Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Etiopathogenesis: Investigation in
Etiopathogenesis: Investigation in
Uploaded by
snehasishk51Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Statement For 2022-1Document2 pagesStatement For 2022-1Hengki Yono100% (2)
- Brine Shrimp Lab ReportDocument3 pagesBrine Shrimp Lab ReportKaisen Yao100% (3)
- PlasticSurgery-SummaryDocument17 pagesPlasticSurgery-SummarymohamedNo ratings yet
- 72 - Skin CancerDocument1 page72 - Skin CancerRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- Skin and Endo 2022Document10 pagesSkin and Endo 2022Sure NavyasriNo ratings yet
- OpthalmologyDocument6 pagesOpthalmologyeilyabashir315No ratings yet
- Dermatology PYQ's by DR SaraDocument50 pagesDermatology PYQ's by DR SaraHemant GargNo ratings yet
- Breast-SummaryDocument10 pagesBreast-SummarymohamedNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology Dent1411Document7 pagesOral Pathology Dent1411api-663458841No ratings yet
- Dermatology PYQ's by DR SaraDocument46 pagesDermatology PYQ's by DR SaraaswathiajithNo ratings yet
- C13. Vaginal, Vulvar & CervicalDocument4 pagesC13. Vaginal, Vulvar & Cervicalhari dharshanNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Concept MapDocument1 pageBreast Cancer Concept MapScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Pseudoglandular-Acantholytic Squamous Cell CarcinomaDocument9 pagesPseudoglandular-Acantholytic Squamous Cell CarcinomaMariantonieta Tirado0% (1)
- AIIMS CAPSULE AtfDocument70 pagesAIIMS CAPSULE Atfsimrankaur2003studNo ratings yet
- 409 FullDocument11 pages409 FullMario QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Disease Cheat SheetDocument393 pagesDisease Cheat Sheetsurviving nursing school50% (2)
- URO 3 - Neoplasm in The Genitourinary TractDocument8 pagesURO 3 - Neoplasm in The Genitourinary TractHa Jae kyeongNo ratings yet
- Dermatology NLC DR Manish Soni 2021Document94 pagesDermatology NLC DR Manish Soni 2021akashineeNo ratings yet
- Aula 7 FBMCCR 2324Document16 pagesAula 7 FBMCCR 2324VanessaMarquesNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Revision E6.5 'Document35 pagesDermatology Revision E6.5 'Riya SharmaNo ratings yet
- " Chest:: by Definition Malignant Tumor of The Lung Primary Its EtiologyDocument10 pages" Chest:: by Definition Malignant Tumor of The Lung Primary Its EtiologyAhmed GaberNo ratings yet
- Adrenal IncidentalomaDocument46 pagesAdrenal IncidentalomaFelipe GomezNo ratings yet
- Eca - Cellular Aberration-Neuro-MusculoskeletalDocument29 pagesEca - Cellular Aberration-Neuro-MusculoskeletalFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Revision E6.5 @theboggusdocDocument36 pagesDermatology Revision E6.5 @theboggusdockhushi koliNo ratings yet
- Zoonosis (Plu - ZoonosessDocument8 pagesZoonosis (Plu - Zoonosess6wcdwfcfydNo ratings yet
- Systems 1 Test 4Document59 pagesSystems 1 Test 4bjpalmer100% (2)
- Transplante CorneaDocument5 pagesTransplante CorneaJossie TeneriaNo ratings yet
- Melanoma: Noverissa V. TorralbaDocument51 pagesMelanoma: Noverissa V. Torralbamarian yuqueNo ratings yet
- Edited Patho OspeDocument246 pagesEdited Patho Ospecodingninja7953No ratings yet
- Cutaneous LeishmaniasisDocument23 pagesCutaneous LeishmaniasisScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Wilm's TumourDocument4 pagesWilm's TumourherbsdoktaNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocument8 pagesIron Deficiency Anemiakrithik.2k3No ratings yet
- 12 DetoxificationDocument3 pages12 DetoxificationSu Ling ShihNo ratings yet
