeep SinghNo ratings yet
- Bias and Variance in Machine LearningDocument7 pagesBias and Variance in Machine LearningSHIKHA SHARMANo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 2023Document9 pagesAssignment 2 2023AbdAlrahman SiyamekNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentHabiba KausarNo ratings yet
- Measure of Relative PositionDocument24 pagesMeasure of Relative Positionkrystel basa100% (1)
- Key Concepts of Tests of Hypotheses On The Population Mean and Population ProportionDocument33 pagesKey Concepts of Tests of Hypotheses On The Population Mean and Population ProportionElisha Mae BuenaobraNo ratings yet
- Tutorial STA408 - EstimationDocument11 pagesTutorial STA408 - EstimationNoorNabilaNo ratings yet
- EnsembleDocument2 pagesEnsembleShivareddy GangamNo ratings yet
- SQC CH6Document63 pagesSQC CH6Khaled Toffaha0% (2)
- Research Methods in FinanceDocument97 pagesResearch Methods in FinancedirtyangelNo ratings yet
- Random Forest PDFDocument92 pagesRandom Forest PDFParimal ShivenduNo ratings yet
- Crystal Ball - Excell FunctionsDocument2 pagesCrystal Ball - Excell FunctionsVictor LuzardoNo ratings yet
- OutputDocument11 pagesOutputFARAH AMALIA PUTRI TITIANSYAHNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 Hypothesis TestingDocument49 pagesCHAPTER 10 Hypothesis TestingAyushi JangpangiNo ratings yet
- FIN236 Topic03Document48 pagesFIN236 Topic03Troy_ValiantNo ratings yet
- AS MCQ NewDocument13 pagesAS MCQ NewCHARAN GOPI KRISHNA Kondapalli100% (1)
- Stat Assignmet 2Document13 pagesStat Assignmet 2serachguruNo ratings yet
- Psych Stat Reviewer MidtermsDocument10 pagesPsych Stat Reviewer MidtermsROSEFEL GARNETT AGORNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 4th QuarterDocument13 pagesGrade 10 4th QuarterJaninne Villa Del ReyNo ratings yet
- Exam C FormulasDocument57 pagesExam C FormulasararararagiNo ratings yet
- Sessions 21-24 Factor Analysis - Ppt-RevDocument61 pagesSessions 21-24 Factor Analysis - Ppt-Revnandini swamiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document9 pagesAssignment 2Shreya SingiNo ratings yet
- Data Classification: Classes or Groups, With Each Class Represented A UniqueDocument12 pagesData Classification: Classes or Groups, With Each Class Represented A UniqueSaif RehmanNo ratings yet
- Investments 10Th Edition Bodie Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesInvestments 10Th Edition Bodie Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFWilliamCartersafg100% (11)
- Anderson 1997 Decision Support SystemsDocument18 pagesAnderson 1997 Decision Support SystemsIim MucharamNo ratings yet