Professional Documents
Culture Documents
L13: Urinary System: Lecturer: Dr. Frederick Abellana
L13: Urinary System: Lecturer: Dr. Frederick Abellana
Uploaded by
Filicidad EleseoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
L13: Urinary System: Lecturer: Dr. Frederick Abellana
L13: Urinary System: Lecturer: Dr. Frederick Abellana
Uploaded by
Filicidad EleseoCopyright:
Available Formats
L13: Urinary System
Lecturer: Dr. Frederick Abellana
Lecture Link: https://web.microsoftstream.com/video/c375f50b-9156-4a82-addc-
3a1059f2b0e9
⭐ Summary
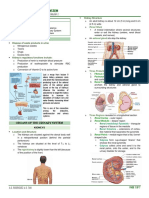
A. Parts/Components of the Urinary System
B. Basic Functions of the Urinary System
C. Kidney
C1. Classification as a Gland
C2. Gross Features of a Kidney
C3. Histologic Parts of a Kidney
A. Stroma
B. Parenchyma
C4. Lobulation of the Kidney
C4. Blood Supply of the Kidney
D. Uriniferous Tubules
D1. Parts of a Nephron
1. Renal Corpuscle
1.1 Glomerulus
1.2 Bowman’s Capsule
1.3 Bowman’s Space
2. Proximal tubule
3. Loop of Henle
4. Distal tubule
D2. Collecting Tubules
E. Excretory Passages
E1. Structure of All the Segments
Differences for the Male and Female Urethra
L13: Urinary System 1
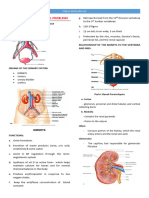
A. Parts/Components of the Urinary System
Kidneys Excretory Passages of the Kidney
passages of urine to the outside Composed of:
In number: 1. Normally - 2 2. Pathologically -
1. Calyces (Minor & Major) 2. Renal Pelvis 3.
sometimes 1 or 3
Ureter 4. Urinary Bladder 5. Urethra
‼️ Details were not said in the lec
B. Basic Functions of the Urinary System
1. Excretory function 2. Regulations of homeostasis
elimination of waste
products of metabolism
(such as Urea or BUN)
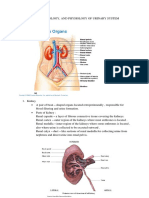
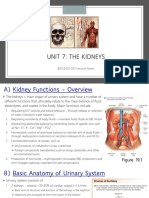
C. Kidney
Location Extend from the:
Right kidney is slightly lower
12th thoracic vertebra down to than the left kidney because of
Retroperitoneal (outside the
the third lumbar vertebrae the presence of the liver (large
peritoneal cavity)
(T12 - L3) organ in the right
hypochondriac region)
C1. Classification as a Gland
Based on Secretion Morphological Classification
Exocrine and Endocrine Compound tubular gland
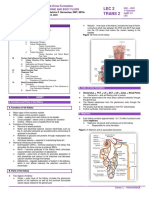
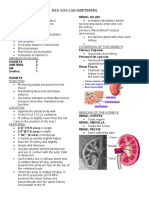
C2. Gross Features of a Kidney
L13: Urinary System 2
Shape Hilus/Hilum Renal Sinus
a cavity that will extend
inwards from the hilus/hilum
Contains: 1. renal blood
vessels — renal artery and
indentation in 1 side of the
bean-shaped vein) 2. renal pelvis of the
kidney
excretory passages of the
urinary system — funnel-
shaped upper part of the
ureter 3. adipose CT
Diagramatic Section of a Kidney
💡 Renal pelvis > Renal artery > Renal vein (nerve)
Usual arrangement
⭐ ACRONYM: RAN
L13: Urinary System 3
⭐ REMEMBER: If it is classified as a SOLID ORGAN, it will have a Stroma and
Parenchyma.
C3. Histologic Parts of a Kidney
A. Stroma
Reticular fiber
Capsule Trabecula and Septa Interstitial CT
network
2 types of capsule
1. Renal Capsule • Thin but
tough CT capsule •
membranous • adherent to
the substance of kidney 2.
