Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Science Task Number 1
Science Task Number 1
Uploaded by
karragan ツ0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pagePeriodic trends, atomic size, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity, metallic properties, and non-metallic properties are defined. Periodic trends refer to patterns in properties revealed in the periodic table including atomic radii, ionization energy, and electronegativity. Atomic size is the distance from the nucleus to the outer electron shells. Ionization energy is the minimum energy to remove an electron from an isolated atom. Electron affinity is the energy released when an electron attaches to form a negative ion. Electronegativity describes an atom's ability to attract shared electrons. Metallic properties refer to behaving like metals by losing electrons, while non-metallic properties accept electrons and increase across the periodic table
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPeriodic trends, atomic size, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity, metallic properties, and non-metallic properties are defined. Periodic trends refer to patterns in properties revealed in the periodic table including atomic radii, ionization energy, and electronegativity. Atomic size is the distance from the nucleus to the outer electron shells. Ionization energy is the minimum energy to remove an electron from an isolated atom. Electron affinity is the energy released when an electron attaches to form a negative ion. Electronegativity describes an atom's ability to attract shared electrons. Metallic properties refer to behaving like metals by losing electrons, while non-metallic properties accept electrons and increase across the periodic table
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views1 pageScience Task Number 1
Science Task Number 1
Uploaded by
karragan ツPeriodic trends, atomic size, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity, metallic properties, and non-metallic properties are defined. Periodic trends refer to patterns in properties revealed in the periodic table including atomic radii, ionization energy, and electronegativity. Atomic size is the distance from the nucleus to the outer electron shells. Ionization energy is the minimum energy to remove an electron from an isolated atom. Electron affinity is the energy released when an electron attaches to form a negative ion. Electronegativity describes an atom's ability to attract shared electrons. Metallic properties refer to behaving like metals by losing electrons, while non-metallic properties accept electrons and increase across the periodic table
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
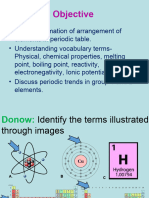
Science Task Number #1
Define the following:
1. Periodic trends - Periodic trends are specific patterns in the properties of chemical elements
that are revealed in the periodic table of elements. Major periodic trends include
electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radii, ionic radius, metallic
character, and chemical reactivity.
2. Atomic size - The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of its atoms,
usually the mean or typical distance from the center of the nucleus to the boundary of the
surrounding shells of electrons.
3. Ionization Energy- In physics and chemistry, ionization energy or ionisation energy, denoted
Eᵢ, is the minimum amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron, the
valence electron, of an isolated neutral gaseous atom or molecule.
4. Electron affinity - The electron affinity of an atom or molecule is defined as the amount of
energy released when an electron is attached to a neutral atom or molecule in the gaseous
state to form a negative ion.
5. Electronegativity - Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a concept that describes the tendency of
an atom to attract a shared pair of electrons towards itself. An atom's electronegativity is
affected by both its atomic number and the distance at which its valence electrons reside from
the charged nucleus.
6. Metallic property – An element’s metallic properties refer to its propensity to behave
like the elements that are classified as metals in the periodic table. This depends on the set
of chemical properties commonly associated with the metallic elements, specifically the
ability of an element to lose its outer valence electrons.
7. Non-metallic Property – Relates to the tendency to accept electrons during chemical
reactions and non- metallic tendency increases going from left to right across the periodic
table.
You might also like
- Asych2 - Periodic TrendsDocument1 pageAsych2 - Periodic Trendspauleenbernadette13No ratings yet
- The Periodic Trends - 20240320 - 212118 - 0000Document9 pagesThe Periodic Trends - 20240320 - 212118 - 0000donchelvelasco14No ratings yet
- Periodic Trends VocabDocument2 pagesPeriodic Trends Vocabyufeimou2007No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument27 pagesChemical BondingLovejoy TiñaNo ratings yet
- Atoms and The Periodic TableDocument9 pagesAtoms and The Periodic TableShivaniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry PDFDocument3 pagesChemistry PDFSukfcNo ratings yet
- Copy of Copy of Clean Brown Paper Texture Background Page Border - 20240608 - 154937 - 0000Document16 pagesCopy of Copy of Clean Brown Paper Texture Background Page Border - 20240608 - 154937 - 0000prithish090407No ratings yet
- ETPaper 2Document159 pagesETPaper 2shid kumarNo ratings yet
- Engineering Crash Course NotesDocument4 pagesEngineering Crash Course Notesjpiquero2007No ratings yet
- The Periodic Trends Updated 2023Document58 pagesThe Periodic Trends Updated 2023stutireddy1912No ratings yet
