Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Surgery I Important Qs
General Surgery I Important Qs
Uploaded by
Dwivith ReddyOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Surgery I Important Qs
General Surgery I Important Qs
Uploaded by
Dwivith ReddyCopyright:
Available Formats
2020-09
2020-02
2019-02
2018-12
2018-02
2017-12
2017-02
2016-12
2016-06
2015-12
2015-06
2014-12
2014-06
2013-12
2013-06
2012-12
2012-06
2011-12
2011-06
2010-12
2010-06
2009-12
2009-06
2008-12
2008-06
2007-12
2007-06
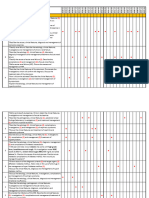
Times General Surgery I
Essays - General Surgery
*What are the types of/classify haemorrhage (2). Describe in
detail the aetiology, clinical features, investigations and
management (3) of haemorrhagic (hypovolemic) shock.
*Define (2) and classify (2) shock. Describe the pathogenesis,
clinical features and management (2) of septic shock.
8 *Define (2) and classify (2) (the various types of) shock. Describe ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
the aetiology, pathogenesis/pathophysiology, clinical features (2)
and management (2) of hypovolemic shock.
*Define shock. Classify the various aetiological factors causing
shock. Describe the clinical features, investigations and
management of hypovolemic shock.
Describe/discuss the aetiology, clinical features (3),
3 investigations/diagnosis and management (2)/treatment of ● ● ●
tetanus.
*Define haemorrhagic shock. Discuss various methods of
haemostasis. Discuss indications for and complications of blood
transfusions.
2
*What are the indications for blood transfusion? Mention the
● ●
various complications of blood transfusion. Add a note on fresh
frozen plasma.
*Classify burns. Describe the management of burns.
2
*Discuss the management of an adult with 50% burns.
● ●
Explain the aetiopathology, clinical features, investigations and
1
treatment of early breast carcinoma.
●
Classify tumours of the salivary glands. Describe the pathology,
1 clinical features, investigations and treatment of pleomorphic ●
adenoma.
Describe the aetiology, clinical features and management of
1
carcinoma rectum.
●
Cases - General Surgery
*40-year-old lady weighing 52 kg sustained burn injuries
extensively over the chest, back and abdominal wall.
a) Give an account of the assessment of the burn area and the
pathophysiology of burn injury.
b) How will you resuscitate this patient and manage the burn
wound? (2)
3 ● ● ●
*40-year-old lady weighing 50 kg tried to self-immolate herself by
pouring kerosene. She did not succeed and sustained burn
injuries.
a) How will you calculate the burnt surface area of the body?
b) Explain the management if she has 50% mixed thermal burns.
*30-year-old male sustains multiple injuries in a road traffic
accident and is brought to the emergency room.
O/E: Conscious (GCS - 13/15).
Multiple lacerations over the extremities and abdominal
distension.
Vitals: Pulse - 130/min, BP - 80/?, RR - 20/min.
Sweating profusely with cold extremities.
a) What are the types of haemorrhage? [2 marks]
b) Define and classify shock. [3 marks]
c) Describe the clinical features and management of a patient
2 with hypovolemic shock. [10 marks] ● ●
*65-year-old diabetic presents to the emergency department.
H/O: Swelling over nape of neck for 5-6 days associated with
pain, now discharging pus.
O/E: Temperature - 101°F (Febrile), Pulse - 126/min, BP - 80/?.
a) What type of shock is this patient suffering from
b) Define and classify shock.
c) Describe the aetiology, pathophysiology, clinical features and
management of septic shock.
d) Add a note on SIRS and MODS.
*22-year old lady.
H/O: Insomnia, weight loss, heat intolerance and diarrhoea.
O/E: Tachycardia and a diffuse swelling over the anterior aspect
2 of neck. ● ●
a) What is your diagnosis?
b) Describe the aetiology, pathophysiology, clinical features and
treatment of this condition.
*55-year-old male presents with a slow-growing swelling below
and behind his left ear of 6 years duration.
a) Enumerate the differential diagnoses.
