Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chap - 1 Types of Buildings and Building Drawings
Chap - 1 Types of Buildings and Building Drawings
Uploaded by
tekalignCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Professional Ethics Ll.b. Project FileDocument3 pagesProfessional Ethics Ll.b. Project Filemanoj103563% (16)
- Civil Engineering Words in EnglishDocument17 pagesCivil Engineering Words in EnglishMateus PachecoNo ratings yet
- EXPERIENCE RECORD For Personal Informati PDFDocument10 pagesEXPERIENCE RECORD For Personal Informati PDFThiwakkaran Muagan100% (1)
- Supersheds: The Architecture of Long-Span, Large-Volume BuildingsFrom EverandSupersheds: The Architecture of Long-Span, Large-Volume BuildingsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- BCA-122 Mathematics & Statistics PDFDocument242 pagesBCA-122 Mathematics & Statistics PDFDinesh Gaikwad100% (7)
- Service Parts+Ml 3050,+Ml 3051nd XfaDocument190 pagesService Parts+Ml 3050,+Ml 3051nd Xfaabm503181No ratings yet
- Chapter03 Entity Relationship ModelingDocument59 pagesChapter03 Entity Relationship Modelingbianca09sh57% (7)
- Thickness Monitoring Location Guide PDFDocument16 pagesThickness Monitoring Location Guide PDFdosetiadi100% (4)
- Basic Building Materials and Construction-Part I & IIDocument184 pagesBasic Building Materials and Construction-Part I & IIGãlväñ FôxNo ratings yet
- GBC - MODULE - 1 (2) - Lecture NotesDocument88 pagesGBC - MODULE - 1 (2) - Lecture Notesqjh2wwx7smNo ratings yet
- House Plan and Construction: Guided By: Submitted byDocument33 pagesHouse Plan and Construction: Guided By: Submitted byShivam KashyapNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document21 pagesCH 1IshworRaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Intro To CTDocument38 pagesChapter 1 - Intro To CTKhairi AzharNo ratings yet
- ARCH UPDA Questions - PREPARATIONDocument77 pagesARCH UPDA Questions - PREPARATIONMohammed YacobNo ratings yet
- ARCH MMUP EXAM (Important)Document8 pagesARCH MMUP EXAM (Important)arch usamaNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Analysis and DesignDocument14 pagesA Project Report On Analysis and Designyoyo 9585873163100% (1)
- Lecture 1 - Overview of Construction IndustryDocument52 pagesLecture 1 - Overview of Construction IndustryWong Yi RenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Architectural Drawing, Concept of Line and Developed Plan, Plan Elevation and Section, Is 962 RecommendationsDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Architectural Drawing, Concept of Line and Developed Plan, Plan Elevation and Section, Is 962 RecommendationsSaurabh KasliwalNo ratings yet
- Project Report-12Document89 pagesProject Report-12Sri RamyaNo ratings yet
- Types of Buildings: - Occupancy WiseDocument23 pagesTypes of Buildings: - Occupancy WiseMd. Tariqul IslamNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Building ServicesDocument17 pages01 Introduction To Building ServicesAr Anuj ChandraNo ratings yet
- Construction Engineering: Topic 1Document14 pagesConstruction Engineering: Topic 1Wei MingNo ratings yet
- Material Studies: Dr. Trịnh Thị Thanh Huyền October 2022Document60 pagesMaterial Studies: Dr. Trịnh Thị Thanh Huyền October 2022Bich Nga BuiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Construction SystemsDocument53 pagesIntroduction To Construction SystemsChuck LewisNo ratings yet
- Construction History2014Document22 pagesConstruction History2014Nicholas KinotiNo ratings yet
- Buildng Construction PDFDocument130 pagesBuildng Construction PDFfirst name last nameNo ratings yet
- PD Requirements IEEDocument7 pagesPD Requirements IEEJan Felix DonsalNo ratings yet
- EQ12 ADocument83 pagesEQ12 Ahram_phdNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Loads - ByelawsDocument26 pagesModule 2 - Loads - ByelawsCuckoomodiNo ratings yet
