Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Product Management: Assignment
Product Management: Assignment
Uploaded by
Rohan KumarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Product Management: Assignment
Product Management: Assignment
Uploaded by
Rohan KumarCopyright:
Available Formats
Product Management
Assignment
9/26/2011 VVISM Hyderabad Rohan
1|Page
Questions
1. Explain levels of a product with a suitable example. 2. What are the various stages of new product development? 3. Define PLC. Bring out significance of each stage. 4. What's product line? Why packaging is called silent salesman? 5. Elaborate on idea generation techniques. 6. What is innovation? Why firms have to innovate? 7. Explain the significance of BCG matrix. 8. Why do new products fail? Justify with suitable example.
2|Page
1. Explain levels of a product with a suitable example.
Product levels are classified into three parts: 1. Core Product. The CORE product is NOT the tangible, physical product. You can't touch it. That's because the core product is the BENEFIT of the product that makes it valuable to you. So with the car example, the benefit is convenience i.e. the ease at which you can go where you like, when you want to. Another core benefit is speed since you can travel around relatively quickly. 2. Actual product. The ACTUAL product is the tangible, physical product. You can get some use out of it. Again with the car example, it is the vehicle that you test drive, buy and then collect. 3. Augmented product. The AUGMENTED product is the non-physical part of the product. It usually consists of lots of added value, for which you may or may not pay a premium. So when you buy a car, part of the augmented product would be the warranty, the customer service support offered by the car's manufacture, and any after-sales service.
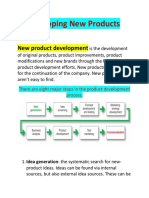
2. What are the various stages of new product development?
Ans. The complete process of bringing a new product to market. A product is a set of benefits offered for exchange and can be tangible (that is, something physical you can touch) or intangible (like a service, experience, or belief). There are two parallel paths involved in the NPD process: one involves the idea generation, product design and detail engineering; the other involves market research and marketing analysis. Companies typically see new product development as the first stage in generating and commercializing new products within the overall strategic process of product life cycle management used to maintain or grow their market share.
The process 1. Idea Generation
o
Ideas for new products can be obtained from basic research using a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities & Threats), Market and
3|Page
consumer trends, company's R&D department, competitors, focus groups, employees, salespeople, corporate spies, trade shows, or Ethnographic discovery methods (searching for user patterns and habits) may also be used to get an insight into new product lines or product features. 2. Idea Screening
o
The object is to eliminate unsound concepts prior to devoting resources to them.
3. Concept Development and Testing
o o
Develop the marketing and engineering details Testing the Concept by asking a sample of prospective customers what they think of the idea. Usually via Choice Modeling.
4. Business Analysis
o
Estimate likely selling price based upon competition and customer feedback.
Beta Testing and Market Testing
o o
Produce a physical prototype or mock-up Test the product (and its packaging) in typical usage situations
5. Technical Implementation
o o o
New program initiation Finalize Quality management system Resource estimation
6. Commercialization (often considered post-NPD)
o o
Launch the product Produce and place advertisements and other promotions
7. New Product Pricing
o o
Impact of new product on the entire product portfolio Value Analysis (internal & external)
4|Page
3. Define
PLC. Bring out significance of each stage.
Product life-cycle (PLC) like human beings, products also have a life-cycle. From birth to death, human beings pass through various stages e.g. birth, growth, maturity, decline and death. A similar life-cycle is seen in the case of products. The product life cycle goes through multiple phases, involves many professional disciplines, and requires many skills, tools and processes. Product life cycle (PLC) has to do with the life of a product in the market with respect to business/commercial costs and sales measures. To say that a product has a life cycle is to assert three things:
Products have a limited life, Product sales pass through distinct stages, each posing different challenges, opportunities, and problems to the seller,
Products require different marketing, financing, manufacturing, purchasing, and human resource strategies in each life cycle stage.