1
b) Classify tumour of the salivary glands.
●
c) Describe the pathology, clinical features, investigations and
treatment of pleomorphic adenoma.
*45-year-old woman presents with a lump in the breast, of 2
1 months duration. ●
Discuss the differential diagnosis and management.
Essays - Orthopaedics
*Describe/discuss the classification, clinical features (3)/clinical
presentation, radiological features, complications (3) and
management (4) of fracture of neck of femur in adults/in a 60-
year-old female (in the elderly).
6
*Describe the mechanism, clinical features and management of
● ● ● ● ● ●
intracapsular fracture of neck of femur.
*Classify supracondylar fracture of femur and describe its clinical
features, treatment and complications.
*Describe the classification, clinical features, complications and
management of supracondylar fracture of humerus in children.
(3)
*Describe/explain the mechanism of injury, clinical features (2),
6
investigations and management (2) of supracondylar fracture of
● ● ● ● ● ●
humerus.
*Discuss the clinical features, diagnosis and different treatment
modalities for fracture of shaft of humerus in an adult.
*Classify bone tumours. Explain/discuss the clinical features and
management of osteosarcoma of distal end of femur. (2)
3
*Classify bone tumours. Describe in detail the clinical features
● ● ●
and management of osteoclastoma.
*Define Colles' fracture. Describe the clinical features,
management and complications of Colles' fracture. (2)
3 *Discuss the differential diagnosis of fractures that occur due to ● ● ●
fall on an outstretched hand. Describe the management of any
one of them.
Describe the aetiology, pathology, investigations, differential
1
diagnosis and treatment of acute osteomyelitis.
●
Describe the aetiology, classification, pathological anatomy,
1
clinical features and treatment of club foot.
●
Describe the clinical features, radiological findings and
1
management of dislocation of the shoulder.
●
Describe the pathogenesis, clinical features, diagnosis and
1
management of tuberculosis of spine.
●
Cases - Orthopaedics
*16-year-old boy/13-year-old girl presents with a swelling in the
region of distal part of femur, of 2 months duration.
O/E: Ill-defined mass fixed to the bone.
3 a) What are the differential diagnoses? ● ● ●
b) What are the clinical and radiological features of
osteosarcoma?
c) What are the principles of management of osteosarcoma?
*72-year-old lady sustained a fall on her outstretched hand and
developed a wrist swelling.
1 a) Enumerate the differential diagnosis. ●
b) Describe in detail the clinical features, management and
complications of Colles' fracture.
*80-year-old lady had a fall in the bathroom and sustained a
fracture of neck of femur on the right side.
1
Describe the clinical features, investigations and treatment of
●
fracture of neck of femur.
Short Notes - General Surgery
*Subdural hematoma/haemorrhage
*Extradural hematoma (6)
10 *Types of intracranial hematoma with a brief note on lucid ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
interval
*Lucid interval
*Gas gangrene (4):
8 - Clinical features (2) ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
- Management (2)
*Electrical burns (4)
- Management (2)
8
*Assessment of burn wound
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
*Assessment of depth of burns
*Carbuncle (3)
*Dermoid cyst (2)
8
*Cold abscess (2)
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
*Cold abscess in the neck
