Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Phy1701 - Physics For - Engineers
Phy1701 - Physics For - Engineers
Uploaded by
rajubai630Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter2 - WorkedSolutions Ib Chemistry PearsonDocument8 pagesChapter2 - WorkedSolutions Ib Chemistry PearsonGowthamPodalaNo ratings yet
- A Lazy Layman's Guide To Quantum Physics PDFDocument6 pagesA Lazy Layman's Guide To Quantum Physics PDFFrancisco De AssisNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT I - 2023-24 - SEM II at UNIT I IIDocument3 pagesASSIGNMENT I - 2023-24 - SEM II at UNIT I IImagicianofgames518No ratings yet
- FY BTech - AS - Engineering Physics - SEM-I - Mar 2023Document3 pagesFY BTech - AS - Engineering Physics - SEM-I - Mar 2023kumbhalkarvalay8No ratings yet
- EEE3515 RI Mid-Term (Sec-F) Aut-2021Document2 pagesEEE3515 RI Mid-Term (Sec-F) Aut-2021riazNo ratings yet
- FT Model Papers 18EE52Document6 pagesFT Model Papers 18EE521DA19EE004 AMBUJ KUMAR MISHRANo ratings yet
- ST1 Set B N y Even 2023 24Document2 pagesST1 Set B N y Even 2023 24ARPITNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Atom - ExamDocument4 pagesStructure of The Atom - Examzehra giyoriNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Burdwan University Question PaperDocument2 pagesPHYSICS Burdwan University Question Paperb718535740No ratings yet
- Cbse 12th Question Bank PhysicsDocument6 pagesCbse 12th Question Bank Physicsramayodi223No ratings yet
- IAS Previous Year Test PapersDocument4 pagesIAS Previous Year Test PapersRavinder Singh100% (2)
- Rollno. Anna University (University Departments) B.E. (Full Time) - End Semester Examinations, Nov/Dec 2021Document3 pagesRollno. Anna University (University Departments) B.E. (Full Time) - End Semester Examinations, Nov/Dec 2021hihelloNo ratings yet
- Course Code: PHT 101 Itsj/Rw - 17 / 1007 First / Second Semester Bachelor of Engineering ExaminationDocument3 pagesCourse Code: PHT 101 Itsj/Rw - 17 / 1007 First / Second Semester Bachelor of Engineering ExaminationFightingNo ratings yet
- PhysicsQPSet2 48210Document5 pagesPhysicsQPSet2 48210sanjeev bishnoiNo ratings yet
- Physics Exclusive Sample Paper With SolutionDocument25 pagesPhysics Exclusive Sample Paper With SolutionA KNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2011 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4Document6 pagesCBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2011 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4Chandan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Phy Set-2 QPDocument5 pagesPhy Set-2 QPSiddhartha HadimaniNo ratings yet
- Class-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-2Document7 pagesClass-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-2kamali.v777No ratings yet
- Part A (2 Marks) : Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Model ExaminationDocument8 pagesPart A (2 Marks) : Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Model ExaminationdonavallishanmukasaiNo ratings yet
- CY4302Document2 pagesCY4302422399aak82No ratings yet
- FLT - Iii (2016-17)Document4 pagesFLT - Iii (2016-17)ChetanNo ratings yet
- S.S.Dav Public School, Khunti Sub:-Physics Second Mock Test Fm:-70Document4 pagesS.S.Dav Public School, Khunti Sub:-Physics Second Mock Test Fm:-70sharique alamNo ratings yet
- Mid1 EEE SMHMDocument4 pagesMid1 EEE SMHMeesaikumar039No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper 2015 Physics Set 1Document9 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper 2015 Physics Set 1PallavNo ratings yet
- TPH 201 As01Document1 pageTPH 201 As01TRiO TriKALNo ratings yet
- B-1111-Final ExamPhysics1 - HK222 - DethiDocument3 pagesB-1111-Final ExamPhysics1 - HK222 - DethiNhật Thanh TôNo ratings yet
- EngineDocument3 pagesEngineHarshita GauravNo ratings yet
- @sachin - Sir - Physics: Version 2.ODocument9 pages@sachin - Sir - Physics: Version 2.OPrakharNo ratings yet
