Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Types of Bank
Types of Bank
Uploaded by
ashisghadai02Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Daddy - Loup DurandDocument456 pagesDaddy - Loup DurandHarle LyzaNo ratings yet
- Unit-Vii Types of BanksDocument18 pagesUnit-Vii Types of Bankssheetal rajputNo ratings yet
- Devast IncDocument19 pagesDevast IncPiyush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Banking Management: Presented by C. KavyaDocument27 pagesBanking Management: Presented by C. KavyaKaviya KaviNo ratings yet
- Ufi M 4Document42 pagesUfi M 4sresthapatel28No ratings yet
- Unit 6Document107 pagesUnit 6Avinaash PraveenNo ratings yet
- 01 Indian Banking SystemDocument11 pages01 Indian Banking SystemAmir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Types of Banks IndiaDocument3 pagesTypes of Banks India17-075 Upgna PatelNo ratings yet
- 1627995243-Lecture - 1 HISTORY OF BANKING IN INDIADocument5 pages1627995243-Lecture - 1 HISTORY OF BANKING IN INDIAKhushraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Banking in IndiaDocument6 pagesBanking in IndiaAmandeep KambojNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking StructureDocument20 pagesIndian Banking Structureneha16septNo ratings yet
- Banking StructureDocument11 pagesBanking Structureaditi_espeaksNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking System History and StructureDocument47 pagesIndian Banking System History and StructureRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Alternative Division of Scheduled Banks and Non Scheduled Banks (Without Non Scheduled Bank Structure)Document2 pagesAlternative Division of Scheduled Banks and Non Scheduled Banks (Without Non Scheduled Bank Structure)Samuel HranlehNo ratings yet
- Overview of Banking SystemDocument45 pagesOverview of Banking SystemShabri MayekarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document57 pagesUnit 1Anurag VarmaNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking .. ..SECTORDocument30 pagesIndian Banking .. ..SECTORShakshi Arvind GuptaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of BanksDocument8 pagesDifferent Types of BanksRahul DalviNo ratings yet
- History of Banking System in IndiaDocument37 pagesHistory of Banking System in IndiaSrijan DubeyNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking StructureDocument24 pagesIndian Banking StructureRENUKA CHAUHANNo ratings yet
- Banking Structure in IndiaDocument5 pagesBanking Structure in IndiaCharu Saxena16No ratings yet
- Introduction To Indian Banking SystemDocument78 pagesIntroduction To Indian Banking SystemJessina JoyNo ratings yet
- Banking Sector in India: BY Divyabharathi (109) Vamsiprakash (110) DEEPAK (111) Goutham Reddy (112) HEMALATHADocument31 pagesBanking Sector in India: BY Divyabharathi (109) Vamsiprakash (110) DEEPAK (111) Goutham Reddy (112) HEMALATHAamulrocksNo ratings yet
- Types of BanksDocument5 pagesTypes of BanksAsif AliNo ratings yet
- Banking Structure in IndiaDocument31 pagesBanking Structure in IndiaRishabhShuklaNo ratings yet
- Banks in IndiaDocument13 pagesBanks in IndiaSumedha TutejaNo ratings yet
- Types of BanksDocument20 pagesTypes of BanksYog MehtaNo ratings yet
- Principles OF Banking - 1Document36 pagesPrinciples OF Banking - 1Pulkit_Saini_789No ratings yet
- L15 Scheduled BANKS PDFDocument14 pagesL15 Scheduled BANKS PDFakshita raoNo ratings yet
- Banking Practice Unit 1Document13 pagesBanking Practice Unit 1Nandhini VirgoNo ratings yet
- Banking Management: Presented by C. KavyaDocument28 pagesBanking Management: Presented by C. KavyaKaviya KaviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document24 pagesChapter 02JuManHaqZzNo ratings yet
- 18.04 - COMMERCIAL BANKS, NBFCS, COOPERATIVE BANKSDocument12 pages18.04 - COMMERCIAL BANKS, NBFCS, COOPERATIVE BANKSramixudinNo ratings yet
- Banking System in IndiaDocument4 pagesBanking System in Indiaanirudha.kanhaNo ratings yet
- Banking Management Additional NotesDocument118 pagesBanking Management Additional NotesLokesh ChNo ratings yet