*Pleomorphic adenoma
*Pre-malignant lesions of the oral cavity (2)
8 *Warthin tumour (2) ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
*Ranula (2)
*Epulis
*Basal cell carcinoma (2)
*Rodent ulcer (basal cell carcinoma) (2)
6
*Marjolin's ulcer
● ● ● ● ● ●
*Pre-malignant lesions of skin cancer
*Indications of nutritional support and complications of total
parenteral nutrition (TPN)
6
*(Total) (par)enteral nutrition (1):
● ● ● ● ● ●
- Complications (3)
*Tetanus (tetany) (2):
5 - Clinical features (3) ● ● ● ● ●
- Management (2)
3 Glasgow coma scale ● ● ●
*Types of haemorrhage
3 *Septic shock ● ● ●
*Hypovolemic shock
*Hydatid cyst (2)
3
*Hepatic hydatid disease
● ● ●
3 Thyroglossal cyst ● ● ●
*Complications of blood transfusion
3 *Blood transfusion and its complications ● ● ●
*Fresh frozen plasma
3 Keloid(s) ● ● ●
2 Tubercular/Tuberculous lymphadenitis ● ●
2 Skin grafting ● ●
2 Phyllo(i)des tumour ● ●
*Torsion testis
2
*Varicocele
● ●
1 Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis ●
1 Universal precautions ●
1 Surgical site infection ●
1 Intussusception ●
1 HIV and the surgeon ●
1 Hypokalemia ●
1 Flail chest ●
1 Cystic hygroma ●
1 Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy ●
1 Nerve injuries ●
1 Lymphoedema ●
1 Psoas abscess ●
1 Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) ●
1 Decubitus ulcers ●
1 Epidural anaesthesia ●
1 Pilonidal sinus ●
1 Day-care surgery ●
1 Madura foot ●
1 Lingual thyroid ●
*Thyroid neoplasms:
1 - Classification ●
- Clinical features
1 Obstructed inguinal hernia ●
1 Differential diagnosis of bleeding per rectum ●
Short Notes - Orthopaedics
*Osteosarcoma (osteogenic sarcoma) (2)
*Metastatic bone tumours
*Osteoclastoma (4)
*Giant cell tumour of bone (2)
15
*Chondrosarcoma
● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
*Ewing's sarcoma (2)
*Exostosis
*Plasmacytoma
*Claw hand (2)
*Ulnar claw hand
●
11 *Wrist drop (6) ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
*Erb's palsy ●
*Tardy ulnar nerve palsy
*Osteomyelitis (6)
●
10 *Chronic osteomyelitis ● ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
*Sequestrum (3) ●
7 Volkmann's (ischaemic) contracture ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
*Colles' fracture (5):
- Causes
7 - Diagnosis ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
- Complications
*Smith's fracture
*Carpal tunnel syndrome (3)
7 *Compound palmar ganglion (3) ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
*Ganglion
*Club foot (congenital talipes equinovarus) (5):
7 - Pathogenesis ● ● ● ● ● ● ●
*Hammer toe
5 Pathological fracture ● ● ● ● ●
5 Myositis ossificans ● ● ● ● ●
5 Baker's cyst ● ● ● ● ●
4 Non-union ● ● ● ●
*Seddon classification of nerve injuries (3)
4
*Classification of nerve injury
● ● ● ●
*Fracture patella
2
*Cysts around the knee joint
● ●
*Perthes disease (1):
2
- Radiological features
● ●
*Bennett fracture
2
*Scaphoid fracture
● ●
*Anterior dislocation of shoulder
2
*Frozen shoulder
● ●
*Fracture olecranon ●
2
*Tennis elbow ●
*Septic arthritis
2
*Osteoarthritis
● ●
2 Greenstick fracture ● ●
1 Below-knee amputation ●
1 Rickets ●
1 Arthroscopy ●
1 Osteogenesis imperfecta ●
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and its management in a polytrauma
1
patient
●
1 Acute compartment syndrome ●
1 Osteoporosis ●
1 Trendelenburg sign ●
You might also like
- Review ATLS & Post TestDocument41 pagesReview ATLS & Post TestNugraha Arganda Ginting100% (4)