- Miltefosine Induced Keratitis in Patients With Post Kala Azar Dermal LeishmaniasisDocument1 pageMiltefosine Induced Keratitis in Patients With Post Kala Azar Dermal LeishmaniasisR KusumeshNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 6 Vaccines MODERNA PFIZER BIONTECH ASTRAZENECA KeyDocument1 pageCOVID 19 6 Vaccines MODERNA PFIZER BIONTECH ASTRAZENECA KeyKhalid HabibNo ratings yet
- Mist Pune March 5Document159 pagesMist Pune March 5Dikshant DaswatNo ratings yet
- Group 2: CPC#3: Salivary Gland: Primary Mucinous AdenocarcinomaDocument5 pagesGroup 2: CPC#3: Salivary Gland: Primary Mucinous AdenocarcinomaZazaNo ratings yet
- Newsletter Isu-24 PathOut DermPathDocument4 pagesNewsletter Isu-24 PathOut DermPathLuis CoronadoNo ratings yet
- (SURG) 5.4b Management of Soft Tissue SarcomaDocument6 pages(SURG) 5.4b Management of Soft Tissue SarcomaKenneth TorresNo ratings yet
- Kelly 2014Document4 pagesKelly 2014maisaokadaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: FunctionDocument2 pagesIntegumentary System: FunctionAngelynNo ratings yet
- Dermatology SummariesDocument7 pagesDermatology SummariesShiv KolheNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: Key PointsDocument16 pagesNeoplasia: Key PointsskNo ratings yet
- Skin Cancer 1Document15 pagesSkin Cancer 1marina wezlyNo ratings yet
- pm0150 LooksteinRobert Debulki MondayDocument27 pagespm0150 LooksteinRobert Debulki MondayVimal NishadNo ratings yet
- Malignant Tumor: 1. Basal Cell CarcinomaDocument3 pagesMalignant Tumor: 1. Basal Cell CarcinomaERIKA MARIZ DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- 3 2564 Oral Defence Mechanism-2Document13 pages3 2564 Oral Defence Mechanism-2thitiwut.peeNo ratings yet
- Trans 4 Malignant Proliferations of The Skin DR GuillanoDocument7 pagesTrans 4 Malignant Proliferations of The Skin DR GuillanofredrrgNo ratings yet
- Patho 2 Important QuestionsDocument54 pagesPatho 2 Important QuestionsSadanand DubeyNo ratings yet
- Notes DermaDocument17 pagesNotes DermaCiullaeNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgery Summaryupdated PDFDocument16 pagesNeurosurgery Summaryupdated PDFEl FaroukNo ratings yet
- MS NTBKDocument10 pagesMS NTBKARIANE DOLINONo ratings yet
- OB - GYN Clerkship Charts - Google Drive PDFDocument1 pageOB - GYN Clerkship Charts - Google Drive PDFrpascua123No ratings yet
- Discomfort Glandular: PituitaryDocument7 pagesDiscomfort Glandular: PituitaryEdward XiamNo ratings yet
- Oncology (Tra Intl)Document9 pagesOncology (Tra Intl)Cess MarigondonNo ratings yet
- Ocr 439989329 Practice Questions For Dermatology Specialty Examinati 5Document50 pagesOcr 439989329 Practice Questions For Dermatology Specialty Examinati 5Andrés WunderwaldNo ratings yet
- Genetic DisordersDocument3 pagesGenetic Disordersdia akuNo ratings yet
- TumorDocument5 pagesTumori gede ricky jaya purnawarmanNo ratings yet
- A22M0163DR - ArponDocument7 pagesA22M0163DR - ArponAnton CornelNo ratings yet
- DV 1Document32 pagesDV 1Mujahidin ArismanNo ratings yet
- Family Neisseriaceae and Their AttributesDocument2 pagesFamily Neisseriaceae and Their AttributesJesette KhoNo ratings yet
- Disability Report V03 SinglePagesDocument44 pagesDisability Report V03 SinglePagesAmerlia AdzianNo ratings yet
- Factories and Works Act 15:04 RGN 264: Building, Structural and Excavation WorkDocument19 pagesFactories and Works Act 15:04 RGN 264: Building, Structural and Excavation WorkCourageNo ratings yet
- ReferensiDocument4 pagesReferensiluluNo ratings yet
- Terex Genie Rl4000 Operation Manual d1Document6 pagesTerex Genie Rl4000 Operation Manual d1florine100% (60)
- 1-Introduction To Food ScienceDocument2 pages1-Introduction To Food SciencepavanidhawanNo ratings yet