- Banking & Financial Institutions in India: Historical BackgroundDocument6 pagesBanking & Financial Institutions in India: Historical BackgroundRUPA GOELNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions & MarketsDocument62 pagesFinancial Institutions & MarketsSaurav UchilNo ratings yet
- History 2Document5 pagesHistory 2bickyboom96No ratings yet
- Chapter 1banking and Isurance Calicut UniversirtyDocument47 pagesChapter 1banking and Isurance Calicut UniversirtyJuManHaqZzNo ratings yet
- BANKING INSTITUTIONS-History About Banking in IndiaDocument15 pagesBANKING INSTITUTIONS-History About Banking in IndiaGinu GeorgeNo ratings yet
- SelvakumarDocument14 pagesSelvakumarSelvakumarNo ratings yet
- 3. StructureDocument8 pages3. StructureishikaNo ratings yet
- Banking IndustryDocument77 pagesBanking Industryprashant mhatreNo ratings yet
- Banking Awarness Meritshine MaterialDocument162 pagesBanking Awarness Meritshine MaterialRagavi JoNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To BankingDocument41 pagesIntoduction To BankingAbhilash ShahNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking StructureDocument5 pagesIndian Banking StructurevivekNo ratings yet
- PPBIDocument24 pagesPPBIChandni ParikhNo ratings yet
- Banking Process and Basics of Operations.Document34 pagesBanking Process and Basics of Operations.amritaa chaurrasiaNo ratings yet
- Mission Vission and ValuesDocument8 pagesMission Vission and ValuesJiby JohnNo ratings yet
- Structure of Commercial Banking in IndiaDocument43 pagesStructure of Commercial Banking in IndiaViral PathakNo ratings yet
- Banking System in IndiaDocument3 pagesBanking System in Indiahello707No ratings yet
- History of Indian BankingDocument23 pagesHistory of Indian BankingLaxman KambleNo ratings yet
- Types of Banks: BankingDocument11 pagesTypes of Banks: BankingKaviya KaviNo ratings yet
- ICICI Project ReportDocument53 pagesICICI Project ReportPawan MeenaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Commercial Banks in IndiaDocument11 pagesStructure of Commercial Banks in IndiaVijayalakshmi100% (2)
- 2. Types of BanksDocument14 pages2. Types of BanksishikaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Banks and Their FunctionsDocument25 pagesDifferent Types of Banks and Their FunctionsIshita GuptaNo ratings yet
- Types of BankingDocument10 pagesTypes of BankingJinu SajiNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: Introduction To Indian Banking SystemDocument109 pagesUnit - 1: Introduction To Indian Banking SystemDr. S. Nellima KPRCAS-CommerceNo ratings yet
- Banking System: An OverviewDocument22 pagesBanking System: An OverviewPankajNo ratings yet
- Banking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingFrom EverandBanking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingNo ratings yet
- OpTransactionHistoryUX511 01 2024Document24 pagesOpTransactionHistoryUX511 01 2024Nishant ThakerNo ratings yet
- BCA Fee Slip 200678 101057 01102023Document1 pageBCA Fee Slip 200678 101057 01102023AyaanNo ratings yet
- Session 1Document31 pagesSession 1KARAN KAPOOR PGP 2021-23 BatchNo ratings yet
- David - sm15 - Case - Im - 07 JP MorganDocument15 pagesDavid - sm15 - Case - Im - 07 JP MorganМаша ИльеваNo ratings yet
- Feeding Branch Operation & Cash Handling & Maintenance Related To ATM OperationDocument4 pagesFeeding Branch Operation & Cash Handling & Maintenance Related To ATM OperationRayhan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Card Banking 2Document66 pagesCard Banking 2markos mamadeNo ratings yet
- Miap405i 12818783 0000988016 Sce240m 93XV8 4Document2 pagesMiap405i 12818783 0000988016 Sce240m 93XV8 4sce mduNo ratings yet
- Discussion Exercises Accounts ReceivableDocument2 pagesDiscussion Exercises Accounts ReceivableFrancine Thea M. LantayaNo ratings yet
- Manfaat Debit BCADocument1 pageManfaat Debit BCANia ニア MulyaningsihNo ratings yet
- BCG Global Wealth 2021 Jun 2021Document25 pagesBCG Global Wealth 2021 Jun 2021Shahin Akanda100% (1)
- YLlq 6 QSGFGF 0 Uyz 8Document2 pagesYLlq 6 QSGFGF 0 Uyz 8Praveen SainiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial AccountingDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Financial AccountingMwesigwa DaniNo ratings yet
- 0452 s02 ErDocument9 pages0452 s02 ErAhmed SherifNo ratings yet