Adipose capsule • found on
top of the thin tough CT
capsule • maintain the
location of the kidney •
prevent ptosis (drooping and
sagging)
B. Parenchyma
L13: Urinary System 4
Description Cortex and Medulla
functional component of organ composed of composed of uriniferous tubules which form
cells the parenchyma of the kidney
Cortex Medulla
peripheral darker part inner paler part of the kidney (in section)
Composed mainly of: Renal pyramid conical
Composed of: 1. Renal Columns of Bertini 2. structures oriented towards the hilus/hilum
Medullary rays of Ferrein (Pars radiata) ◦ Parts of the Renal Pyramid 1. Base - directed
radiata meaning “radiating” part 3. Cortical towards the capsule/cortex 2. Apex - directed
labyrinth (Pars convoluta) 4. Cortex cortices towards the renal sinus and capped by the
minor calyx
Parts of the Renal Cortex
Medullary rays of
Renal columns of Cortical labyrinth
Ferrein (Pars Cortex Cortices
Bertini (Pars Convoluta)
Radiata)
medullary tissue
extending towards the
cortical tissue cortex BUT will not
extending to the reach the capsule (so
medulla pyramids there is a part of the
cortex without the
medullary rays)
Located
immediately:
beneath the capsule
Located beween: the Located between: where the pars
pyramids the pars radiata radiata do not
extend and where the
renal corcpuscles
are absent
Composed of: Composed of: ◦ Composed ONLY of:
Straight collecting Renal corpuscles ◦ Convoluted tubules
tubules appears Convoluted tubules of the uriniferous
striated where you will of the uriniferous tubules ❗ No renal
find rays extending tubules corpuscle If no renal
L13: Urinary System 5
Medullary rays of
Renal columns of Cortical labyrinth
Ferrein (Pars Cortex Cortices
Bertini (Pars Convoluta)
Radiata)
from the base of the corpuscles, it could be
pyramid towards the renal cortices of
periphery pars radiata
C4. Lobulation of the Kidney
Renal lobe Renal lobule
Located at: the base of pyramid Composed
of: 1 medullary ray + half of the contiguous
(adjoining) cortical labyrinth on both sides
Composed of: 1 pyramid + cortical tissue whose nephrons will drain into the collecting
(overlying its base & covering its sides) tubules of that particular ray Central axis:
Cortical tissue: Renal columns of Bertin medullary ray Description: Lateral boundary
formed by interlobular blood vessels ◦
Structure that will divide the cortical labyrinth
into halves
L13: Urinary System 6
Picture: One renal lobe wherein only one lobule is presented. In actual specimen, there would be many
renal lobules in one renal pyramid.
C4. Blood Supply of the Kidney
⭐ Just trace the blood vessels
L13: Urinary System 7
• artery directly supplying the kidney which is a direct branch of the
1. Renal artery abdominal aorta • will enter the hilus of the kidney and becomes the
segmental artery
2. Segmental
artery
3. Lobar artery
4. Interlobar • in between the lobes of the kidney • will proceed to the base of the pyramid
artery and arch over the base of the pyramid to become the…
5. Arcuate artery
6. Interlobular
if you take one interlobular artery, it will give off the…
arteries
7. Afferent
supplying blood to the…
arteriole
8. Glomerulus
blood is then drained by…
(capillaries)
9. Efferent
drained by
arteriole
10. Peritubular
capillaries
L13: Urinary System 8
11. Interlobular
form the boundary of renal lobule
vein
12. Arcuate vein vein that arches at the base of the pyramid to the…
13. Interlobar
vein
14. Renal vein
15. Inferior vena
cava
‼️ NOTE:
Segmental vein is ABSENT in the venous side of circulation
💭 RECAP: Special Connection of Blood Vessels
Rete Mirable Portal System
Arteriole - Capillary - Arteriole Capillary - Arteriole - Capillary
Afferent arteriole - Glomerulus Glomerulus (capillaries) - Efferent
(capillaries) - Efferent arteriole arteriole - Peritubular capillaries
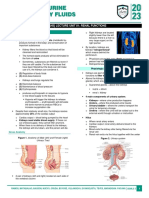
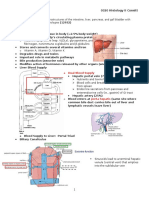
D. Uriniferous Tubules
Description Divided into
Form the parenchyma of the kidney • nephron • collecting tubules
⭐ NOTE: The kidney is classified as compound tubular
The structure inside the kidneys that makes it compound tubular is the
