Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Population, Sample and Sampling Methods
Population, Sample and Sampling Methods
Uploaded by
Mayra MartinezOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Population, Sample and Sampling Methods
Population, Sample and Sampling Methods
Uploaded by
Mayra MartinezCopyright:
Available Formats
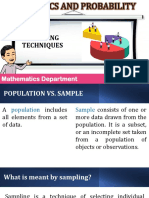
SAMPLE POPULATION
GROUP #3 Sample is a smaller set of data
that a researcher chooses or Population in research refers to
selects from a larger population the entire group that you want
using a pre-defined selection to draw conclusions about.
method.
Non-Probability
PROBABILITY Sampling
SAMPLING
SAMPLING
This involves non-random
This involves random selection, selection based on convenience
allowing you to make strong or other criteria, allowing you
statistical inferences about the
whole group. METHODS to easily collect data.
Simple Random Sampling: Every member of the
Convenience Sampling: The sample is taken from
population has an equal chance of being selected.
a group of people easy to contact or to reach.
Systematic Sampling: Similar to simple random sampling,
Judgmental Sampling: The researcher selects the
but usually slightly easier to implement.
individuals to be included in the sample based on
Stratified Sampling: The population is divided into
their judgment.
subgroups (or strata) based on a specific characteristic.
Quota Sampling: The researcher ensures equal or
Then, a simple random sample is drawn from each
proportionate representation of subjects depending
subgroup.
on the trait of interest.
Cluster Sampling: researchers divide a population into
Snowball Sampling: Existing study subjects recruit
smaller groups known as clusters. They then randomly
future subjects from among their acquaintances.
select among these clusters to form a sample.
You might also like
- The Heaven On EarthDocument400 pagesThe Heaven On EarthValentimPiratNo ratings yet
- Imaging & Signalling: Topic NotesDocument32 pagesImaging & Signalling: Topic Notesapi-2545477230% (1)
- Sampling and Sampling Distribution - Part 1Document38 pagesSampling and Sampling Distribution - Part 1littlemakzmathNo ratings yet
- PR2 - Reviewer Learning JournalDocument2 pagesPR2 - Reviewer Learning JournalImee Kaye RodillaNo ratings yet
- PSS - Researcj Methodology FinalsDocument2 pagesPSS - Researcj Methodology FinalsRuthyNo ratings yet
- Types of Samples QVS.Q DATADocument4 pagesTypes of Samples QVS.Q DATAFirstylieNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument14 pagesReportNovy EbaratNo ratings yet
- 1 Random SamplingDocument24 pages1 Random SamplingeliNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument13 pagesSamplingOnycha SyNo ratings yet
- STATS ReviewerDocument3 pagesSTATS ReviewerDianne BarceloNo ratings yet
- Local Media5026080788931008114Document25 pagesLocal Media5026080788931008114Norsaifah AbduljalalNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Research Method Assignment (Summary) Instructor: DR - Rizwana Raseed Submitted By: Shahzaib Salim (56028)Document6 pagesQualitative Research Method Assignment (Summary) Instructor: DR - Rizwana Raseed Submitted By: Shahzaib Salim (56028)navin aslam jumaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Adv. & Mktg. Research)Document15 pagesChapter 4 (Adv. & Mktg. Research)ArushiNo ratings yet
- 5 - Non Probability Sampling - pr2Document9 pages5 - Non Probability Sampling - pr2Yerenika CalypseNo ratings yet
- Last Handour Research 2Document8 pagesLast Handour Research 2Maria ElizaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Statistical ThinkingDocument6 pagesStatistics and Statistical ThinkingMarietoni PallanNo ratings yet