- The Geochemistry of Rocks and Natural WatersDocument25 pagesThe Geochemistry of Rocks and Natural WatersJuanNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding, Structure and Shapes of Molecules and CompoundsDocument70 pagesChemical Bonding, Structure and Shapes of Molecules and Compoundsann wamburaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Electron TheoryDocument5 pages3.1 Electron TheoryArun RajeevNo ratings yet
- Upload - The Periodic Table and TrendsDocument14 pagesUpload - The Periodic Table and TrendsMbuyotiNo ratings yet
- Periodic TrendsDocument14 pagesPeriodic TrendsMarra Alyssa SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry ProjectDocument10 pagesChemistry ProjectIshan AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Ppt-Periodic TableDocument5 pagesPpt-Periodic TableNeil John Santos ParasNo ratings yet
- Activity in Chem Q2Document2 pagesActivity in Chem Q2harveyocbinaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-5Document3 pagesLecture-5mfaida272No ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument5 pagesChemical BondingStellaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Chemistry Notes UNIT 4Document9 pagesEngineering Chemistry Notes UNIT 4Nivetha ENo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends Resource 1Document8 pagesPeriodic Trends Resource 1anitNo ratings yet
- Periodic TableDocument2 pagesPeriodic TableshadnawazkhanNo ratings yet
- NAME Aneela Aftab Semester Second Subject Fiber Science Submitted To Sir Muhammad QasimDocument22 pagesNAME Aneela Aftab Semester Second Subject Fiber Science Submitted To Sir Muhammad QasimAnila AftabNo ratings yet
- Kangwon ProjectDocument2 pagesKangwon ProjectJhastine Mhae De VeraNo ratings yet
- Periodicity of PropertiesDocument5 pagesPeriodicity of PropertiesHaYem AlnNo ratings yet
- Geochemistry IntroductionDocument25 pagesGeochemistry Introductionkristiano97100% (1)
- Dental Biomaterial Book (61-71)Document146 pagesDental Biomaterial Book (61-71)Abdelruhman SobhyNo ratings yet
- Periodic TrendsDocument12 pagesPeriodic TrendsSam EsclitoNo ratings yet
- Module 2, Chemistry, PDFDocument11 pagesModule 2, Chemistry, PDFMARIA CORAZON CONTANTENo ratings yet
- Periodic TrendsDocument11 pagesPeriodic TrendsFern HofileñaNo ratings yet
- 3 2 Physical PropertiesDocument4 pages3 2 Physical PropertiesNguyenHoangMinhDucNo ratings yet
- CHM 122 Notes 19 20Document21 pagesCHM 122 Notes 19 20Stephen VictorNo ratings yet
- Chem 5 Classwork 1Document16 pagesChem 5 Classwork 1Lordsfavour AnukamNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRY-TOPIC-3-TrendsDocument4 pagesCHEMISTRY-TOPIC-3-TrendsCherry CieloNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Periodicity PPT (Autosaved)Document40 pagesGrade 11 Periodicity PPT (Autosaved)prateekshadharaniNo ratings yet
- LEC - Metal How Reactive Are YouDocument1 pageLEC - Metal How Reactive Are YouMariz RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Crystallography and Mineralogy NotesDocument220 pagesCrystallography and Mineralogy NotesSyed Aquib ShamshadNo ratings yet
- Ambag KoDocument11 pagesAmbag KorycaprincessNo ratings yet
- Wa0030.Document2 pagesWa0030.abdallahmahmoud19732006No ratings yet
- The Solids Have Definite Volume and Definite Shape) Model of An AtomDocument5 pagesThe Solids Have Definite Volume and Definite Shape) Model of An AtomKat OrcinoNo ratings yet
- Unit IaDocument44 pagesUnit Iadawa penjorNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 2NDDocument4 pagesGen Chem 2NDrenmarseyerNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary: Ionic BondsDocument1 pageVocabulary: Ionic BondsGrace CinoNo ratings yet
- Periodic Trends: ElectronegativityDocument2 pagesPeriodic Trends: ElectronegativityZaara RyeenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Atomic Structure and BondingDocument29 pagesLecture 2 - Atomic Structure and BondingMercylin MakambureNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument5 pagesScience ReviewerAzel RheadalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry GRADE 9 MODULE CHemical BondingDocument18 pagesChemistry GRADE 9 MODULE CHemical BondingKelvin MarinasNo ratings yet
- Properties of Molecules Based On PolarityDocument23 pagesProperties of Molecules Based On PolarityyourarmoristakenNo ratings yet
- ELEN 20023 ENGINEERING UTILITIES - Module 1Document9 pagesELEN 20023 ENGINEERING UTILITIES - Module 1Lopez ReyNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lectures Week 1 and 2Document6 pagesChemistry Lectures Week 1 and 2Bliven GarciaNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table Periodic Properties and Variations of PropertiesDocument4 pagesPeriodic Table Periodic Properties and Variations of PropertiesSANDEEP SINGHNo ratings yet
- ES III Midterm Module 6 WK 6Document5 pagesES III Midterm Module 6 WK 6Oct Toberey MendozaNo ratings yet
- Group 3: Periodic Relationship: Wendell Bandiola (THE PERIODIC TABLE)Document66 pagesGroup 3: Periodic Relationship: Wendell Bandiola (THE PERIODIC TABLE)Kristel Ann LaudeNo ratings yet
- Periodic Properties and The Periodic TableDocument6 pagesPeriodic Properties and The Periodic TableAurobinda MaharanaNo ratings yet
- AtomDocument4 pagesAtomanjaliNo ratings yet
- Organic - Chemistry 1Document32 pagesOrganic - Chemistry 1ajyfsthNo ratings yet
- CHM Postlab#4 Group4Document15 pagesCHM Postlab#4 Group4Anchie VillajinNo ratings yet
- Worksheet: "Characteristic Periodic Table of Elements"Document10 pagesWorksheet: "Characteristic Periodic Table of Elements"utariNo ratings yet
- Script Documentation (Kharl)Document1 pageScript Documentation (Kharl)karragan ツNo ratings yet
- SS Timeline ww2Document3 pagesSS Timeline ww2karragan ツNo ratings yet
- Speech On HonestyDocument1 pageSpeech On Honestykarragan ツNo ratings yet
- Cebu Flight MarkDocument6 pagesCebu Flight Markkarragan ツNo ratings yet
- Leading Excellence Challenges AttestationDocument1 pageLeading Excellence Challenges Attestationkarragan ツNo ratings yet
- Activity 4.1 (Kharl)Document1 pageActivity 4.1 (Kharl)karragan ツNo ratings yet