- FY BTech - AS - Physics Engineering Physics - Jan 2023Document2 pagesFY BTech - AS - Physics Engineering Physics - Jan 2023kumbhalkarvalay8No ratings yet
- Physics QP Common Pre BoardDocument8 pagesPhysics QP Common Pre Boardsiddharth.vivek2000No ratings yet
- Model Question Paper 2022-23 Class Xii PhysicsDocument8 pagesModel Question Paper 2022-23 Class Xii PhysicsyuvanithanrNo ratings yet
- Awp (2022)Document2 pagesAwp (2022)souravchdhry029941No ratings yet
- Tom Mboya University College: SCH 202: Inorganic Chemistry I DATE: 16/12/2019 Time: 3 HoursDocument4 pagesTom Mboya University College: SCH 202: Inorganic Chemistry I DATE: 16/12/2019 Time: 3 HoursEZEKIEL IGOGONo ratings yet
- Xii-Board 3RD 33% Physics QP - 18.11.2023Document7 pagesXii-Board 3RD 33% Physics QP - 18.11.2023eashwarsiddhaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering College of Engineering ThalasseryDocument6 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering College of Engineering ThalasseryBinesh KannothNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice Paper - IIIDocument3 pagesPhysics Practice Paper - IIImehul yoNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term: ExaminationDocument2 pagesMid-Term: ExaminationrahulNo ratings yet
- MM: 70 TIME: 3h: Class - XII Subject - PhysicsDocument5 pagesMM: 70 TIME: 3h: Class - XII Subject - Physicspankajsharma1983No ratings yet
- Xii Second Pre Board Exam - Physics (15-02-2024)Document7 pagesXii Second Pre Board Exam - Physics (15-02-2024)siddhaarth2511No ratings yet
- Mid Sem QuestionsDocument7 pagesMid Sem Questionsdevashishkumar693No ratings yet
- ALL QB's PDFDocument36 pagesALL QB's PDFanimesh0gargNo ratings yet
- Cl-12 PHY Preboard-2 Set-1Document5 pagesCl-12 PHY Preboard-2 Set-1Extreme clashersNo ratings yet
- Phy EndsemDocument2 pagesPhy EndsemK04Anoushka TripathiNo ratings yet
- Phy 1701 - MTT - 1 3Document9 pagesPhy 1701 - MTT - 1 3Manoj GonuguntlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document5 pagesChapter 12ramcharanneeli4No ratings yet
- 2018jan R2Document14 pages2018jan R2nadiaNo ratings yet
- Paper - 4Document24 pagesPaper - 4Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- 2011 12 Lyp Physics 01Document60 pages2011 12 Lyp Physics 01abhishekprasad677No ratings yet
- Sample Papers SolvedDocument185 pagesSample Papers Solvedjovanbhaskaran10No ratings yet
- 1asp MergedDocument73 pages1asp MergedHarrison BennettNo ratings yet
- KV Sample Paper With SolutionDocument17 pagesKV Sample Paper With Solutionrohan gk gamingNo ratings yet
- Institute of Aeronautical EngineeringDocument5 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical EngineeringAshok BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom-hsslive-AnilDocument4 pagesStructure of Atom-hsslive-AnilDhana Aryal100% (1)
- Unit 6. Atomic Structure: Upon Successful Completion of This Unit, The Students Should Be Able ToDocument7 pagesUnit 6. Atomic Structure: Upon Successful Completion of This Unit, The Students Should Be Able TobillingsleyNo ratings yet
- Atoms & NucleiDocument15 pagesAtoms & NucleixkryxxzNo ratings yet
- Semester End Exam Question EEE 3621 AU 23 MSHDocument2 pagesSemester End Exam Question EEE 3621 AU 23 MSHnayma1621newazNo ratings yet
- Spring 2006 Qualifying Exam: - 34 - 34 B - 23 - 19 A 23 8 e - 31 P - 27 N - 27 0 - 11 C e - 12 0 - 7 2 0 0 2 - 11 3 2Document5 pagesSpring 2006 Qualifying Exam: - 34 - 34 B - 23 - 19 A 23 8 e - 31 P - 27 N - 27 0 - 11 C e - 12 0 - 7 2 0 0 2 - 11 3 2paimoNo ratings yet
- Review - 2018 - Final ExamDocument3 pagesReview - 2018 - Final ExamQuang LinhNo ratings yet
- ModelPapers MODELPAPER10 Physics12Document1 pageModelPapers MODELPAPER10 Physics12Maulik KarasaliyaNo ratings yet
- Exam EEE 2215 Electromagnetics I - 2013-2014 Latest August 2013-1Document16 pagesExam EEE 2215 Electromagnetics I - 2013-2014 Latest August 2013-1IAMMARKSNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Tunnel DiodeDocument23 pagesTunnel Diodeakhilesh3775% (4)