- Lead Bank Scheme (LBS)Document14 pagesLead Bank Scheme (LBS)m.s.machi raju100% (6)
- Grievance Redressal MechanismDocument4 pagesGrievance Redressal MechanismParikshit SachdevNo ratings yet
- Scope of Concurrent AuditDocument17 pagesScope of Concurrent AuditAnandNo ratings yet
- FORM TP 2017101 Test Code 01239010 MAY/JUNE 2017: Paper 01 - General ProficiencyDocument14 pagesFORM TP 2017101 Test Code 01239010 MAY/JUNE 2017: Paper 01 - General ProficiencyChelsea BynoeNo ratings yet
- Role of Financial Derivatives in Risk Management: Imran RamzanDocument15 pagesRole of Financial Derivatives in Risk Management: Imran RamzanSana Ullah100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Managing Transaction RisksDocument22 pagesChapter 8 Managing Transaction Risksmatthew kobulnickNo ratings yet
- Financial Education and Invesemtn Awareness Question BankDocument19 pagesFinancial Education and Invesemtn Awareness Question BankSyedNo ratings yet
- Ledger & Trial BalanceDocument45 pagesLedger & Trial BalancealihussainpidNo ratings yet
- Test Series: March, 2022 Mock Test Paper 1 Foundation Course Paper - 1: Principles and Practice of AccountingDocument5 pagesTest Series: March, 2022 Mock Test Paper 1 Foundation Course Paper - 1: Principles and Practice of AccountingVinithaNo ratings yet
- A Study ON Liquidity Analysis of Nic Asia Bank Limited: A Project Work ReportDocument41 pagesA Study ON Liquidity Analysis of Nic Asia Bank Limited: A Project Work ReportPradip Kumar ShahNo ratings yet
- IFS - CIA - III Group 6Document15 pagesIFS - CIA - III Group 6NAVYA JUNEJA 2023323No ratings yet
- New Balance $26,711.29 Minimum Payment Due $337.00 Payment Due Date 11/23/22Document13 pagesNew Balance $26,711.29 Minimum Payment Due $337.00 Payment Due Date 11/23/22Rahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- An Internship Report On Investment OperaDocument75 pagesAn Internship Report On Investment Operaআত্মজীবনীNo ratings yet
- What Is Money: The Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets, 8 EditionDocument34 pagesWhat Is Money: The Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets, 8 Editionjulita08No ratings yet
- Application PKG NewDocument7 pagesApplication PKG Newjyselle domingoNo ratings yet
- 04 BELL, Stephanie e Wray, L. Randall. Fiscal Effects On Reserves and The In-Dependence of The FedDocument11 pages04 BELL, Stephanie e Wray, L. Randall. Fiscal Effects On Reserves and The In-Dependence of The FedGuilherme UchimuraNo ratings yet
Types of Bank
Types of Bank
Uploaded by
ashisghadai02Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Types of Bank
Types of Bank
Uploaded by
ashisghadai02Copyright:
Available Formats
BANKING AVENUE: NAVIN SIR
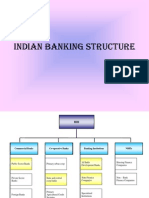
TYPES OF BANKS
Scheduled Banks?
• By definition, any bank which is listed in the 2nd schedule of the Reserve Bank of India
Act, 1934 is considered a scheduled bank.
• To qualify as a scheduled bank, the paid-up capital and collected funds of the bank must
not be less than Rs5 lakh.
Non-Scheduled Banks?
Non-scheduled banks by definition are those which are not listed in the 2nd schedule of the
RBI act, 1934.
• number of scheduled banks in our country:
• Scheduled Public Sector Banks – 12
• Scheduled Private Sector Banks – 22
• Scheduled Regional Rural Banks – 43
• Scheduled Foreign Banks in India – 46
Commercial Banks
• According to the RBI, “Commercial Banks refer to both scheduled and non-scheduled
commercial banks which are regulated under Banking Regulation Act, 1949.”
• Commercial banks operate on a ‘for-profit’ basis.
Types of Commercial Banks
Commercial banks are of three types-
• Public sector Banks
• Private sector Banks
• Foreign Banks.
Public Sector Banks
• Public Sector Banks (PSBs) are banks where a common stake (i.e. more than 50%) is held by a
government.
• The shares of these banks are listed on stock exchanges.
• Example- State Bank of India, Corporation Bank, Bank of Baroda, Punjab National Bank, Canara
Bank, Bank of India.:
Private Sectors Banks
• In the case of private sector banks, the majority of the share capital of the Bank is held by
private individuals.
