Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Req IRIS
Req IRIS
Uploaded by
Sanae Hafdaoui0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesThe document discusses the key capabilities that a rail management system should provide. It states that the system should have modules to track asset maintenance and optimize schedules, create and manage complex operations and crew schedules, manage safety compliance and incident reporting, and provide financial planning and reporting features. Additionally, it notes the system should offer customer relationship management, real-time data monitoring and reporting, integration with other systems, mobile access, scalability, and robust security and data privacy controls.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
ODS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the key capabilities that a rail management system should provide. It states that the system should have modules to track asset maintenance and optimize schedules, create and manage complex operations and crew schedules, manage safety compliance and incident reporting, and provide financial planning and reporting features. Additionally, it notes the system should offer customer relationship management, real-time data monitoring and reporting, integration with other systems, mobile access, scalability, and robust security and data privacy controls.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as ODS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ods, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
7 views2 pagesReq IRIS
Req IRIS
Uploaded by
Sanae HafdaouiThe document discusses the key capabilities that a rail management system should provide. It states that the system should have modules to track asset maintenance and optimize schedules, create and manage complex operations and crew schedules, manage safety compliance and incident reporting, and provide financial planning and reporting features. Additionally, it notes the system should offer customer relationship management, real-time data monitoring and reporting, integration with other systems, mobile access, scalability, and robust security and data privacy controls.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as ODS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as ods, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
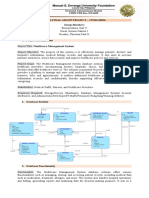
1.
Asset Management: Rail organizations deal with a
large number of physical assets, such as trains, tracks,
signaling equipment, and maintenance tools. The
business management system should have robust asset
management capabilities to track the condition, location,
maintenance history, and lifecycle of these assets. This
helps in optimizing maintenance schedules, minimizing
downtime, and improving asset utilization.
2. Scheduling and Planning: Rail organizations need to
manage complex schedules for train operations, crew
assignments, maintenance activities, and infrastructure
projects. The management system should include
features for creating and managing schedules, resource
allocation, real-time updates, and optimizing routes and
timetables to ensure efficient operations.
1. Safety and Compliance: Safety is of paramount
importance in rail operations. The management system
should have modules to manage safety protocols,
incident reporting, compliance with regulatory
standards, and training requirements. It should facilitate
the documentation and analysis of safety-related data to
identify trends, implement corrective actions, and ensure
compliance with industry regulations.
2. Financial Management: Rail organizations need to
effectively manage their financial resources, including
budgeting, procurement, invoicing, and revenue
tracking. The management system should provide
modules for financial planning, cost tracking, contract
management, and financial reporting to support
accurate budgeting, expense control, and revenue
optimization.
3.Financial Management: Rail organizations need to
effectively manage their financial resources, including
budgeting, procurement, invoicing, and revenue
tracking. The management system should provide
modules for financial planning, cost tracking, contract
management, and financial reporting to support
accurate budgeting, expense control, and revenue
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Rail
optimization.
organizations interact with passengers, freight
customers, and other stakeholders. A CRM module
within the management system can help in
managing customer data, ticketing, complaints, and
feedback. It enables better communication,
personalized services, and improved customer
satisfaction.
Real-time Monitoring and Reporting: Rail operations
generate a vast amount of data in real-time,
including train positions, maintenance status,
signaling information, and passenger loads. The
management system should have real-time
monitoring capabilities to capture, analyze, and
visualize this data. It should provide customizable
reports and dashboards to help management make
informed decisions and respond quickly to
Integration and Interoperability: Rail organizations
often have multiple systems and applications for
various functions like ticketing, passenger
information, maintenance, and finance. The
management system should support integration
with these existing systems to enable seamless data
exchange and interoperability.
Mobile Access and Connectivity: Rail organizations
have a distributed workforce, including train crews,
maintenance teams, and field supervisors. The
management system should offer mobile access and
connectivity options to ensure that personnel can
access relevant information, update data in real-
time, and collaborate efficiently from anywhere,
using mobile devices or ruggedized equipment.
Scalability and Flexibility: Rail organizations may
experience growth and operational changes over
time. The management system should be scalable to
accommodate increasing data volumes, user
accounts, and functionality requirements. It should
also be flexible enough to adapt to changing
business processes and industry standards.
Security and Data Privacy: Given the sensitivity of rail
operations and the potential impact of security breaches,
the management system should have robust security
measures in place. This includes access controls, data
encryption, audit trails, and compliance with data
protection regulations to ensure the confidentiality,
integrity, and availability of data.
