Professional Documents
Culture Documents
New
New
Uploaded by
Ab To zine doCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology With PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology With PathophysiologyAngelika Park60% (5)
- Ppendix J Answers To TriageDocument16 pagesPpendix J Answers To TriageGraciela Villa100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Chapter 1Document6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Chapter 1Cza Mae ArsenalNo ratings yet
- Roth Emily Bioc426 Experiment1Document10 pagesRoth Emily Bioc426 Experiment1api-593584147No ratings yet
- Morphology of The Rice PlantDocument40 pagesMorphology of The Rice Plantforeversk100% (4)
- User's Manual-ESU100Document11 pagesUser's Manual-ESU100Pedro100% (1)
- Greek Organisms Tissues: A Dissected Body, Lying Prone On A Table, byDocument1 pageGreek Organisms Tissues: A Dissected Body, Lying Prone On A Table, byrajan civilNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Anatomē Anatémnō Aná TémnōDocument2 pagesAnatomy: Anatomē Anatémnō Aná TémnōsylNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument2 pagesAnatomyMason PeinNo ratings yet
- Med 6Document3 pagesMed 6Lef RJNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument1 pageAnatomyRom Yu NasolNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (Greek Anatomē, "Dissection") Is The Branch ofDocument1 pageAnatomy (Greek Anatomē, "Dissection") Is The Branch ofankamraojNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (Greek Anatomē, 'Dissection') Is The Branch ofDocument1 pageAnatomy (Greek Anatomē, 'Dissection') Is The Branch ofTrasnea IonutNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument16 pagesAnatomywakhalewakhaleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: 1 DefinitionDocument17 pagesAnatomy: 1 DefinitionMeghan LangNo ratings yet
- Biology: Plant Anatomy Anatomy (Disambiguation) Andreas VesaliusDocument2 pagesBiology: Plant Anatomy Anatomy (Disambiguation) Andreas VesaliusJonee SansomNo ratings yet
- GenBio AnatomyDocument2 pagesGenBio AnatomyReniel V. Broncate (REHNIL)No ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument2 pagesHuman AnatomyYhamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (Greek Anatomē, 'Dissection') Is The Branch of Biology Concerned With TheDocument1 pageAnatomy (Greek Anatomē, 'Dissection') Is The Branch of Biology Concerned With TheMarvin Espenocilla EspeñoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument2 pagesAnatomy: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchMakhanVermaNo ratings yet
- An211 - Lecture - IntroductionDocument17 pagesAn211 - Lecture - IntroductionEzri ChilengweNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy by Khanoshah ShaltaloDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy by Khanoshah ShaltaloHasin's QueenNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument4 pagesHuman AnatomyaprilNo ratings yet
- Topic: AnatomyDocument10 pagesTopic: AnatomyTess TessNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Is Primarily The Scientific Study of The Morphology of The Adult Human BodyDocument1 pageHuman Anatomy Is Primarily The Scientific Study of The Morphology of The Adult Human BodypowerleaderNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyBibi Hayath AnamNo ratings yet
- 1 1 Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pages1 1 Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyRyan FootitNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument8 pagesAnatomyK WangNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument2 pagesAnatomyGhh TyuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument1 pageAnatomy and PhysiologyJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy and Physiology HandoutDocument9 pagesBasic Anatomy and Physiology HandoutKhenfred Emerald AlaroNo ratings yet
- Evsu - Bsed-Biosci - Anatomy and Physiology Study GuideDocument3 pagesEvsu - Bsed-Biosci - Anatomy and Physiology Study GuideMARY ANGELA LERIOSNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 FixtDocument22 pagesUnit 1 Fixt1035 Nur AfdaliaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyMichelle BilayaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Is The Identification and Description of The Structures of Living ThingsDocument3 pagesAnatomy Is The Identification and Description of The Structures of Living Thingsczenea velasquezNo ratings yet