The four main stages of a product's life cycle and the accompanying characteristics are: Stage Characteristics 1. Market introduction stage 1. costs are very high 2. slow sales volumes to start 3. little or no competition 4. demand has to be created 5. customers have to be prompted to try the product 6. makes no money at this stage 2. Growth stage 1. costs reduced due to economies of scale 2. sales volume increases significantly 3. profitability begins to rise
5|Page
4. public awareness increases 5. competition begins to increase with a few new players in establishing market 6. increased competition leads to price decreases 3. Maturity stage 1. costs are lowered as a result of production volumes increasing and experience curve effects 2. sales volume peaks and market saturation is reached 3. increase in competitors entering the market 4. prices tend to drop due to the proliferation of competing products 5. brand differentiation and feature diversification is emphasized to maintain or increase market share 6. Industrial profits go down 4. Saturation and decline stage 1. costs become counter-optimal 2. sales volume decline 3. prices, profitability diminish 4. Profit becomes more a challenge of production/distribution efficiency than increased sales.
5. What's product line? Why packaging is called silent salesman?
A product line refers to a number of products that are related and developed by the same manufacturer. Product lines are not to be confused with product bundling, which combines various items into one type of product. Items within a product line generally share the same basic theme, and with the help of a successful marketing plan these products can be entirely effective. Frequently, a product line includes different products that are offered to the public at varying price points. This way, a manufacturer or company can ensure that all products within
6|Page
a line will be purchased by all kinds of people. Product line extension refers to any additional products that may be added to a current product line. Packaging acts as a silent Sales person. In today's marketplace a good package design must differentiate a product from the masses on the retail shelf, increase sales volume in flat market categories and provide the consumer with a positive experience. The packaging is the silent salesperson sitting next to the competition. As we know, your packaging must not only get busy consumers attention, but scream buy me' as they pass by. Today's packaging designers and marketers are breaking away from tradition and designing new packaging for a world that is dramatically different from the past. Modern consumers are on the go and think in modern terms. Designers must not remain stuck in the past, but look to the future. Products and packaging that project a forward-looking image and philosophy will be successful.
6. Elaborate on idea generation techniques.
The different techniques of idea generation areModifying Techniques
Three idea-generation techniques that emphasize the Modifying style are Force-field, Attribute listing, and SCAMPER. Use these techniques when you want to generate ideas that build on what is already known and when you want to develop versatility with this style.
Force-field Attribute listing "SCAMPER"
Experimenting Techniques
Three idea-generation techniques that emphasize the Experimenting style are Matrix analysis, Morphological Analysis, and Alternate scenarios. Use these techniques when you want to
7|Page
generate ideas that combine different elements in new ways and when you want to develop versatility with this style.
Matrix analysis Morphological Analysis Alternate scenarios
Visioning Techniques
Three idea-generation techniques that emphasize the Visioning style are Alter-ego, History of the future, and Vision circle. Use these techniques when you want to generate ideas by creating a mental picture of an ideal future and when you want to develop versatility with this style.
Alter-ego History of the future Vision circle
Exploring Techniques
Three idea-generation techniques that emphasize the Exploring style are Analogy, Nature symbol, and Dreaming. Use these techniques when you want to generate ideas using metaphors, symbols and analogies and when you want to develop versatility with this style.
Guided imagery Nature symbol Forced association
6. What is innovation? Why firms have to innovate?
The term innovation derives from the Latin word innovatus, which is the noun form of innovare "to renew or change," stemming from in-"into" novus-"new". Although the term is broadly used, innovation
8|Page generally refers to the creation of better or more effective products, processes, technologies, or ideas that are accepted by markets, governments, and society. Innovation differs from invention or renovation in that innovation generally signifies a substantial positive change compared to incremental changes. Firms need to innovate because we in live in a world which is very dynamic and the taste and preferences of the customers are changing fast, people are expecting new product innovations to match their requirements. To remain competitive in the market and earn more profits firms are continuously working on product innovation, they have a dedicated department within them called as Research & development which is working on product innovation night & day.
7. Explain the significance of BCG matrix.
This technique is particularly useful for multi-divisional or multiproduct companies. The divisions or products compromise the organizations business portfolio. The composition of the portfolio can be critical to the growth and success of the company. The BCG matrix considers two variables, namely1. MARKET GROWTH RATE 2. RELATIVE MARKET SHARE
The market growth rate is shown on the vertical (y) axis and is expressed as a %. The range is set somewhat arbitrarily. The overhead shows a range of 0 to 20% with division between low And high growth at 10% (the original work by B Headley Strategy and the business portfolio, Long Range Planning, Feb 1977 used these criteria). Inflation and/or Gross National Product have some impact on the range and thus the vertical axis can be modified to represent an index where the dividing line between low and high growth is at 1.0. Industries expanding faster than inflation or GNP would show above the line and those growing at less than inflation or GNP would be classed as low growth and show below the line. The horizontal (x) axis shows relative market share. The share is calculated by reference to the largest competitor in the market. Again the range and division between high and low shares is arbitrary. The original work used a scale of 0.1, i.e. market leadership occurs when the relative market share exceeds 1.0.The BCG
9|Page
growth/share matrix is divided into four cells or quadrants, each of which represent a particular type of business. Divisions or products are represented by circles. The size of the circle reflects the relative significance of the division/product to group sales. A development of the matrix is to reflect the relative profit contribution of each division and this is shown as a pie segment within the circle.
