Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8 Parts of Speech
8 Parts of Speech
Uploaded by
ariannepauleensacil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesThe document defines and provides examples of the eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. It explains that nouns represent people, places, things, or ideas. Pronouns replace nouns to avoid repetition. Verbs express actions or states of being. Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns, and adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Prepositions show relationships between elements in a sentence. Conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses. Interjections express strong emotions independently. For each part of speech, it provides a type of example to illustrate
Original Description:
English
Original Title
8-parts-of-speech
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines and provides examples of the eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. It explains that nouns represent people, places, things, or ideas. Pronouns replace nouns to avoid repetition. Verbs express actions or states of being. Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns, and adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Prepositions show relationships between elements in a sentence. Conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses. Interjections express strong emotions independently. For each part of speech, it provides a type of example to illustrate
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pages8 Parts of Speech
8 Parts of Speech
Uploaded by
ariannepauleensacilThe document defines and provides examples of the eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. It explains that nouns represent people, places, things, or ideas. Pronouns replace nouns to avoid repetition. Verbs express actions or states of being. Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns, and adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Prepositions show relationships between elements in a sentence. Conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses. Interjections express strong emotions independently. For each part of speech, it provides a type of example to illustrate
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
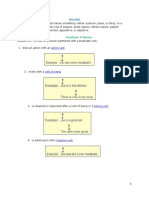
1. Noun: Represents a person, place, thing, or idea.
There are types different types of nouns
such as proper nouns
Proper Noun: A proper noun is a specific name given to an individual person, place, thing, or idea. It is
capitalized, regardless of its position in a sentence.
For example:
"I have always wanted to visit Paris.", the proper noun there is paris
2. Pronoun: Replaces nouns to avoid repetition.
Personal Pronoun A personal pronoun is a pronoun that represents a specific person or thing and indicates
the grammatical person (first person, second person, or third person).
For example:
"John forgot his keys at home, so he had to return to get them." the personal pronoun
there is he
3. Verb: Expresses action or a state of being.
Action Verb: An action verb is a verb that expresses physical or mental action. It describes what
someone or something is doing.
For example:
"She likes to run in the park every morning for exercise." the action verb there is run.
4. Adjective: Modifies or describes nouns or pronouns.
Descriptive adjective: is a type of adjective that provides more information about the characteristics or
qualities of a noun or pronoun.
For example :
The beautiful flowers bloomed in the garden. The descriptive adjective there is “beautiful”
5. Adverb: Modifies verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
Adverb of manner is a type of adverb that describes how an action is performed. It provides information about the
way in which an action occurs.
For example:
She completed the puzzle quickly, impressing everyone with her speed. The adverb of manner
there is “quickly”
6. Preposition: Shows the relationship between elements in a sentence.
Preposition of Place: A preposition of place is a type of preposition that indicates the location or
position of one thing in relation to another.
For example:
The cat is in the box, hiding from the rain. The preposition of place there is “in”
7. Conjunction: Connects words, phrases, or clauses.
Coordinating Conjunction: is a type of conjunction that connects words, phrases, or independent clauses
that are of equal grammatical rank.
For example:
She loves to read novels, but she also enjoys watching movies. The coordinating conjuction there is
“but”
8. Interjection: Expresses strong emotions independently.
Expressive Interjection: An expressive interjection is a type of interjection that conveys strong emotion, such
as surprise, joy, excitement, or disgust.
For example:
Wow! That magic trick was amazing!. The expressive interjection there is “ wow!”