- Zener DiodeDocument13 pagesZener DiodePhenoमिनल IdiotsNo ratings yet
- EC111:Fundamental of Electronics Engineering: Assistant Professor, ECE DepartmentDocument51 pagesEC111:Fundamental of Electronics Engineering: Assistant Professor, ECE DepartmentrupeshNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument55 pagesAtomic StructureIndigo GroupNo ratings yet
- Preperation of CDS Quantum DotsDocument14 pagesPreperation of CDS Quantum Dots코발No ratings yet
- Dynamic-Light-Scattering - MDLDocument5 pagesDynamic-Light-Scattering - MDLJose Daniel Izquierdo MorenoNo ratings yet
- Fig. 62. Schematic Representation of Nc-Tin/A-Si N Nanocomposite Coating Consisting of Tin Nanocrystalline Phase Embedded in A-Si N Amorphous MatrixDocument3 pagesFig. 62. Schematic Representation of Nc-Tin/A-Si N Nanocomposite Coating Consisting of Tin Nanocrystalline Phase Embedded in A-Si N Amorphous MatrixAliakbar MonfaredNo ratings yet
- J.P. Wesley - Classical Quantum TheoryDocument6 pagesJ.P. Wesley - Classical Quantum TheoryJuiomSDFNo ratings yet
- XRD Lab Report 2 1Document3 pagesXRD Lab Report 2 1Aina SyaqinaNo ratings yet
- Shakeel Final Copy ThesisDocument81 pagesShakeel Final Copy ThesisshakelNo ratings yet
- Principles of Semiconductor Devices-L27Document24 pagesPrinciples of Semiconductor Devices-L27LIAKMANNo ratings yet
- 1 Fundamentals of Piezoelectricity: Lead-Free Piezoelectric MaterialsDocument18 pages1 Fundamentals of Piezoelectricity: Lead-Free Piezoelectric MaterialsJHNo ratings yet
- 02 - KristalografiDocument43 pages02 - KristalografiRoy Agus SalehNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 KKEE1133 SoalanDocument3 pagesTutorial 1 KKEE1133 SoalanAimanKPGNo ratings yet
- Chem 1008 Lab Midterms 2Document6 pagesChem 1008 Lab Midterms 2Jie Ann Faith AusmoloNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of MatterDocument11 pagesElectronic Structure of Matterangelic kvsbunNo ratings yet
- Pilani Campus: Birla Institute of Technology and Science, PilaniDocument2 pagesPilani Campus: Birla Institute of Technology and Science, PilaniANSHUMAN MISHRANo ratings yet
- VSEPR Lab Activity ANSWER KEY 1n4fw0dDocument5 pagesVSEPR Lab Activity ANSWER KEY 1n4fw0dalmira villarealNo ratings yet
- EE ESE PrelimsPaper 2020 RevisedDocument61 pagesEE ESE PrelimsPaper 2020 RevisedpksvampireNo ratings yet
- 1997, Angerer Et Al, APLDocument4 pages1997, Angerer Et Al, APLAbheek BardhanNo ratings yet
- Impact of Donor Traps On The 2deg and Electrical Behavior of Algan/Gan MisfetsDocument3 pagesImpact of Donor Traps On The 2deg and Electrical Behavior of Algan/Gan Misfetsankita6298No ratings yet
- Band Gap - PVEducationDocument3 pagesBand Gap - PVEducationRiazAhmadNo ratings yet
- NanochemistryDocument29 pagesNanochemistryTej Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Structure of Atom ppt2Document18 pagesClass 8 - Structure of Atom ppt2mau_chak5449No ratings yet
- 9.4 Giant Ionic StructuresDocument2 pages9.4 Giant Ionic StructureshadenluiNo ratings yet
- Laser Heating Effect On Raman Spectra of Si NanocrDocument6 pagesLaser Heating Effect On Raman Spectra of Si NanocrDani AmayaNo ratings yet
- Index: Modern Diffraction Methods, First Edition. Edited by Eric J. Mittemeijer and Udo WelzelDocument10 pagesIndex: Modern Diffraction Methods, First Edition. Edited by Eric J. Mittemeijer and Udo WelzelalkimiaNo ratings yet
Phy1701 - Physics For - Engineers
Phy1701 - Physics For - Engineers
Uploaded by
rajubai630Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Phy1701 - Physics For - Engineers
Phy1701 - Physics For - Engineers
Uploaded by
rajubai630Copyright:
Available Formats
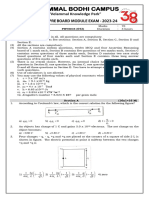
Name:
Enrolment No:
Recourse Examination – March 2023
Course: PHY1701 – PHYSICS FOR ENGINEERS
Programme: B.Tech. CSE Semester: I
Duration: 2 hrs. Max. Marks: 40
Instructions:
⮚ All Questions are compulsory.