- I. Introduction To Anatomical Terms and Organization of The Human BodyDocument94 pagesI. Introduction To Anatomical Terms and Organization of The Human BodyAradani Ongchi Frena100% (1)
- Introduction To Human Anatomy: Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy: Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyNeymar santos jrNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument34 pagesHuman Anatomy & PhysiologyJape GarridoNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY20230Document39 pagesANATOMY20230Ruben ToralloNo ratings yet
- Organ (Anatomy) : Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument9 pagesOrgan (Anatomy) : Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchSecret PersonNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument30 pagesBiologyChristel Ramos100% (1)
- Title: Planes, Landmarks, Directions, Quadrants & RegionsDocument6 pagesTitle: Planes, Landmarks, Directions, Quadrants & RegionsShane GempasaoNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument1 pageAnatomyJez VaNo ratings yet
- 2304 Intro AnatomyDocument6 pages2304 Intro AnatomyLiezel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument18 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKatrina ParbaNo ratings yet
- Module 1A - Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesModule 1A - Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyRafael SumayaNo ratings yet
- Vet Science-1Document51 pagesVet Science-1Fira'ol BogalaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPart 1 Anatomy and Physiologyzy- SBGNo ratings yet
- A&p Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology-3Document114 pagesA&p Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology-3seanghbirdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument39 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Human AnatomyPramisshila Nurnatasha Abd SamatNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 1 (Introduction)Document13 pagesAnatomy Lec 1 (Introduction)abdulsaboor30No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lab1Document11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lab14dkh9jx7fsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument17 pagesAnatomy - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaalsdjflakjdfNo ratings yet
- Health Science Tool Kit Text BookDocument278 pagesHealth Science Tool Kit Text BookAidan Glasby100% (1)
- Students Hand Out Notes in Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument73 pagesStudents Hand Out Notes in Anatomy and PhysiologyCza Mae Arsenal100% (1)
- Anatomy Assignment 1 KuDocument8 pagesAnatomy Assignment 1 KuAshley Tanya GilbertNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Assignment 1Document8 pagesAnatomy Assignment 1Ashley Tanya GilbertNo ratings yet
- Ped 2 LP 1 2022 2023Document7 pagesPed 2 LP 1 2022 2023Sherrizah AlidoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy LectureDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lecturealthea jade villadongaNo ratings yet
- 2 basic approach to study anatomy Systemic anatomy 》Is the study of the body by systemDocument3 pages2 basic approach to study anatomy Systemic anatomy 》Is the study of the body by systemKatherineNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy: EndosDocument1 pageGross Anatomy: EndosjellNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Lec-1Document18 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Lec-1aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Subjects and Topics in Basic Medical Science: A Imhotep Virtual Medical School PrimerDocument168 pagesSubjects and Topics in Basic Medical Science: A Imhotep Virtual Medical School PrimerMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (3)
- BhrmaDocument6 pagesBhrmaAb To zine doNo ratings yet
- Yogi BookDocument4 pagesYogi BookAb To zine doNo ratings yet
- YogaDocument7 pagesYogaAb To zine doNo ratings yet
- Yin Yoga .Doc 2Document19 pagesYin Yoga .Doc 2Ab To zine doNo ratings yet
- Gherandasamh YogaDocument18 pagesGherandasamh YogaAb To zine doNo ratings yet
- Plasma Proteins 1Document46 pagesPlasma Proteins 1Faisal_Khatib_juNo ratings yet
- HEMATOPOIESISDocument7 pagesHEMATOPOIESISritaoktasariNo ratings yet
- M2 - Check-In Activity 3Document6 pagesM2 - Check-In Activity 3Erika TatelNo ratings yet
- Antiplatelets & AnticoagulantsDocument10 pagesAntiplatelets & AnticoagulantsJosa Camille BungayNo ratings yet