“uriniferous tubules”
Divisions of the Uriniferous Tubules
L13: Urinary System 9
Nephron Collecting tubules
Secretory portion Excretory portion
⭐ Structural and functional unit of the kidney Location in the cortex: Pars radiata
This is one uriniferous tubule, nephron (secretory part), and collectible tubule (excretory part)
D1. Parts of a Nephron
1. Renal Corpuscle
AKA Description Location Composition
Rounded structure
1st part of a 3 parts: • Glomerulus •
present in the pars
“Malpighian body” nephron is a Bowman’s capsule •
convoluta (cortical
globular structure Bowman’s space
labyrinth) of the kidney
L13: Urinary System 10
1.1 Glomerulus
Description network of capillaries
Parts of a Glomerulus
Juxta-glomerular cells Mesangium Mesangial Cells
As the afferent
arterioles enters the
corpuscle, the
smooth muscle in
the tunica media: (1)
becomes
Specialized
differentiated (2) the Interstitial CT a thin
fibroblast that will
nucleus becomes layer of connective
Description form the fibers in the
round, turning into tissue surrounding
mesangium of the
specialized cells the glomerulus
renal corpuscles
Specialized smooth
muscle cells in the
wall of the afferent
arteriole as the
arteriole approaches
the renal corpuscle
L13: Urinary System 11
Juxta-glomerular cells Mesangium Mesangial Cells
Mesangial cells
Vascular pole part
NOT found in the
where the blood
Composition Cells of
vessels enter and
Goormaghtigh
leave the renal
corpuscle are found
◦ Cells responsible for
Renin production
the production of
Function of Renin:
connective tissue in
Function Part of RAAS (renin-
mesangium ◦ Cells
angiotensin-
that will secrete the
aldosterone system)
connective tissue
Mesangial Cells are
aka: 1. Lacis cells 2.
Polkissen cells (“pin
Other Information cushion”) 3. Cells of
Goormaghtigh (form
part of the juxta-
glomerular complex)
1.2 Bowman’s Capsule
Description 2 Layers
Chalice-shaped double-walled epithelial
1. parietal layer 2. visceral layer
capsule surrounding the glomerulus
2 Layers of the Bowman’s Capsule
Parietal Layer (outer wall of capsule) Visceral Layer
Podocytes • Special type of cells immediately
surrounding capillaries • Star-stellate shaped
Lining Epithelium: Simple Squamous cells with foot processes (primary and
Epithelium secondary foot processes) → Foot processes
of adjacent podocyte cells will interdigitate to
form filtration slits
L13: Urinary System 12
📔 Filtration slit
Barrier between blood and ultrafiltrate the urine
Foot processes won’t stick to each other because of negative charges,
instead they repel each other, maintaining an area without any structure
1.3 Bowman’s Space
Narrow space between the visceral and parietal layers of Bowman’s capsule
Description Content of bowman’s space: urine filtrate This is where you will find the
urine
Structures pointed/mentioned: afferent
arteriole, efferent arteriole, Bowman’s At higher to ultra-magnification of glomerular capillary
capsule, parietal and visceral layers, and podocytes. Lining epithelium of glomerular capillary
Glomerulus and podocytes, Bowman’s has pores/opening/gaps between endothelium.
space, vascular pole, urinary pole. However, basement membrane is a continuous type,
no gaps/pores present. What type of capillary is this
one?
L13: Urinary System 13
📔 Urinary pole
is the point of emergence of the second part of the uriniferous tubule which is
the proximal tubule
📔 Podocytes
Primary foot processes and Secondary foot processes
📔 Secondary foot processes
will interdigitate with adjacent secondary foot processes of another podocyte
Not in contact with each other, there are spaces in between to form the
filtration slit where the fluid from the blood to form urine passes through
2. Proximal tubule
Composition composed of the straight part of the proximal tubule
Description Origin Composition Function Lining Epithelium
has a convoluted
& straight parts:
1. Convoluted
• 2nd part of Simple
part located in Reabsorption
nephron • Cuboidal
the pars (due to the
Longest and epithelium with
Arise from the convoluta of the presence of
broadest distinct microvilli
segment of the
urinary pole of
the renal
cortex 2.