• These Banks are registered as companies with limited liability.
• Example- ICICI Bank Ltd, ING Vysya Bank.
Foreign Banks
• These banks are registered and have their headquarters in a foreign country but operate their
branches in our country.
• Some foreign banks operating in our country are Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation
(HSBC), Citibank, American Express Bank, Standard & Chartered Bank.
YOUTUBE BANKINGAVENUE TELEGRAM
BANKING AVENUE: NAVIN SIR
Regional Rural Banks
• Regional Rural Banks or RRBs, simply put, serve the rural areas and agricultural sectors with
basic banking and adequate financial services.
• They were set up in 1975, based on the recommendations of a committee.
• Based in Moradabad, Prathama Bank, established on 2 October 1975, is the first RRB to open in
India. It was sponsored by Syndicate Bank.
• The RRBs are owned by the central government (50%), the state government (15%) and the
sponsor bank (35%).
Co-operative Banking
• All banks registered under the Cooperative Societies Act, 1912 are considered Co-
operative Banking Societies.
• These are regulated by the Reserve Bank of India under the Banking Regulation Act, 1949
and Banking Laws (Application to Co-operative Societies) Act, 1965
• In rural areas, such institutions primarily cater to agricultural-based activities.
YOUTUBE BANKINGAVENUE TELEGRAM
You might also like
- Daddy - Loup DurandDocument456 pagesDaddy - Loup DurandHarle LyzaNo ratings yet
- Unit-Vii Types of BanksDocument18 pagesUnit-Vii Types of Bankssheetal rajputNo ratings yet
- Devast IncDocument19 pagesDevast IncPiyush SharmaNo ratings yet
- Banking Management: Presented by C. KavyaDocument27 pagesBanking Management: Presented by C. KavyaKaviya KaviNo ratings yet
- Ufi M 4Document42 pagesUfi M 4sresthapatel28No ratings yet
- Unit 6Document107 pagesUnit 6Avinaash PraveenNo ratings yet
- 01 Indian Banking SystemDocument11 pages01 Indian Banking SystemAmir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Types of Banks IndiaDocument3 pagesTypes of Banks India17-075 Upgna PatelNo ratings yet
- 1627995243-Lecture - 1 HISTORY OF BANKING IN INDIADocument5 pages1627995243-Lecture - 1 HISTORY OF BANKING IN INDIAKhushraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Banking in IndiaDocument6 pagesBanking in IndiaAmandeep KambojNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking StructureDocument20 pagesIndian Banking Structureneha16septNo ratings yet
- Banking StructureDocument11 pagesBanking Structureaditi_espeaksNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking System History and StructureDocument47 pagesIndian Banking System History and StructureRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Alternative Division of Scheduled Banks and Non Scheduled Banks (Without Non Scheduled Bank Structure)Document2 pagesAlternative Division of Scheduled Banks and Non Scheduled Banks (Without Non Scheduled Bank Structure)Samuel HranlehNo ratings yet
- Overview of Banking SystemDocument45 pagesOverview of Banking SystemShabri MayekarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document57 pagesUnit 1Anurag VarmaNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking .. ..SECTORDocument30 pagesIndian Banking .. ..SECTORShakshi Arvind GuptaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of BanksDocument8 pagesDifferent Types of BanksRahul DalviNo ratings yet
- History of Banking System in IndiaDocument37 pagesHistory of Banking System in IndiaSrijan DubeyNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking StructureDocument24 pagesIndian Banking StructureRENUKA CHAUHANNo ratings yet
- Banking Structure in IndiaDocument5 pagesBanking Structure in IndiaCharu Saxena16No ratings yet
- Introduction To Indian Banking SystemDocument78 pagesIntroduction To Indian Banking SystemJessina JoyNo ratings yet