- 2002 CE L1 Building ConstructionDocument164 pages2002 CE L1 Building ConstructionKalum ChandraNo ratings yet
- Quantity Surveying - Quantity Surveying PDFDocument33 pagesQuantity Surveying - Quantity Surveying PDFMohannad S ZebariNo ratings yet
- Ad 3Document4 pagesAd 3Monica LisingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Basic ConceptsDocument31 pagesChapter 1-Basic Conceptsazamislam726537No ratings yet
- 3 & 4 Eurocodes and Design ProcessDocument30 pages3 & 4 Eurocodes and Design ProcessSarah HaiderNo ratings yet
- Construction - Week 8Document34 pagesConstruction - Week 8Sarah HaiderNo ratings yet
- BSYDES Reviewer Part 2Document4 pagesBSYDES Reviewer Part 2jakexsanchez1515No ratings yet
- Peb 2Document6 pagesPeb 2Ayush GargNo ratings yet
- Epic ProposalDocument8 pagesEpic ProposalMahpuja JulangNo ratings yet
- BFT Handbook 2Document69 pagesBFT Handbook 2battybussaNo ratings yet
- Ceo ReviewerDocument10 pagesCeo Reviewermagistrado.rozzNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Drawings of AW WorksDocument10 pagesComparative Study of Drawings of AW WorksWajid MalikNo ratings yet
- Building Constructio N LDocument55 pagesBuilding Constructio N LOliver Del CarmenNo ratings yet
- CV501-Advanced Construction TechnologyDocument4 pagesCV501-Advanced Construction TechnologyNANDHINI SNo ratings yet
- GBC 1Document4 pagesGBC 1Coloneli JamesNo ratings yet
- Building Construction Is The Engineering Deals With The Construction of Building Such AsDocument36 pagesBuilding Construction Is The Engineering Deals With The Construction of Building Such AsMichaelNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument19 pagesIntroductionRandom SwagNo ratings yet
- 1 - Orientation of BuildingDocument31 pages1 - Orientation of BuildingM Bilal Zahid100% (1)
- B.Arch Syllabus 5th SemDocument9 pagesB.Arch Syllabus 5th SemMirza IsmaelNo ratings yet
- BSD Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesBSD Midterm ReviewerJames CapacilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introcduction Copy 2Document83 pagesChapter 1 - Introcduction Copy 2Shaik HussainNo ratings yet
- Civil Technology: Subject RequirementsDocument2 pagesCivil Technology: Subject RequirementsVengatesh VelusamyNo ratings yet
- MC TEC 01 Module 1Document23 pagesMC TEC 01 Module 1Joshua HerreraNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of A Multi Storied Residential Building of (Ung-2+G+10) by Using Most Economical Column MethodDocument8 pagesAnalysis and Design of A Multi Storied Residential Building of (Ung-2+G+10) by Using Most Economical Column MethoddhanashekarVNo ratings yet
- W1-Intro To Construction SystemDocument29 pagesW1-Intro To Construction SystemNUR AIN SUHAILA AFANDINo ratings yet
- 201001: Building Technology and Materials: Second Year Civil Engineering (Document4 pages201001: Building Technology and Materials: Second Year Civil Engineering (SumantKulkarniNo ratings yet
- Chap 12345Document64 pagesChap 12345paulin100% (1)
- Building Construction LDocument55 pagesBuilding Construction LRoland CepedaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Notes 2011-6Document68 pagesConcrete Notes 2011-6Kaveesh NCDNo ratings yet
- Dr. Anil Joseph PDFDocument104 pagesDr. Anil Joseph PDFmaran2326No ratings yet
- CE Shop 1: 1 Year StandingDocument33 pagesCE Shop 1: 1 Year StandingChristian Nathaniel Ramon PalmaNo ratings yet
- Beijing National Stadium: The Bird 'S NestDocument31 pagesBeijing National Stadium: The Bird 'S NestMichelle Lie100% (2)
- 1-Introduction, Site Selection & OrientationDocument25 pages1-Introduction, Site Selection & OrientationMuhammad Basit100% (1)
- Film Institute Theses Report ScribdDocument13 pagesFilm Institute Theses Report ScribdMOHD ASIFNo ratings yet
- Chap2 RC IDocument24 pagesChap2 RC ItekalignNo ratings yet
- RC 1 2015 16 Lecture NoteDocument92 pagesRC 1 2015 16 Lecture NotetekalignNo ratings yet