You might also like
- 5th Grade Ela Study GuideDocument5 pages5th Grade Ela Study Guideapi-292325707100% (6)
- Part of SpeechDocument23 pagesPart of SpeechTimilehin GbengaNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument21 pagesEnglish Grammar232No ratings yet
- Grammatical-Categories 2.5Document12 pagesGrammatical-Categories 2.5arl somarNo ratings yet
- The Sentence of EnglishDocument16 pagesThe Sentence of EnglishBilal HassanNo ratings yet
- The Roles Played by Referring Expression Called Participant Roles IntoDocument3 pagesThe Roles Played by Referring Expression Called Participant Roles IntoSiti FaizahNo ratings yet
- Pronouns WPS OfficeDocument21 pagesPronouns WPS OfficeYukino MichinariNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument11 pagesParts of SpeechAccu Xii BhianNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech Figure of SpeechDocument8 pagesParts of Speech Figure of SpeechMiyuki KazuyaNo ratings yet
- Adjectives - Docxwith UnderlineDocument2 pagesAdjectives - Docxwith UnderlineMargie Ballesteros ManzanoNo ratings yet
- Quick SearchDocument3 pagesQuick SearchBerenice RojasNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument20 pagesPart of SpeechGewie Shane Blanco SumayopNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument10 pagesParts of SpeechsalahudinNo ratings yet
- Stucture Word ClassesDocument10 pagesStucture Word ClassesDwiNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Grade 7Document1 pageGrammar - Grade 7Saira FaisalNo ratings yet
- Verbs and PrepositionsDocument17 pagesVerbs and PrepositionsVeronica Cañamo LaranjoNo ratings yet
- Part of SpeechDocument13 pagesPart of SpeechtiffiNo ratings yet
- f1bl5 Or8i2Document20 pagesf1bl5 Or8i2bhaichuzaNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech ModuleDocument12 pagesPart of Speech ModuleAlayka BalangiNo ratings yet
- PARTS OF SPEECH UpdatedDocument12 pagesPARTS OF SPEECH UpdatedMCC Gilgit-BaltistanNo ratings yet
- Figures of Speech - 1Document31 pagesFigures of Speech - 1Jannica Mae D SacristiaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument3 pagesParts of SpeechK-ann DemonteverdeNo ratings yet
- English GrammarDocument21 pagesEnglish Grammarcontact.asif.directNo ratings yet
- Individual Task Last Examination Syntax: Faculty of Teacher Training and Education Universitas Islam Syekh-YusufDocument9 pagesIndividual Task Last Examination Syntax: Faculty of Teacher Training and Education Universitas Islam Syekh-YusufmattNo ratings yet
- Syntax As Parts of Speech by Christine Joy B. OroDocument39 pagesSyntax As Parts of Speech by Christine Joy B. OroAnamie Dela Cruz ParoNo ratings yet
- El 11Document5 pagesEl 11Krissa Jean KingNo ratings yet
- Overview of Different Parts of SpeechDocument11 pagesOverview of Different Parts of Speechbenbelkacem.israaaNo ratings yet
- Part of Speech OverviewDocument44 pagesPart of Speech OverviewSufyan Ashraf100% (1)
- Class of wordDocument4 pagesClass of wordMitha NurNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Semantics of Phrase and Sentence - Lecture Notes2022 2023Document3 pagesWeek 7 Semantics of Phrase and Sentence - Lecture Notes2022 2023Maria TeodorescuNo ratings yet
- The Eight Parts of Speech: NounsDocument17 pagesThe Eight Parts of Speech: NounsSTENLY PONTOLONDONo ratings yet
- The Eight Parts of Speech: NounsDocument17 pagesThe Eight Parts of Speech: NounsValensia SumampouwNo ratings yet
- Parts of Speech English Language - 220612 - 135325Document16 pagesParts of Speech English Language - 220612 - 135325mealia jamesNo ratings yet
- Panganiban ProjectDocument9 pagesPanganiban ProjectColyn Joy Sumande MantacNo ratings yet
- Soe ReviewerDocument23 pagesSoe ReviewersymerdavedangoNo ratings yet
- Grammar English For BasicDocument9 pagesGrammar English For BasicBidur KhanalNo ratings yet
- Basic EnglishDocument4 pagesBasic EnglishwuhemosesNo ratings yet
- English Parts of SpeechDocument4 pagesEnglish Parts of Speechnuril khoirina08No ratings yet
- Grammar Friska SipayungDocument36 pagesGrammar Friska SipayungLesbra SandyNo ratings yet
- Nouns: Action VerbDocument15 pagesNouns: Action VerbJerica PalomariaNo ratings yet
- Basic Parts of Speech: NounsDocument8 pagesBasic Parts of Speech: NounsNinaNo ratings yet
- LanguageDocument2 pagesLanguageВікторія Михайлівна МикитюкNo ratings yet
- Grammatical ConceptsDocument38 pagesGrammatical Conceptsjoy canda50% (2)
- Grammar Notes For Class 9 & 10 PDFDocument85 pagesGrammar Notes For Class 9 & 10 PDFKarma Kuenzang WangdiNo ratings yet
- What Is NOUNDocument24 pagesWhat Is NOUNHan YouNo ratings yet
- Grammar SummaryDocument4 pagesGrammar Summarynojuanno12No ratings yet