Straight parts
brush border)
Substances
on the surface ⭐
uriniferous tubule For exam
corpuscle descend towards reabsorbed: 1.
• Form the main purposes, specify
the medulla to Salt 2. Water 3.
bulk of the renal as brush border
form the thick Glucose
cortex (for absorption)
descending
limb of the loop
of Henle
3. Loop of Henle
L13: Urinary System 14
Segments of the Loop of Henley
Thin segment Thick segment
Lining simple squamous
simple cuboidal epithelium
Epithelium epithelium
• ascend towards the cortex • straight part of the
Description part that form a loop
distal tubule
4. Distal tubule
Description Composition Macula densa Lining Epithelium
Shorter and thinner 1. convoluted part 2. As the distal tubule Simple cuboidal w/ no
than the proximal straight part — forms ascend towards its distinct striate border
tubule the ascending thick renal corpuscle of
limb of the loop of origin, it will be
Henle) juxtaposed to the
afferent arteriole of
its parent renal
corpuscle and the
L13: Urinary System 15
Description Composition Macula densa Lining Epithelium
cells that is opposed
to the afferent
arteriole becomes
specialized to form
the macula densa
⭐ is the sensor for
Na (sodium)
concentration of the
blood
Juxtaglomerular apparatus Juxtaglomerular complex
• Macula densa • Juxtaglomerular cells • Lacis
• Macula densa • Juxtaglomerular cells
cells
straight part of the proximal tubule forms the descending thick limb of the loop of Henle; straight part of
the distal tubule forming the ascending thick limb of the loop of Henle. Juxtaposed to the afferent
arteriole to form the juxtaglomerular complex: macula densa + juxtaglomerular cells + lacis cells
L13: Urinary System 16
D2. Collecting Tubules
Description Divided into
• Arched collecting tubule • Straight collecting
2nd portion of the Uriniferous tubules
tubule • Papillary duct of Bellini
Divisions of the Collecting Tubules
Arched collecting Straight collecting Papillary duct of
tubule tubule Bellini
shortest segment of longest segment of
dilated terminal part
the collecting tubules the collecting tubules
Will empty to the
straight collecting
tubule Area cribrosa
Will empty to the
a holey area in the
straight collecting
apex of the pyramid
tubule
where many Papillary
ducts of Bellini will
open to
simple cuboidal w/o simple cuboidal w/o
Lining epithelium simple columnar
microvilli microvilli
L13: Urinary System 17
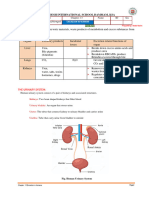
E. Excretory Passages
4. Urinary
1. Renal Calyces 2. Renal Pelvis 3. Ureter 5. Urethra
bladder
minor and major
💡 These are hollow organs, thus consider the lumens and the layers/tunics
in the wall of the organ.
E1. Structure of All the Segments
Renal pelvis Ureter Urinary bladder Urethra
Epithelium Transitional Transitional Transitional Males: has
Glands of Littre -
multicellular
intraepithelial
glands (similar to
the goblet cells)
Since the glands
L13: Urinary System 18
Renal pelvis Ureter Urinary bladder Urethra
of Littre does not
have an excretory
duct, the
secretions will be
transported to a
cavity/sinus in the
epithelium known
as the sinus of
Morgagni
Lamina propria Areolar CT Areolar CT Areolar CT Areolar CT
T. submucosa Absent Absent Absent Absent
Thick, interlacing
ILMCOL MC -
Well- defined
forms the internal
Upper: ILOC Thin layer of
Thin, ill- defined sphincter
T. muscularis Lower: ILMCOL smooth muscle
ILOC Detrusor muscle
MC - middle ILOC
• smooth muscle
circular
in the urinary
bladder
T. adventitia -
posteriorly T.