- Chap - 3 Elements of BuilldingDocument52 pagesChap - 3 Elements of BuilldingtekalignNo ratings yet
- Chap-4 Damp PreventionDocument3 pagesChap-4 Damp PreventiontekalignNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Earthquake LoadDocument79 pagesChapter 2 Earthquake LoadtekalignNo ratings yet
- 2 4 Hole 2 3 Hole 4 Hole Puncher Unit A1 SMDocument91 pages2 4 Hole 2 3 Hole 4 Hole Puncher Unit A1 SMAashish ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- API 6D Valves Bonney Forge PDFDocument12 pagesAPI 6D Valves Bonney Forge PDFSQUALO_122No ratings yet
- TOPSIM - General Management II: Participants' ManualDocument38 pagesTOPSIM - General Management II: Participants' ManualMaria AdelineNo ratings yet
- Akira LCT-32V82ST - LCD TVC - Manual de Servicio PDFDocument41 pagesAkira LCT-32V82ST - LCD TVC - Manual de Servicio PDFJosé Nicolás Auciello I100% (1)
- Catálogo Ricoh MP 4001-MP 5001Document6 pagesCatálogo Ricoh MP 4001-MP 5001Andrew JacobNo ratings yet
- Sleeping Raccoon: Level 80 Parts Time To Create 15 HourDocument24 pagesSleeping Raccoon: Level 80 Parts Time To Create 15 HourleidyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Science V2 1617Document10 pagesMathematics Science V2 1617Hatem Ghassan GharzeddineNo ratings yet
- Farm Structures in Tropicalo ClimatesDocument421 pagesFarm Structures in Tropicalo Climatesed327100% (2)
- DS ECO P2235dn P2235dw 4ml PDFDocument2 pagesDS ECO P2235dn P2235dw 4ml PDFblazaNo ratings yet
- Crank Effort DiagramsDocument4 pagesCrank Effort DiagramsDirajen PMNo ratings yet
- Crow Tengu HalfmaskDocument10 pagesCrow Tengu HalfmaskMelissa Yaclara TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Canon Laser Shot Lbp3300Document2 pagesCanon Laser Shot Lbp3300meenadarlingNo ratings yet
- Heidenhain Ik 121v ManualDocument116 pagesHeidenhain Ik 121v ManualmasinemaNo ratings yet
- Bizhub Press c1100 c1085 Catalog eDocument12 pagesBizhub Press c1100 c1085 Catalog eAndy IoNo ratings yet
- Copystar Copier CS-1650-2050 Parts & ServiceDocument381 pagesCopystar Copier CS-1650-2050 Parts & Servicebrslaser100% (2)
- A Paper Sizes - A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10Document3 pagesA Paper Sizes - A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10RajaKuppanNo ratings yet
- QS Book PDFDocument191 pagesQS Book PDFBrilliant Temp100% (2)
- Manual PHPDocument90 pagesManual PHPAngellColmenaresNo ratings yet
- Game Controller DBDocument13 pagesGame Controller DBfirmanNo ratings yet
- Copic Catalog 2015Document25 pagesCopic Catalog 2015GREY WEATHERSNo ratings yet
- HP Designjet T630 36-In Printer: Simply The World'S Easiest Large-Format Plotters - Affordability Without TradeoffsDocument2 pagesHP Designjet T630 36-In Printer: Simply The World'S Easiest Large-Format Plotters - Affordability Without Tradeoffsahmedmy4nNo ratings yet
- Introduction To OpenOffice CalcDocument7 pagesIntroduction To OpenOffice CalcAina Shoib100% (1)
- Is 15726 2006 - Iso 13715 PDFDocument20 pagesIs 15726 2006 - Iso 13715 PDFPippozzo Pipini0% (2)
Chap - 1 Types of Buildings and Building Drawings
Chap - 1 Types of Buildings and Building Drawings
Uploaded by
tekalignOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chap - 1 Types of Buildings and Building Drawings
Chap - 1 Types of Buildings and Building Drawings
Uploaded by
tekalignCopyright:
Available Formats
Arba Minch University Department of Civil Engineering
Chapter -1
Types of Building and Drawing
Introduction:
Building Construction is a traditional Science which deals with the modern methods of sound
construction incorporating appropriate use of materials, sufficient strength and permanence,
maximum utility and good proportion and grace. The building design has traditionally been
the responsibility of the Architect though the building construction has been the responsibility
of the civil Engineer. However, the structural design of the building is the responsibility of a
civil Engineer.