8. Why do new products fail? Justify with suitable example.
The main reasons why new products fail are-
1. Faulty product idea 2. Distribution related problems 3. Poor timing of launch 4. Improper Positioning Other reasons may-be
* Lack of differential advantage * Poor planning * Technical problems in the product * Competitors fighting back harder than expected * Poor market research
Some of the examples of product failure are-
Kelloggs failed miserably in India in the beginning. Mercedes Benz failed to impress Indians with the E-class Sedan in 1997. MTV with its Western music offerings was not impressive in the initial years. Whirlpool had launched the larger sized refrigerators which was not popular amongst Indians.
You might also like
- Kalyan Jewellers HSBC 3oct2022Document33 pagesKalyan Jewellers HSBC 3oct2022Ankk Tenderz100% (1)
- Nike Environmental Analysis 1216536910789066 8Document26 pagesNike Environmental Analysis 1216536910789066 8Re YaNo ratings yet
- Scott Financial Accounting Theory Chapter 2Document18 pagesScott Financial Accounting Theory Chapter 2Diny Fariha ZakhirNo ratings yet
- Tech and InnovationDocument6 pagesTech and InnovationChristopherNo ratings yet
- CH 04 Product & Service ConceptDocument8 pagesCH 04 Product & Service ConceptWondmageneUrgessaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Class 1Document9 pagesWeek 6 Class 1Abrar YasinNo ratings yet
- NPD & PLC StrategiesDocument4 pagesNPD & PLC StrategiesHamza NaeemNo ratings yet
- Mkt243-Chapter 6Document9 pagesMkt243-Chapter 6Bibi Shafiqah Akbar ShahNo ratings yet
- The Idea Generation ProcessDocument26 pagesThe Idea Generation ProcessDaud ShafeeqNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6Document9 pagesTutorial 6FADZLIN SYAFIQAHNo ratings yet
- Name. Moin Khan Roll No. 12 Subject. International Business Assignment No.3 Submitted To .Sir Zafar IqbalDocument6 pagesName. Moin Khan Roll No. 12 Subject. International Business Assignment No.3 Submitted To .Sir Zafar IqbalMoin KhanNo ratings yet
- Tatanexon New Product DevelopmentDocument29 pagesTatanexon New Product DevelopmentGAURAV SHARMA100% (1)
- Chapter 19 The Marketing Mix Product and PackagingDocument4 pagesChapter 19 The Marketing Mix Product and PackagingVincent ChurchillNo ratings yet
- Product Development: Development (NPD), The Discipline Is Focused On Developing Systematic MethodsDocument9 pagesProduct Development: Development (NPD), The Discipline Is Focused On Developing Systematic MethodsKaranjit NathNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 IMDocument38 pagesUnit 3 IMMOHAMMAD ZUBERNo ratings yet
- Product DevelopmentDocument41 pagesProduct DevelopmentJohn Rey SR SoveranoNo ratings yet
- Alice Nail Polish Proect 2nd Term...Document52 pagesAlice Nail Polish Proect 2nd Term...Samara Simba Colge67% (3)
- Product Life Cycle 1. Introduction StageDocument49 pagesProduct Life Cycle 1. Introduction StageanushkaNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Handout PDFDocument7 pagesWeek 6 Handout PDFkiks fernsNo ratings yet
- New Product Development and Managing Innovation VDFFDDVDDocument13 pagesNew Product Development and Managing Innovation VDFFDDVDNehaNo ratings yet
- 3 Module Eng PDFDocument32 pages3 Module Eng PDFMist FactorNo ratings yet
- IBM-mte TopicsDocument15 pagesIBM-mte Topicsomkar kumarNo ratings yet
- FinalpdndDocument32 pagesFinalpdndPulkit Garg100% (1)
- 1) Explain The Various Stages of NPD: New Product Development StagesDocument33 pages1) Explain The Various Stages of NPD: New Product Development StagesROHITNo ratings yet
- IM 4th SemDocument20 pagesIM 4th Semdarthvader005No ratings yet
- BAMK1205 - Ch4 - Topic 4Document21 pagesBAMK1205 - Ch4 - Topic 4bashairNo ratings yet
