Professional Documents
Culture Documents
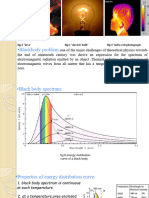
1.18 Quantization of Electromagnetic Radiation: 22 1 Introduction To Modern Physics
1.18 Quantization of Electromagnetic Radiation: 22 1 Introduction To Modern Physics
Uploaded by
Kareem TalaatOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1.18 Quantization of Electromagnetic Radiation: 22 1 Introduction To Modern Physics
1.18 Quantization of Electromagnetic Radiation: 22 1 Introduction To Modern Physics
Uploaded by
Kareem TalaatCopyright:
Available Formats
22 1 Introduction to Modern Physics
emitted in the form of a photon with an energy hν, i.e.,
∆E = E1 − E2 = hν = hc/λ , (1.18)
where
h is the Planck’s constant,
ν is the frequency of the photon,
c is the speed of light in vacuum,
λ is the wavelength of the photon.
• Radiation, such as light, is emitted, transmitted, and absorbed in discrete
energy quanta characterized by the product of frequency ν and Planck’s
constant h.
• Planck’s postulate of energy quantization lead to the atomic model with
its angular momentum quantization introduced by Niels Bohr in 1913 and
to quantum wave mechanics developed by Erwin Schrödinger in 1926.
• The so-called Schrödinger equation (see Sect. 1.22), used extensively in
atomic, nuclear and solid-state physics as well as in quantum mechanics,
is a wave equation describing probability waves (wave functions) that
govern the motion of small atomic particles. The equation has the same
fundamental importance to quantum mechanics as Newton’s laws have
for large dimension phenomena of classical mechanics.
1.18 Quantization of Electromagnetic Radiation
Electromagnetic (EM) radiation incident on metallic surface may eject
charged particles from the surface, as first observed by Heinrich Hertz in
1887. Joseph Thomson proved that the emitted charged particles were elec-
trons and Albert Einstein in 1905 explained the effect by proposing that EM
radiation was quantized similarly to the quantization of oscillator levels in
matter introduced by Max Planck in 1900.
A quantum of electromagnetic radiation is called a photon and has the
following properties:
• It is characterized by frequency ν and wavelength λ = c/ν where c is the
speed of light in vacuum.
• It carries an energy hν and momentum pν = h/λ where h is Planck’s
constant.
• It has zero rest mass.
In a metal the outer electrons move freely from atom to atom and behave
like a gas with a continuous spectrum of energy levels. To release an electron
from a metal a minimum energy characteristic of the given metal and referred
to as the work function eφ must be supplied to the electron. Einstein postu-
lated that the maximum kinetic energy (EK )max of the electron ejected from
You might also like
- Ch1 Revision of EP203Document31 pagesCh1 Revision of EP203mirckyNo ratings yet
- Unit II QuantummechanicsDocument28 pagesUnit II QuantummechanicsKiran ThunuguntlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five (2) - 2Document68 pagesChapter Five (2) - 2Wengelu evanNo ratings yet
- Unit Ii - Quantum Mechanics: D e A D EDocument25 pagesUnit Ii - Quantum Mechanics: D e A D EChiraag ChiruNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics Lecture Note Dr.H. RathDocument60 pagesQuantum Mechanics Lecture Note Dr.H. RathSoumya Ranjan PandaNo ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument15 pagesModern Physicsabdogh93No ratings yet
- Chem Bonding - Sukanta - Class LectureDocument85 pagesChem Bonding - Sukanta - Class LecturePavan Kethavath100% (1)
- Quantum MechanicsDocument35 pagesQuantum MechanicsJonNo ratings yet
- Schroedinger EssayDocument19 pagesSchroedinger EssayMark MoodyNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Quantum MechanicsDocument41 pagesUnit 1 Quantum MechanicsVimala H CNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of AtomsDocument59 pagesElectronic Structure of Atomstalktotiffanycheng100% (1)
- 5) Quantum Mechanics - UpdatedDocument86 pages5) Quantum Mechanics - UpdatedGame 1No ratings yet
- 02 IntroQuantumPhysicsDocument8 pages02 IntroQuantumPhysicscychan410No ratings yet
- Che 402 e Photochemistry NotesDocument20 pagesChe 402 e Photochemistry NotesKEVIN OMONDINo ratings yet
- CH 12 NotesDocument2 pagesCH 12 NotesAila Kublai-sikNo ratings yet