⮚ Start each answer on a fresh page and number your answers clearly. Answer all parts of the same Question
together and in sequence.
⮚ Use of scientific calculators is permitted.
Section A (Total 10 Marks) Marks CO & BL
1. Find the relation between nearest neighbour distance and lattice constant in BCC and 2 CO1 & U
FCC structures.
2. Plot E vs. k graph and clearly show the forbidden energy gaps. 2 CO1 & U
3. An excited atom emits a photon in a spontaneous emission. The average time that CO1, CO2
-8
elapses between excitation of an atom and emission is 1.0×10 s. Using Heisenberg's 2 & U, AP
uncertainty principle, determine the uncertainty in the frequency of a photon.
4. What is the de Broglie wavelength of an electron traveling at a speed of 5×10 6 m/s? CO1, CO2
Compare this value with the wavelength of a proton which is 1836 times heavier than 2
the electron traveling at the same speed. & U, AP
5. Describe the working of step and graded index optical fibers using ray diagrams. 2 CO1 & U
Section B (Total 30 Marks) Marks CO & BL
6. A) Find the Miller Indices of a crystallographic plane that intersects the coordinate 1+2 CO1 & U
axes at a/3, b/2 and c/2 along x-, y-, and z-axis respectively. a, b and c are the lattice
parameters along the x-, y-, and z- axis respectively. Use neat sketches & steps to
explain. 2
B) Sketch the planes having Miller Indices (0 0 2) and (2 4 0).
7. A) Write the Schrödinger equation of motion for a free particle confined in a box CO1, CO2
(of infinite potential well) and derive the energy using the basic boundary 3
conditions. & U, AP
B) What does the Hamiltonian operator represent in the Schrödinger equation? 3
8. A) Discuss three different phases of liquid crystals.
B) What do you understand about holes in a semiconductor?
C) Current is allowed to flow along +x direction, field is applied along +z direction. Draw CO3 & U,
3+2+3
diagram to indicate the direction of the Hall field in (i) n-type semiconductor and (ii) AP
p-type semiconductor.
