Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Different Types of Sorghum
Different Types of Sorghum
Uploaded by
Meryana LinomeOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Different Types of Sorghum
Different Types of Sorghum
Uploaded by
Meryana LinomeCopyright:
Available Formats
DIVERSITY of SORGHUM
Dr. Magdalena Buschmann
KWS
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
SORGHUM ORIGIN
Sorghum is from the family POACEAE
Sorghum has it’s origin in Northeastern Africa
as a wild plant
Earliest known record of sorghum comes from
Egyptian-Sudanese border and had been dated
at 8.000 B.C.
Sorghum belt is between 40 degrees North and
40 degrees South of the equator, in warm and
hot countries characteristic for semi arid
environment
Sorghum is usually grown in areas that are too
hot and dry for maize
Over 50% of World sorghum varieties are
hybrid, the lowest concentration of hybrid
varieties is in Africa
Hybrid production system is CMS
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
SORGHUM CLASSIFICATIONS
Botanical classification
Classification according usage
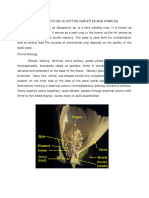
What do we see in the picture?
Source: KWS
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
SORGHUM TAXONOMY
Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench)
a tropical grass grown primarily in semiarid
parts of the world, particularly in Africa, India
and Asia, where it is an important staple food
crop. It is a member of the family Poaceae
and the tribe Andropogoneae, of which there
are three main species:
S. bicolor - diploid (2n=20) all annual
and domesticated types, including
stabilized weedy derivatives such as
Sudangrass. Widely distributed.
S. halepense - Johnsongrass.
Tetraploid, native perennial of southern
Eurasia, east to India.
S. propinquum - Diploid, native
perennial of Sri Lanka and southern
Source:Cirad
India.
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
BOTANICAL RACES OF CULTIVATED RACES OF S. BICOLOR
SSP BICOLOR
I. Basic races: II. Intermediate races: (all combinations of
basic races)
bicolor (B)
guinea (G) - Sudanian area guinea-bicolor (GB)
caudatum (C) – Eastern Africa caudatum-bicolor (CB)
kafir (K) – South Africa, mainly short kafir-bicolor (KB)
plants durra-bicolor (DB)
durra (D) - East Africa, Middle East and guinea-caudatum (GC)
India guinea-kafir (GK)
guinea-durra (GD)
kafir-caudatum (KC)
durra-caudatum (DC)
kafir-durra (KD)
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
BOTANICAL RACES OF WILD SORGHUM (SORGHUM BICOLOR
SSP VERTICILLIFLORUM)
III. Wild sorghum races: S. bicolor ssp
arundinaceum.
arundinaceum
aethiopicum
virgatum
verticilliflorum
(courtesy of J Hancock: Plant Evolution and the Origin of Crop Species; art work
by Marlene Cameron)
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
RACES OF SORGHUM BICOLOR - PANICLE TYPES
Source: KWS
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
TAXONOMY OF SORGHUM TYPES USED IN AGRICULTURE
Sorghum
sudanense
S. bicolor x S. sudanense S. bicolor ssp. bicolor S. bicolor ssp. bicolor
Sorghum bicolor x
Sorghum
sudanense
Sorghum bicolor x
Sorghum Bicolor
slight tillering type
with diverse directions
of usage:
Sugar type
Forage type for
silage
BMR
Grain type Source: KWS
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
SORGHUM PANICLE TYPES - OPENESS
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