Building Definition:
Any structure for whatsoever purpose and of whatsoever materials constructed and every part
thereof whether used as human habitation or not and includes foundations , plinth walls
floors, roofs , chimneys, plumbing and building services, verandah, balcony, cornice or
projections, any thing affixed there to or any wall enclosing the building.
Types of Building
1. Residential Building
Those building in which sleeping accommodation is provided for normal residential
purposes with or with out cooking or dinning or both facilities.
Example: Dormitories, apartment houses (flats), hotels
2. Educational Building:
These include any building used for school, college or day care purposes for more than
8 hours per week involving assembly for instruction, education or recreation.
3. Institutional Building:
Includes any building or part thereof which is used for purposes such as medical or
other treatment or care of persons suffering from physical or mental illness, disease,
for penal or correctional purposes.
-Institutional buildings ordinarily provide sleeping accommodation for the
occupants.
Example: Hospitals , penal institutions.
4. Assembly Building
Includes any building or part of building where group of people congregate or gather for
amusement, recreation, social, religious, patriotic, civil, travel and similar purposes
Example: Theatres, dance halls, assembly halls etc
Building Construction Lecture Notes 1
Arba Minch University Department of Civil Engineering
5. Business Buildings
Includes buildings for the transaction of business for the keeping of accounts and records.
Example: City halls, court houses, libraries
6. Mercantile Buildings
Includes any building or part of building which is used as shops, stores, markets, for
display and sale of merchandise, either whole sale or retail.
7. Industrial buildings
Any building or part of a building or structure in which products or materials of all kinds
and properties are fabricated, assembled or processed.
e.g. Assembly plants, laboratories, power plant, pumping stations refineries
8. Storage Buildings
Used primarily for the storage or sheltering of goods, wares, merchandise
Example: Warehouses, cold storage, store houses, freight deposit.
9. Hazardous Buildings
Used for storage, handling, manufacturing or processing of highly combustible or
explosive materials or products which are liable to burnt with extreme rapidity and/ or
which produces poisonous fumes or explosions.
The main Considerations in the architectural design of buildings for all purposes are
- Climate and its effects
- People and their requirements
- Materials for Construction and method of construction
- regulations and by laws
1.2 Building Drawing:
Drawing Basics
1) Drawing sheets (ISO- standard)
Designation Size (mm x mm)
A0 841 x 1189
A1 594 x 841
A2 420 x 594
A3 297 x 420
A4 210 x 297
A5 148 x 210
Building Construction Lecture Notes 2
Arba Minch University Department of Civil Engineering
2) Instruments
- T Square
- Pencil with leads of different hardness
6B, 5B,….. 2B , B, HB, F, H,………, 4H, ……9H
Soft Medium Hard
- Erasers
- Pencil sharpeners
- Reduction scales
- Brush
- Drawing boards
- Protractor
- Case instruments (Divider, Compass)
- Templates
- Fastening Tapes, etc
Scale
Enlarged Same Size Reduced
2000:1 1:1 1:2
1000:1 Machine 1:5
500:1 Drawing 1:50
200:1 1:100
100:1 1:500
50:1 1:1000
5:1 1:2000
2:1
Building Construction Lecture Notes 3
Arba Minch University Department of Civil Engineering
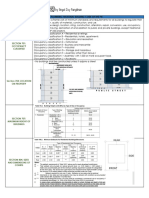
Common symbols
Symbol Description
0.000 Existing level on plan
0.000 Existing level on a Section
0.000 Required level on a Plan
0.000 Required level on a Section
Centerline
Property line
Typical door opening
Window section plan
General purpose brick and
stone construction
Concrete Construction
Earth
H.C.B (Hollow
Concrete Block)
Building Construction Lecture Notes 4
Arba Minch University Department of Civil Engineering
Beds
Cup
board
s
Fixtures (plumbing and Electrical)
Water closet – Wall hang (WC)
0
Water closet – Floor outlet hang ( W C)
Water closet – Tank tyre (WC)
Urinals – Wall hang (U)
Wash fountain –Circular (WF)
Hand wash basin
Or Kitchen
Boiler Boiler
Electrical stove
Refrigerator
Building Construction Lecture Notes 5
Arba Minch University Department of Civil Engineering
1.3 BUILDING CONSTRUCTION
Definition: A construction is some thing made by man for one or another purpose; Road,
Bridge, dam etc.
