Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Jautajumi CVS Colloquium
3 Jautajumi CVS Colloquium
Uploaded by
migas1996Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Responses To Altered Oxygenation, Cardiac and Tissue - Anatomy To AssessmentDocument254 pagesResponses To Altered Oxygenation, Cardiac and Tissue - Anatomy To Assessmentlouradel100% (1)
- 40.neural (Extrinsic) Regulation of Cardiac Performance, Sympathetci and Parasympathetic Effects. Humoral Factors Affecting Cardiac PerformanceDocument3 pages40.neural (Extrinsic) Regulation of Cardiac Performance, Sympathetci and Parasympathetic Effects. Humoral Factors Affecting Cardiac PerformanceNektarios TsakalosNo ratings yet
- What Is The Cardiovascular System? The Heart Is A Double Pump Heart Arteries Arterioles Veins Venules CapillariesDocument24 pagesWhat Is The Cardiovascular System? The Heart Is A Double Pump Heart Arteries Arterioles Veins Venules CapillariesSriram SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Heart Rate Blood PressureDocument128 pagesHeart Rate Blood PressureShubhra ShettyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure and MicrocirculationDocument20 pagesChapter 7 Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure and Microcirculationaisyahasrii_No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Properties of Myocardium and Cardiac Cycle 2020-2021Document43 pagesLecture 4 Properties of Myocardium and Cardiac Cycle 2020-2021badarbhai222No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PharmacologyDocument20 pagesCardiovascular PharmacologyAliceAliceNo ratings yet
- CVS PharmacologyDocument19 pagesCVS Pharmacologymug ashNo ratings yet
- Physio Control 1Document323 pagesPhysio Control 1Mahmoud IdlbiNo ratings yet
- Print Z 2014Document11 pagesPrint Z 2014Nathan BlancoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument40 pagesCardiovascular SystemHeidi MobarakNo ratings yet
- Cardiology 2 F2018Document51 pagesCardiology 2 F2018TkNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure RegulationDocument3 pagesBlood Pressure RegulationiMaibelle BelleNo ratings yet
- MF-local Circulation 2016Document61 pagesMF-local Circulation 2016OnSolomonNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument26 pagesBlood PressureEniola DaramolaNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure RegulationDocument35 pagesBlood Pressure Regulationبراءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Circulation SystemDocument52 pagesPhysiology of Circulation SystemReni TeeWeeNo ratings yet
- The CardioVascular SystemDocument10 pagesThe CardioVascular SystemMrs DanebuniNo ratings yet
- Circulation: Dara Rosmailina Pabittei, MD, PHD Dept. of Physiology, Unhas Dept. of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Amc-UvaDocument48 pagesCirculation: Dara Rosmailina Pabittei, MD, PHD Dept. of Physiology, Unhas Dept. of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Amc-UvaYudi1223No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Feghiu I., Tacu L., Iarovoi ADocument25 pagesPathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Feghiu I., Tacu L., Iarovoi ALunguVictoriaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14-Oct.23 Haemodynamics of Circulation, Circulatory Mechanics, ResistanceDocument29 pagesLecture 14-Oct.23 Haemodynamics of Circulation, Circulatory Mechanics, ResistanceAparmitNo ratings yet
- CVSassessmentDocument19 pagesCVSassessmentriadharthy2No ratings yet
- Cardio Basic Physiology Class 03 Pt10Document33 pagesCardio Basic Physiology Class 03 Pt10bakuNo ratings yet
- Shock PresentaionDocument30 pagesShock PresentaionKennedy Ng'andweNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Cardiovascular System: Inquiry Into Life, Thirteenth EditionDocument3 pagesChapter 12: Cardiovascular System: Inquiry Into Life, Thirteenth Edition117320No ratings yet
- Chapter 05 4EDocument41 pagesChapter 05 4Elikhovandy10No ratings yet
- The Miraculous Pump - A Comprehensive Study of The Human HeartDocument2 pagesThe Miraculous Pump - A Comprehensive Study of The Human HeartYienNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument43 pagesCirculatory SystemRestu DwikelanaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiologi CA Dr. FaesolDocument71 pagesPathophysiologi CA Dr. FaesolNaya PebrianaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument51 pagesThe Circulatory SystemMohammed ahmedNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System Structure of The Heart The Cardiac Cycle Structure and Organization of Blood VesselsDocument46 pagesThe Cardiovascular System Structure of The Heart The Cardiac Cycle Structure and Organization of Blood VesselsMrJim1953No ratings yet
- NCM 118 LECTURE Hemodynamics Understanding The Basic Principles 2021 For Canvas UpdatedDocument59 pagesNCM 118 LECTURE Hemodynamics Understanding The Basic Principles 2021 For Canvas UpdatedPollen Siega BunalNo ratings yet