- Toyota Forklift 8fbet15!20!8fbekt16 18 8fbmt15 20 Repair ManualDocument22 pagesToyota Forklift 8fbet15!20!8fbekt16 18 8fbmt15 20 Repair Manualalexhughes210188dzo100% (133)
- HB1202Document5 pagesHB1202WTVCNo ratings yet
- VSTEP-Reading Test 9Document15 pagesVSTEP-Reading Test 9Lê Đặng Minh ThảoNo ratings yet
- Gfps 6470 Brochure Exhaust Gas Scrubber enDocument12 pagesGfps 6470 Brochure Exhaust Gas Scrubber enYao WeiNo ratings yet
- BS 476 Class 0Document8 pagesBS 476 Class 0Tomek BudaNo ratings yet
- G8 Radial Groundwater Flow in Confined AquiferDocument12 pagesG8 Radial Groundwater Flow in Confined AquiferkurtieberberNo ratings yet
- Blood TestDocument2 pagesBlood TestKhalid GulNo ratings yet
- Tokomama 1Document960 pagesTokomama 1gerry zonathanNo ratings yet
- Foreclosed Property BidDocument14 pagesForeclosed Property BidJessah JaliqueNo ratings yet
- 3A2988C - XM PFP Mix Manifold, Instructions - Parts, EnglishDocument22 pages3A2988C - XM PFP Mix Manifold, Instructions - Parts, Englishjorge ChavezNo ratings yet
- Methods For The Assessment of Productivity of Small Hold FarmsDocument49 pagesMethods For The Assessment of Productivity of Small Hold FarmsMonaliz NagrampaNo ratings yet
- Force and Pressure MCQDocument6 pagesForce and Pressure MCQnitikaNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Social Sciences and Health Research - FinalDocument24 pagesEthics in Social Sciences and Health Research - FinalRyan Michael OducadoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4: Creating The Logical ArchitectureDocument20 pagesAssignment 4: Creating The Logical Architectureapi-651266391No ratings yet
- Kronoxonic EN 2018Document12 pagesKronoxonic EN 2018vladimirmarkovski8119No ratings yet
- Addiction and Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games (Mmorpgs) : An In-Depth Study of Key AspectsDocument46 pagesAddiction and Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games (Mmorpgs) : An In-Depth Study of Key AspectsInna MaynizaNo ratings yet
- Exp 8Document18 pagesExp 8goblinsbrideNo ratings yet
- Goodhormonehealth News Jan16 PDFDocument10 pagesGoodhormonehealth News Jan16 PDFBrian CoxNo ratings yet
- SOP For Safety WalkthroughDocument5 pagesSOP For Safety WalkthroughNeshar AhmadNo ratings yet
- WWW - Bis.gov - In: Products Indian Standards For Preparation of DocumentsDocument22 pagesWWW - Bis.gov - In: Products Indian Standards For Preparation of DocumentsC. M. JebinNo ratings yet
- RAP-RM-2-1 Risk Mapping Technical SpecificationDocument65 pagesRAP-RM-2-1 Risk Mapping Technical SpecificationjlmontesrauroszmNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms v11 I03 20230622Document15 pagesMicroorganisms v11 I03 20230622Editor IJDMNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Aditya SirDocument39 pagesLecture 5 Aditya Sirankur soniNo ratings yet
Etiopathogenesis: Investigation in
Etiopathogenesis: Investigation in
Uploaded by
snehasishk51Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Etiopathogenesis: Investigation in
Etiopathogenesis: Investigation in
Uploaded by
snehasishk51Copyright:
Available Formats
.
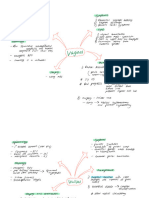
1 Tumor type : Malignant Squamous Cell Carcinoma
2 . Cell
of Origin : Keratinocytes
.
1 Crusted or
scaly patch T red inflamed Base .
.
2 Nodular Lession Proliferative Growth
feature
.
Clinical
non-healing
5
. : .
3 A ulcer
.
M
Age - > 50
years
Presentation
-
Prediliction Exposed Sun Areas alw Long standing Inflamation .
-
,
Para
neoplasticSyndrome --
Risk factor :
.
4
Etiopathogenesis : 1) X-Ray
-> Loss
of P53 -X
Apoptosis d/t UU
Exposure 1) Arsenic vI) Marjolin Uker .