Human beings are motivated by the desire for better living condition.
Steps of development of building
i) Cave – no furniture
- the floor was used for all purposes
- no door
ii) Door was invented
iii) Development of progress and the house started to be divided into rooms.
Requirement for construction
Site on which to build a house
material
permission
Labour
A building consists not only of the house, but also the sites, roads, the garden, the gate,… etc.
It should be planned and well adopted to its purpose so that the combination result a complete
harmonious unit.
House construction in Ethiopia
Low lands :- Rain is scarce, usually dry and windy, timber is not abundantly available, stone
is available.
Branchs
Earth
log
Mortar Temperature
>surrounding
GL temp.
GL Fig _ Typical House construction in
Low lands
30-40cm
- Openings for doors and windows is
difficult
40-60cm
Building Construction Lecture Notes 6
Arba Minch University Department of Civil Engineering
High lands: There is heavy rain and is usually wet, timber is abundant, stone is less
available.
Timber
Corrugated
iron sheet
Typical house
construction in High lands
Steps in building construction
Site work Fundamental of design
& construction
Building construction
Office work
Building drawing
Design is of a process of:
- Blending various aspects of a certain given problem with the aim of arriving at a best
solution with in a given scope.
- Selecting the best solution for a problem under given circumstance.
- Performance of social and cultural acts of an individual with in a society.
- Creation
- Act of conveying human message
The most important design in civil Engineering
1. Architectural design
2. Structural design
3. electrical installation design
4. sanitary design
Building Construction Lecture Notes 7
Arba Minch University Department of Civil Engineering
Functional relations of Rooms
Garage
Kitchen Store Entrance
W.C
Break fast Dinning
Room Office
Living Room
Bed Room
Bath or shower
House plan
Functions and positions of rooms in a house
1. Entrance hall
- must be protected from weather
- should have Space for receiving visitors
- Should give access to other rooms with out entering the living room
2. Living Room
-Used for general day time activities, services mainly as focus of social activities of
family, round fire place, fed or coffee table and for leisure activities.
3. Kitchen:
-Should be placed in the rear of the building in one corner opposite to the direction of
flowing wind.
-Best placed towards North-east or North- west of house.
-It relates horizontally to front door, dinning room or meal space, food store,
vertically to bath room, W.C and other areas requiring water supply and
drainage.
-It may also be enlarged to contain dinning table and chairs for breakfast.
-There should be an adequate space for work, free from interruption and if
possible a space for additional equipment or larger items, likely to be used in
future.
Building Construction Lecture Notes 8
Arba Minch University Department of Civil Engineering
-May also be provided with chimney for smoke to escape and other utensils like
stove and refrigerator.
4. Dining Room
- direct access from hall or entrance or corridor, not necessarily, but from kitchen
it is essential.
- Sufficient space to accommodate guests in dinning room
- Out side dinning room verandah should lie on wind protected sunny
side of the house in front of dinning or living room
5. Studio or office
- frequently serves as office or work room, rear entrance and living room
- Space for required furniture in sensible arrangements
- orientation: east, west and south
6. Bed Room
- Should be located on the sides of the building with at least one wall exposed
open for ventilation and lighting.
- Space for required furniture in sensible arrangements
- orientation: East, west and south
7. Bath Room
- Space for appropriate bath room equipment, hanging towels, w.c , bidet washing
basin, etc.
8. Corridor
It is a passage affording independent entrance to various rooms and compartments.
9. Verandah:-
Should be located in the front and rear of the building.
Maximum and minimum areas for different parts of a building:
Name of rooms Floor area for Floor area for Min. floor
standard building ordinary building Area (m2)
(m2) (m2)
Living Room 20-28 Up to 20 13.5
Dining Room 17-20 - 10
Bed Room 15-25 15-20 11
Office 7-9 - 6.5
Guest room 9-10.50 - 7.0
Kitchen 7-9 7-8.5 5.5
Store 7-9 5.50-6.00 5.5
Dressing Room 4-7 - 5.5
Servant Room 9-10 - 8.0
Garage 15-18 - 11
Verandah 2.5-3.00 m wide 1.8-2.5 1.5 m wide.
Building Construction Lecture Notes 9
Arba Minch University Department of Civil Engineering
Minimum height of rooms
Height of main rooms: 3 -3.50m
Height of kitchen, store and bath room = 2.70m
For residential building the covered area should be at least as given below.