- CV AnatomyDocument49 pagesCV AnatomymichaelNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - CIrculation Part 1 - BLOODDocument28 pagesTopic 3 - CIrculation Part 1 - BLOODSANA ZAMANNo ratings yet
- Cardiovasular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovasular SystemAsher Eby VargeeseNo ratings yet
- Special CirculationsDocument29 pagesSpecial Circulationslessank12100% (1)
- Circulatory Response To ExerciseDocument31 pagesCirculatory Response To ExerciseFarhad GulNo ratings yet
- Week 5-14 Notes 3 (Dragged) 2Document1 pageWeek 5-14 Notes 3 (Dragged) 2navkkirangillNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Changes in CardiogenicDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Changes in CardiogenicBaso AgusofyangNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Aterial Blood PressureDocument18 pagesRegulation of Aterial Blood Pressurenihal handNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument58 pagesBlood PressureAyurveda PgNo ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and Physiology of Blood Vessels and BloodDocument9 pagesReview of Anatomy and Physiology of Blood Vessels and BloodDan Ataniel EnsaladaNo ratings yet
- CirculationDocument11 pagesCirculationRishikaphriya RauichandranNo ratings yet
- 5 - Cardio, RespiDocument287 pages5 - Cardio, RespiBeth CuntapayNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure AssignmentDocument19 pagesBlood Pressure AssignmentADITYAROOP PATHAKNo ratings yet
- CVS - Circuitery & HemodynamicsDocument44 pagesCVS - Circuitery & Hemodynamicsspitzmark2030No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular System Medical Surgical NursingDocument68 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular System Medical Surgical NursingFelix NjakeNo ratings yet
- Technical DefinitionDocument3 pagesTechnical DefinitionErin BarnesNo ratings yet
- Cardio Notes 1Document8 pagesCardio Notes 1Lindsay Grace MandarioNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument5 pagesCardioMkhize KhabazelaNo ratings yet
- CV 3 Circulatory System Notes CopyrightDocument7 pagesCV 3 Circulatory System Notes Copyrightmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- The Circulation: Blood Pressure RegulationDocument42 pagesThe Circulation: Blood Pressure RegulationLouis JinNo ratings yet
- Exercise PhysiologyDocument24 pagesExercise PhysiologyMohammed AlharbiNo ratings yet
- Long & Short Term Regulation of BPDocument50 pagesLong & Short Term Regulation of BPntambik21No ratings yet
- Department of PhysiologyDocument8 pagesDepartment of Physiologynaresh sharmaNo ratings yet
- The Normal Physiology of The Heart: Vikkineshwaran Siva SubramaniamDocument4 pagesThe Normal Physiology of The Heart: Vikkineshwaran Siva SubramaniamSivamala MalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Care of The Clients With Cardiovascular DisordersDocument226 pagesChapter 5 Care of The Clients With Cardiovascular DisordersDon Felicisimo EbronNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument51 pagesCirculatory SystemTina TalmadgeNo ratings yet
- Beating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartFrom EverandBeating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartNo ratings yet
- ProtocoloDocument6 pagesProtocolomigas1996No ratings yet
- Lab. Work 5Document22 pagesLab. Work 5migas1996No ratings yet
- Heart 4Document28 pagesHeart 4migas1996No ratings yet
- Ficha Ingles 9 VolunteeringDocument2 pagesFicha Ingles 9 Volunteeringmigas1996No ratings yet
- Physio PROTOCOL 1Document6 pagesPhysio PROTOCOL 1migas1996No ratings yet
- 3-DNA Replication 2.lecture ENGDocument51 pages3-DNA Replication 2.lecture ENGmigas1996No ratings yet
- 4.4 - Ficha de Trabalho - Modal Verbs (1) - SoluçõesDocument1 page4.4 - Ficha de Trabalho - Modal Verbs (1) - Soluçõesmigas1996No ratings yet
- 2-Structure of Nucleic Acids ENGDocument69 pages2-Structure of Nucleic Acids ENGmigas1996No ratings yet
- Diplozoon ParadoxumDocument2 pagesDiplozoon Paradoxummigas1996No ratings yet
- 4.4 - Ficha de Trabalho - Modal VerbsDocument1 page4.4 - Ficha de Trabalho - Modal Verbsmigas1996No ratings yet
- EX Ing550 F1 2023 - Net - RemovedDocument3 pagesEX Ing550 F1 2023 - Net - Removedmigas1996No ratings yet
3 Jautajumi CVS Colloquium
3 Jautajumi CVS Colloquium
Uploaded by
migas1996Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Jautajumi CVS Colloquium
3 Jautajumi CVS Colloquium
Uploaded by
migas1996Copyright:
Available Formats
Overview of the circulation (hemodynamics): interrelationships among pressure, flow, and resistance (the
Ohm's law); the resistance to blood flow (the Poiseuille's law); total peripheral resistance; vascular compliance;
law of Laplace. Arterial pressure: a pressure pulse contour; transmission of pressure pulses; measuring of
maximum and minimum arterial pressures.