- Gramma IDocument49 pagesGramma ITesfu HettoNo ratings yet
- Modul Bahasa Inggris OLNASDocument25 pagesModul Bahasa Inggris OLNASRizki SalamiNo ratings yet
- Person Animal Place Thing Idea: Identifying A NounDocument4 pagesPerson Animal Place Thing Idea: Identifying A NounKryzl Rey del FierroNo ratings yet
- The VERB, Main - Auxilary.link...Document15 pagesThe VERB, Main - Auxilary.link...tahire.revan13No ratings yet
- The Eight Parts of SpeechDocument25 pagesThe Eight Parts of SpeechCielomina Sotelo PanitNo ratings yet
- Distance Training For Middle School TeachersDocument47 pagesDistance Training For Middle School TeachersMohamed Tayeb SELT100% (2)
- Part of SpeechDocument4 pagesPart of Speechshayenne keilahNo ratings yet
- Word ClassificationDocument28 pagesWord ClassificationmiftaNo ratings yet
- Parts of SpeechDocument17 pagesParts of SpeechJuank_14_12No ratings yet
- Gramatyka Opisowa (Ściąga)Document64 pagesGramatyka Opisowa (Ściąga)Adam DmochowskiNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument10 pagesProject ReportgraciousNo ratings yet
- English Grammar RulesDocument12 pagesEnglish Grammar Rules4069-Sam ChristopherNo ratings yet
- A Deep Dive Into Nouns : A Beginner Study To All Forms of NounsFrom EverandA Deep Dive Into Nouns : A Beginner Study To All Forms of NounsNo ratings yet
- Manners of PossibilityDocument2 pagesManners of Possibilitylisian urbina100% (1)
- Passive Voice For Imperative Sentences - RulesDocument2 pagesPassive Voice For Imperative Sentences - RulesjulioNo ratings yet
- Essay Term: Translation Theory: Topic: Summarize Translation MethodsDocument5 pagesEssay Term: Translation Theory: Topic: Summarize Translation MethodsKb NguyenNo ratings yet
- MSBSHSE Class 12 English Syllabus 2022 2023Document6 pagesMSBSHSE Class 12 English Syllabus 2022 2023Anita ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- Verb.: I Still Haven'T Found What I'M Looking For-U2Document3 pagesVerb.: I Still Haven'T Found What I'M Looking For-U2CRISTIANE SEVERO BASTOSNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Model 3 English 1ac First TermDocument2 pagesTest 1 Model 3 English 1ac First TermEl Mouriki YassineNo ratings yet
- 2.1 InglesDocument17 pages2.1 InglesFelix Eduardo Neme DazaNo ratings yet
- Importance Verb TenseDocument2 pagesImportance Verb TenseFailan MendezNo ratings yet
- Goodwin, W.W.: Syntax of Moods and Tenses of The Greek VerbDocument498 pagesGoodwin, W.W.: Syntax of Moods and Tenses of The Greek VerbDavid-Artur DaixNo ratings yet
- SYLLABUS GRADE - 5-Indian High DubaiDocument1 pageSYLLABUS GRADE - 5-Indian High DubaiShermNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Inglés 4Document2 pagesQuiz 2 Inglés 4Ivette CepedaNo ratings yet
- El108 ModulesDocument77 pagesEl108 ModulesClarizze Orteza ApionNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 07 File 56Document4 pagesWorksheet 07 File 56Ilham CahayatiNo ratings yet
- Word TypesDocument20 pagesWord Typesarcher70No ratings yet
- Unit 6 - More On Verbs Auxiliary VPsDocument74 pagesUnit 6 - More On Verbs Auxiliary VPsMeiNo ratings yet
- 1st Periodical Test in English 5Document9 pages1st Periodical Test in English 5ArrieneNo ratings yet
- 90 English Phonetics and PhonologyDocument7 pages90 English Phonetics and PhonologyAlejandro PDNo ratings yet
- Thesis KolokiumDocument40 pagesThesis KolokiumSyafaruddin MarpaungNo ratings yet
- Bridge Course For Class-X - Final - Level-1Document51 pagesBridge Course For Class-X - Final - Level-1LOVEJEET SINGH RATHORENo ratings yet
- Eagle Learning Centre Palembang: English Work Sheet PrimaryDocument6 pagesEagle Learning Centre Palembang: English Work Sheet PrimaryDini Aulia DwintanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document16 pagesUnit 3tranhoanicdNo ratings yet
- Ingles 5 Clase 1 Reductions Part 1Document20 pagesIngles 5 Clase 1 Reductions Part 1Duglas OlivaNo ratings yet
- Naplan Year7 Lit Lang Conv 12 PDFDocument9 pagesNaplan Year7 Lit Lang Conv 12 PDFJeniNo ratings yet
- SIlverzone English SampleDocument2 pagesSIlverzone English SampleSujal SNo ratings yet
- French Grammar PDFDocument338 pagesFrench Grammar PDFDicu AndreiArmandNo ratings yet
- Superstition - B2 - 07.04 PDFDocument4 pagesSuperstition - B2 - 07.04 PDFAlejandro GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Kuis Gerund or InfinitiveDocument2 pagesKuis Gerund or InfinitivekristyNo ratings yet
- PunctuationDocument9 pagesPunctuationSam JeromeNo ratings yet
- FCE - Summer Homework - KeyDocument11 pagesFCE - Summer Homework - KeyYaskoNo ratings yet
- Possessive Pronoun RaceDocument3 pagesPossessive Pronoun RaceAlicia MontenegroNo ratings yet