Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Tugas BIH
Tugas BIH
Uploaded by
Dirga0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views8 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views8 pagesTugas BIH
Tugas BIH
Uploaded by
DirgaCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf
You are on page 1of 8
wee a to him as a surprise:
ppving done anything wrong legally.
ei. (v) — (n) detention — the state of keepin,
wil penahanan 8 People Waiting or in
he police the man for further inquiries about th,
cebut (8) (n) rebuttal — to disprove: to — . bank tobbery,
tangkisan Proof, bantahan,
inhis_____—- the lawyers stated that his cliem
le (v) — (n) embezzl 2 Was not guilty,
_embezz! ement — penggelapan a
He could easily
the chief accountant.
rob (v) - (n) robbery ~ act of stealing; perampokan
During the bank two bank tellers and several customers
were held as hostages by the robbers.
bribe (v) — (n) bribery — giving ortaking of bribes; enyuapan
The newspaper was to state nothing in the paper about
the murder of the beauty queen.
just (adj) ~ (n) justice ~ the quality of being right and fair; kebe-
naran
ey
he had Rot thought of
t! +
the company’s money because he was
He received a sentence for the crimes he had commited.
10. juridical (adj) — (n) jurisdiction — legal authority; hak hukum
The district court has over the old as we] I as the new
settlers.
STRUCTURE FOCUS 1: Adjective Clauses
Asthename suggests, adjective clauses are dependent clauses that function
Sadjectives, and as adjectives they modify nouns or pronouns. The subor-
nate conjunctions or clause signals for the adjective clause’
‘caperson — who, whom, whose, that
‘athing — which, that
“time — when
"race — where
"reason —why
§ are:
229
ig are sentences containing the adjective aie
inate conjunctions or clause signals i s, Oy,
i is in itali
adjective clause cs and the Word att
1. The 40-year-old lady who was just acquitted (dibebas, kan) - ite,
charge, had trouble looking for a job. pa
2. The lady, whose husband has been detained by Police, has 10%
to support her family of four children. rk bay
She works in an office which is about 60 km from her i
|. With her educational background, that is one of the few oftees
she can get employment. Whey,
5. They were discussing the period when the Dutch were sti) in
Indonesia.
6. He never told his lawyer the reason why he wanted to leave fos
7. The witness from whom the public prosecutor tried to get infsy.
on the case was reluctant to talk much.
8. He needs some facts that concern the defendant ‘s past buries
ties.
The followin
the use of the subordi
in the field of law. The
is in boldface.
Power,
information
STRUCTURE ACTIVITY I
In the following exercises the adjective clauses are in boldface. Try to ind.
cate the nouns or pronouns they modify.
Example:
- The experience which nearly killed him has changed his life.
(The adjective clause in boldface modifies the noun ‘experience.’)
Mr. Kismodiningrat, who is the director of the corporate firm,
: ate designing Tecreational programs for his workers.
eee Programs which will develop in-group feelings amott
ers are necessary for the employees.
1.
3. Besid
i = Such programs can also reduce the mental and physical ®
‘mployees whose minds may have b tense after
week’s labor, y have become
4.
Some offices Provide a
can have recreational Vacant lot where workers and other peor
activities,
230 es.
ao such activities people have OPPOTtUnities Wh
5M sonalities. * Which can develop 1h
ey may also reveal hidden qualities of | ei
. eneficial (bermanfaat) to the firm, aden
or the employers of the firm, a Weekend s
me when promotable manpower may be
Ship which can be
ers Program can be
el
‘To some employees, the weekend is simply a mee
just relax. where they can
of course, for young girls, itis a period when they ¢
single men in the company. 'Y can get to know
‘At any rate (namun), workers who have work
ced hi A
week, should promote their well-being, ard during the
_ Sports programs are physically enriching to those who enjo}
door activities. \joy out-
1, That is the reason why even senior workers take part in sports
programs.
3. Today there are national sports programs where everybody is sup-
posed to participate.
STRUCTURE ACTIVITY I
The following passage contains adj
rick out the adjective clauses and indicate the nouns or pronouns they
modify.