- Paramedical Syllabus PDFDocument374 pagesParamedical Syllabus PDFAman GuptaNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument20 pagesThyroidheartaoneNo ratings yet
- Portal HypertensionDocument29 pagesPortal HypertensionPhilip LingNo ratings yet
- Common Medical - Surgical Cases/ Disorder: Irregular Heartbeat Fast Heart Rate FatigueDocument12 pagesCommon Medical - Surgical Cases/ Disorder: Irregular Heartbeat Fast Heart Rate FatigueEvelyn Marollano-AtienzaNo ratings yet
- 2 The Cell (PDFDrive)Document51 pages2 The Cell (PDFDrive)audiNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi Dan Patofisiologi KardiovaskulerDocument18 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Dan Patofisiologi KardiovaskulerWd. Isti RamadaniNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGCFTCNo ratings yet
- Heart Health TriviaDocument11 pagesHeart Health TriviaBobbie RaveloNo ratings yet
- Biological Control Systems: Biomedical Engineering - Bcs - Short Questions and AnswersDocument15 pagesBiological Control Systems: Biomedical Engineering - Bcs - Short Questions and AnswersNoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Central Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy of The Central Nervous SystemKristine AlejandroNo ratings yet
- The Human Body Through Images: Human Structure and Development: ANHB 2212 - 2009Document31 pagesThe Human Body Through Images: Human Structure and Development: ANHB 2212 - 2009dawadhaliNo ratings yet
- Foundation Module d24Document8 pagesFoundation Module d24Rabia OwaisNo ratings yet
- Human Remains Documentation PacketDocument22 pagesHuman Remains Documentation Packetselk_namNo ratings yet
- Effects of Acute Prolactin Manipulation On Sexual Drive and Function in MalesDocument9 pagesEffects of Acute Prolactin Manipulation On Sexual Drive and Function in MalesAudi GohNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PlantsDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Plantslanie_bluegirlNo ratings yet
- Emerging Concepts of Brain Function PDFDocument23 pagesEmerging Concepts of Brain Function PDFFrancisco Vicent PachecoNo ratings yet
- MindsEye Guide 2016Document64 pagesMindsEye Guide 2016Luis Vicente RomeroNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue Culture Callus InductionDocument7 pagesPlant Tissue Culture Callus InductionBoon ChiaNo ratings yet
- 382 Thyroid Gland Physiology and TestingDocument7 pages382 Thyroid Gland Physiology and TestingJetmoon BlackNo ratings yet
- Value Based Questions in Science For Class 9 Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesValue Based Questions in Science For Class 9 Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeBrijesh DeviNo ratings yet
- Exploring Psychology 7th Edition David Myers Emotions StressDocument4 pagesExploring Psychology 7th Edition David Myers Emotions StressEEO_MurphyNo ratings yet
- 15 Ferementation Study Guide PDFDocument4 pages15 Ferementation Study Guide PDFGhostNo ratings yet
New
New
Uploaded by
Ab To zine doOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
New
New
Uploaded by
Ab To zine doCopyright:
Available Formats
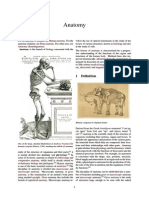
Derived from the Greek ἀνατομή anatomē "dissection" (from ἀνατέμνω anatémnō "I cut
up, cut open" from ἀνά aná "up", and τέμνω témnō "I cut"),[7] anatomy is the scientific
study of the structure of organismsincluding their systems, organs and tissues. It
includes the appearance and position of the various parts, the materials from which
they are composed, and their relationships with other parts. Anatomy is quite distinct
from physiology and biochemistry, which deal respectively with the functions of those
parts and the chemical processes involved. For example, an anatomist is concerned
with the shape, size, position, structure, blood supply and innervation of an organ
such as the liver; while a physiologist is interested in the production of bile, the role
of the liver in nutrition and the regulation of bodily functions. [8]
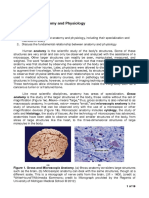
The discipline of anatomy can be subdivided into a number of branches, including
gross or macroscopicanatomy and microscopic anatomy.[9] Gross anatomyis the study of
structures large enough to be seen with the naked eye, and also includes superficial
anatomyor surface anatomy, the study by sight of the external body
