Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Endo
Endo
Uploaded by
M Tabish0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesThe study found a statistically significant correlation between higher levels of HbA1c and more severe grades of diabetic foot ulcers. Patients with grade 1 ulcers mostly had HbA1c levels below 11%, while those with grade 5 ulcers generally had levels above 11%. A table and figure show that higher ulcer grades were associated with higher HbA1c ranges.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe study found a statistically significant correlation between higher levels of HbA1c and more severe grades of diabetic foot ulcers. Patients with grade 1 ulcers mostly had HbA1c levels below 11%, while those with grade 5 ulcers generally had levels above 11%. A table and figure show that higher ulcer grades were associated with higher HbA1c ranges.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesEndo
Endo
Uploaded by
M TabishThe study found a statistically significant correlation between higher levels of HbA1c and more severe grades of diabetic foot ulcers. Patients with grade 1 ulcers mostly had HbA1c levels below 11%, while those with grade 5 ulcers generally had levels above 11%. A table and figure show that higher ulcer grades were associated with higher HbA1c ranges.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
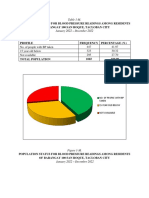
Results:
Our investigation highlights a statistically significant correlation between grades of
diabetic foot ulcer and HBA1C levels of the patients (p-value <0.001). Patients
with higher levels of HBA1C suffered foot ulcer of higher grades. Specifically,
patients with Grade 1 foot ulcers primarily had HBA1C levels of ≤11.00 with
6(50%) falling in the group “7.01-9.00” while patients with Grade 5 ulcers had
higher HBA1C levels with bulk of patients having levels of >11.00. Summarized
result is given in Table-1.
Table-1: Correlation of Grades of diabetic foot ulcer with HBAIC
HBA1C
<7.00 7.01-9.00 9.01-11.00 11.01-13.00 13.01-15.00 >15.01 P-value
Foot ulcer <0.001
grade 1 3(25.0%) 6(50.0%) 3(25.0%) 0(0.0%) 0(0.0%) 0(0.0%)
grade 2 12(36.4%) 19(57.6%) 2(6.1%) 0(0.0%) 0(0.0%) 0(0.0%)
grade 3 0(0.0%) 18(30.5%) 25(42.4%) 16(27.1%) 0(0.0%) 0(0.0%)
grade 4 0(0.0%) 15(9.6%) 40(25.5%) 90(57.3%) 9(5.7%) 3(1.9%)
grade 5 0(0.0%) 15(15.2%) 6(6.1%) 35(35.4%) 25(25.3%) 18(18.2%)
Figure-1 further clarifies the relation between diabetic foot ulcer and HBA1C
levels having patients with higher grader ulcers scattered along the higher HBA1C
levels as compared to those of lower grades scattered at the lower HBA1C levels.
Figure-1: Scatter line graph correlating Diabetic foot ulcer with HBAIC
You might also like
- Nicholas Signorine Week 3 Midterm Exam COH315 Intro To EpidemiologyDocument5 pagesNicholas Signorine Week 3 Midterm Exam COH315 Intro To EpidemiologyFarah FarahNo ratings yet
- Correlation and RegressionDocument24 pagesCorrelation and Regressionkaushalsingh2080% (5)
- Endo Final EditedDocument7 pagesEndo Final EditedM TabishNo ratings yet
- Subgroup Analysis of Exercise Test Results: 1.1 Treadmill TestingDocument14 pagesSubgroup Analysis of Exercise Test Results: 1.1 Treadmill Testinganon_179117738No ratings yet
- Heart Disease Risk Factor Data Analysis Midterm Data 2 - Jupyter NotebookDocument20 pagesHeart Disease Risk Factor Data Analysis Midterm Data 2 - Jupyter Notebookapi-702453557No ratings yet