9. What is a wave function? Write the four basic requirements for a function to be an CO1 & U
acceptable wave function. 2+3
10. Draw the schematic diagram of He-Ne laser and the associated atomic level 2+1+1 CO1 & U
transitions. Label clearly the lasing transition of He-Ne laser. What is the purpose of
He in He-Ne laser? Write two advantages of He-Ne laser over Ruby laser. +2
You might also like
- Chapter2 - WorkedSolutions Ib Chemistry PearsonDocument8 pagesChapter2 - WorkedSolutions Ib Chemistry PearsonGowthamPodalaNo ratings yet
- A Lazy Layman's Guide To Quantum Physics PDFDocument6 pagesA Lazy Layman's Guide To Quantum Physics PDFFrancisco De AssisNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT I - 2023-24 - SEM II at UNIT I IIDocument3 pagesASSIGNMENT I - 2023-24 - SEM II at UNIT I IImagicianofgames518No ratings yet
- FY BTech - AS - Engineering Physics - SEM-I - Mar 2023Document3 pagesFY BTech - AS - Engineering Physics - SEM-I - Mar 2023kumbhalkarvalay8No ratings yet
- EEE3515 RI Mid-Term (Sec-F) Aut-2021Document2 pagesEEE3515 RI Mid-Term (Sec-F) Aut-2021riazNo ratings yet
- FT Model Papers 18EE52Document6 pagesFT Model Papers 18EE521DA19EE004 AMBUJ KUMAR MISHRANo ratings yet
- ST1 Set B N y Even 2023 24Document2 pagesST1 Set B N y Even 2023 24ARPITNo ratings yet
- Structure of The Atom - ExamDocument4 pagesStructure of The Atom - Examzehra giyoriNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS Burdwan University Question PaperDocument2 pagesPHYSICS Burdwan University Question Paperb718535740No ratings yet
- Cbse 12th Question Bank PhysicsDocument6 pagesCbse 12th Question Bank Physicsramayodi223No ratings yet
- IAS Previous Year Test PapersDocument4 pagesIAS Previous Year Test PapersRavinder Singh100% (2)
- Rollno. Anna University (University Departments) B.E. (Full Time) - End Semester Examinations, Nov/Dec 2021Document3 pagesRollno. Anna University (University Departments) B.E. (Full Time) - End Semester Examinations, Nov/Dec 2021hihelloNo ratings yet
- Course Code: PHT 101 Itsj/Rw - 17 / 1007 First / Second Semester Bachelor of Engineering ExaminationDocument3 pagesCourse Code: PHT 101 Itsj/Rw - 17 / 1007 First / Second Semester Bachelor of Engineering ExaminationFightingNo ratings yet
- PhysicsQPSet2 48210Document5 pagesPhysicsQPSet2 48210sanjeev bishnoiNo ratings yet
- Physics Exclusive Sample Paper With SolutionDocument25 pagesPhysics Exclusive Sample Paper With SolutionA KNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2011 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4Document6 pagesCBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2011 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4Chandan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Phy Set-2 QPDocument5 pagesPhy Set-2 QPSiddhartha HadimaniNo ratings yet
- Class-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-2Document7 pagesClass-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-2kamali.v777No ratings yet
- Part A (2 Marks) : Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Model ExaminationDocument8 pagesPart A (2 Marks) : Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Model ExaminationdonavallishanmukasaiNo ratings yet
- CY4302Document2 pagesCY4302422399aak82No ratings yet
- FLT - Iii (2016-17)Document4 pagesFLT - Iii (2016-17)ChetanNo ratings yet
- S.S.Dav Public School, Khunti Sub:-Physics Second Mock Test Fm:-70Document4 pagesS.S.Dav Public School, Khunti Sub:-Physics Second Mock Test Fm:-70sharique alamNo ratings yet
- Mid1 EEE SMHMDocument4 pagesMid1 EEE SMHMeesaikumar039No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Question Paper 2015 Physics Set 1Document9 pagesCBSE Class 12 Question Paper 2015 Physics Set 1PallavNo ratings yet
- TPH 201 As01Document1 pageTPH 201 As01TRiO TriKALNo ratings yet