- Methods of Sampling: Practical Research 1Document18 pagesMethods of Sampling: Practical Research 1Black&Grey StrongNo ratings yet
- Sampling TechniquesDocument4 pagesSampling TechniquesJANE MARIEL ATIENZANo ratings yet
- RMM 3Document18 pagesRMM 3porseenaNo ratings yet
- Content - Probability Vs Non-ProbabilityDocument3 pagesContent - Probability Vs Non-ProbabilityPankajNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 Instrument Sampling Interview DataAnalysisDocument44 pagesChapter3 Instrument Sampling Interview DataAnalysisJoy Ledesma Fabros DomingoNo ratings yet
- SamplingDocument34 pagesSamplingPulkit Sharma100% (1)
- Business Research Method: Census Vs SamplingDocument8 pagesBusiness Research Method: Census Vs SamplingPulkit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Sampling Techniques: by Fatima NaqviDocument23 pagesSampling Techniques: by Fatima NaqviDania AhmadNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument3 pagesBrochurenglc srzNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Population and SamplingDocument6 pagesModule 1 - Population and SamplingKanika1908No ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of Different Sampling Techniques: Gaganpreet SharmaDocument4 pagesPros and Cons of Different Sampling Techniques: Gaganpreet SharmaKyla RodriguezaNo ratings yet
- Sampling WorksheetDocument2 pagesSampling WorksheetMaedot HaddisNo ratings yet
- Basic Concepts in Sampling and Sampling TechniquesDocument22 pagesBasic Concepts in Sampling and Sampling TechniquesLeah Moyao-DonatoNo ratings yet
- Probability Sampling in ResearchDocument8 pagesProbability Sampling in Researchkeshav kumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Sampling Data Collection MethodsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 - Sampling Data Collection MethodsAdilah ShamsuddinNo ratings yet
- Sampling DistributionDocument22 pagesSampling DistributionMaria Fe DomondonNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics Assignment Sample, Sampling, Population Sample Sampling PopulationDocument3 pagesBiostatistics Assignment Sample, Sampling, Population Sample Sampling Populationsadaf jaan mohammadNo ratings yet
- L.sampling TechniqueDocument17 pagesL.sampling TechniqueTinTin EscosarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To StatisticsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To StatisticsRifat Hassan RabbyNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Sampling PDFDocument40 pagesWeek 7 Sampling PDFheyheyNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 8604-2Document23 pagesUnit 7 8604-2rabiaamin29No ratings yet
- Pros and Cons of Sampling-With-Cover-Page-V2Document5 pagesPros and Cons of Sampling-With-Cover-Page-V2musawar420No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 2 PDFparklong16No ratings yet
- Sampling ADocument31 pagesSampling Apatrick clarkeNo ratings yet
- Module 3Document15 pagesModule 3abejero22212550mNo ratings yet
- Sampling Techniques: Farqan Waheed M.Phil EducationDocument23 pagesSampling Techniques: Farqan Waheed M.Phil EducationIslam Din RahimoonNo ratings yet
- Types of SamplingDocument13 pagesTypes of SamplingROSHAN SAFREEN.T 18BBA123100% (1)
- Sampling Methodology: It Is Cheaper It Is FasterDocument5 pagesSampling Methodology: It Is Cheaper It Is FasterLaish Christle CapiendoNo ratings yet
- SAMPLING TECHNIQUES HandoutsDocument1 pageSAMPLING TECHNIQUES HandoutsMORENO BACONo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 Subjects or Respondents of The Study and Sampling TechniquesDocument3 pagesLesson 8 Subjects or Respondents of The Study and Sampling TechniquesMary Joyce GaliguerNo ratings yet