- Study Session 4 - Classifications of Innovation in BusinessesDocument15 pagesStudy Session 4 - Classifications of Innovation in BusinessesMariam OdusolaNo ratings yet
- New Product DevelopmentDocument15 pagesNew Product DevelopmentRasmi RanjanNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 - Product DecisionsDocument39 pagesChap 1 - Product Decisions2852 Takmoge AdityaNo ratings yet
- Marketing SubjectDocument38 pagesMarketing SubjectshivakeerthanNo ratings yet
- MKT 380 - Test 1 Review QuestionsDocument6 pagesMKT 380 - Test 1 Review QuestionsShannon UeberflussNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Class 2Document5 pagesWeek 6 Class 2Abrar YasinNo ratings yet
- International Product Development Strategy: Few ExampleDocument20 pagesInternational Product Development Strategy: Few ExamplePankaj MishraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Product/Service DevelopmentDocument11 pagesChapter 4: Product/Service Developmentfeyeko aberaNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument10 pagesProduct Life CycleibeNo ratings yet
- Product Planning and DevelopmentDocument5 pagesProduct Planning and Developmentbabunaidu2006No ratings yet
- PRODUCTDocument6 pagesPRODUCTAbhishek SinhaNo ratings yet
- CH 9 New Product and Product LifecycleDocument4 pagesCH 9 New Product and Product LifecycleFatima AsifNo ratings yet
- New Product Development ProcessDocument33 pagesNew Product Development Processvinaycool12344150100% (1)
- New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesDocument59 pagesNew Product Development and Product Life-Cycle StrategiesSarahNo ratings yet
- Product Life CycleDocument6 pagesProduct Life CycleJosé Alfredo Moreno Jr.No ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle:: Group MembersDocument18 pagesProduct Life Cycle:: Group MembersimykoNo ratings yet
- New Product Development and Product Life CycleDocument14 pagesNew Product Development and Product Life Cyclebhagshard05No ratings yet
- Week 10 Module 6 Product DevelopmentDocument25 pagesWeek 10 Module 6 Product DevelopmentHyunrii ParkNo ratings yet
- New Product Steps and LifecycleDocument3 pagesNew Product Steps and LifecycleMd. Ziawr RahmanNo ratings yet
- Marketing ManagementDocument15 pagesMarketing Managementyatinthukral758545No ratings yet
- New Product Development and Challenges Report Final DraftDocument21 pagesNew Product Development and Challenges Report Final DraftUzma SalmanNo ratings yet
- The New Product Development ProcessDocument5 pagesThe New Product Development Processkhalid100% (1)
- KNC-Design Thinking Skills-UNIT-1Document27 pagesKNC-Design Thinking Skills-UNIT-1Rohit kumarNo ratings yet
- Product and Brand MGT Unit 1Document22 pagesProduct and Brand MGT Unit 1Muskan ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- PRP 111 Chapter 9 Notes Week 9Document8 pagesPRP 111 Chapter 9 Notes Week 9Selen BİLGİNER HALEFOĞLUNo ratings yet
- Bba1styrmarketing U-3Document6 pagesBba1styrmarketing U-3Md FerozNo ratings yet
- MARKETING MANG NOTES Unit-3 AKTUDocument18 pagesMARKETING MANG NOTES Unit-3 AKTURUBA NASIMNo ratings yet
- MGT303Document18 pagesMGT303KELVIN KWESI HOWARDNo ratings yet
- Marketing Lesson 6Document5 pagesMarketing Lesson 6Shanley Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Product and Brand ManagementDocument172 pagesProduct and Brand ManagementfarhatafajaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management: 1. Idea GenerationDocument8 pagesMarketing Management: 1. Idea GenerationShakshi kediaNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship 12 Q2 Week 2Document11 pagesEntrepreneurship 12 Q2 Week 2Dariel LayogNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Product Design - 1676004757 - 1709702419Document14 pagesUnit 1 - Product Design - 1676004757 - 1709702419Praveen LobaniyaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - ProductDocument7 pagesLesson 6 - ProductShanley Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Dealing with Darwin (Review and Analysis of Moore's Book)From EverandDealing with Darwin (Review and Analysis of Moore's Book)No ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting - NCG Pre Final Question PaperDocument4 pagesAdvanced Accounting - NCG Pre Final Question PaperKarthikeya PeddhaboinaNo ratings yet