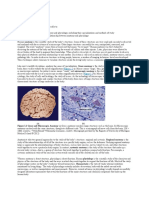
features. Microscopic anatomy is the study of structures on a microscopic scale, along
with histology(the study of tissues), and embryology (the study of an organism in its
immature condition).[3] Regional anatomy is the study of the interrelationships of all
of the structures in a specific body region, such as the abdomen. In contrast, systemic
anatomy is the study of the structures that make up a discrete body system—that is,
a group of structures that work together to perform a unique body function, such as
the digestive system.[10]
Anatomy can be studied using both invasive and non-invasive methods with the goal
of obtaining information about the structure and organization of organs and
systems.[3] Methods used include dissection, in which a body is opened and its organs
studied, and endoscopy, in which a video camera-equipped instrument is inserted
through a small incision in the body wall and used to explore the internal organs and
other structures. Angiographyusing X-rays or magnetic resonance angiography are
methods to visualize blood vessels.[11][12][13][14]
The term "anatomy" is commonly taken to refer to human anatomy. However,
substantially similar structures and tissues are found throughout the rest of the
animal kingdom, and the term also includes the anatomy of other animals. The
term zootomy is also sometimes used to specifically refer to non-human animals. The
structure and tissues of plants are of a dissimilar nature and they are studied in plant
anatomy.[8]
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology With PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology With PathophysiologyAngelika Park60% (5)
- Ppendix J Answers To TriageDocument16 pagesPpendix J Answers To TriageGraciela Villa100% (2)
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Chapter 1Document6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Chapter 1Cza Mae ArsenalNo ratings yet
- Roth Emily Bioc426 Experiment1Document10 pagesRoth Emily Bioc426 Experiment1api-593584147No ratings yet
- Morphology of The Rice PlantDocument40 pagesMorphology of The Rice Plantforeversk100% (4)
- User's Manual-ESU100Document11 pagesUser's Manual-ESU100Pedro100% (1)
- Greek Organisms Tissues: A Dissected Body, Lying Prone On A Table, byDocument1 pageGreek Organisms Tissues: A Dissected Body, Lying Prone On A Table, byrajan civilNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Anatomē Anatémnō Aná TémnōDocument2 pagesAnatomy: Anatomē Anatémnō Aná TémnōsylNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument2 pagesAnatomyMason PeinNo ratings yet
- Med 6Document3 pagesMed 6Lef RJNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument1 pageAnatomyRom Yu NasolNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (Greek Anatomē, "Dissection") Is The Branch ofDocument1 pageAnatomy (Greek Anatomē, "Dissection") Is The Branch ofankamraojNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (Greek Anatomē, 'Dissection') Is The Branch ofDocument1 pageAnatomy (Greek Anatomē, 'Dissection') Is The Branch ofTrasnea IonutNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument16 pagesAnatomywakhalewakhaleNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: 1 DefinitionDocument17 pagesAnatomy: 1 DefinitionMeghan LangNo ratings yet
- Biology: Plant Anatomy Anatomy (Disambiguation) Andreas VesaliusDocument2 pagesBiology: Plant Anatomy Anatomy (Disambiguation) Andreas VesaliusJonee SansomNo ratings yet
- GenBio AnatomyDocument2 pagesGenBio AnatomyReniel V. Broncate (REHNIL)No ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument2 pagesHuman AnatomyYhamNo ratings yet
- Anatomy (Greek Anatomē, 'Dissection') Is The Branch of Biology Concerned With TheDocument1 pageAnatomy (Greek Anatomē, 'Dissection') Is The Branch of Biology Concerned With TheMarvin Espenocilla EspeñoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument2 pagesAnatomy: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchMakhanVermaNo ratings yet
- An211 - Lecture - IntroductionDocument17 pagesAn211 - Lecture - IntroductionEzri ChilengweNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy by Khanoshah ShaltaloDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy by Khanoshah ShaltaloHasin's QueenNo ratings yet
- Human AnatomyDocument4 pagesHuman AnatomyaprilNo ratings yet