- 01-09 2022 Pharm Chronic Care in Cardiology 2022 R4Document62 pages01-09 2022 Pharm Chronic Care in Cardiology 2022 R4Amira HelayelNo ratings yet
- OBGYN I Important QsDocument11 pagesOBGYN I Important QsDwivith ReddyNo ratings yet
- General Medicine II Important QsDocument8 pagesGeneral Medicine II Important QsDwivith ReddyNo ratings yet
- General Medicine I Important QsDocument8 pagesGeneral Medicine I Important QsDwivith ReddyNo ratings yet
- OBGYN II Important QsDocument10 pagesOBGYN II Important QsDwivith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Microbiology I Important QsDocument5 pagesMicrobiology I Important QsSeerat Ul irfanNo ratings yet
- Maloprodaja EuDocument6 pagesMaloprodaja EuIndex.hrNo ratings yet
- Paper TopicDocument2 pagesPaper Topicbrian mochez01No ratings yet
- Industrial Production Down by 0.5% in Euro AreaDocument6 pagesIndustrial Production Down by 0.5% in Euro AreaValter SilveiraNo ratings yet
- Industrial Production Up by 0.4% in Euro AreaDocument6 pagesIndustrial Production Up by 0.4% in Euro AreaDartonni SimangunsongNo ratings yet
- MBA20291 - Deepak Raj Tool Used: Do We Receive More Likes On Certain Days of The Week?Document3 pagesMBA20291 - Deepak Raj Tool Used: Do We Receive More Likes On Certain Days of The Week?deepak rajNo ratings yet
- Module 5 PMDocument22 pagesModule 5 PMmeghna devuNo ratings yet
- 4 02072019 Ap en PDFDocument6 pages4 02072019 Ap en PDFValter SilveiraNo ratings yet
- 2020Q2 CR Commercial Lending Whitepaper ENDocument14 pages2020Q2 CR Commercial Lending Whitepaper ENziad saberiNo ratings yet
- Rancangan Pengajaran Dan Pembelajaran Perlaksanaan Program Kod Kursus Ht-012-2:2012 Food Preparation and ProductionDocument1 pageRancangan Pengajaran Dan Pembelajaran Perlaksanaan Program Kod Kursus Ht-012-2:2012 Food Preparation and ProductionNurul Nasuha RazalliNo ratings yet
- Tim Carmona To Rcbc-Ipc For RiseDocument5 pagesTim Carmona To Rcbc-Ipc For RiseAlfredo Osana QuejadasNo ratings yet
- BP2 BoxlabelDocument1 pageBP2 BoxlabelAugusto SoaresNo ratings yet
- Odisha SpeechDocument16 pagesOdisha SpeechHari SahooNo ratings yet
- 1q 22 Ir Roadshow PresentationDocument68 pages1q 22 Ir Roadshow PresentationIosu Arrue GanzarainNo ratings yet
- Budget 2009-10: Preview: Expectations A Mirage or RealityDocument11 pagesBudget 2009-10: Preview: Expectations A Mirage or Realityapi-12317095No ratings yet
- China+Property+Market+Overview Q4+2020 Logistics enDocument14 pagesChina+Property+Market+Overview Q4+2020 Logistics enKhriztopher PhayNo ratings yet
- 101022-Ecowrap 20221010 PDFDocument6 pages101022-Ecowrap 20221010 PDFVindhuja VijayanNo ratings yet
- Myths About Moneyball For GovernmentDocument12 pagesMyths About Moneyball For GovernmentWaqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- RINU FINAL MSTR 2019 BatchDocument9 pagesRINU FINAL MSTR 2019 BatchDelphy VargheseNo ratings yet
- Kantar Worldpanel ComtechDocument2 pagesKantar Worldpanel ComtechStorm WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Materi Kebijakan Pa KabidDocument27 pagesMateri Kebijakan Pa KabidFiekry MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Repowering of The Indian Wind Sector Opportunities and The Way Ahead FactsheetDocument12 pagesRepowering of The Indian Wind Sector Opportunities and The Way Ahead FactsheetNATARAJAN VENKATARAMANAN BHARATHVAJNo ratings yet
- Third Year B.SC Nursing Master PlanDocument1 pageThird Year B.SC Nursing Master PlanDinesh JoyNo ratings yet
- GRC Arc: Elevation SectionDocument1 pageGRC Arc: Elevation SectionROSE STONENo ratings yet