Example:
~ Istill remember the time when I first met my
(The adjective clause is ‘when | first met my hi
the noun ‘time.’)
“Here is a tale that tells about young lawyers. The law professor aid
800d-bye to his favorite pupil, who was graduating and leaving (© pee
tice law. “If ever you are in trouble and eed advice on comple®
Sues, don’t hesitate to call on me.’ The years passed. Then i
Young lawyer got the biggest case in his career, rie
dant in a lurid (penuh sensasi) murder trial. Becaus® ofthe
ik) analytical
Ofthe lepal i. sderable (cukup bana
legal issues, he needed considerable 21
ective clauses. Read it thoroughly and
husband/wife.
usband/wife.” It modifies
to his old professor whose Ady;
pt back ; ce
assistance, ® a Fepaomptly (eePar< epat) Senta long joy hg
always reme! red. egal issues of the case as he saw them hie,
described the re the professor. He sent @ special detivg rey,
(jawaban) came The trial started, and, sensing (meray, ;
and still no ain of his trouble, he sent a night letter Which ” the
depth (dale case to the professor. But more silence fll leg
the testimony cee lawyer finally rested his case, our ne rw
When the cies upset. He sent a long telegram which pa 0
was violently ‘the prosecution witnesses. He also begged for he
the statements 0! nting his side in trial testimony, he despin,
0 days of pres
After 7 s ps then justin time (tepat pada waktunya), bis ass.
tus o 2
= in front of him a telegram which came from the elusive Professor.
“Don’t worry. I am arriving on the one 0 clock plane with three Wit
nesses.”
STRUCTURE ACTIVITY III ve
Briefly look over the reading selection at the beginning ofthis chapter ang
indicate the adjective clauses contained in the selection.
STRUCTURE FOCUS IT: Noun Clauses
In this chapter and the previous one you have studied two types of clauses
namely the adverb clause and the adjective clause. Thus, you have leamed
that the function of a dependent clause in a sentence determines whether it
is an adverbial clause or an adjective clause. If the dependent clause serves
as a modifier of a verb, it is an adverbial clause; if it modifies a noun or
pronoun, it is an adjective clause. You may have also noticed that in some
sentences the clauses may have the same clause signals; however, the samt
subordinate conjunction introduces two different clauses: one modifyins#
oe = other explaining a noun as shown below:
rn P j essor was reading a report when came in. '
(The clause in boldface is an adverb clause of time modifying the ¥“
was reading,’)
2. That was the time when everybody was talking about the sensation!
232
se of the beauty queen,
der
on clause in boldface is an adjective cl,
‘aUSe modify
ing the noun
-ime:”)
‘ne Nout Clause
jus unit, YOU will learn some of the basic functions of n
ae suggests, noun clauses 2 not modify as cre nclas. a
ses 40> put noun clauses function as nouns. Like no ial and adjective
iect of a verb, object of a verb, object of a canes * used
|, Subjective
*atement and appositive. The following are some of the ;
orintroductory words for noun clauses: ee
thst which how many how lon
who whom whatever me
whose what whenever whoever
where why now often how soon
when. how how old how far
whether, etc.
Noun clause as the subject of a verb:
That frustration and anxiety may
lawyer’s defense for his client.
wun clause in boldface is used as the subject of the v
is insane needs no proof.
clause in boldface is used as $
is none of your business.
in boldface is used as su
1e violent acts
be the cause of som
rb is.’)
subject of the verb *needs.”)
ject of the verb “is.”)
| problems ean also cause violent acty
na
innocent
was at home the whole day.
had put the knife.
poldface is used 48 object of the verb forgo :
hether or not he will bring the case tg =
is used as object of the negative verb by
said (tha) emotion
)he was
Het
2 He forgot whe
(The noun clause in
He has not decided w
(The noun clause 1 boldface
not decided.")
Noun clause as # subjec
|. His problem is that he
(The noun clause in bol
2. The prisoner Is what he appears to be.
(The noun clause in boldface is used as complement of the verh is
3. The winner was whoever could answer the question,
(The noun clause in boldface is used as complement of the =e
tive complement:
cannot produce evidence against her,
idface is used as complement of the verb, ;
‘was.")