- Assignment Subject: Inferential Statistics Topic: Sampling Prepared By: Khawaja Danish Farooq Id: BB-26119 Submitted To: Ibadullah ChoudaryDocument6 pagesAssignment Subject: Inferential Statistics Topic: Sampling Prepared By: Khawaja Danish Farooq Id: BB-26119 Submitted To: Ibadullah ChoudaryDanish FarooqNo ratings yet
- 1 Random Sampling Parameter StatisticsDocument3 pages1 Random Sampling Parameter StatisticsWilliam RamosNo ratings yet
- Ch4 - Sampling DesignDocument40 pagesCh4 - Sampling Designshagun.2224mba1003No ratings yet
- Q:-Explain The Probability and Nonprobability Sampling TechniquesDocument3 pagesQ:-Explain The Probability and Nonprobability Sampling TechniquesSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Sampling TechniquesDocument27 pagesSampling TechniquesSheen Sta CruzNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mohd Amir Department of Management Uttaranchal UniversityDocument40 pagesDr. Mohd Amir Department of Management Uttaranchal UniversitySuhotra GuptaNo ratings yet
- Research Assignment: Name: Khadija Mahak Roll No - DPT02161019 Semester:9 Submitted To: Miss Sadia Date:23-4-2020Document7 pagesResearch Assignment: Name: Khadija Mahak Roll No - DPT02161019 Semester:9 Submitted To: Miss Sadia Date:23-4-2020Assiduous FacetiousNo ratings yet
- Sampling Design: Basic Concepts and Procedure: Sampling Frame. Known. Random SamplesDocument18 pagesSampling Design: Basic Concepts and Procedure: Sampling Frame. Known. Random SamplesJohn Aaron MirabelNo ratings yet
- Sampling Techiniques: Presenting by Athira R Archana VijayanDocument14 pagesSampling Techiniques: Presenting by Athira R Archana VijayanATHIRA RNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology: SamplingDocument31 pagesResearch Methodology: SamplingAyu MulyaniNo ratings yet
- Stats Reviewer CompleteDocument8 pagesStats Reviewer CompleteLewAndrewCortesNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Sampling TechniquesDocument34 pagesTopic 2 - Sampling TechniquesCarlyne Guiang FijerNo ratings yet
- Cluster SamplingDocument2 pagesCluster Samplingas gamingNo ratings yet
- Sampling IntroductionDocument18 pagesSampling IntroductionDivyaNo ratings yet
- MRM-Unit 3Document14 pagesMRM-Unit 3Rakshith gowda H DNo ratings yet
- Language VS DialectDocument1 pageLanguage VS DialectMayra MartinezNo ratings yet
- Group 3 - Mind Map About ResearchDocument1 pageGroup 3 - Mind Map About ResearchMayra MartinezNo ratings yet
- Group 8 - Communcative ApproachesDocument12 pagesGroup 8 - Communcative ApproachesMayra MartinezNo ratings yet
- Deductive and Inductive Approaches - Examples - Group 1Document5 pagesDeductive and Inductive Approaches - Examples - Group 1Mayra MartinezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3 Measures For Grouped DataDocument4 pagesAssignment 3 Measures For Grouped DataMayra MartinezNo ratings yet
- Tutoring Activity - Modals 25-Jan-2023Document1 pageTutoring Activity - Modals 25-Jan-2023Mayra MartinezNo ratings yet
- 2ND Conditional WorksheetDocument1 page2ND Conditional WorksheetMayra Martinez0% (1)
- Tutoring Activity - Be Going To - 04 Jan 2022 PDFDocument1 pageTutoring Activity - Be Going To - 04 Jan 2022 PDFMayra MartinezNo ratings yet
- Tutoring Activity - So Such Too Very (09-Jan-2023)Document1 pageTutoring Activity - So Such Too Very (09-Jan-2023)Mayra MartinezNo ratings yet
- Family Tree NamesDocument2 pagesFamily Tree NamesMayra MartinezNo ratings yet
- Writing Activity 1 (Autonomous Activity 13-Dec-2021)Document1 pageWriting Activity 1 (Autonomous Activity 13-Dec-2021)Mayra MartinezNo ratings yet
- Frequency Adverbs Practice (10-Jan-2023) PDFDocument1 pageFrequency Adverbs Practice (10-Jan-2023) PDFMayra MartinezNo ratings yet