The microcirculation. The regulatory role of arterioles. Functional structure of capillary system; vasomotion;
average function of the capillary system. Exchange of nutrients and other substances between the blood and
interstitial fluid (the Starling forces). Formation of lymph and the lymph flow. The veins and their functions.
Venous pressure and venous flow. Factors that determine venous flow and lymph flow.
The functional anatomy of the heart. Physiology of cardiac muscle: action potentials and refractory period in
cardiac muscle; cardiac muscle as a syncytium. The specialized excitatory and conductive system of the heart.
The mechanism of sinus nodal rhythmicity. Ectopic pacemakers; extrasystoles; cardiac arrhythmias.
The heart as a pump. The cardiac cycle. Function of the valves. Heart sounds and
phonocardiography. Heart rate, stroke volume, and cardiac output in various conditions.
The electrocardiogramm (ECG). Electrocardiographic leads: the three bipolar limb leads; chest leads. Analysis
of the ECG (waves, intervals, the mean electrical axis of the heart; the rhythmicity of the heart).
Regulation of heart pumping. Heterometric regulation: Frank-Starling's law and regulation of venous return.
Homeometric regulation of cardiac output. Control of the heart by the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves:
chronotropic and inotropic effects.
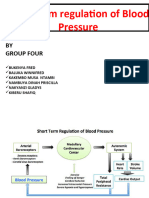
Regulation of arterial pressure. The baroreceptor reflexes; control of arterial pressure by the carotid and aortic
chemoreceptors.The sympathetic vasoconstrictor system; the vasomotor center.
Renin-angiotensin system, vasopressin, atrial natriuretic peptide, and sympathoadrenal system in long-term
regulation of arterial pressure and body fluid content.
Local control of blood flow - humoral mechanisms. Role of endothelium. Vasodilator metabolites. Tissue
hormones: kinins, prostaglandins, angiotensins, histamine.
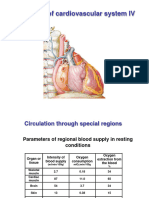
Circulation through special regions: cerebral circulation; coronary circulation; the cardiovascular system and
skeletal muscle blood flow in the rest and during exercise.