- Nominal Variables Tests and Outcome Measures - Lecture 4Document39 pagesNominal Variables Tests and Outcome Measures - Lecture 4black.hadi194No ratings yet
- Interaction (Effect Modification) : Interaction Between Two Variables Is Said To Exist When The AssociationDocument22 pagesInteraction (Effect Modification) : Interaction Between Two Variables Is Said To Exist When The AssociationPalwasha MalikNo ratings yet
- Detection Levels of FBS, Hba1C and Lipid Profile in Patients With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Diyala ProvinceDocument6 pagesDetection Levels of FBS, Hba1C and Lipid Profile in Patients With Polycystic Ovary Syndrome in Diyala Provincelanarame932No ratings yet
- البحث للنشرDocument14 pagesالبحث للنشرZAhraa MohhamedNo ratings yet
- Objective: 2. Context of DataDocument5 pagesObjective: 2. Context of DataShubham ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- ExampleProtocol BayesFactorBinaryDocument4 pagesExampleProtocol BayesFactorBinaryAri Surya AbdiNo ratings yet
- The Accuracy Evaluation StudyDocument16 pagesThe Accuracy Evaluation StudyWendyNo ratings yet
- Análisis Con Ácido Fórmico: Analyze Experiment - Ef AFDocument10 pagesAnálisis Con Ácido Fórmico: Analyze Experiment - Ef AFJuan GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Cera-Chek HB Plus Accuracy Data (Eng)Document3 pagesCera-Chek HB Plus Accuracy Data (Eng)saufibs4966100% (1)
- Final ManuscriptDocument17 pagesFinal ManuscriptSandesh GautamNo ratings yet
- 4 BE Evaluation Parallel Replicate Two Stage Design Botswana 2019Document66 pages4 BE Evaluation Parallel Replicate Two Stage Design Botswana 2019Nelson MoreriNo ratings yet
- Correlation Analysis in SPSSDocument5 pagesCorrelation Analysis in SPSSMartin OdhiamboNo ratings yet
- PSI and KS StatisticDocument6 pagesPSI and KS StatisticGaneshNo ratings yet
- 01-Biostat AFCM-Descriptives and Data PresentationDocument59 pages01-Biostat AFCM-Descriptives and Data PresentationwheelplusappNo ratings yet
- Community Diagnosis HPN BmiDocument10 pagesCommunity Diagnosis HPN BmiFiel Andrei BorataNo ratings yet
- Association Between Serum Vitamin D Deficiency and Knee OsteoarthritisDocument5 pagesAssociation Between Serum Vitamin D Deficiency and Knee OsteoarthritisMuhammad Bayu Zohari HutagalungNo ratings yet
- Mean Age Group Analysis: Tables of ComparisonDocument3 pagesMean Age Group Analysis: Tables of ComparisonAnup ChaliseNo ratings yet
- Diabetes - NGSP: HbA1c Assay Interferences (CHECKED)Document2 pagesDiabetes - NGSP: HbA1c Assay Interferences (CHECKED)pixoguiasNo ratings yet
- Ryu2011 5Document1 pageRyu2011 5cepel manNo ratings yet
- Santoshkumaryadav BPPaper 12 OctDocument7 pagesSantoshkumaryadav BPPaper 12 OctemmyNo ratings yet
- Analysis of EQ VAS DataDocument9 pagesAnalysis of EQ VAS DataMuhammad ilyas ApotekerNo ratings yet
- Maternal Early WarningDocument10 pagesMaternal Early WarningJEFFERSON MUÑOZNo ratings yet
- Sample Size CalculationDocument53 pagesSample Size CalculationAkhileshNo ratings yet
- Sample Size CalculationDocument52 pagesSample Size CalculationAkhileshNo ratings yet
- Two CasesDocument42 pagesTwo Casessq.baoNo ratings yet
- Obesitas Dan PadDocument3 pagesObesitas Dan PaddonkeyendutNo ratings yet