- Topic: AnatomyDocument10 pagesTopic: AnatomyTess TessNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy Is Primarily The Scientific Study of The Morphology of The Adult Human BodyDocument1 pageHuman Anatomy Is Primarily The Scientific Study of The Morphology of The Adult Human BodypowerleaderNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyBibi Hayath AnamNo ratings yet
- 1 1 Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument3 pages1 1 Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyRyan FootitNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument8 pagesAnatomyK WangNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument2 pagesAnatomyGhh TyuNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument1 pageAnatomy and PhysiologyJohanine VillasantiagoNo ratings yet
- Basic Anatomy and Physiology HandoutDocument9 pagesBasic Anatomy and Physiology HandoutKhenfred Emerald AlaroNo ratings yet
- Evsu - Bsed-Biosci - Anatomy and Physiology Study GuideDocument3 pagesEvsu - Bsed-Biosci - Anatomy and Physiology Study GuideMARY ANGELA LERIOSNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 FixtDocument22 pagesUnit 1 Fixt1035 Nur AfdaliaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyMichelle BilayaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Is The Identification and Description of The Structures of Living ThingsDocument3 pagesAnatomy Is The Identification and Description of The Structures of Living Thingsczenea velasquezNo ratings yet
- I. Introduction To Anatomical Terms and Organization of The Human BodyDocument94 pagesI. Introduction To Anatomical Terms and Organization of The Human BodyAradani Ongchi Frena100% (1)
- Introduction To Human Anatomy: Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument10 pagesIntroduction To Human Anatomy: Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyNeymar santos jrNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument34 pagesHuman Anatomy & PhysiologyJape GarridoNo ratings yet
- ANATOMY20230Document39 pagesANATOMY20230Ruben ToralloNo ratings yet
- Organ (Anatomy) : Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument9 pagesOrgan (Anatomy) : Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchSecret PersonNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument30 pagesBiologyChristel Ramos100% (1)
- Title: Planes, Landmarks, Directions, Quadrants & RegionsDocument6 pagesTitle: Planes, Landmarks, Directions, Quadrants & RegionsShane GempasaoNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument1 pageAnatomyJez VaNo ratings yet
- 2304 Intro AnatomyDocument6 pages2304 Intro AnatomyLiezel CauilanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument18 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKatrina ParbaNo ratings yet
- Module 1A - Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesModule 1A - Overview of Anatomy and PhysiologyRafael SumayaNo ratings yet
- Vet Science-1Document51 pagesVet Science-1Fira'ol BogalaNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPart 1 Anatomy and Physiologyzy- SBGNo ratings yet
- A&p Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology-3Document114 pagesA&p Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology-3seanghbirdNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Human AnatomyDocument39 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To Human AnatomyPramisshila Nurnatasha Abd SamatNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec 1 (Introduction)Document13 pagesAnatomy Lec 1 (Introduction)abdulsaboor30No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lab1Document11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lab14dkh9jx7fsNo ratings yet
- Anatomy - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument17 pagesAnatomy - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaalsdjflakjdfNo ratings yet
- Health Science Tool Kit Text BookDocument278 pagesHealth Science Tool Kit Text BookAidan Glasby100% (1)
- Students Hand Out Notes in Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument73 pagesStudents Hand Out Notes in Anatomy and PhysiologyCza Mae Arsenal100% (1)
- Anatomy Assignment 1 KuDocument8 pagesAnatomy Assignment 1 KuAshley Tanya GilbertNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Assignment 1Document8 pagesAnatomy Assignment 1Ashley Tanya GilbertNo ratings yet
- Ped 2 LP 1 2022 2023Document7 pagesPed 2 LP 1 2022 2023Sherrizah AlidoNo ratings yet