- Planck Constant Using PhotocellDocument6 pagesPlanck Constant Using PhotocellEagle DesignsNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument11 pagesPhotoelectric EffectRivu BasuNo ratings yet
- Max Planck and Black Body RadiationDocument3 pagesMax Planck and Black Body RadiationMarie Joy EngayNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document10 pagesLecture 2Ifra NoorNo ratings yet
- Blackbody Radiation PDFDocument24 pagesBlackbody Radiation PDFAtul SinghNo ratings yet
- Physics HSCDocument2 pagesPhysics HSCmothermonkNo ratings yet
- Intro To Quantum MechanicsDocument48 pagesIntro To Quantum Mechanicskaisbarboura99No ratings yet
- Atomic Hydrogen Spectrum and The Bohr Model of The AtomDocument29 pagesAtomic Hydrogen Spectrum and The Bohr Model of The AtomJohn Wanyoike MakauNo ratings yet
- Che101 Chap 7Document47 pagesChe101 Chap 7David MaranzhyanNo ratings yet
- Elementary Quantum Physics 20160926Document81 pagesElementary Quantum Physics 20160926Aruna KumarasiriNo ratings yet
- Lec FailureDocument54 pagesLec Failureshahin alamNo ratings yet
- Quantum MechanicsDocument5 pagesQuantum MechanicsBADGER I AVINo ratings yet
- Che101 Chap 7Document48 pagesChe101 Chap 7Ruhi AfsaraNo ratings yet
- Physics112 - Chapter40Document72 pagesPhysics112 - Chapter40Gurpreet SohalNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of Atoms - General ChemistryDocument92 pagesElectronic Structure of Atoms - General ChemistryDuc Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- 8-Ch7 (Struktur Atom)Document91 pages8-Ch7 (Struktur Atom)Mia YukimuraNo ratings yet
- Wien Displacement Law and OtherDocument18 pagesWien Displacement Law and OtherbsgoleNo ratings yet
- Quantum MechanicsDocument46 pagesQuantum MechanicsAbhilash Nair50% (2)
- Quantum Theory and The AtomDocument18 pagesQuantum Theory and The AtomIrish de LeonNo ratings yet
- Photo-Electric Effect and ComptonDocument7 pagesPhoto-Electric Effect and ComptonMohammad Irfan YousufNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Quantum PhysicsDocument69 pagesIntroduction To Quantum PhysicsEr Ishan SharmaNo ratings yet
- QM BasicsDocument12 pagesQM Basicsh.anurag248No ratings yet
- Waves o ParticlesDocument6 pagesWaves o ParticlesFlor Ruiz VelaNo ratings yet
- Photoelectric EffectDocument7 pagesPhotoelectric EffectrujintoNo ratings yet
- Mahasiswa Mampu Menjelaskan Konsep Kuantisasi Energi: Kompetensi 1Document43 pagesMahasiswa Mampu Menjelaskan Konsep Kuantisasi Energi: Kompetensi 1Imam SyNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter and Radiation Class 12 All DerivationsDocument2 pagesDual Nature of Matter and Radiation Class 12 All Derivationsmohitjangra9238100% (1)
- Wave Mechanics and The SCHR Odinger Equation: 1.1 Historical Foundations of Quantum PhysicsDocument9 pagesWave Mechanics and The SCHR Odinger Equation: 1.1 Historical Foundations of Quantum PhysicsPhyo ThihaNo ratings yet
- 4) Quantum MechanicsDocument75 pages4) Quantum MechanicsGame 1No ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Lesson 1Document4 pagesChapter 1-Lesson 1Bùi Hữu ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics PyEd 342Document113 pagesQuantum Mechanics PyEd 342mesfint100% (3)
- Assignment 1Document7 pagesAssignment 1Noor ul HudaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Atomic Structure and PreriodicityDocument87 pagesChapter 7 Atomic Structure and PreriodicitydeemahhwNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument9 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentAritra SahaNo ratings yet
- Quantum Mechanics - Britannica Online Encyclopedia PDFDocument29 pagesQuantum Mechanics - Britannica Online Encyclopedia PDFMahesh MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- EP - UNIT 2 - Quantum MechanicsDocument34 pagesEP - UNIT 2 - Quantum Mechanicsthetop10nerdNo ratings yet
- Fisica Moderna PonceDocument74 pagesFisica Moderna PonceWilmer MoncadaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument7 pagesElectromagnetic Wavesmary ann leddaNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument13 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectDêêpák Sîñgh ÑîtwálNo ratings yet
- The Development of A New Atomic ModelDocument40 pagesThe Development of A New Atomic Modelahmad batataNo ratings yet
- Black Body RadiationDocument33 pagesBlack Body RadiationSafnas Kariapper100% (1)