MAIN TRAITS OF BICOLOR TYPE
Almost no tillering
Broad leaves
Robust stem
Lower sowing density
Differences also according genetic origin or variety type
Closed panicles = Potentially of high sugar content
Broomcorn panicles = high yield potential and high lignin
content
Kaoliang = good cold tolerance and earliness
Sorghum Bicolor x Sorghum Bicolor
Source: KWS
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
MAIN CARACTER OF SUDANENSE TYPES
Tillers – depending on type – sudanense pure has more
tillers than crossing with Bicolor
thin leaves
thin stem
Higher sowing density
Weak to normal standability
Weaker yield potential
Earliness
Good cold tolerance
Sorghum Bicolor x Sorghum Sudanense
Source: KWS
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
SEGMENTATION ACCORDING USAGE
BIOMASS SORGHUM SWEET SORGHUM
FORAGE SORGHUM
Source: http://grao.cnpms.embrapa.br
Source: http://www.heritageseeds.com.au
Source: KWS, Buschmann
DUAL TYPES SORGHUM
MULTICUT
GRAIN SORGHUM SORGHUM
Source: http://oklahoma4h.okstate.edu
Source: KWS, Buschmann
Source:BBF Project
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
UTILISATION OF SORGHUM NON GRAIN TYPES
Biomass sorghum (including dual
types)
Biogas plants Energy
Combustion plants Energy
Feed
Broom sorghum
Forage sorghum (including BMR types)
Feed as fresh forage
Feed as hay
Multicut Sorghum
PPS Sorghum
Sweet sorghum
Feed
Bioethanol productions
Source: http://sirak.rs/hu/ciroksepru-forgalmazasa Source:Cirad
Sweeteners (Syrup, molasse, sugar)
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
BMR TYPE OF SORHUM
High sugar content
Lower Lignin content (about 40- main markers
60 % of normal biomass
sorghum)
Lower standability
High digestibility
High methane formation
Source: KWS
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
UTILISATION OF SORGHUM GRAIN TYPES
Grain sorghum
Feed
Food
Tanin containing sorghum - alcohol production – e.g.
Baijiu in China or beer
Tanin free sorghum - dry milling products and non gluten
food products e.g. bread, flakes, pasta, puffs, crisps and
chips
Bioethanol production
Source: https://nulifemarket.com
Source: https://nulifemarket.com
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
Thank you for your
attention!
2nd European Sorghum
Congress 2018
You might also like
- Maize Business PlanDocument4 pagesMaize Business Planpreetjukeboxi77% (22)
- Truffle Farming Today. A Comprehensive World Guide. 2015Document9 pagesTruffle Farming Today. A Comprehensive World Guide. 2015Bob100% (1)
- Millet Booklet PDFDocument21 pagesMillet Booklet PDFViswanatha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Pengembangan Agroindustry Sorghum Di IndonesiaDocument22 pagesPengembangan Agroindustry Sorghum Di IndonesiaAriga PratamaNo ratings yet
- SorghumDocument6 pagesSorghumASHUTOSH MOHANTYNo ratings yet
- Sorghum Bicolor (2n 20)Document8 pagesSorghum Bicolor (2n 20)KavieswarNo ratings yet
- CROP EVOLUTION Sorghum FINALDocument9 pagesCROP EVOLUTION Sorghum FINALRonalyn AmparoNo ratings yet
- Taxonomy and Distribution of Bumblebees (Hymenoptera: Apidae) of District Skardu, Gilgit BaltistanDocument7 pagesTaxonomy and Distribution of Bumblebees (Hymenoptera: Apidae) of District Skardu, Gilgit BaltistansaleemNo ratings yet