Size of plot Covered area of building Space left (m)
(m2) Front Rear Sides
Plot < 200 66% of the site area 3.0 3.6 1.5
201-500 50% of the site area or 150 4.5 6.0 2.0
m2 which ever is more
501-1000 40% of the area or 250m2 6.0 7.5 3.0
which ever is more
>1000 33% of the area or 400m2 9.0 10.5 3.0
which ever is more
Maximum area occupied by wall= 20% of the total area of the building
Maximum area occupied by verandah= 10-20% of the total area of the bldg
4
Floor area of room and verandah = A-20%A = A
5
Where A= area of building.
Building Construction Lecture Notes 10
You might also like
- Professional Ethics Ll.b. Project FileDocument3 pagesProfessional Ethics Ll.b. Project Filemanoj103563% (16)
- Civil Engineering Words in EnglishDocument17 pagesCivil Engineering Words in EnglishMateus PachecoNo ratings yet
- EXPERIENCE RECORD For Personal Informati PDFDocument10 pagesEXPERIENCE RECORD For Personal Informati PDFThiwakkaran Muagan100% (1)
- Supersheds: The Architecture of Long-Span, Large-Volume BuildingsFrom EverandSupersheds: The Architecture of Long-Span, Large-Volume BuildingsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- BCA-122 Mathematics & Statistics PDFDocument242 pagesBCA-122 Mathematics & Statistics PDFDinesh Gaikwad100% (7)
- Service Parts+Ml 3050,+Ml 3051nd XfaDocument190 pagesService Parts+Ml 3050,+Ml 3051nd Xfaabm503181No ratings yet
- Chapter03 Entity Relationship ModelingDocument59 pagesChapter03 Entity Relationship Modelingbianca09sh57% (7)
- Thickness Monitoring Location Guide PDFDocument16 pagesThickness Monitoring Location Guide PDFdosetiadi100% (4)
- Basic Building Materials and Construction-Part I & IIDocument184 pagesBasic Building Materials and Construction-Part I & IIGãlväñ FôxNo ratings yet
- GBC - MODULE - 1 (2) - Lecture NotesDocument88 pagesGBC - MODULE - 1 (2) - Lecture Notesqjh2wwx7smNo ratings yet
- House Plan and Construction: Guided By: Submitted byDocument33 pagesHouse Plan and Construction: Guided By: Submitted byShivam KashyapNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document21 pagesCH 1IshworRaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Intro To CTDocument38 pagesChapter 1 - Intro To CTKhairi AzharNo ratings yet
- ARCH UPDA Questions - PREPARATIONDocument77 pagesARCH UPDA Questions - PREPARATIONMohammed YacobNo ratings yet
- ARCH MMUP EXAM (Important)Document8 pagesARCH MMUP EXAM (Important)arch usamaNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Analysis and DesignDocument14 pagesA Project Report On Analysis and Designyoyo 9585873163100% (1)
- Lecture 1 - Overview of Construction IndustryDocument52 pagesLecture 1 - Overview of Construction IndustryWong Yi RenNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Architectural Drawing, Concept of Line and Developed Plan, Plan Elevation and Section, Is 962 RecommendationsDocument27 pagesIntroduction To Architectural Drawing, Concept of Line and Developed Plan, Plan Elevation and Section, Is 962 RecommendationsSaurabh KasliwalNo ratings yet
- Project Report-12Document89 pagesProject Report-12Sri RamyaNo ratings yet
- Types of Buildings: - Occupancy WiseDocument23 pagesTypes of Buildings: - Occupancy WiseMd. Tariqul IslamNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Building ServicesDocument17 pages01 Introduction To Building ServicesAr Anuj ChandraNo ratings yet
- Construction Engineering: Topic 1Document14 pagesConstruction Engineering: Topic 1Wei MingNo ratings yet
- Material Studies: Dr. Trịnh Thị Thanh Huyền October 2022Document60 pagesMaterial Studies: Dr. Trịnh Thị Thanh Huyền October 2022Bich Nga BuiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Construction SystemsDocument53 pagesIntroduction To Construction SystemsChuck LewisNo ratings yet