You might also like
- Responses To Altered Oxygenation, Cardiac and Tissue - Anatomy To AssessmentDocument254 pagesResponses To Altered Oxygenation, Cardiac and Tissue - Anatomy To Assessmentlouradel100% (1)
- 40.neural (Extrinsic) Regulation of Cardiac Performance, Sympathetci and Parasympathetic Effects. Humoral Factors Affecting Cardiac PerformanceDocument3 pages40.neural (Extrinsic) Regulation of Cardiac Performance, Sympathetci and Parasympathetic Effects. Humoral Factors Affecting Cardiac PerformanceNektarios TsakalosNo ratings yet
- What Is The Cardiovascular System? The Heart Is A Double Pump Heart Arteries Arterioles Veins Venules CapillariesDocument24 pagesWhat Is The Cardiovascular System? The Heart Is A Double Pump Heart Arteries Arterioles Veins Venules CapillariesSriram SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Heart Rate Blood PressureDocument128 pagesHeart Rate Blood PressureShubhra ShettyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure and MicrocirculationDocument20 pagesChapter 7 Regulation of Arterial Blood Pressure and Microcirculationaisyahasrii_No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Properties of Myocardium and Cardiac Cycle 2020-2021Document43 pagesLecture 4 Properties of Myocardium and Cardiac Cycle 2020-2021badarbhai222No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular PharmacologyDocument20 pagesCardiovascular PharmacologyAliceAliceNo ratings yet
- CVS PharmacologyDocument19 pagesCVS Pharmacologymug ashNo ratings yet
- Physio Control 1Document323 pagesPhysio Control 1Mahmoud IdlbiNo ratings yet
- Print Z 2014Document11 pagesPrint Z 2014Nathan BlancoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument40 pagesCardiovascular SystemHeidi MobarakNo ratings yet
- Cardiology 2 F2018Document51 pagesCardiology 2 F2018TkNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure RegulationDocument3 pagesBlood Pressure RegulationiMaibelle BelleNo ratings yet
- MF-local Circulation 2016Document61 pagesMF-local Circulation 2016OnSolomonNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument26 pagesBlood PressureEniola DaramolaNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure RegulationDocument35 pagesBlood Pressure Regulationبراءة أحمد السلاماتNo ratings yet
- Physiology of Circulation SystemDocument52 pagesPhysiology of Circulation SystemReni TeeWeeNo ratings yet
- The CardioVascular SystemDocument10 pagesThe CardioVascular SystemMrs DanebuniNo ratings yet
- Circulation: Dara Rosmailina Pabittei, MD, PHD Dept. of Physiology, Unhas Dept. of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Amc-UvaDocument48 pagesCirculation: Dara Rosmailina Pabittei, MD, PHD Dept. of Physiology, Unhas Dept. of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Amc-UvaYudi1223No ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Feghiu I., Tacu L., Iarovoi ADocument25 pagesPathophysiology of Cardiovascular System Feghiu I., Tacu L., Iarovoi ALunguVictoriaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 14-Oct.23 Haemodynamics of Circulation, Circulatory Mechanics, ResistanceDocument29 pagesLecture 14-Oct.23 Haemodynamics of Circulation, Circulatory Mechanics, ResistanceAparmitNo ratings yet
- CVSassessmentDocument19 pagesCVSassessmentriadharthy2No ratings yet
- Cardio Basic Physiology Class 03 Pt10Document33 pagesCardio Basic Physiology Class 03 Pt10bakuNo ratings yet
- Shock PresentaionDocument30 pagesShock PresentaionKennedy Ng'andweNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Cardiovascular System: Inquiry Into Life, Thirteenth EditionDocument3 pagesChapter 12: Cardiovascular System: Inquiry Into Life, Thirteenth Edition117320No ratings yet
- Chapter 05 4EDocument41 pagesChapter 05 4Elikhovandy10No ratings yet
- The Miraculous Pump - A Comprehensive Study of The Human HeartDocument2 pagesThe Miraculous Pump - A Comprehensive Study of The Human HeartYienNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument43 pagesCirculatory SystemRestu DwikelanaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiologi CA Dr. FaesolDocument71 pagesPathophysiologi CA Dr. FaesolNaya PebrianaNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument51 pagesThe Circulatory SystemMohammed ahmedNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System Structure of The Heart The Cardiac Cycle Structure and Organization of Blood VesselsDocument46 pagesThe Cardiovascular System Structure of The Heart The Cardiac Cycle Structure and Organization of Blood VesselsMrJim1953No ratings yet