- B-1111-Final ExamPhysics1 - HK222 - DethiDocument3 pagesB-1111-Final ExamPhysics1 - HK222 - DethiNhật Thanh TôNo ratings yet
- EngineDocument3 pagesEngineHarshita GauravNo ratings yet
- @sachin - Sir - Physics: Version 2.ODocument9 pages@sachin - Sir - Physics: Version 2.OPrakharNo ratings yet
- FY BTech - AS - Physics Engineering Physics - Jan 2023Document2 pagesFY BTech - AS - Physics Engineering Physics - Jan 2023kumbhalkarvalay8No ratings yet
- Physics QP Common Pre BoardDocument8 pagesPhysics QP Common Pre Boardsiddharth.vivek2000No ratings yet
- Model Question Paper 2022-23 Class Xii PhysicsDocument8 pagesModel Question Paper 2022-23 Class Xii PhysicsyuvanithanrNo ratings yet
- Awp (2022)Document2 pagesAwp (2022)souravchdhry029941No ratings yet
- Tom Mboya University College: SCH 202: Inorganic Chemistry I DATE: 16/12/2019 Time: 3 HoursDocument4 pagesTom Mboya University College: SCH 202: Inorganic Chemistry I DATE: 16/12/2019 Time: 3 HoursEZEKIEL IGOGONo ratings yet
- Xii-Board 3RD 33% Physics QP - 18.11.2023Document7 pagesXii-Board 3RD 33% Physics QP - 18.11.2023eashwarsiddhaNo ratings yet
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering College of Engineering ThalasseryDocument6 pagesDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering College of Engineering ThalasseryBinesh KannothNo ratings yet
- Physics Practice Paper - IIIDocument3 pagesPhysics Practice Paper - IIImehul yoNo ratings yet
- Mid-Term: ExaminationDocument2 pagesMid-Term: ExaminationrahulNo ratings yet
- MM: 70 TIME: 3h: Class - XII Subject - PhysicsDocument5 pagesMM: 70 TIME: 3h: Class - XII Subject - Physicspankajsharma1983No ratings yet
- Xii Second Pre Board Exam - Physics (15-02-2024)Document7 pagesXii Second Pre Board Exam - Physics (15-02-2024)siddhaarth2511No ratings yet
- Mid Sem QuestionsDocument7 pagesMid Sem Questionsdevashishkumar693No ratings yet
- ALL QB's PDFDocument36 pagesALL QB's PDFanimesh0gargNo ratings yet
- Cl-12 PHY Preboard-2 Set-1Document5 pagesCl-12 PHY Preboard-2 Set-1Extreme clashersNo ratings yet
- Phy EndsemDocument2 pagesPhy EndsemK04Anoushka TripathiNo ratings yet
- Phy 1701 - MTT - 1 3Document9 pagesPhy 1701 - MTT - 1 3Manoj GonuguntlaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document5 pagesChapter 12ramcharanneeli4No ratings yet
- 2018jan R2Document14 pages2018jan R2nadiaNo ratings yet
- Paper - 4Document24 pagesPaper - 4Sunil KumarNo ratings yet
- 2011 12 Lyp Physics 01Document60 pages2011 12 Lyp Physics 01abhishekprasad677No ratings yet
- Sample Papers SolvedDocument185 pagesSample Papers Solvedjovanbhaskaran10No ratings yet
- 1asp MergedDocument73 pages1asp MergedHarrison BennettNo ratings yet
- KV Sample Paper With SolutionDocument17 pagesKV Sample Paper With Solutionrohan gk gamingNo ratings yet
- Institute of Aeronautical EngineeringDocument5 pagesInstitute of Aeronautical EngineeringAshok BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Structure of Atom-hsslive-AnilDocument4 pagesStructure of Atom-hsslive-AnilDhana Aryal100% (1)
- Unit 6. Atomic Structure: Upon Successful Completion of This Unit, The Students Should Be Able ToDocument7 pagesUnit 6. Atomic Structure: Upon Successful Completion of This Unit, The Students Should Be Able TobillingsleyNo ratings yet
- Atoms & NucleiDocument15 pagesAtoms & NucleixkryxxzNo ratings yet
- Semester End Exam Question EEE 3621 AU 23 MSHDocument2 pagesSemester End Exam Question EEE 3621 AU 23 MSHnayma1621newazNo ratings yet
- Spring 2006 Qualifying Exam: - 34 - 34 B - 23 - 19 A 23 8 e - 31 P - 27 N - 27 0 - 11 C e - 12 0 - 7 2 0 0 2 - 11 3 2Document5 pagesSpring 2006 Qualifying Exam: - 34 - 34 B - 23 - 19 A 23 8 e - 31 P - 27 N - 27 0 - 11 C e - 12 0 - 7 2 0 0 2 - 11 3 2paimoNo ratings yet