- Ss1 Agric Cultivation of Legumes + Roots & TubersDocument4 pagesSs1 Agric Cultivation of Legumes + Roots & TubersIsraelNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of West African Sorghum Varieties For Resistance To Striga in The Sudano-Sahelian Zone of MaliDocument6 pagesEvaluation of West African Sorghum Varieties For Resistance To Striga in The Sudano-Sahelian Zone of MaliInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Sorghum Practice in Sindh, Pakistan by Mrs.Document6 pagesSorghum Practice in Sindh, Pakistan by Mrs.asadbajwaamtnNo ratings yet
- Sunflower: Helianthus AnnuusDocument9 pagesSunflower: Helianthus Annuusashes kumar jenaNo ratings yet
- CNPGL 2017 CropBreedAppBiot Pereira BRSDocument4 pagesCNPGL 2017 CropBreedAppBiot Pereira BRSRafaelNo ratings yet
- Sorghum AgriDocument16 pagesSorghum Agrialexhawi00No ratings yet
- Evaluation of The Planting Method, and Auxin Hormone For Vegetative Multiplication of Opuntia SPP Varieties Resistant To Dactylopuis OpuntiaDocument27 pagesEvaluation of The Planting Method, and Auxin Hormone For Vegetative Multiplication of Opuntia SPP Varieties Resistant To Dactylopuis OpuntiafoodengineeringlaboratoryNo ratings yet
- Agrocybe Erebia (FR.) Köhner-SingerDocument2 pagesAgrocybe Erebia (FR.) Köhner-Singerrmonica26No ratings yet
- 20bscagh315agrn (PCC) G2 1Document20 pages20bscagh315agrn (PCC) G2 1Chitralekha SinghNo ratings yet
- Bremer 2016 Amarygmus LXXII PapuanDocument28 pagesBremer 2016 Amarygmus LXXII PapuanDávid RédeiNo ratings yet
- Sweet Sorghum ( Sorghum Bicolor (L.) Moench) Bioenergy Value - Importance For PortugalDocument8 pagesSweet Sorghum ( Sorghum Bicolor (L.) Moench) Bioenergy Value - Importance For PortugalMaryam AsdNo ratings yet
- Technique de Production Intensive Du Poisson ChatDocument11 pagesTechnique de Production Intensive Du Poisson ChatChiakaNo ratings yet
- Wheat Complete Guide. - 012334Document4 pagesWheat Complete Guide. - 012334joeshoniwa2100% (1)
- Round The Year Mushroom & EconomicsDocument22 pagesRound The Year Mushroom & EconomicsShivendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Calidad Nutricional y Consumo de Morera Morus AlbaDocument6 pagesCalidad Nutricional y Consumo de Morera Morus AlbaJOSE BNo ratings yet
- BreedingDocument49 pagesBreedingrgopinath5No ratings yet
- Agriculture Class X ECONTENTSDocument12 pagesAgriculture Class X ECONTENTSBrazil XxxNo ratings yet
- Practical Manual - AGR 101 a-1Document36 pagesPractical Manual - AGR 101 a-1jeevamass246No ratings yet
- Turkish Journal of Agriculture - Food Science and TechnologyDocument4 pagesTurkish Journal of Agriculture - Food Science and TechnologyFabio MarcelNo ratings yet
- Natural ResosurcesDocument3 pagesNatural ResosurcesRaimundo TruccoNo ratings yet
- Agro-Techniques For Kalmegh: Andrographis Paniculata (Acanthaceae), Kalmegh Should Be Grown DuringDocument9 pagesAgro-Techniques For Kalmegh: Andrographis Paniculata (Acanthaceae), Kalmegh Should Be Grown DuringSuraj Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Apiculture PDFDocument75 pagesApiculture PDFMini singh100% (2)
- Sugar CaneDocument10 pagesSugar CaneparfreeNo ratings yet
- Biodiversity of Sugar Crops in BangladeshDocument5 pagesBiodiversity of Sugar Crops in BangladeshIsabela JonathonNo ratings yet
- 5th Symposium Proceedings 0027 217Document18 pages5th Symposium Proceedings 0027 217Babatunde Idowu EbenezerNo ratings yet
- WCR Coffee Research Intro Deck WebDocument11 pagesWCR Coffee Research Intro Deck WebKameshi KohomangeNo ratings yet