-> Mut
of BeLc and RAS (1) UV
~ alt .
Epidermal Growth factor .
4 (v) Actinic Keratosis
v) Immunosuppression
Investigation in ↓
: 4 HPV 5 and S
· Patho-
Biopsy ->
Histopathology
· radio-O Broder's
Classification
·
Micro- Y L &
.
6
Microscopic Examinat :
Diff
Well Mod .
diff Poorly Diff.
1 . Keratin pearl (Keratinpear1) (single cell) (few sq .
Cell)
.
2 Desmosomes
(high power) Keratinizat Nu atypia
Variants >
a) Acantholytic SCC I H 2
. .
- CK
, p63
b) Spindle all SCC
.
7
.
Gross : Crusted scaly patch ,
Nodular Lession , inflamed red Base
.
Ulceration (+/-)
.
8
Prognosticfactors : Well
Diff>NoMet > Better
Prognosis
.
9 Treatment : -
Interesting fact:
and Most
Malignancy
10
. Common Skin .
You might also like
- Statement For 2022-1Document2 pagesStatement For 2022-1Hengki Yono100% (2)
- Brine Shrimp Lab ReportDocument3 pagesBrine Shrimp Lab ReportKaisen Yao100% (3)
- PlasticSurgery-SummaryDocument17 pagesPlasticSurgery-SummarymohamedNo ratings yet
- 72 - Skin CancerDocument1 page72 - Skin CancerRica Alyssa PepitoNo ratings yet
- Skin and Endo 2022Document10 pagesSkin and Endo 2022Sure NavyasriNo ratings yet
- OpthalmologyDocument6 pagesOpthalmologyeilyabashir315No ratings yet
- Dermatology PYQ's by DR SaraDocument50 pagesDermatology PYQ's by DR SaraHemant GargNo ratings yet
- Breast-SummaryDocument10 pagesBreast-SummarymohamedNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology Dent1411Document7 pagesOral Pathology Dent1411api-663458841No ratings yet
- Dermatology PYQ's by DR SaraDocument46 pagesDermatology PYQ's by DR SaraaswathiajithNo ratings yet
- C13. Vaginal, Vulvar & CervicalDocument4 pagesC13. Vaginal, Vulvar & Cervicalhari dharshanNo ratings yet
- Breast Cancer Concept MapDocument1 pageBreast Cancer Concept MapScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Pseudoglandular-Acantholytic Squamous Cell CarcinomaDocument9 pagesPseudoglandular-Acantholytic Squamous Cell CarcinomaMariantonieta Tirado0% (1)
- AIIMS CAPSULE AtfDocument70 pagesAIIMS CAPSULE Atfsimrankaur2003studNo ratings yet
- 409 FullDocument11 pages409 FullMario QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Disease Cheat SheetDocument393 pagesDisease Cheat Sheetsurviving nursing school50% (2)
- URO 3 - Neoplasm in The Genitourinary TractDocument8 pagesURO 3 - Neoplasm in The Genitourinary TractHa Jae kyeongNo ratings yet
- Dermatology NLC DR Manish Soni 2021Document94 pagesDermatology NLC DR Manish Soni 2021akashineeNo ratings yet
- Aula 7 FBMCCR 2324Document16 pagesAula 7 FBMCCR 2324VanessaMarquesNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Revision E6.5 'Document35 pagesDermatology Revision E6.5 'Riya SharmaNo ratings yet
- " Chest:: by Definition Malignant Tumor of The Lung Primary Its EtiologyDocument10 pages" Chest:: by Definition Malignant Tumor of The Lung Primary Its EtiologyAhmed GaberNo ratings yet
- Adrenal IncidentalomaDocument46 pagesAdrenal IncidentalomaFelipe GomezNo ratings yet
- Eca - Cellular Aberration-Neuro-MusculoskeletalDocument29 pagesEca - Cellular Aberration-Neuro-MusculoskeletalFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Revision E6.5 @theboggusdocDocument36 pagesDermatology Revision E6.5 @theboggusdockhushi koliNo ratings yet
- Zoonosis (Plu - ZoonosessDocument8 pagesZoonosis (Plu - Zoonosess6wcdwfcfydNo ratings yet
- Systems 1 Test 4Document59 pagesSystems 1 Test 4bjpalmer100% (2)
- Transplante CorneaDocument5 pagesTransplante CorneaJossie TeneriaNo ratings yet