- Construction History2014Document22 pagesConstruction History2014Nicholas KinotiNo ratings yet
- Buildng Construction PDFDocument130 pagesBuildng Construction PDFfirst name last nameNo ratings yet
- PD Requirements IEEDocument7 pagesPD Requirements IEEJan Felix DonsalNo ratings yet
- EQ12 ADocument83 pagesEQ12 Ahram_phdNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Loads - ByelawsDocument26 pagesModule 2 - Loads - ByelawsCuckoomodiNo ratings yet
- 2002 CE L1 Building ConstructionDocument164 pages2002 CE L1 Building ConstructionKalum ChandraNo ratings yet
- Quantity Surveying - Quantity Surveying PDFDocument33 pagesQuantity Surveying - Quantity Surveying PDFMohannad S ZebariNo ratings yet
- Ad 3Document4 pagesAd 3Monica LisingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Basic ConceptsDocument31 pagesChapter 1-Basic Conceptsazamislam726537No ratings yet
- 3 & 4 Eurocodes and Design ProcessDocument30 pages3 & 4 Eurocodes and Design ProcessSarah HaiderNo ratings yet
- Construction - Week 8Document34 pagesConstruction - Week 8Sarah HaiderNo ratings yet
- BSYDES Reviewer Part 2Document4 pagesBSYDES Reviewer Part 2jakexsanchez1515No ratings yet
- Peb 2Document6 pagesPeb 2Ayush GargNo ratings yet
- Epic ProposalDocument8 pagesEpic ProposalMahpuja JulangNo ratings yet
- BFT Handbook 2Document69 pagesBFT Handbook 2battybussaNo ratings yet
- Ceo ReviewerDocument10 pagesCeo Reviewermagistrado.rozzNo ratings yet
- Comparative Study of Drawings of AW WorksDocument10 pagesComparative Study of Drawings of AW WorksWajid MalikNo ratings yet
- Building Constructio N LDocument55 pagesBuilding Constructio N LOliver Del CarmenNo ratings yet
- CV501-Advanced Construction TechnologyDocument4 pagesCV501-Advanced Construction TechnologyNANDHINI SNo ratings yet
- GBC 1Document4 pagesGBC 1Coloneli JamesNo ratings yet
- Building Construction Is The Engineering Deals With The Construction of Building Such AsDocument36 pagesBuilding Construction Is The Engineering Deals With The Construction of Building Such AsMichaelNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument19 pagesIntroductionRandom SwagNo ratings yet
- 1 - Orientation of BuildingDocument31 pages1 - Orientation of BuildingM Bilal Zahid100% (1)
- B.Arch Syllabus 5th SemDocument9 pagesB.Arch Syllabus 5th SemMirza IsmaelNo ratings yet
- BSD Midterm ReviewerDocument5 pagesBSD Midterm ReviewerJames CapacilloNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introcduction Copy 2Document83 pagesChapter 1 - Introcduction Copy 2Shaik HussainNo ratings yet
- Civil Technology: Subject RequirementsDocument2 pagesCivil Technology: Subject RequirementsVengatesh VelusamyNo ratings yet
- MC TEC 01 Module 1Document23 pagesMC TEC 01 Module 1Joshua HerreraNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of A Multi Storied Residential Building of (Ung-2+G+10) by Using Most Economical Column MethodDocument8 pagesAnalysis and Design of A Multi Storied Residential Building of (Ung-2+G+10) by Using Most Economical Column MethoddhanashekarVNo ratings yet
- W1-Intro To Construction SystemDocument29 pagesW1-Intro To Construction SystemNUR AIN SUHAILA AFANDINo ratings yet
- 201001: Building Technology and Materials: Second Year Civil Engineering (Document4 pages201001: Building Technology and Materials: Second Year Civil Engineering (SumantKulkarniNo ratings yet
- Chap 12345Document64 pagesChap 12345paulin100% (1)
- Building Construction LDocument55 pagesBuilding Construction LRoland CepedaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Notes 2011-6Document68 pagesConcrete Notes 2011-6Kaveesh NCDNo ratings yet
- Dr. Anil Joseph PDFDocument104 pagesDr. Anil Joseph PDFmaran2326No ratings yet