- Renal Function On The Basis Serum Urea and Creatinine in Diabetic and Nondiabetic Persons in A Tertiary Teaching HospitalDocument8 pagesRenal Function On The Basis Serum Urea and Creatinine in Diabetic and Nondiabetic Persons in A Tertiary Teaching Hospitalijmb333No ratings yet
- Manuscript - GEH - Noviari Liara JDocument10 pagesManuscript - GEH - Noviari Liara JRama TanjungNo ratings yet
- Overweight in Celiac Disease: Prevalence, Clinical Characteristics, and Effect of A Gluten-Free DietDocument4 pagesOverweight in Celiac Disease: Prevalence, Clinical Characteristics, and Effect of A Gluten-Free DietSEPTIA SRI EKA PUTRINo ratings yet
- Excercise 15.10 12.6Document8 pagesExcercise 15.10 12.6Kogi JeyaNo ratings yet
- ABSTRACTDocument7 pagesABSTRACTSudha SathishNo ratings yet
- LogitDocument3 pagesLogitHenry DunaNo ratings yet
- WHO RHR 11.10 EngDocument121 pagesWHO RHR 11.10 EngSven OrdanzaNo ratings yet
- 04 Fact Sheet HME712 Bos - 20Document2 pages04 Fact Sheet HME712 Bos - 20jackbane69No ratings yet
- Acute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaDocument5 pagesAcute Lymphoblastic LeukemiaJansen Arquilita RiveraNo ratings yet
- Mombasa Growth Monitoring Baseline Report 2023Document7 pagesMombasa Growth Monitoring Baseline Report 2023JoeWallapaLyncolineNo ratings yet
- Factors Contributing To Lower Value of Life ExpectancyDocument18 pagesFactors Contributing To Lower Value of Life ExpectancyNgân KhổngNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Prima WekaDocument53 pagesDiabetes Prima Weka'Aamer Anwer Hayat Khan'No ratings yet
- Results DCI PareadosDocument5 pagesResults DCI PareadosAlfonsoSánchezNo ratings yet
- EC503 - AssignmentDocument14 pagesEC503 - Assignmentaradsaha2No ratings yet
- 1 Age Table 1: Age of The Respondents Scale No. of Respon Dents Percent AgeDocument14 pages1 Age Table 1: Age of The Respondents Scale No. of Respon Dents Percent AgeKunal PatelNo ratings yet
- Palliative Prognostic ScoreDocument2 pagesPalliative Prognostic ScoreAnastasia Yovita SariNo ratings yet
- Invited Commentary - No Volume-Outcome Relationship For Opcabg (Plomondon Et Al)Document2 pagesInvited Commentary - No Volume-Outcome Relationship For Opcabg (Plomondon Et Al)fluid_man_brazilNo ratings yet
- Appendix 1 Tonatiuh Barrientos Gutierrez Ana Basto AbreuDocument3 pagesAppendix 1 Tonatiuh Barrientos Gutierrez Ana Basto AbreuRaulDurandeAlbaNo ratings yet
- Final Year Project PresentationDocument32 pagesFinal Year Project PresentationAin Shii AmirNo ratings yet
- Journal Reading EswlDocument8 pagesJournal Reading Eswlsandranamahen2No ratings yet
- Kiran NLR PaperDocument12 pagesKiran NLR PaperkiranNo ratings yet
- PREDICTORSDocument15 pagesPREDICTORSorthopaedicdepttNo ratings yet
- Con Linearity of Drug Content in Microspheres 0 0 0 0.139 0.03 0.274 0.04 0.416 0.03 0.554 0.02 0.706 0.03 0.837 0.02Document8 pagesCon Linearity of Drug Content in Microspheres 0 0 0 0.139 0.03 0.274 0.04 0.416 0.03 0.554 0.02 0.706 0.03 0.837 0.02yashpandya01No ratings yet
- Idf Diabetes Atlas: Presentation of The NewDocument29 pagesIdf Diabetes Atlas: Presentation of The NewApril ApriliantyNo ratings yet
- IDF Atlas 8e PPT 2018.Document29 pagesIDF Atlas 8e PPT 2018.Bela NovitaNo ratings yet
- Idf Diabetes Atlas: Presentation of The NewDocument29 pagesIdf Diabetes Atlas: Presentation of The NewApril ApriliantyNo ratings yet
- IDF Atlas 8e PPT 2018.Document29 pagesIDF Atlas 8e PPT 2018.Predrag PetrovicNo ratings yet