- Review - 2018 - Final ExamDocument3 pagesReview - 2018 - Final ExamQuang LinhNo ratings yet
- ModelPapers MODELPAPER10 Physics12Document1 pageModelPapers MODELPAPER10 Physics12Maulik KarasaliyaNo ratings yet
- Exam EEE 2215 Electromagnetics I - 2013-2014 Latest August 2013-1Document16 pagesExam EEE 2215 Electromagnetics I - 2013-2014 Latest August 2013-1IAMMARKSNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Tunnel DiodeDocument23 pagesTunnel Diodeakhilesh3775% (4)
- Zener DiodeDocument13 pagesZener DiodePhenoमिनल IdiotsNo ratings yet
- EC111:Fundamental of Electronics Engineering: Assistant Professor, ECE DepartmentDocument51 pagesEC111:Fundamental of Electronics Engineering: Assistant Professor, ECE DepartmentrupeshNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument55 pagesAtomic StructureIndigo GroupNo ratings yet
- Preperation of CDS Quantum DotsDocument14 pagesPreperation of CDS Quantum Dots코발No ratings yet
- Dynamic-Light-Scattering - MDLDocument5 pagesDynamic-Light-Scattering - MDLJose Daniel Izquierdo MorenoNo ratings yet
- Fig. 62. Schematic Representation of Nc-Tin/A-Si N Nanocomposite Coating Consisting of Tin Nanocrystalline Phase Embedded in A-Si N Amorphous MatrixDocument3 pagesFig. 62. Schematic Representation of Nc-Tin/A-Si N Nanocomposite Coating Consisting of Tin Nanocrystalline Phase Embedded in A-Si N Amorphous MatrixAliakbar MonfaredNo ratings yet
- J.P. Wesley - Classical Quantum TheoryDocument6 pagesJ.P. Wesley - Classical Quantum TheoryJuiomSDFNo ratings yet
- XRD Lab Report 2 1Document3 pagesXRD Lab Report 2 1Aina SyaqinaNo ratings yet
- Shakeel Final Copy ThesisDocument81 pagesShakeel Final Copy ThesisshakelNo ratings yet
- Principles of Semiconductor Devices-L27Document24 pagesPrinciples of Semiconductor Devices-L27LIAKMANNo ratings yet
- 1 Fundamentals of Piezoelectricity: Lead-Free Piezoelectric MaterialsDocument18 pages1 Fundamentals of Piezoelectricity: Lead-Free Piezoelectric MaterialsJHNo ratings yet
- 02 - KristalografiDocument43 pages02 - KristalografiRoy Agus SalehNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 KKEE1133 SoalanDocument3 pagesTutorial 1 KKEE1133 SoalanAimanKPGNo ratings yet
- Chem 1008 Lab Midterms 2Document6 pagesChem 1008 Lab Midterms 2Jie Ann Faith AusmoloNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of MatterDocument11 pagesElectronic Structure of Matterangelic kvsbunNo ratings yet
- Pilani Campus: Birla Institute of Technology and Science, PilaniDocument2 pagesPilani Campus: Birla Institute of Technology and Science, PilaniANSHUMAN MISHRANo ratings yet
- VSEPR Lab Activity ANSWER KEY 1n4fw0dDocument5 pagesVSEPR Lab Activity ANSWER KEY 1n4fw0dalmira villarealNo ratings yet
- EE ESE PrelimsPaper 2020 RevisedDocument61 pagesEE ESE PrelimsPaper 2020 RevisedpksvampireNo ratings yet
- 1997, Angerer Et Al, APLDocument4 pages1997, Angerer Et Al, APLAbheek BardhanNo ratings yet
- Impact of Donor Traps On The 2deg and Electrical Behavior of Algan/Gan MisfetsDocument3 pagesImpact of Donor Traps On The 2deg and Electrical Behavior of Algan/Gan Misfetsankita6298No ratings yet
- Band Gap - PVEducationDocument3 pagesBand Gap - PVEducationRiazAhmadNo ratings yet
- NanochemistryDocument29 pagesNanochemistryTej Pratap SinghNo ratings yet
- Class 8 - Structure of Atom ppt2Document18 pagesClass 8 - Structure of Atom ppt2mau_chak5449No ratings yet
- 9.4 Giant Ionic StructuresDocument2 pages9.4 Giant Ionic StructureshadenluiNo ratings yet
- Laser Heating Effect On Raman Spectra of Si NanocrDocument6 pagesLaser Heating Effect On Raman Spectra of Si NanocrDani AmayaNo ratings yet
- Index: Modern Diffraction Methods, First Edition. Edited by Eric J. Mittemeijer and Udo WelzelDocument10 pagesIndex: Modern Diffraction Methods, First Edition. Edited by Eric J. Mittemeijer and Udo WelzelalkimiaNo ratings yet