- Melanoma: Noverissa V. TorralbaDocument51 pagesMelanoma: Noverissa V. Torralbamarian yuqueNo ratings yet
- Edited Patho OspeDocument246 pagesEdited Patho Ospecodingninja7953No ratings yet
- Cutaneous LeishmaniasisDocument23 pagesCutaneous LeishmaniasisScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Wilm's TumourDocument4 pagesWilm's TumourherbsdoktaNo ratings yet
- Iron Deficiency AnemiaDocument8 pagesIron Deficiency Anemiakrithik.2k3No ratings yet
- 12 DetoxificationDocument3 pages12 DetoxificationSu Ling ShihNo ratings yet
- Miltefosine Induced Keratitis in Patients With Post Kala Azar Dermal LeishmaniasisDocument1 pageMiltefosine Induced Keratitis in Patients With Post Kala Azar Dermal LeishmaniasisR KusumeshNo ratings yet
- COVID 19 6 Vaccines MODERNA PFIZER BIONTECH ASTRAZENECA KeyDocument1 pageCOVID 19 6 Vaccines MODERNA PFIZER BIONTECH ASTRAZENECA KeyKhalid HabibNo ratings yet
- Mist Pune March 5Document159 pagesMist Pune March 5Dikshant DaswatNo ratings yet
- Group 2: CPC#3: Salivary Gland: Primary Mucinous AdenocarcinomaDocument5 pagesGroup 2: CPC#3: Salivary Gland: Primary Mucinous AdenocarcinomaZazaNo ratings yet
- Newsletter Isu-24 PathOut DermPathDocument4 pagesNewsletter Isu-24 PathOut DermPathLuis CoronadoNo ratings yet
- (SURG) 5.4b Management of Soft Tissue SarcomaDocument6 pages(SURG) 5.4b Management of Soft Tissue SarcomaKenneth TorresNo ratings yet
- Kelly 2014Document4 pagesKelly 2014maisaokadaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: FunctionDocument2 pagesIntegumentary System: FunctionAngelynNo ratings yet
- Dermatology SummariesDocument7 pagesDermatology SummariesShiv KolheNo ratings yet
- Neoplasia: Key PointsDocument16 pagesNeoplasia: Key PointsskNo ratings yet
- Skin Cancer 1Document15 pagesSkin Cancer 1marina wezlyNo ratings yet
- pm0150 LooksteinRobert Debulki MondayDocument27 pagespm0150 LooksteinRobert Debulki MondayVimal NishadNo ratings yet
- Malignant Tumor: 1. Basal Cell CarcinomaDocument3 pagesMalignant Tumor: 1. Basal Cell CarcinomaERIKA MARIZ DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- 3 2564 Oral Defence Mechanism-2Document13 pages3 2564 Oral Defence Mechanism-2thitiwut.peeNo ratings yet
- Trans 4 Malignant Proliferations of The Skin DR GuillanoDocument7 pagesTrans 4 Malignant Proliferations of The Skin DR GuillanofredrrgNo ratings yet
- Patho 2 Important QuestionsDocument54 pagesPatho 2 Important QuestionsSadanand DubeyNo ratings yet
- Notes DermaDocument17 pagesNotes DermaCiullaeNo ratings yet
- Neurosurgery Summaryupdated PDFDocument16 pagesNeurosurgery Summaryupdated PDFEl FaroukNo ratings yet
- MS NTBKDocument10 pagesMS NTBKARIANE DOLINONo ratings yet
- OB - GYN Clerkship Charts - Google Drive PDFDocument1 pageOB - GYN Clerkship Charts - Google Drive PDFrpascua123No ratings yet
- Discomfort Glandular: PituitaryDocument7 pagesDiscomfort Glandular: PituitaryEdward XiamNo ratings yet
- Oncology (Tra Intl)Document9 pagesOncology (Tra Intl)Cess MarigondonNo ratings yet
- Ocr 439989329 Practice Questions For Dermatology Specialty Examinati 5Document50 pagesOcr 439989329 Practice Questions For Dermatology Specialty Examinati 5Andrés WunderwaldNo ratings yet
- Genetic DisordersDocument3 pagesGenetic Disordersdia akuNo ratings yet
- TumorDocument5 pagesTumori gede ricky jaya purnawarmanNo ratings yet
- A22M0163DR - ArponDocument7 pagesA22M0163DR - ArponAnton CornelNo ratings yet
- DV 1Document32 pagesDV 1Mujahidin ArismanNo ratings yet