- Banking Sector in India: BY Divyabharathi (109) Vamsiprakash (110) DEEPAK (111) Goutham Reddy (112) HEMALATHADocument31 pagesBanking Sector in India: BY Divyabharathi (109) Vamsiprakash (110) DEEPAK (111) Goutham Reddy (112) HEMALATHAamulrocksNo ratings yet
- Types of BanksDocument5 pagesTypes of BanksAsif AliNo ratings yet
- Banking Structure in IndiaDocument31 pagesBanking Structure in IndiaRishabhShuklaNo ratings yet
- Banks in IndiaDocument13 pagesBanks in IndiaSumedha TutejaNo ratings yet
- Types of BanksDocument20 pagesTypes of BanksYog MehtaNo ratings yet
- Principles OF Banking - 1Document36 pagesPrinciples OF Banking - 1Pulkit_Saini_789No ratings yet
- L15 Scheduled BANKS PDFDocument14 pagesL15 Scheduled BANKS PDFakshita raoNo ratings yet
- Banking Practice Unit 1Document13 pagesBanking Practice Unit 1Nandhini VirgoNo ratings yet
- Banking Management: Presented by C. KavyaDocument28 pagesBanking Management: Presented by C. KavyaKaviya KaviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 02Document24 pagesChapter 02JuManHaqZzNo ratings yet
- 18.04 - COMMERCIAL BANKS, NBFCS, COOPERATIVE BANKSDocument12 pages18.04 - COMMERCIAL BANKS, NBFCS, COOPERATIVE BANKSramixudinNo ratings yet
- Banking System in IndiaDocument4 pagesBanking System in Indiaanirudha.kanhaNo ratings yet
- Banking Management Additional NotesDocument118 pagesBanking Management Additional NotesLokesh ChNo ratings yet
- Banking & Financial Institutions in India: Historical BackgroundDocument6 pagesBanking & Financial Institutions in India: Historical BackgroundRUPA GOELNo ratings yet
- Financial Institutions & MarketsDocument62 pagesFinancial Institutions & MarketsSaurav UchilNo ratings yet
- History 2Document5 pagesHistory 2bickyboom96No ratings yet
- Chapter 1banking and Isurance Calicut UniversirtyDocument47 pagesChapter 1banking and Isurance Calicut UniversirtyJuManHaqZzNo ratings yet
- BANKING INSTITUTIONS-History About Banking in IndiaDocument15 pagesBANKING INSTITUTIONS-History About Banking in IndiaGinu GeorgeNo ratings yet
- SelvakumarDocument14 pagesSelvakumarSelvakumarNo ratings yet
- 3. StructureDocument8 pages3. StructureishikaNo ratings yet
- Banking IndustryDocument77 pagesBanking Industryprashant mhatreNo ratings yet
- Banking Awarness Meritshine MaterialDocument162 pagesBanking Awarness Meritshine MaterialRagavi JoNo ratings yet
- Intoduction To BankingDocument41 pagesIntoduction To BankingAbhilash ShahNo ratings yet
- Indian Banking StructureDocument5 pagesIndian Banking StructurevivekNo ratings yet
- PPBIDocument24 pagesPPBIChandni ParikhNo ratings yet
- Banking Process and Basics of Operations.Document34 pagesBanking Process and Basics of Operations.amritaa chaurrasiaNo ratings yet
- Mission Vission and ValuesDocument8 pagesMission Vission and ValuesJiby JohnNo ratings yet
- Structure of Commercial Banking in IndiaDocument43 pagesStructure of Commercial Banking in IndiaViral PathakNo ratings yet
- Banking System in IndiaDocument3 pagesBanking System in Indiahello707No ratings yet
- History of Indian BankingDocument23 pagesHistory of Indian BankingLaxman KambleNo ratings yet
- Types of Banks: BankingDocument11 pagesTypes of Banks: BankingKaviya KaviNo ratings yet
- ICICI Project ReportDocument53 pagesICICI Project ReportPawan MeenaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Commercial Banks in IndiaDocument11 pagesStructure of Commercial Banks in IndiaVijayalakshmi100% (2)
- 2. Types of BanksDocument14 pages2. Types of BanksishikaNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Banks and Their FunctionsDocument25 pagesDifferent Types of Banks and Their FunctionsIshita GuptaNo ratings yet
- Types of BankingDocument10 pagesTypes of BankingJinu SajiNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1: Introduction To Indian Banking SystemDocument109 pagesUnit - 1: Introduction To Indian Banking SystemDr. S. Nellima KPRCAS-CommerceNo ratings yet
- Banking System: An OverviewDocument22 pagesBanking System: An OverviewPankajNo ratings yet
