Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nerve (Ganong)
Nerve (Ganong)
Uploaded by
swap07shrma02Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- SB2a Mitosis 1. SB2b Growth in Animals SB2c Growth in PlantsDocument4 pagesSB2a Mitosis 1. SB2b Growth in Animals SB2c Growth in PlantsSiaNo ratings yet
- St. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: Block 1Document9 pagesSt. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: Block 1Mavic Villanueva100% (1)
- Year7ScienceHomeLearning Cycle9Document11 pagesYear7ScienceHomeLearning Cycle9Jayasri JeevaNo ratings yet
- Proximate Tissue InductionDocument5 pagesProximate Tissue InductionMigs MedinaNo ratings yet
- Guide Questions Answers: Muscles Contract, They Contribute To Gross and FineDocument7 pagesGuide Questions Answers: Muscles Contract, They Contribute To Gross and FinePrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Revised Introduction To The Pharmacology of CNS DrugsDocument9 pagesRevised Introduction To The Pharmacology of CNS DrugsJoshua Ty CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Physiology: Table 1. Distinguishing Properties of Electrical and Chemical SynapsesDocument5 pagesPhysiology: Table 1. Distinguishing Properties of Electrical and Chemical SynapsesMavic VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 PDFDocument8 pagesWorksheet 3 PDFjung minsuckNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Mitosis and MeiosisDocument19 pagesUnit 2 Mitosis and MeiosisErnest TolentinoNo ratings yet
- B4.1 - Cell Structure (Combined Science) : The Central Vacuole Maintains Turgor Pressure Against The Cell WallDocument1 pageB4.1 - Cell Structure (Combined Science) : The Central Vacuole Maintains Turgor Pressure Against The Cell WallNazimNo ratings yet
- 1 Hist Sept 13 HL11 Nerve Tissuestudent2020Document43 pages1 Hist Sept 13 HL11 Nerve Tissuestudent2020n-gorNo ratings yet
- 2nd HandoutDocument6 pages2nd HandoutMa FheNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Cell Structure Practice (1) - 3Document3 pagesKami Export - Cell Structure Practice (1) - 3Achionta NandyNo ratings yet
- The Dynamic SynapseDocument13 pagesThe Dynamic SynapseHucomanserNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1rida ikramNo ratings yet
- Human HistologyDocument5 pagesHuman Histologyشمس عقيل سالم C2No ratings yet
- Year 9 Revision BookletDocument17 pagesYear 9 Revision BookletmrsfarahnaazNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Parts 1 Amd 2 HBDocument27 pagesTopic 1 Parts 1 Amd 2 HBazankha1990No ratings yet
- Topic 1 Cell BiologyDocument2 pagesTopic 1 Cell BiologyEklavya GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous TissueDocument29 pagesThe Nervous TissueRO OMNo ratings yet
- Midtern LabDocument21 pagesMidtern LabJustine Mae OyongNo ratings yet
- LabEx4 - Eukaryotic CellDocument7 pagesLabEx4 - Eukaryotic Cellrjdc972No ratings yet
- Pidlaoan, Coleen - Cell Structure PracticeDocument5 pagesPidlaoan, Coleen - Cell Structure PracticeColeenNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: ReinforcementDocument2 pagesAnswer Key: ReinforcementCherifa AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Genral Biology 1Document3 pagesWeek 4 Genral Biology 1Spade ObusaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lec - Quiz 1 HandoutsDocument7 pagesGenetics Lec - Quiz 1 Handoutsvada_soNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 CellsDocument1 pageTopic 2 CellsKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- AS Biology Revision Pack UNIT 2Document16 pagesAS Biology Revision Pack UNIT 2George Noorland100% (2)
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- CH2 Mitosis and MeiosisDocument4 pagesCH2 Mitosis and MeiosisHaqua HerminiumNo ratings yet
- Types of CellsDocument5 pagesTypes of Cellsmalika.ahmed.sNo ratings yet
- 101lyb w6 Dayot ZaballeroDocument14 pages101lyb w6 Dayot ZaballeroMichael ZaballeroNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 BioP Notes - 090340Document13 pagesCHAPTER 3 BioP Notes - 090340Kate PedritaNo ratings yet