- NCM 118 LECTURE Hemodynamics Understanding The Basic Principles 2021 For Canvas UpdatedDocument59 pagesNCM 118 LECTURE Hemodynamics Understanding The Basic Principles 2021 For Canvas UpdatedPollen Siega BunalNo ratings yet
- CV AnatomyDocument49 pagesCV AnatomymichaelNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - CIrculation Part 1 - BLOODDocument28 pagesTopic 3 - CIrculation Part 1 - BLOODSANA ZAMANNo ratings yet
- Cardiovasular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovasular SystemAsher Eby VargeeseNo ratings yet
- Special CirculationsDocument29 pagesSpecial Circulationslessank12100% (1)
- Circulatory Response To ExerciseDocument31 pagesCirculatory Response To ExerciseFarhad GulNo ratings yet
- Week 5-14 Notes 3 (Dragged) 2Document1 pageWeek 5-14 Notes 3 (Dragged) 2navkkirangillNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Changes in CardiogenicDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Changes in CardiogenicBaso AgusofyangNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Aterial Blood PressureDocument18 pagesRegulation of Aterial Blood Pressurenihal handNo ratings yet
- Blood PressureDocument58 pagesBlood PressureAyurveda PgNo ratings yet
- Review of Anatomy and Physiology of Blood Vessels and BloodDocument9 pagesReview of Anatomy and Physiology of Blood Vessels and BloodDan Ataniel EnsaladaNo ratings yet
- CirculationDocument11 pagesCirculationRishikaphriya RauichandranNo ratings yet
- 5 - Cardio, RespiDocument287 pages5 - Cardio, RespiBeth CuntapayNo ratings yet
- Blood Pressure AssignmentDocument19 pagesBlood Pressure AssignmentADITYAROOP PATHAKNo ratings yet
- CVS - Circuitery & HemodynamicsDocument44 pagesCVS - Circuitery & Hemodynamicsspitzmark2030No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular System Medical Surgical NursingDocument68 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Cardiovascular System Medical Surgical NursingFelix NjakeNo ratings yet
- Technical DefinitionDocument3 pagesTechnical DefinitionErin BarnesNo ratings yet
- Cardio Notes 1Document8 pagesCardio Notes 1Lindsay Grace MandarioNo ratings yet
- CardioDocument5 pagesCardioMkhize KhabazelaNo ratings yet
- CV 3 Circulatory System Notes CopyrightDocument7 pagesCV 3 Circulatory System Notes Copyrightmaxwell amponsahNo ratings yet
- The Circulation: Blood Pressure RegulationDocument42 pagesThe Circulation: Blood Pressure RegulationLouis JinNo ratings yet
- Exercise PhysiologyDocument24 pagesExercise PhysiologyMohammed AlharbiNo ratings yet
- Long & Short Term Regulation of BPDocument50 pagesLong & Short Term Regulation of BPntambik21No ratings yet
- Department of PhysiologyDocument8 pagesDepartment of Physiologynaresh sharmaNo ratings yet
- The Normal Physiology of The Heart: Vikkineshwaran Siva SubramaniamDocument4 pagesThe Normal Physiology of The Heart: Vikkineshwaran Siva SubramaniamSivamala MalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Care of The Clients With Cardiovascular DisordersDocument226 pagesChapter 5 Care of The Clients With Cardiovascular DisordersDon Felicisimo EbronNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument51 pagesCirculatory SystemTina TalmadgeNo ratings yet
- Beating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartFrom EverandBeating with Precision: The Science of Cardiology: Understand the Intricacies of the Human HeartNo ratings yet
- ProtocoloDocument6 pagesProtocolomigas1996No ratings yet
- Lab. Work 5Document22 pagesLab. Work 5migas1996No ratings yet
- Heart 4Document28 pagesHeart 4migas1996No ratings yet
- Ficha Ingles 9 VolunteeringDocument2 pagesFicha Ingles 9 Volunteeringmigas1996No ratings yet
- Physio PROTOCOL 1Document6 pagesPhysio PROTOCOL 1migas1996No ratings yet
- 3-DNA Replication 2.lecture ENGDocument51 pages3-DNA Replication 2.lecture ENGmigas1996No ratings yet
- 4.4 - Ficha de Trabalho - Modal Verbs (1) - SoluçõesDocument1 page4.4 - Ficha de Trabalho - Modal Verbs (1) - Soluçõesmigas1996No ratings yet
- 2-Structure of Nucleic Acids ENGDocument69 pages2-Structure of Nucleic Acids ENGmigas1996No ratings yet
- Diplozoon ParadoxumDocument2 pagesDiplozoon Paradoxummigas1996No ratings yet
- 4.4 - Ficha de Trabalho - Modal VerbsDocument1 page4.4 - Ficha de Trabalho - Modal Verbsmigas1996No ratings yet
- EX Ing550 F1 2023 - Net - RemovedDocument3 pagesEX Ing550 F1 2023 - Net - Removedmigas1996No ratings yet