- CapparisEur Foodres Tech 2002Document6 pagesCapparisEur Foodres Tech 2002Ashkan “A.N” AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Assignment of ChariDocument10 pagesAssignment of ChariSantosh BhandariNo ratings yet
- Rust OverviewDocument3 pagesRust OverviewJIBIN JOSENo ratings yet
- I1070e04 PDFDocument142 pagesI1070e04 PDFJaru JackyNo ratings yet
- The Tractor Factor (June 2024)Document8 pagesThe Tractor Factor (June 2024)The Livingston County NewsNo ratings yet
- GPP Presentation Day 2 (Maynard M. Baluyut)Document113 pagesGPP Presentation Day 2 (Maynard M. Baluyut)maynardNo ratings yet
- Extraction and Characterization of Sorghum (Sorghum Bicolor L. Moench) StarchDocument6 pagesExtraction and Characterization of Sorghum (Sorghum Bicolor L. Moench) StarchJohn Georvin DuranNo ratings yet
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionDocument10 pagesJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Verm I CompostingDocument16 pagesVerm I Composting5605 Priyanka BaruaNo ratings yet
- BGRI Poster - 2020 - SunitaDocument1 pageBGRI Poster - 2020 - SunitaPoudyal SunitaNo ratings yet
- I Shall Not Go: ThereDocument29 pagesI Shall Not Go: ThereYash KediaNo ratings yet
- AEN 354 Sericulture & Lac Culture AssignmentDocument19 pagesAEN 354 Sericulture & Lac Culture Assignmentnehamonday9No ratings yet
- Sweet Sorghum: Food, Feed, Fodder and Fuel CropDocument24 pagesSweet Sorghum: Food, Feed, Fodder and Fuel CropJakka V ReddyNo ratings yet
- 1 PBDocument17 pages1 PBDharrafi TvNo ratings yet
- GramDocument21 pagesGramdasjay185No ratings yet
- Bees For DevelopmentDocument18 pagesBees For DevelopmentAnatol PaladeNo ratings yet
- Lec 14Document14 pagesLec 14Kanimozhi TNo ratings yet
- Alimentaion de GranosDocument7 pagesAlimentaion de GranosJohanita Elt Bonillas RomeroNo ratings yet
- 6practical Vermiculture - Without Capital Expenditures PDFDocument62 pages6practical Vermiculture - Without Capital Expenditures PDFmae montecilloNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Mycorrhiza-05-063Document8 pagesJurnal Mycorrhiza-05-063Azhari RizalNo ratings yet
- Barley in Archaeology and Early HistoryDocument26 pagesBarley in Archaeology and Early HistoryKenny LetsoinNo ratings yet
- L8 Potato HRT 255Document5 pagesL8 Potato HRT 255flaming butterflyNo ratings yet
- Production Methods For The Common Carp - The Fish SiteDocument1 pageProduction Methods For The Common Carp - The Fish SiteYasir AljuboryNo ratings yet
- CP&M PDFDocument282 pagesCP&M PDFBEMS InstitutionNo ratings yet
- A Pictorial Guide For The IdentificationDocument128 pagesA Pictorial Guide For The IdentificationChristopher SuarezNo ratings yet
- The Compendium of Currant and Gooseberry Growing - Including Information on Propagation, Planting, Pruning, Pests, VarietiesFrom EverandThe Compendium of Currant and Gooseberry Growing - Including Information on Propagation, Planting, Pruning, Pests, VarietiesNo ratings yet
- Economic BotanyDocument27 pagesEconomic BotanyAnanth Kulkarni0% (1)
- SIP Chapter 2 & 3Document3 pagesSIP Chapter 2 & 3Aoki kazeNo ratings yet
- FoodCompatibilityList. HistaminaDocument8 pagesFoodCompatibilityList. HistaminacarlosselfaNo ratings yet
- Seeds and Seeds: DiscussDocument9 pagesSeeds and Seeds: DiscusssudhirvatsaNo ratings yet