Noun clause as an appositive:
1, The fact, that he could not prove his alibi, was strong evidence against
him.
(The noun clause in boldface is used in apposition to the noun ’fact.’)
2. One problem, that is of his mental instability, will be hard to deal with
: (The noun clause in boldface is used in apposition to the noun ‘problem.’)
. The question, whether or not he could win the ease, is still up in the air.
(The noun clause in boldface i i -
as ‘ace is used in apposition to the noun “ques-
a Clause as object of 9 Preposition;
He is k ‘ the jury will decide.
looking forward to what the memb, j i
( : 'mbers of the j '
‘ause in, ;
boldface is Used as object of the preposition ‘t.)
2. The lady was w,
Orried about
Would pay for her joa r not the insurance comp
(The noun clause
in boldfac
ace is used as object of the preposition ‘about )
234
ser” in ae examples below that ‘that
7 with anticipatory ‘it.’ Noun Clauses
( im| ortant that we follow orders, Also occu in
I , ‘ necessary that you read the small print
was pvious that the testimony was not Pa
ul was possible that he had broken into the oe oath,
sight ; in the middle ofthe
Nout clauses are sometimes referred to by some
at clauses” since they are very frequently used as anna re
verbs given below, are mostly verbs of mental activi a Of verbs. These
he insurance
lize notice see remembei
i" tell decide Gee on A
think answer ask complain remark a
inquire Know wonder mention state ae
Observe the following examples of noun clauses used as object clauses
afer some of the verbs given above.
|, The man told me that he and his co-workers were out on strike (mogok
kerja).
2, He said that he was the president
3. lasked why they went on strike.
He explained that they had deman
ter I asked how many workers ha
id not know exactly how many men
Jearned that the union
‘ime
of the union.
ded a salary increase
d. picketed the department store.
had joined the strike.
ys later, I
ize that it was a cr"
persuade others not to work scones
in a Pancasila democracy,
face is used aS object of the verb “had ny
fact
lc.
in bold!
the noun clause bol
| issio!
ni ber 0! the Home ee
i mmf that manipula’
Home
n II reported to the Min,
had caused lang disp. of
Utes i,
rokers were involved in most of the Cases,
t most of the land owners ene uneducateg
the victims of ‘conmen’ (penipu).
landowner did not understand how he could be Paig
land.
here he could get information Concerning
i The problem, Mai
"iterate peorle
‘The uneducaded lance
amarket price for his
He did not even know W!
the sale of his land.
In such a situation, it is imj
How and where legal aid can
lem to landowners.
Many landowners did not agree with what the unethical brokers
offered for the land in question.
The legal Aid Institution protects whoever deserves justice,
0. The question, how those land brokers could cheat the people, was
quite easy to answer.
- The people said that the brokers came and forced them to sell
their land.
12. What the price for a square meter of land was did not come up in
the discussion about land prices,
13. The brokers only thought about how much profit they could gain by
speculating, :
>
portant that landowners get lega] aid,
be obtained becomes a major Prob.
ae
=
Fortunately the government took
Speculators were,
. So People do not have
their land or not,
Measures against whoever the
‘0 Worry whether some brokers would buy
STRUCTURE Actiyypy y
© Passage that f
follo '
‘OVBhly. Indicate the pe: Noun clauses. Read the selection tho
Claus, :
236 °S and state their functions.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5823)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Sentence Class: Tugas Analisis Phrase Class, Clause Class DanDocument6 pagesSentence Class: Tugas Analisis Phrase Class, Clause Class DanDirgaNo ratings yet
- Through Ray Bradbury: A Literary Criticism of The VeldtDocument6 pagesThrough Ray Bradbury: A Literary Criticism of The VeldtDirgaNo ratings yet
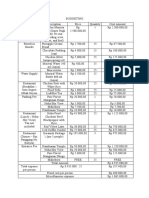
- BudgetingDocument2 pagesBudgetingDirgaNo ratings yet
- Security Management Services and Security Culture. I Am Interested in Gaining A MoreDocument1 pageSecurity Management Services and Security Culture. I Am Interested in Gaining A MoreDirgaNo ratings yet