serosa -
anteriorly &
superiorly (urinary
bladder protrude
Last layer T. adventitita T. adventitia T. adventitia
to the pelvic
cavity or
abdominal cavity,
it is covered now
by serous
membrane)
Shape of Male: Stellate
Lumen (X- Crescentric Stellate Crescentric Female:
section) Crescentic
Differences for the Male and Female Urethra
L13: Urinary System 19
Bases Male Urethra Female Urethra
Length 20 cm (8 inches) because there are 4 segments 1-3 cm (1 inch)
Function Both urinary & reproductive Urinary only
Anterior vaginal
Location Prostate glands & penis
wall
1. Prostatic transitional 2. Membranous stratified
columnar 3. Penile (urethra inside the penis) stratified
Lining Epithelium
pseudostratified columnar plain 4. Fossa navicularis squamous
(dilated end of penile) stratified squamous
Shape of Lumen
stellate crescentric
(X-section)
L13: Urinary System 20
You might also like
- MintomanorDocument23 pagesMintomanorAlexCooperRTRNo ratings yet
- Final Exam Review - Bio 172Document21 pagesFinal Exam Review - Bio 172Erin McElhaney QuirkNo ratings yet
- Urinary System TransesDocument5 pagesUrinary System Transesadrielvamos28No ratings yet
- Kidney and Urinary SystmDocument5 pagesKidney and Urinary Systmambadyaparna14No ratings yet
- Urinary System and Fluid BalanceDocument3 pagesUrinary System and Fluid BalanceAiris Ramos AgillonNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument22 pagesUrinary SystemGray Odyssey M.No ratings yet
- Aubf Lec 2 Trans 2Document4 pagesAubf Lec 2 Trans 2Aj MondejarNo ratings yet
- Finals Reviewer Medsurg LecDocument117 pagesFinals Reviewer Medsurg LecKylle AlimosaNo ratings yet
- The Urinary System Kidneys: Calcitriol - Active Form of Vitamin D, Circulates As A HormoneDocument10 pagesThe Urinary System Kidneys: Calcitriol - Active Form of Vitamin D, Circulates As A HormonemasorNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument2 pagesUrinary SystemIzelwyn DaguioNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemCUESCANO, CRISTEL G. BSMT 2-ANo ratings yet
- LECTURE Urinary SystemDocument45 pagesLECTURE Urinary Systemjaveria choudharyNo ratings yet
- ANPH M3 CU11. Urinary SystemDocument13 pagesANPH M3 CU11. Urinary Systemmia LoremiaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Kidney 2015-2-13Document25 pagesHistology of Kidney 2015-2-13Chris Jardine LiNo ratings yet
- 13 Gross and Microscopic Structure of The Urinary SystemDocument23 pages13 Gross and Microscopic Structure of The Urinary SystemAubrey Cissé MwakayeNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument53 pagesUrinary SystemKatherineVoNo ratings yet
- A Level Yr 2 Module 5: Communication, Homeostasis and EnergyDocument52 pagesA Level Yr 2 Module 5: Communication, Homeostasis and EnergyDanielNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument30 pagesIntroductionSarvesh SoganiNo ratings yet
- Excretory System 2.0Document6 pagesExcretory System 2.0Kim DahyunNo ratings yet
- Urinalysis PDFDocument10 pagesUrinalysis PDFJoydee Liza MarcoNo ratings yet
- YU - Activity 11 - Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesYU - Activity 11 - Urinary SystemDenise Kyla Bernadette YuNo ratings yet
- URS SummaryDocument26 pagesURS SummaryMohamed HaridyNo ratings yet
- PPT14-Histology of Urinary SystemDocument17 pagesPPT14-Histology of Urinary SystemElvie ArriolaNo ratings yet
- Urinary System (Ch. 25) : "Kidney"Document3 pagesUrinary System (Ch. 25) : "Kidney"mira zosNo ratings yet