- Family Neisseriaceae and Their AttributesDocument2 pagesFamily Neisseriaceae and Their AttributesJesette KhoNo ratings yet
- Disability Report V03 SinglePagesDocument44 pagesDisability Report V03 SinglePagesAmerlia AdzianNo ratings yet
- Factories and Works Act 15:04 RGN 264: Building, Structural and Excavation WorkDocument19 pagesFactories and Works Act 15:04 RGN 264: Building, Structural and Excavation WorkCourageNo ratings yet
- ReferensiDocument4 pagesReferensiluluNo ratings yet
- Terex Genie Rl4000 Operation Manual d1Document6 pagesTerex Genie Rl4000 Operation Manual d1florine100% (60)
- 1-Introduction To Food ScienceDocument2 pages1-Introduction To Food SciencepavanidhawanNo ratings yet
- Toyota Forklift 8fbet15!20!8fbekt16 18 8fbmt15 20 Repair ManualDocument22 pagesToyota Forklift 8fbet15!20!8fbekt16 18 8fbmt15 20 Repair Manualalexhughes210188dzo100% (133)
- HB1202Document5 pagesHB1202WTVCNo ratings yet
- VSTEP-Reading Test 9Document15 pagesVSTEP-Reading Test 9Lê Đặng Minh ThảoNo ratings yet
- Gfps 6470 Brochure Exhaust Gas Scrubber enDocument12 pagesGfps 6470 Brochure Exhaust Gas Scrubber enYao WeiNo ratings yet
- BS 476 Class 0Document8 pagesBS 476 Class 0Tomek BudaNo ratings yet
- G8 Radial Groundwater Flow in Confined AquiferDocument12 pagesG8 Radial Groundwater Flow in Confined AquiferkurtieberberNo ratings yet
- Blood TestDocument2 pagesBlood TestKhalid GulNo ratings yet
- Tokomama 1Document960 pagesTokomama 1gerry zonathanNo ratings yet
- Foreclosed Property BidDocument14 pagesForeclosed Property BidJessah JaliqueNo ratings yet
- 3A2988C - XM PFP Mix Manifold, Instructions - Parts, EnglishDocument22 pages3A2988C - XM PFP Mix Manifold, Instructions - Parts, Englishjorge ChavezNo ratings yet
- Methods For The Assessment of Productivity of Small Hold FarmsDocument49 pagesMethods For The Assessment of Productivity of Small Hold FarmsMonaliz NagrampaNo ratings yet
- Force and Pressure MCQDocument6 pagesForce and Pressure MCQnitikaNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Social Sciences and Health Research - FinalDocument24 pagesEthics in Social Sciences and Health Research - FinalRyan Michael OducadoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4: Creating The Logical ArchitectureDocument20 pagesAssignment 4: Creating The Logical Architectureapi-651266391No ratings yet
- Kronoxonic EN 2018Document12 pagesKronoxonic EN 2018vladimirmarkovski8119No ratings yet
- Addiction and Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games (Mmorpgs) : An In-Depth Study of Key AspectsDocument46 pagesAddiction and Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Games (Mmorpgs) : An In-Depth Study of Key AspectsInna MaynizaNo ratings yet
- Exp 8Document18 pagesExp 8goblinsbrideNo ratings yet
- Goodhormonehealth News Jan16 PDFDocument10 pagesGoodhormonehealth News Jan16 PDFBrian CoxNo ratings yet
- SOP For Safety WalkthroughDocument5 pagesSOP For Safety WalkthroughNeshar AhmadNo ratings yet
- WWW - Bis.gov - In: Products Indian Standards For Preparation of DocumentsDocument22 pagesWWW - Bis.gov - In: Products Indian Standards For Preparation of DocumentsC. M. JebinNo ratings yet
- RAP-RM-2-1 Risk Mapping Technical SpecificationDocument65 pagesRAP-RM-2-1 Risk Mapping Technical SpecificationjlmontesrauroszmNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms v11 I03 20230622Document15 pagesMicroorganisms v11 I03 20230622Editor IJDMNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Aditya SirDocument39 pagesLecture 5 Aditya Sirankur soniNo ratings yet