- ML in Financial Crisis Prediction SurveyDocument16 pagesML in Financial Crisis Prediction SurveyNAGA KUMARI ODUGUNo ratings yet
- Rona Gabinete-Sta. Rita Nhs Action ResearchDocument20 pagesRona Gabinete-Sta. Rita Nhs Action Researchrona gabineteNo ratings yet
- Column Instrumentation BasicsDocument8 pagesColumn Instrumentation BasicsAmbuja SharmaNo ratings yet
- M408L Exam 2Document9 pagesM408L Exam 2Nathan ThaiNo ratings yet
- DQ 0 Hez 58 Lfca 4 VBPMK 4Document23 pagesDQ 0 Hez 58 Lfca 4 VBPMK 4api-3827500No ratings yet
- Math9 Quarter 1 Module 2 Final v3 1Document20 pagesMath9 Quarter 1 Module 2 Final v3 1MxxinneNo ratings yet
- Engineering 3A: Seive AnalysisDocument11 pagesEngineering 3A: Seive AnalysisCarl MigaelNo ratings yet
- SPM Add Maths Formula List Form5Document28 pagesSPM Add Maths Formula List Form5Sayantani GhoshNo ratings yet
- Exam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) : Grid Back EMF Time (S)Document10 pagesExam Electrical Machines and Drives (ET4117) : Grid Back EMF Time (S)chidoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Engineering InformaticsDocument15 pagesAdvanced Engineering InformaticsAstrid KumalaNo ratings yet
- Modeling Data in The Organization (Data Analysis)Document38 pagesModeling Data in The Organization (Data Analysis)Madiha Abu Saied Tazul Islam 1721217No ratings yet
- Wang2016 PDFDocument25 pagesWang2016 PDFCristina RacoareNo ratings yet
- XE324 Product Innovation and Management: DR Steve Plummer Principal Lecturer in ManufactureDocument55 pagesXE324 Product Innovation and Management: DR Steve Plummer Principal Lecturer in ManufactureKish ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Elastic Parameters of SoilsDocument12 pagesElastic Parameters of SoilsTomas Santiago Hanccoccallo PauccaraNo ratings yet
- A Compilation of Mastery Tests and Enrichment Activities in Math 411 (Differential Equation)Document35 pagesA Compilation of Mastery Tests and Enrichment Activities in Math 411 (Differential Equation)Jianne Mei VenturaNo ratings yet
- Solid Mensuration: PinoybixDocument10 pagesSolid Mensuration: PinoybixsbelodoNo ratings yet
- Chapter Four: Risk and ReturnDocument16 pagesChapter Four: Risk and ReturnTerefe DubeNo ratings yet
- Central Academy Senior Secondary School, ChittorgarhDocument9 pagesCentral Academy Senior Secondary School, ChittorgarhjubleeNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Modelling of The Effect of Human Learning in The Finite Production Inventory ModelDocument3 pagesMathematical Modelling of The Effect of Human Learning in The Finite Production Inventory ModelRenzo ErikssonNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Mapping ArticleDocument19 pagesCognitive Mapping Articleal60No ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument11 pagesReviewerMelliza Andrea BautistaNo ratings yet
- A12 Logarithms BP 9-22-14Document7 pagesA12 Logarithms BP 9-22-14aaoneNo ratings yet
- FAANG Puzzle CombineDocument40 pagesFAANG Puzzle CombineYASH VARDHANNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Test PaperDocument2 pagesThermodynamics Test PaperKrishnaKishoreReddyNo ratings yet
- Abenion, Nikka - System of Linear EquationDocument24 pagesAbenion, Nikka - System of Linear EquationNikka Ybañez Abenion - RosalesNo ratings yet
- Atv31 Mapa ModbusDocument56 pagesAtv31 Mapa ModbusOsoHonguitoMurteNo ratings yet
- Practical Process Control Textbook 20060612 PDFDocument296 pagesPractical Process Control Textbook 20060612 PDFMuhammad SabihNo ratings yet
- Genetic Algorithm For Solving The Economic Load DispatchDocument6 pagesGenetic Algorithm For Solving The Economic Load DispatchSatyendra Pratap SinghNo ratings yet