- Chap OutlineDocument8 pagesChap OutlinedurrieNo ratings yet
- Glial Cells Its FunctionDocument1 pageGlial Cells Its Functiongebrewahidbiniam75No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Neuroscience and Behavior, Myers 8e PsychologyDocument30 pagesChapter 2 Neuroscience and Behavior, Myers 8e Psychologymrchubs100% (14)
- BCHE4040 2023 Lecture 5B (Sept 21)Document24 pagesBCHE4040 2023 Lecture 5B (Sept 21)2K FaustusNo ratings yet
- Neural Control & Coordination PowernotesDocument2 pagesNeural Control & Coordination PowernotesSushmit Srivastava100% (1)
- (PSY 304) Chapter 1 - Nerve Cells and Nerve ImpulsesDocument9 pages(PSY 304) Chapter 1 - Nerve Cells and Nerve ImpulsesJJJJJJJJJNo ratings yet
- Ph1F1-PhBioSCi1a-Activity 2-Individual-GloriaDocument7 pagesPh1F1-PhBioSCi1a-Activity 2-Individual-GloriaAllysa GloriaNo ratings yet
- Neurons NervousDocument10 pagesNeurons NervousAldi RegarNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument2 pagesMitosisKimberly DalagNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Cell CommunicationDocument60 pagesAP Bio Cell CommunicationLavinia DonaldNo ratings yet
- Science Revision Chapter 1 -Year 7Document40 pagesScience Revision Chapter 1 -Year 7MUHAMMAD HAFIZUDDIN BIN KAMARULLZAMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Cell Communication: AP BiologyDocument60 pagesCell Communication: AP BiologyVanessa SunadaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesNervous SystemShriram100% (2)
- Exercise 2 Mitosis and MeiosisDocument5 pagesExercise 2 Mitosis and MeiosisRichelle MasingNo ratings yet
- Bmat Biology KnowledgeDocument22 pagesBmat Biology KnowledgeAngel SyNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument7 pagesConnective TissueSheena Pasion100% (1)
- Anaphy Lab NotesDocument8 pagesAnaphy Lab NotesDudil GoatNo ratings yet
- Year 11 BiologyDocument27 pagesYear 11 Biologyvy9423400No ratings yet
- C15 Control and Co-OrdinationDocument71 pagesC15 Control and Co-OrdinationmilanlochamNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Biosci2Document32 pagesModule 2 - Biosci2Jahzel JacaNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Brain-Computer Interface Technologies: Accelerating Neuro-Technology for Human BenefitFrom EverandBrain-Computer Interface Technologies: Accelerating Neuro-Technology for Human BenefitNo ratings yet
- Somatosensory Teachers Manual: for Somatosensory Science FactsFrom EverandSomatosensory Teachers Manual: for Somatosensory Science FactsNo ratings yet
Nerve (Ganong)
Nerve (Ganong)
Uploaded by
swap07shrma02Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nerve (Ganong)
Nerve (Ganong)
Uploaded by
swap07shrma02Copyright:
Available Formats
Nerve (Ganong)
Monday, 14 October 2019 10:23 PM
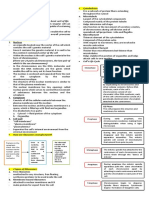
If the extracellular level of K+ is increased (hyperkalemia), the resting potential moves closer to the
threshold for eliciting an action potential and the neuron becomes more excitable. If the extracellular
level of K+ is decreased (hypokalemia), the membrane potential is reduced and the neuron is
hyperpolarized.
notably Ca2+, can affect the membrane potential through both channel movement and membrane
interactions. A decrease in extracellular Ca2+ concentration increases the excitability of nerve and
muscle cells by decreasing the amount of depolarization needed to initiate the changes in the Na+ and
K+ conductance that produce the action potential. Conversely, an increase in extracellular Ca2+
concentration can stabilize the membrane by reducing excitability
Local potential Action potential
Nature of Sub-threshold Threshold or supra
stimulus threshold
Types of Graded: depending on the strength of stimulus; May Fixes amplitude;
Potential change be positive or negative; excitatory or inhibitory Always positive
Propagation Conducted over short distance with a reduction of Conducted over entire
magnitude of potential cell membrane
Summation Can be summated Can not be summated.