- Summary of November 2018 Existing Home Sales StatisticsDocument10 pagesSummary of November 2018 Existing Home Sales StatisticsBlitz CapitalNo ratings yet
- Second Year B.SC Nursing Master PlanDocument1 pageSecond Year B.SC Nursing Master Planshubham vermaNo ratings yet
- Second Year B.SC Nursing Master PlanDocument1 pageSecond Year B.SC Nursing Master PlanJessica MerilynNo ratings yet
- Main Switch: General Specifications 7/27/2016 BWDocument6 pagesMain Switch: General Specifications 7/27/2016 BWfolkendanNo ratings yet
- 4q22 Investor Presentaion February 2023Document34 pages4q22 Investor Presentaion February 2023mukeshindpatiNo ratings yet
- Tagline Report PDFDocument5 pagesTagline Report PDFArnab BhattacharyaNo ratings yet
- Analyse The Relationship Between Government Spending and Investment Spending For The US Economy in The Past 20 YearsDocument7 pagesAnalyse The Relationship Between Government Spending and Investment Spending For The US Economy in The Past 20 YearsNeil VictorNo ratings yet
- DFG - Agriculture 2018-19Document8 pagesDFG - Agriculture 2018-19India CountryNo ratings yet
- Centro de Control de Motores Center LineDocument4 pagesCentro de Control de Motores Center LineJorge Johnny Chipana MachacaNo ratings yet
- 08-Trade and PaymentsDocument25 pages08-Trade and PaymentsAli AsgherNo ratings yet
- Elevation Section: Dia 10. MM Galvanized Steel Screw With Acmon BoltDocument1 pageElevation Section: Dia 10. MM Galvanized Steel Screw With Acmon BoltROSE STONENo ratings yet
- Southeast Texas Labor StatisticsDocument1 pageSoutheast Texas Labor StatisticsCharlie FoxworthNo ratings yet
- Roboguide Training Manual FRDE Z KAE TRN Roboguide 1 01 enDocument1 pageRoboguide Training Manual FRDE Z KAE TRN Roboguide 1 01 enpitNo ratings yet
- Ground Floor 0Document1 pageGround Floor 0Solaf ZeinNo ratings yet
- Trip 4Document1 pageTrip 4Anggraini IsmailNo ratings yet
- (Share) Chocozip - 2024FreePlanner - Line - MonoDocument93 pages(Share) Chocozip - 2024FreePlanner - Line - Monoปภังกร มาแพNo ratings yet
- Arq A2Document1 pageArq A2WILBUR JAVIER RAMOS LLANOSNo ratings yet
- Using Big Data To Improve Clinical CareDocument32 pagesUsing Big Data To Improve Clinical CareXiaodong WangNo ratings yet
- Ose 53cyl Etoile Ose 3 Sisters OkDocument2 pagesOse 53cyl Etoile Ose 3 Sisters OkJulio Almanza100% (1)
- Construction Output Up by 7.6% in Euro AreaDocument6 pagesConstruction Output Up by 7.6% in Euro AreamlubosNo ratings yet
- Small Change Big Difference: Joy Industrial Co., LTDDocument20 pagesSmall Change Big Difference: Joy Industrial Co., LTDcip2009No ratings yet
- Disjabar Lt3 Apd-Pt PLN Area Cirebon: Rev. Date Description Approved by Manager DrafterDocument1 pageDisjabar Lt3 Apd-Pt PLN Area Cirebon: Rev. Date Description Approved by Manager DrafterAlizar NurrachmanNo ratings yet
- Industy Output EU November: - 1,1%Document6 pagesIndusty Output EU November: - 1,1%Frode HaukenesNo ratings yet
- 4-Mahe Noor April-2012Document56 pages4-Mahe Noor April-2012Naushad AlamNo ratings yet
- 01 - Sheet 1 KM 100+000 To KM 101+300 Railway ReserveDocument1 page01 - Sheet 1 KM 100+000 To KM 101+300 Railway Reservedavid selekaNo ratings yet
- Annual Outlook 2023Document51 pagesAnnual Outlook 2023AbdusNo ratings yet
- Statutory ReportsDocument46 pagesStatutory Reportsguptadeepu905No ratings yet
- A Prosperous New ChinaDocument1 pageA Prosperous New ChinamuanaserNo ratings yet