- Daftar PustakaDocument4 pagesDaftar PustakaZaini AkbarNo ratings yet
- Production Technology of LucerneDocument14 pagesProduction Technology of LucerneAnonymous x7gqMPvZIwNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: Department of Horticulture, C. P. College of AgricultureDocument72 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: Department of Horticulture, C. P. College of Agriculturech meghana100% (3)
- Honest Products CG List & CombosDocument9 pagesHonest Products CG List & CombosAthira SomanNo ratings yet
- Filipino To English - JPDocument4 pagesFilipino To English - JPNicoloNo ratings yet
- Cuadros y Gráficos Artículo TLC 2022 VFDocument936 pagesCuadros y Gráficos Artículo TLC 2022 VFmartinastocondorNo ratings yet
- Event Attendee List: Client Id First Name Last Name Start Date Start Yearorg Code OrganisationDocument28 pagesEvent Attendee List: Client Id First Name Last Name Start Date Start Yearorg Code OrganisationKAPIL MBA 2021-23 (Delhi)No ratings yet
- Classification of Crops CSB 211 2018Document23 pagesClassification of Crops CSB 211 2018Thabo ChuchuNo ratings yet
- Coffee - An International Plan - Brief History and Current EvolutionDocument23 pagesCoffee - An International Plan - Brief History and Current EvolutionAndreea CristianaNo ratings yet
- FODMAPs - BulsiewiczDocument2 pagesFODMAPs - BulsiewiczMartyna100% (1)
- Bahasa Inggris Kelas 2Document2 pagesBahasa Inggris Kelas 2Jati Ayu Puspitarini100% (1)
- Omega 3 and 6 in Fats Oils Nuts Seeds Meat and Seafood 2Document3 pagesOmega 3 and 6 in Fats Oils Nuts Seeds Meat and Seafood 2Arhip CojocNo ratings yet
- List of FPOs in The State of Madhya PradeshDocument11 pagesList of FPOs in The State of Madhya PradeshAkshay Jadhav100% (1)
- Zimbabwe Primary School ZIMSEC Grade 5 Agriculture Exam Paper 1 Set 2Document3 pagesZimbabwe Primary School ZIMSEC Grade 5 Agriculture Exam Paper 1 Set 2veemusi95No ratings yet
- Broccoli and Cauliflower Production GuideDocument3 pagesBroccoli and Cauliflower Production GuidearnoldalejadoNo ratings yet
- Acid Alkaline Food ChartDocument4 pagesAcid Alkaline Food ChartcgonzagaaNo ratings yet
- Seed Production Techniques For VegetablesDocument10 pagesSeed Production Techniques For VegetablesAgyapal MandNo ratings yet
- HAPAG-Quarterly ReportDocument1 pageHAPAG-Quarterly ReportPamahalaang Barangay Ng Sapang IINo ratings yet
- Iv. Learning Phases and Learning Activities I. Introduction (Time Frame: 90 Minutes) PresentationDocument4 pagesIv. Learning Phases and Learning Activities I. Introduction (Time Frame: 90 Minutes) PresentationGrace cabiliNo ratings yet
- Useful Wild PlantsDocument276 pagesUseful Wild PlantsMatt StephensNo ratings yet
- List of FPOs in The State of OrissaDocument5 pagesList of FPOs in The State of OrissaAmanNo ratings yet
- 19-Article Text-24-1-10-20171211Document8 pages19-Article Text-24-1-10-20171211MilaNo ratings yet
- Agriculture 1Document4 pagesAgriculture 1Tom CruiseNo ratings yet
- Contingency Crop Planning For District Sukma State: ChhattisgarhDocument17 pagesContingency Crop Planning For District Sukma State: ChhattisgarhRavi S. SharmaNo ratings yet
- Podar International School (Cbse) MCQ Grade: X Topic: Ch4 Agriculture Subject:Social Science Maximum Marks: 20Document3 pagesPodar International School (Cbse) MCQ Grade: X Topic: Ch4 Agriculture Subject:Social Science Maximum Marks: 20Vipul NanawareNo ratings yet