- Banking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingFrom EverandBanking India: Accepting Deposits for the Purpose of LendingNo ratings yet
- OpTransactionHistoryUX511 01 2024Document24 pagesOpTransactionHistoryUX511 01 2024Nishant ThakerNo ratings yet
- BCA Fee Slip 200678 101057 01102023Document1 pageBCA Fee Slip 200678 101057 01102023AyaanNo ratings yet
- Session 1Document31 pagesSession 1KARAN KAPOOR PGP 2021-23 BatchNo ratings yet
- David - sm15 - Case - Im - 07 JP MorganDocument15 pagesDavid - sm15 - Case - Im - 07 JP MorganМаша ИльеваNo ratings yet
- Feeding Branch Operation & Cash Handling & Maintenance Related To ATM OperationDocument4 pagesFeeding Branch Operation & Cash Handling & Maintenance Related To ATM OperationRayhan AhmedNo ratings yet
- Card Banking 2Document66 pagesCard Banking 2markos mamadeNo ratings yet
- Miap405i 12818783 0000988016 Sce240m 93XV8 4Document2 pagesMiap405i 12818783 0000988016 Sce240m 93XV8 4sce mduNo ratings yet
- Discussion Exercises Accounts ReceivableDocument2 pagesDiscussion Exercises Accounts ReceivableFrancine Thea M. LantayaNo ratings yet
- Manfaat Debit BCADocument1 pageManfaat Debit BCANia ニア MulyaningsihNo ratings yet
- BCG Global Wealth 2021 Jun 2021Document25 pagesBCG Global Wealth 2021 Jun 2021Shahin Akanda100% (1)
- YLlq 6 QSGFGF 0 Uyz 8Document2 pagesYLlq 6 QSGFGF 0 Uyz 8Praveen SainiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Financial AccountingDocument43 pagesIntroduction To Financial AccountingMwesigwa DaniNo ratings yet
- 0452 s02 ErDocument9 pages0452 s02 ErAhmed SherifNo ratings yet
- Lead Bank Scheme (LBS)Document14 pagesLead Bank Scheme (LBS)m.s.machi raju100% (6)
- Grievance Redressal MechanismDocument4 pagesGrievance Redressal MechanismParikshit SachdevNo ratings yet
- Scope of Concurrent AuditDocument17 pagesScope of Concurrent AuditAnandNo ratings yet
- FORM TP 2017101 Test Code 01239010 MAY/JUNE 2017: Paper 01 - General ProficiencyDocument14 pagesFORM TP 2017101 Test Code 01239010 MAY/JUNE 2017: Paper 01 - General ProficiencyChelsea BynoeNo ratings yet
- Role of Financial Derivatives in Risk Management: Imran RamzanDocument15 pagesRole of Financial Derivatives in Risk Management: Imran RamzanSana Ullah100% (1)
- Chapter 8 Managing Transaction RisksDocument22 pagesChapter 8 Managing Transaction Risksmatthew kobulnickNo ratings yet
- Financial Education and Invesemtn Awareness Question BankDocument19 pagesFinancial Education and Invesemtn Awareness Question BankSyedNo ratings yet
- Ledger & Trial BalanceDocument45 pagesLedger & Trial BalancealihussainpidNo ratings yet
- Test Series: March, 2022 Mock Test Paper 1 Foundation Course Paper - 1: Principles and Practice of AccountingDocument5 pagesTest Series: March, 2022 Mock Test Paper 1 Foundation Course Paper - 1: Principles and Practice of AccountingVinithaNo ratings yet
- A Study ON Liquidity Analysis of Nic Asia Bank Limited: A Project Work ReportDocument41 pagesA Study ON Liquidity Analysis of Nic Asia Bank Limited: A Project Work ReportPradip Kumar ShahNo ratings yet
- IFS - CIA - III Group 6Document15 pagesIFS - CIA - III Group 6NAVYA JUNEJA 2023323No ratings yet
- New Balance $26,711.29 Minimum Payment Due $337.00 Payment Due Date 11/23/22Document13 pagesNew Balance $26,711.29 Minimum Payment Due $337.00 Payment Due Date 11/23/22Rahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- An Internship Report On Investment OperaDocument75 pagesAn Internship Report On Investment Operaআত্মজীবনীNo ratings yet
- What Is Money: The Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets, 8 EditionDocument34 pagesWhat Is Money: The Economics of Money, Banking, and Financial Markets, 8 Editionjulita08No ratings yet
- Application PKG NewDocument7 pagesApplication PKG Newjyselle domingoNo ratings yet
- 04 BELL, Stephanie e Wray, L. Randall. Fiscal Effects On Reserves and The In-Dependence of The FedDocument11 pages04 BELL, Stephanie e Wray, L. Randall. Fiscal Effects On Reserves and The In-Dependence of The FedGuilherme UchimuraNo ratings yet