- CE Shop 1: 1 Year StandingDocument33 pagesCE Shop 1: 1 Year StandingChristian Nathaniel Ramon PalmaNo ratings yet
- Beijing National Stadium: The Bird 'S NestDocument31 pagesBeijing National Stadium: The Bird 'S NestMichelle Lie100% (2)
- 1-Introduction, Site Selection & OrientationDocument25 pages1-Introduction, Site Selection & OrientationMuhammad Basit100% (1)
- Film Institute Theses Report ScribdDocument13 pagesFilm Institute Theses Report ScribdMOHD ASIFNo ratings yet
- Chap2 RC IDocument24 pagesChap2 RC ItekalignNo ratings yet
- RC 1 2015 16 Lecture NoteDocument92 pagesRC 1 2015 16 Lecture NotetekalignNo ratings yet
- Chap - 3 Elements of BuilldingDocument52 pagesChap - 3 Elements of BuilldingtekalignNo ratings yet
- Chap-4 Damp PreventionDocument3 pagesChap-4 Damp PreventiontekalignNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Earthquake LoadDocument79 pagesChapter 2 Earthquake LoadtekalignNo ratings yet
- 2 4 Hole 2 3 Hole 4 Hole Puncher Unit A1 SMDocument91 pages2 4 Hole 2 3 Hole 4 Hole Puncher Unit A1 SMAashish ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- API 6D Valves Bonney Forge PDFDocument12 pagesAPI 6D Valves Bonney Forge PDFSQUALO_122No ratings yet
- TOPSIM - General Management II: Participants' ManualDocument38 pagesTOPSIM - General Management II: Participants' ManualMaria AdelineNo ratings yet
- Akira LCT-32V82ST - LCD TVC - Manual de Servicio PDFDocument41 pagesAkira LCT-32V82ST - LCD TVC - Manual de Servicio PDFJosé Nicolás Auciello I100% (1)
- Catálogo Ricoh MP 4001-MP 5001Document6 pagesCatálogo Ricoh MP 4001-MP 5001Andrew JacobNo ratings yet
- Sleeping Raccoon: Level 80 Parts Time To Create 15 HourDocument24 pagesSleeping Raccoon: Level 80 Parts Time To Create 15 HourleidyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Science V2 1617Document10 pagesMathematics Science V2 1617Hatem Ghassan GharzeddineNo ratings yet
- Farm Structures in Tropicalo ClimatesDocument421 pagesFarm Structures in Tropicalo Climatesed327100% (2)
- DS ECO P2235dn P2235dw 4ml PDFDocument2 pagesDS ECO P2235dn P2235dw 4ml PDFblazaNo ratings yet
- Crank Effort DiagramsDocument4 pagesCrank Effort DiagramsDirajen PMNo ratings yet
- Crow Tengu HalfmaskDocument10 pagesCrow Tengu HalfmaskMelissa Yaclara TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- Canon Laser Shot Lbp3300Document2 pagesCanon Laser Shot Lbp3300meenadarlingNo ratings yet
- Heidenhain Ik 121v ManualDocument116 pagesHeidenhain Ik 121v ManualmasinemaNo ratings yet
- Bizhub Press c1100 c1085 Catalog eDocument12 pagesBizhub Press c1100 c1085 Catalog eAndy IoNo ratings yet
- Copystar Copier CS-1650-2050 Parts & ServiceDocument381 pagesCopystar Copier CS-1650-2050 Parts & Servicebrslaser100% (2)
- A Paper Sizes - A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10Document3 pagesA Paper Sizes - A0, A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, A10RajaKuppanNo ratings yet
- QS Book PDFDocument191 pagesQS Book PDFBrilliant Temp100% (2)
- Manual PHPDocument90 pagesManual PHPAngellColmenaresNo ratings yet
- Game Controller DBDocument13 pagesGame Controller DBfirmanNo ratings yet
- Copic Catalog 2015Document25 pagesCopic Catalog 2015GREY WEATHERSNo ratings yet
- HP Designjet T630 36-In Printer: Simply The World'S Easiest Large-Format Plotters - Affordability Without TradeoffsDocument2 pagesHP Designjet T630 36-In Printer: Simply The World'S Easiest Large-Format Plotters - Affordability Without Tradeoffsahmedmy4nNo ratings yet
- Introduction To OpenOffice CalcDocument7 pagesIntroduction To OpenOffice CalcAina Shoib100% (1)
- Is 15726 2006 - Iso 13715 PDFDocument20 pagesIs 15726 2006 - Iso 13715 PDFPippozzo Pipini0% (2)