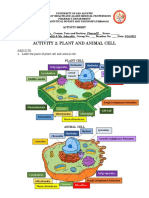
Astrocytes are found throughout the brain and are
subdivided into two groups. Fibrous astrocytes are
found primarily in white matter and contain many
intermediate filaments; protoplasmic astrocytes
are found in gray matter and have a granular
cytoplasm. Both types of astrocytes send processes
to blood vessels, where they induce capillaries to
form the tight junctions making up the blood-brain
barrier. They also send processes that envelop
synapses and the surface of nerve cells.
Protoplasmic astrocytes have a membrane
potential that varies with the external K+
concentration but do not generate propagated
potentials. They produce substances that are tropic
to neurons, and they help maintain the appropriate
concentration of ions and neurotransmitters by
taking up K+ and the neurotransmitters glutamate
and γ-aminobutyrate (GABA
You might also like
- SB2a Mitosis 1. SB2b Growth in Animals SB2c Growth in PlantsDocument4 pagesSB2a Mitosis 1. SB2b Growth in Animals SB2c Growth in PlantsSiaNo ratings yet
- St. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: Block 1Document9 pagesSt. Luke's College of Medicine - William H. Quasha Memorial: Block 1Mavic Villanueva100% (1)
- Year7ScienceHomeLearning Cycle9Document11 pagesYear7ScienceHomeLearning Cycle9Jayasri JeevaNo ratings yet
- Proximate Tissue InductionDocument5 pagesProximate Tissue InductionMigs MedinaNo ratings yet
- Guide Questions Answers: Muscles Contract, They Contribute To Gross and FineDocument7 pagesGuide Questions Answers: Muscles Contract, They Contribute To Gross and FinePrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Revised Introduction To The Pharmacology of CNS DrugsDocument9 pagesRevised Introduction To The Pharmacology of CNS DrugsJoshua Ty CayetanoNo ratings yet
- Physiology: Table 1. Distinguishing Properties of Electrical and Chemical SynapsesDocument5 pagesPhysiology: Table 1. Distinguishing Properties of Electrical and Chemical SynapsesMavic VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 3 PDFDocument8 pagesWorksheet 3 PDFjung minsuckNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Mitosis and MeiosisDocument19 pagesUnit 2 Mitosis and MeiosisErnest TolentinoNo ratings yet
- B4.1 - Cell Structure (Combined Science) : The Central Vacuole Maintains Turgor Pressure Against The Cell WallDocument1 pageB4.1 - Cell Structure (Combined Science) : The Central Vacuole Maintains Turgor Pressure Against The Cell WallNazimNo ratings yet
- 1 Hist Sept 13 HL11 Nerve Tissuestudent2020Document43 pages1 Hist Sept 13 HL11 Nerve Tissuestudent2020n-gorNo ratings yet
- 2nd HandoutDocument6 pages2nd HandoutMa FheNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Cell Structure Practice (1) - 3Document3 pagesKami Export - Cell Structure Practice (1) - 3Achionta NandyNo ratings yet
- The Dynamic SynapseDocument13 pagesThe Dynamic SynapseHucomanserNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document16 pagesChapter 1rida ikramNo ratings yet
- Human HistologyDocument5 pagesHuman Histologyشمس عقيل سالم C2No ratings yet
- Year 9 Revision BookletDocument17 pagesYear 9 Revision BookletmrsfarahnaazNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Parts 1 Amd 2 HBDocument27 pagesTopic 1 Parts 1 Amd 2 HBazankha1990No ratings yet
- Topic 1 Cell BiologyDocument2 pagesTopic 1 Cell BiologyEklavya GuptaNo ratings yet
- The Nervous TissueDocument29 pagesThe Nervous TissueRO OMNo ratings yet
- Midtern LabDocument21 pagesMidtern LabJustine Mae OyongNo ratings yet
- LabEx4 - Eukaryotic CellDocument7 pagesLabEx4 - Eukaryotic Cellrjdc972No ratings yet