- Lec 4 Modern Physics & Electronics Lecture 4Document13 pagesLec 4 Modern Physics & Electronics Lecture 4This Is Me.No ratings yet
- AP Physics Chapter 27 Quantum PhysicsDocument78 pagesAP Physics Chapter 27 Quantum PhysicsMythos EntertainmentNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Chemistry 1semesterDocument12 pagesInorganic Chemistry 1semestermanjunathu731No ratings yet
- Operation:-: ObservationDocument1 pageOperation:-: ObservationKareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- 6 Interactions of Neutrons With Matter - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - 169Document1 page6 Interactions of Neutrons With Matter - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - . - 169Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- 1.11.2 Dose Distributions For Neutron BeamsDocument1 page1.11.2 Dose Distributions For Neutron BeamsKareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Fundamental Physical Constants: Committee On Data For Science and Technology (CODATA), An InterdisciDocument1 page1.1 Fundamental Physical Constants: Committee On Data For Science and Technology (CODATA), An InterdisciKareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- 1.8 Types and Sources of Directly Ionizing Radiation: 1.8.1 ElectronsDocument1 page1.8 Types and Sources of Directly Ionizing Radiation: 1.8.1 ElectronsKareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- 1.19 Einstein's Special Theory of Relativity 23Document1 page1.19 Einstein's Special Theory of Relativity 23Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- F= d p dt, p is the momentum of a particle acted upon by force F - The momentum p is proportional to the velocity υ of a particle through the relationship p = m υ ,Document1 pageF= d p dt, p is the momentum of a particle acted upon by force F - The momentum p is proportional to the velocity υ of a particle through the relationship p = m υ ,Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- A, and Intro-Odinger, Werner Heisenberg and Max Born Are × 10 C, and Introduces C As ADocument1 pageA, and Intro-Odinger, Werner Heisenberg and Max Born Are × 10 C, and Introduces C As AKareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- 1.11 Dose in Water For Various Radiation Beams 11Document1 page1.11 Dose in Water For Various Radiation Beams 11Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- 1.14 Nuclear Binding Energies 17Document1 page1.14 Nuclear Binding Energies 17Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Educational Requirements: X Medical Physics: A Specialty and ProfessionDocument1 pageEducational Requirements: X Medical Physics: A Specialty and ProfessionKareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Ac Power - 5Document1 pageAc Power - 5Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Ac Power - 1Document1 pageAc Power - 1Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Database Design: Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 5, July-December 2004 P. 18-33Document1 pageDatabase Design: Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 5, July-December 2004 P. 18-33Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Extracted Pages From BIECh12 - 4Document1 pageExtracted Pages From BIECh12 - 4Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Examination System 1. Database Design and Implementation For General ChemistryDocument1 pageMultiple Choice Examination System 1. Database Design and Implementation For General ChemistryKareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Leonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 5, July-December 2004 P. 18-33Document1 pageLeonardo Journal of Sciences ISSN 1583-0233 Issue 5, July-December 2004 P. 18-33Kareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Examination System 1. Database Design and Implementation For General ChemistryDocument1 pageMultiple Choice Examination System 1. Database Design and Implementation For General ChemistryKareem TalaatNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Examination System 1. Database Design and Implementation For General ChemistryDocument1 pageMultiple Choice Examination System 1. Database Design and Implementation For General ChemistryKareem TalaatNo ratings yet