- MC I Modular Reviewer Urinary SystemDocument12 pagesMC I Modular Reviewer Urinary SystemSteiner LimNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Urinary SystemDocument7 pagesLesson 1 Urinary SystemJulio De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Renal Function and Related DiseasesDocument3 pagesRenal Function and Related DiseasesMonica DomingoNo ratings yet
- Li 1 Anatomy, Histology, PhysiologyDocument17 pagesLi 1 Anatomy, Histology, PhysiologysandyaadindaNo ratings yet
- Aubf LecDocument97 pagesAubf Lechinata shoyoNo ratings yet
- DR Laxman Khanal Bpkihs 07-06-2013Document86 pagesDR Laxman Khanal Bpkihs 07-06-2013Bilal YimamNo ratings yet
- Seeley GENITODocument20 pagesSeeley GENITOAce Khiel Peralta100% (1)
- The Urinary SystemDocument46 pagesThe Urinary SystemWeb AredomNo ratings yet
- NCERT Class 11th Bio - CHAPTER 16 - EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATIONDocument12 pagesNCERT Class 11th Bio - CHAPTER 16 - EXCRETORY PRODUCTS AND THEIR ELIMINATIONLukesh SadhNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesUrinary Systemvea-ann espesoNo ratings yet
- Kidney: PDF Generated At: Sun, 26 Jan 2014 03:55:26 UTCDocument15 pagesKidney: PDF Generated At: Sun, 26 Jan 2014 03:55:26 UTCVijay RajendiranNo ratings yet
- Ran Ii-Urinary System - 123718Document16 pagesRan Ii-Urinary System - 123718joykibaki066No ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 26 Urinary System Doran MLS 1 FDocument15 pagesAnaphy Chapter 26 Urinary System Doran MLS 1 FayenaNo ratings yet
- Excretion in Humans IX NOTESDocument6 pagesExcretion in Humans IX NOTESEalaf AliNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 Notes - The KidneyDocument39 pagesUnit 7 Notes - The Kidneyshrilpatel2001No ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument3 pagesThe Urinary SystemDaniel NevadoNo ratings yet
- Renal SystemDocument18 pagesRenal SystemS GNo ratings yet
- 0320 Histology II Consitt: o Dual Blood SupplyDocument8 pages0320 Histology II Consitt: o Dual Blood SupplyYvonne ChuehNo ratings yet
- Renal Physiology 1 1aDocument88 pagesRenal Physiology 1 1afentaw melkieNo ratings yet
- Renal Module Histology 2023-24Document28 pagesRenal Module Histology 2023-24ahmed saberNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesUrinary SystemKirsten CruzadoNo ratings yet
- Aubf ModulesDocument373 pagesAubf ModulesLeonora Nathalie Mae CiriacoNo ratings yet
- Case 8 GUS - AKIDocument210 pagesCase 8 GUS - AKIGroup 12 Sofia HanaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument6 pagesUrinary SystemKids JangNo ratings yet
- UNIT 15 - UrinaryDocument18 pagesUNIT 15 - UrinaryrushieraycoturquezaNo ratings yet
- Excretion and Homeostatsis NotesDocument12 pagesExcretion and Homeostatsis NotesrissNo ratings yet
- Urinary Sys TafeDocument54 pagesUrinary Sys TafeRiyaduNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument4 pagesUrinary SystemAntonioNo ratings yet
- Anph FinalsDocument44 pagesAnph FinalsVincent BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 Q4 LAS 4 Module 14Document5 pagesGen Bio 2 Q4 LAS 4 Module 14KatsumiJ Aki100% (1)
- General Zoology 1 LaboratoryDocument4 pagesGeneral Zoology 1 LaboratoryKirsten AletheaNo ratings yet
- Ex13 Urinary Sys Histology LabDocument2 pagesEx13 Urinary Sys Histology LabRod Daniel CalistonNo ratings yet
- Kidney and NephronDocument41 pagesKidney and NephronMd Atikur AminNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument9 pagesUrinary SystemPrincess OrsinoNo ratings yet