- Pidlaoan, Coleen - Cell Structure PracticeDocument5 pagesPidlaoan, Coleen - Cell Structure PracticeColeenNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: ReinforcementDocument2 pagesAnswer Key: ReinforcementCherifa AbdallahNo ratings yet
- Week 4 Genral Biology 1Document3 pagesWeek 4 Genral Biology 1Spade ObusaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lec - Quiz 1 HandoutsDocument7 pagesGenetics Lec - Quiz 1 Handoutsvada_soNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 CellsDocument1 pageTopic 2 CellsKandy Anne Castillo AbuanNo ratings yet
- AS Biology Revision Pack UNIT 2Document16 pagesAS Biology Revision Pack UNIT 2George Noorland100% (2)
- Cell The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument54 pagesCell The Fundamental Unit of LifeAxyahh 99No ratings yet
- CH2 Mitosis and MeiosisDocument4 pagesCH2 Mitosis and MeiosisHaqua HerminiumNo ratings yet
- Types of CellsDocument5 pagesTypes of Cellsmalika.ahmed.sNo ratings yet
- 101lyb w6 Dayot ZaballeroDocument14 pages101lyb w6 Dayot ZaballeroMichael ZaballeroNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 BioP Notes - 090340Document13 pagesCHAPTER 3 BioP Notes - 090340Kate PedritaNo ratings yet
- Chap OutlineDocument8 pagesChap OutlinedurrieNo ratings yet
- Glial Cells Its FunctionDocument1 pageGlial Cells Its Functiongebrewahidbiniam75No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Neuroscience and Behavior, Myers 8e PsychologyDocument30 pagesChapter 2 Neuroscience and Behavior, Myers 8e Psychologymrchubs100% (14)
- BCHE4040 2023 Lecture 5B (Sept 21)Document24 pagesBCHE4040 2023 Lecture 5B (Sept 21)2K FaustusNo ratings yet
- Neural Control & Coordination PowernotesDocument2 pagesNeural Control & Coordination PowernotesSushmit Srivastava100% (1)
- (PSY 304) Chapter 1 - Nerve Cells and Nerve ImpulsesDocument9 pages(PSY 304) Chapter 1 - Nerve Cells and Nerve ImpulsesJJJJJJJJJNo ratings yet
- Ph1F1-PhBioSCi1a-Activity 2-Individual-GloriaDocument7 pagesPh1F1-PhBioSCi1a-Activity 2-Individual-GloriaAllysa GloriaNo ratings yet
- Neurons NervousDocument10 pagesNeurons NervousAldi RegarNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument2 pagesMitosisKimberly DalagNo ratings yet
- AP Bio Cell CommunicationDocument60 pagesAP Bio Cell CommunicationLavinia DonaldNo ratings yet
- Science Revision Chapter 1 -Year 7Document40 pagesScience Revision Chapter 1 -Year 7MUHAMMAD HAFIZUDDIN BIN KAMARULLZAMAN MoeNo ratings yet
- Cell Communication: AP BiologyDocument60 pagesCell Communication: AP BiologyVanessa SunadaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument37 pagesNervous SystemShriram100% (2)
- Exercise 2 Mitosis and MeiosisDocument5 pagesExercise 2 Mitosis and MeiosisRichelle MasingNo ratings yet
- Bmat Biology KnowledgeDocument22 pagesBmat Biology KnowledgeAngel SyNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument7 pagesConnective TissueSheena Pasion100% (1)
- Anaphy Lab NotesDocument8 pagesAnaphy Lab NotesDudil GoatNo ratings yet
- Year 11 BiologyDocument27 pagesYear 11 Biologyvy9423400No ratings yet
- C15 Control and Co-OrdinationDocument71 pagesC15 Control and Co-OrdinationmilanlochamNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Biosci2Document32 pagesModule 2 - Biosci2Jahzel JacaNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Brain-Computer Interface Technologies: Accelerating Neuro-Technology for Human BenefitFrom EverandBrain-Computer Interface Technologies: Accelerating Neuro-Technology for Human BenefitNo ratings yet
- Somatosensory Teachers Manual: for Somatosensory Science FactsFrom EverandSomatosensory Teachers Manual: for Somatosensory Science FactsNo ratings yet