- Wtoi 19aug20 e PDFDocument3 pagesWtoi 19aug20 e PDFMeloNo ratings yet
- GU 20 XX Yy - U Bolt Guía Con TPIDocument1 pageGU 20 XX Yy - U Bolt Guía Con TPIJesús JiménezNo ratings yet
- Mass Event Optimisation Stadion Narodowy": Project Presentation 2015.06.25Document76 pagesMass Event Optimisation Stadion Narodowy": Project Presentation 2015.06.25tarekgaraNo ratings yet
- Ref 27 Mortalitas Pada Malnutrisi DG AMLDocument9 pagesRef 27 Mortalitas Pada Malnutrisi DG AMLmuarifNo ratings yet
- MVR CabgDocument57 pagesMVR CabgRoshani sharma100% (1)
- Medicine 018 Final PDFDocument22 pagesMedicine 018 Final PDFdrkefyalewtayeNo ratings yet
- Quartet TrialDocument23 pagesQuartet Trialapi-647244341No ratings yet
- Safety Practices and Sports Injury ManagementDocument15 pagesSafety Practices and Sports Injury ManagementTrisha PilaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Cardiac Glycosides, Antianginals, and Antidysrhythmics - AntiarrhythmmicsDocument40 pagesLesson 1 Cardiac Glycosides, Antianginals, and Antidysrhythmics - AntiarrhythmmicsXiamen Magsino NolascoNo ratings yet
- Bacteriology Reviewer: Bacteria Important Notes Tests Aerobic Gram-Positive (+) CocciDocument18 pagesBacteriology Reviewer: Bacteria Important Notes Tests Aerobic Gram-Positive (+) CocciAJNo ratings yet
- Subjective:: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventi ONS Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesSubjective:: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventi ONS Rationale EvaluationCuttie Anne GalangNo ratings yet
- Respirology 2023 FinalDocument127 pagesRespirology 2023 FinalBelinda ELISHANo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet Physical Education 10: Quarter 4Document6 pagesLearning Activity Sheet Physical Education 10: Quarter 4Manilyn Naval EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Diabetic Teaching PlanDocument8 pagesDiabetic Teaching PlanChristy NervaisNo ratings yet
- Pgi Radiology ThesisDocument7 pagesPgi Radiology Thesisrehyfnugg100% (1)
- 9 Concept Map Digestive System PDFDocument1 page9 Concept Map Digestive System PDFLuke SmithNo ratings yet
- Granulomatous Diseases Affecting Oral Cavity: A ReviewDocument7 pagesGranulomatous Diseases Affecting Oral Cavity: A ReviewVikrant VazeNo ratings yet
- Form Ams Clinical Pathway Fillable Form Without CatheterDocument1 pageForm Ams Clinical Pathway Fillable Form Without CatheterTeenu JobyNo ratings yet
- Mental Health 2Document20 pagesMental Health 2LD 07No ratings yet
- HistiocytosisDocument19 pagesHistiocytosismednuclpg mednuclpgNo ratings yet
- PICAREDocument2 pagesPICAREagus susantoNo ratings yet
- HPV Amostras AlternativasDocument6 pagesHPV Amostras Alternativasnathaliasantosx3No ratings yet
- CXX - Neurosurgery NSDocument5 pagesCXX - Neurosurgery NSFarah FarahNo ratings yet
- DC - M. Youssry Final WhiteDocument21 pagesDC - M. Youssry Final Whitemarwa abdelmegedNo ratings yet
- MCQs On Urinary Tract InfectionDocument5 pagesMCQs On Urinary Tract InfectionTofik Mohammed100% (2)
- SepsisDocument24 pagesSepsislipu1982No ratings yet
- Teen DepressionDocument6 pagesTeen DepressionEmma WatsonNo ratings yet
- 9 - ABO DiscrpancyDocument16 pages9 - ABO Discrpancyجير يكو (جيريكو)No ratings yet
- BCG Vax DSDocument3 pagesBCG Vax DSSheena Marie M. TarleNo ratings yet
- Julio FormDocument3 pagesJulio Formefrenquesada84No ratings yet
- PE 10 - Lesson 2 - Prevention of Lifesyle DiseasesDocument33 pagesPE 10 - Lesson 2 - Prevention of Lifesyle DiseasesJayvee VillarNo ratings yet