- Excretory System 1Document51 pagesExcretory System 1Victoria TanNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument66 pagesUrinary SystemJustine Vens G. AgustinNo ratings yet
- 9700 s03 QP 2 PDFDocument12 pages9700 s03 QP 2 PDFIG UnionNo ratings yet
- ABB Circuit Breaker 1250ADocument2 pagesABB Circuit Breaker 1250Adejan92No ratings yet
- Las Science 9 Melc 7 q2 Week-7Document7 pagesLas Science 9 Melc 7 q2 Week-7LINDSY MAE SULA-SULANo ratings yet
- TheoryDocument21 pagesTheoryArah Jean Barba DaffonNo ratings yet
- cfd1 IntroDocument6 pagescfd1 IntrowhateverNo ratings yet
- Demo Teaching Online Class DLLDocument14 pagesDemo Teaching Online Class DLLTcher CharleeneNo ratings yet
- Race and History An Ethnological Introduction To History - Pittard EugeneDocument546 pagesRace and History An Ethnological Introduction To History - Pittard EugeneLeonardoLazéraNo ratings yet
- Tillamook Creamery IceCream Menu 07.01.21Document1 pageTillamook Creamery IceCream Menu 07.01.21Samantha AndersonNo ratings yet
- PDF The Marketig Plan of Cocoon Viet Nam CompressDocument36 pagesPDF The Marketig Plan of Cocoon Viet Nam CompressTHUẬN THANH NGUYỄN LÊNo ratings yet
- Exp#1 Diode Characteristics V2Document12 pagesExp#1 Diode Characteristics V2Shehda ZahdaNo ratings yet
- HS-C0964SA3 / HS-C1264SA4 HS-C1865SA4 / HS-C2465SA1: FeaturesDocument1 pageHS-C0964SA3 / HS-C1264SA4 HS-C1865SA4 / HS-C2465SA1: FeaturesklseklseNo ratings yet
- Nut Strudel To GrandmaDocument77 pagesNut Strudel To GrandmaVerfica HandaruniNo ratings yet
- 10.1108@aeat 12 2019 0247Document10 pages10.1108@aeat 12 2019 0247İhsan Alp OzdemirNo ratings yet
- Delicious Egg Salad For Sandwiches: by Wifeyluvs2cookDocument1 pageDelicious Egg Salad For Sandwiches: by Wifeyluvs2cookAntigone Vasiliou MarkolefasNo ratings yet
- POwered Pallet Trucks - Manuals - AtlasCopco - FBW - FBW2440RevADocument16 pagesPOwered Pallet Trucks - Manuals - AtlasCopco - FBW - FBW2440RevAEduardo.s. EurolevaNo ratings yet
- Transportation ProblemDocument53 pagesTransportation ProblemJapa SonNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Biology (8040/9040)Document12 pagesMark Scheme (Results) January 2007: GCE Biology (8040/9040)Fathmath MohamedNo ratings yet
- Vertical Axis Wind TurbinepdfDocument100 pagesVertical Axis Wind TurbinepdfGodfrey EmilioNo ratings yet
- 2020 Big Game Draw SupplementDocument8 pages2020 Big Game Draw SupplementRuger LaclareNo ratings yet
- Smart Mail Box NotifierDocument16 pagesSmart Mail Box NotifierShahrim MohdNo ratings yet
- Transformer Winding Resistance MeterDocument15 pagesTransformer Winding Resistance MeterSyed Haider FaizanNo ratings yet
- ICTP VaporPressureGroup 2 PDFDocument27 pagesICTP VaporPressureGroup 2 PDFHarySetiyawanNo ratings yet
- High Rise Building EffectsDocument51 pagesHigh Rise Building Effectsdphilip96No ratings yet
- Real Life - The Body and Related VerbsDocument2 pagesReal Life - The Body and Related VerbsSuper JudyNo ratings yet
- History of SwimmingDocument3 pagesHistory of SwimmingScuzzy BacolorNo ratings yet
- Hiradc Om - Talian AtasDocument57 pagesHiradc Om - Talian AtasapnadiNo ratings yet
- Lichfield Sutton Coldfield Birmingham Long Bridge RedditchDocument4 pagesLichfield Sutton Coldfield Birmingham Long Bridge RedditchLouisMichaelNo ratings yet
- 2021 Sustainability ReportDocument101 pages2021 Sustainability ReportGrupo DOCStore Brasil LtdaNo ratings yet
- Viscopro 2000: Monitoring and Control For Single-Line Process EnvironmentsDocument4 pagesViscopro 2000: Monitoring and Control For Single-Line Process EnvironmentsLuz Stella Calixto GomezNo ratings yet