- Anaphy LectureDocument5 pagesAnaphy Lecturealthea jade villadongaNo ratings yet
- 2 basic approach to study anatomy Systemic anatomy 》Is the study of the body by systemDocument3 pages2 basic approach to study anatomy Systemic anatomy 》Is the study of the body by systemKatherineNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy: EndosDocument1 pageGross Anatomy: EndosjellNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology Lec-1Document18 pagesAnatomy & Physiology Lec-1aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Subjects and Topics in Basic Medical Science: A Imhotep Virtual Medical School PrimerDocument168 pagesSubjects and Topics in Basic Medical Science: A Imhotep Virtual Medical School PrimerMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.100% (3)
- BhrmaDocument6 pagesBhrmaAb To zine doNo ratings yet
- Yogi BookDocument4 pagesYogi BookAb To zine doNo ratings yet
- YogaDocument7 pagesYogaAb To zine doNo ratings yet
- Yin Yoga .Doc 2Document19 pagesYin Yoga .Doc 2Ab To zine doNo ratings yet
- Gherandasamh YogaDocument18 pagesGherandasamh YogaAb To zine doNo ratings yet
- Plasma Proteins 1Document46 pagesPlasma Proteins 1Faisal_Khatib_juNo ratings yet
- HEMATOPOIESISDocument7 pagesHEMATOPOIESISritaoktasariNo ratings yet
- M2 - Check-In Activity 3Document6 pagesM2 - Check-In Activity 3Erika TatelNo ratings yet
- Antiplatelets & AnticoagulantsDocument10 pagesAntiplatelets & AnticoagulantsJosa Camille BungayNo ratings yet
- Paramedical Syllabus PDFDocument374 pagesParamedical Syllabus PDFAman GuptaNo ratings yet
- ThyroidDocument20 pagesThyroidheartaoneNo ratings yet
- Portal HypertensionDocument29 pagesPortal HypertensionPhilip LingNo ratings yet
- Common Medical - Surgical Cases/ Disorder: Irregular Heartbeat Fast Heart Rate FatigueDocument12 pagesCommon Medical - Surgical Cases/ Disorder: Irregular Heartbeat Fast Heart Rate FatigueEvelyn Marollano-AtienzaNo ratings yet
- 2 The Cell (PDFDrive)Document51 pages2 The Cell (PDFDrive)audiNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Fisiologi Dan Patofisiologi KardiovaskulerDocument18 pagesAnatomi Fisiologi Dan Patofisiologi KardiovaskulerWd. Isti RamadaniNo ratings yet
- How To Read An ECGDocument15 pagesHow To Read An ECGCFTCNo ratings yet
- Heart Health TriviaDocument11 pagesHeart Health TriviaBobbie RaveloNo ratings yet
- Biological Control Systems: Biomedical Engineering - Bcs - Short Questions and AnswersDocument15 pagesBiological Control Systems: Biomedical Engineering - Bcs - Short Questions and AnswersNoor AhmedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Central Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesAnatomy of The Central Nervous SystemKristine AlejandroNo ratings yet
- The Human Body Through Images: Human Structure and Development: ANHB 2212 - 2009Document31 pagesThe Human Body Through Images: Human Structure and Development: ANHB 2212 - 2009dawadhaliNo ratings yet
- Foundation Module d24Document8 pagesFoundation Module d24Rabia OwaisNo ratings yet
- Human Remains Documentation PacketDocument22 pagesHuman Remains Documentation Packetselk_namNo ratings yet
- Effects of Acute Prolactin Manipulation On Sexual Drive and Function in MalesDocument9 pagesEffects of Acute Prolactin Manipulation On Sexual Drive and Function in MalesAudi GohNo ratings yet
- Introduction To PlantsDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Plantslanie_bluegirlNo ratings yet
- Emerging Concepts of Brain Function PDFDocument23 pagesEmerging Concepts of Brain Function PDFFrancisco Vicent PachecoNo ratings yet
- MindsEye Guide 2016Document64 pagesMindsEye Guide 2016Luis Vicente RomeroNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue Culture Callus InductionDocument7 pagesPlant Tissue Culture Callus InductionBoon ChiaNo ratings yet
- 382 Thyroid Gland Physiology and TestingDocument7 pages382 Thyroid Gland Physiology and TestingJetmoon BlackNo ratings yet
- Value Based Questions in Science For Class 9 Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument3 pagesValue Based Questions in Science For Class 9 Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of LifeBrijesh DeviNo ratings yet
- Exploring Psychology 7th Edition David Myers Emotions StressDocument4 pagesExploring Psychology 7th Edition David Myers Emotions StressEEO_MurphyNo ratings yet
- 15 Ferementation Study Guide PDFDocument4 pages15 Ferementation Study Guide PDFGhostNo ratings yet