- Hudson's Bay Company Announces Pricing of Initial Public OfferingDocument3 pagesHudson's Bay Company Announces Pricing of Initial Public OfferingHarshal NaikNo ratings yet
- Export Pricing DecisionDocument24 pagesExport Pricing DecisionZeeshan KhanNo ratings yet
- Walmart SM Group4Document3 pagesWalmart SM Group4AmberNo ratings yet
- ChatLog Affiliate Marketing by MR Saleem Ahrar 2022 - 05 - 07 06 - 32Document5 pagesChatLog Affiliate Marketing by MR Saleem Ahrar 2022 - 05 - 07 06 - 32Tooba ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- TDC Case FinalDocument3 pagesTDC Case Finalbjefferson21No ratings yet
- Case Study-Heritage FurnitureDocument2 pagesCase Study-Heritage FurnitureShubham PawarNo ratings yet
- Sales Management-Chapter 6Document26 pagesSales Management-Chapter 6furqaan tahirNo ratings yet
- Monopolystic CompetitionDocument4 pagesMonopolystic CompetitionKrishna KediaNo ratings yet
- Ashish Krushi Kendra - Te 22-23 3-29-12-2022Document1 pageAshish Krushi Kendra - Te 22-23 3-29-12-2022Kajal PardhiNo ratings yet
- Term Test 1 (Sol.)Document5 pagesTerm Test 1 (Sol.)iamneonkingNo ratings yet
- Training Program For Bhutan Engineers (Civil DEPT) PDFDocument1 pageTraining Program For Bhutan Engineers (Civil DEPT) PDFsuresh babujiNo ratings yet
- Haagen Dazs Group CaseDocument8 pagesHaagen Dazs Group CaseDashmeet KaurNo ratings yet
- CH 5 SlidesDocument36 pagesCH 5 SlidesTooba IshaqueNo ratings yet
- Unit Temporal Evolution of Ancient, Modern, Pre-Industrial and Industrial CitiesDocument11 pagesUnit Temporal Evolution of Ancient, Modern, Pre-Industrial and Industrial CitiesPooja AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Tax Receipt Transport Department, Government of Odisha Registration Authority BALASORE RTO, OdishaDocument1 pageTax Receipt Transport Department, Government of Odisha Registration Authority BALASORE RTO, OdishaDibyajyoti DasNo ratings yet
- Mostafa Oil LTDDocument21 pagesMostafa Oil LTDNafisa Tausif AhmedNo ratings yet
- A Study On Customer Satisfaction Analysis On Digital Marketing at Amazon in AnanthapurDocument9 pagesA Study On Customer Satisfaction Analysis On Digital Marketing at Amazon in AnanthapurEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Current LiabilityDocument1 pageCurrent LiabilitySeunghyun ParkNo ratings yet
- Aleena Amir EM Quiz 7Document3 pagesAleena Amir EM Quiz 7Aleena AmirNo ratings yet
- Applied Eco - PPT Module 3Document25 pagesApplied Eco - PPT Module 3Bernardita Sison-CruzNo ratings yet
- Sip PresentationDocument13 pagesSip Presentationvivekvmathew87No ratings yet
- How Does The Stock Market WorkDocument16 pagesHow Does The Stock Market WorkAl-MuktadirNo ratings yet
- Giant Consumer ProductsDocument9 pagesGiant Consumer ProductsPriyank BavishiNo ratings yet
- Term Paper Digital Marketing Term PaperDocument4 pagesTerm Paper Digital Marketing Term PaperJonathan Jezreel InocencioNo ratings yet
- Wealth-Lab Developer 6.9 Performance: Strategy: Channel Breakout VT Dataset/Symbol: AALDocument1 pageWealth-Lab Developer 6.9 Performance: Strategy: Channel Breakout VT Dataset/Symbol: AALHamahid pourNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document57 pagesLecture 1Zixin GuNo ratings yet