You might also like
- Polo No. 31 / 1: Current Flow DiagramDocument11 pagesPolo No. 31 / 1: Current Flow DiagramIgnacio Rifo NochezNo ratings yet
- Logistic Management: Unit 3Document23 pagesLogistic Management: Unit 3Akhil Crasta100% (1)
- An Automated Transport Management System: Ms Mithlesh ChoudharyDocument5 pagesAn Automated Transport Management System: Ms Mithlesh ChoudharyJohn OluwaTobiNo ratings yet
- Logistics Management Analysis and DesignDocument58 pagesLogistics Management Analysis and DesignDrapeeto0% (1)
- Ais 2015Document5 pagesAis 2015tafraciNo ratings yet
- Trafic Managment ProjectDocument2 pagesTrafic Managment ProjectamlakebirhanuNo ratings yet
- Mis 01Document8 pagesMis 01HARSH NAGNo ratings yet
- LogisticsDocument15 pagesLogisticsyeabsirad18No ratings yet
- Aattral One ProductsDocument16 pagesAattral One ProductsThirumalai VasanNo ratings yet
- Note 03 Logistics Information SystemsDocument7 pagesNote 03 Logistics Information SystemsNantha KumarNo ratings yet
- RTMSDocument12 pagesRTMSRodney MacansantosNo ratings yet
- Computers PlayDocument2 pagesComputers Playemilydaimon578No ratings yet
- Case Study RailwayDocument7 pagesCase Study RailwayParth SarthiNo ratings yet
- Logistics Unit 1Document14 pagesLogistics Unit 1vikivignesh2331No ratings yet
- Warehouse ManagementDocument10 pagesWarehouse ManagementManoj AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Fa22 Rba 003Document7 pagesFa22 Rba 003Taskeen ZafarNo ratings yet
- Activity: 1: The Application of Industrial Engineering Tools in Maintenance Management AreDocument2 pagesActivity: 1: The Application of Industrial Engineering Tools in Maintenance Management AreSaumya SaumyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction: 1.1 CMS Objectives The Objectives of CMS Are: To Improve The Efficiency in Operations byDocument5 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction: 1.1 CMS Objectives The Objectives of CMS Are: To Improve The Efficiency in Operations byChiragNo ratings yet
- Inbound 5677629722088814206Document19 pagesInbound 5677629722088814206rubyrose.andes0224No ratings yet
- Logistics and SCM Information SystemsDocument10 pagesLogistics and SCM Information SystemsJob ThomasNo ratings yet
- Courier Service Management System (CSMS)Document2 pagesCourier Service Management System (CSMS)Nikita RajNo ratings yet
- Airline Reservation SystemDocument24 pagesAirline Reservation Systemvikranthviki083No ratings yet
- Intelligent Infrastructure For Next Generation Rail Systems PDFDocument9 pagesIntelligent Infrastructure For Next Generation Rail Systems PDFNalin_kantNo ratings yet
- Project Proposal Erp For Ministry of PlanningDocument7 pagesProject Proposal Erp For Ministry of PlanningkhalidgabbalNo ratings yet
- DJJ50212 Maintenance Engineering and Management Chapter 5 Computerized Maintenance Management System CMMSDocument51 pagesDJJ50212 Maintenance Engineering and Management Chapter 5 Computerized Maintenance Management System CMMSMOHD AZIZEE BIN SUKOR (POLIBANTING)No ratings yet
- TL 057Document6 pagesTL 057Dennis BriteNo ratings yet
- Supply ChainDocument9 pagesSupply ChainYara SwaisaNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain NETWORKDocument2 pagesSupply Chain NETWORKAreej Riaz uNo ratings yet
- 10 Elements of Logistic ManagementDocument4 pages10 Elements of Logistic ManagementKosasihNo ratings yet
- Ijsrp May 2012 89Document3 pagesIjsrp May 2012 89Rishabh GargNo ratings yet
- SGA CHATgptDocument2 pagesSGA CHATgptLuis ArceNo ratings yet
- Industry: Automobile Manufacturing Industry CompaniesDocument4 pagesIndustry: Automobile Manufacturing Industry CompaniesKushagra SinghalNo ratings yet
- AI PROJECT FinalDocument13 pagesAI PROJECT FinalNetsi FikiruNo ratings yet
- Operation and Supply Chain Strategies - Kumar AnimeshDocument6 pagesOperation and Supply Chain Strategies - Kumar Animeshkumaranimesh2606No ratings yet
- System Design Updated Based On CommentDocument25 pagesSystem Design Updated Based On CommentMulugeta HailegnawNo ratings yet
- What Is Supply Chain Management?Document9 pagesWhat Is Supply Chain Management?satishgwNo ratings yet
- 1st Pre Final AnswerDocument58 pages1st Pre Final Answershaillypandey25No ratings yet
- Sap SCMDocument21 pagesSap SCMAffizul AzuwarNo ratings yet
- Logistic Resource Management (LRM)Document19 pagesLogistic Resource Management (LRM)Mochammad HattaNo ratings yet
- Cargo 1Document8 pagesCargo 1yashwantm2004No ratings yet
- Technology in Logistics & Supply Chain: SubjectDocument5 pagesTechnology in Logistics & Supply Chain: Subjectmanish sharmaNo ratings yet
- Logistics ManagementDocument4 pagesLogistics Managementeduard john antiqueraNo ratings yet
- World Class Asset ManagementDocument4 pagesWorld Class Asset ManagementAndrew NoronhaNo ratings yet
- World Class Asset Management #1Document4 pagesWorld Class Asset Management #1Andrew NoronhaNo ratings yet
- SRS AssignmentDocument3 pagesSRS Assignmentkainatjamil38No ratings yet
- Group Project CP104 Project Identification 1Document6 pagesGroup Project CP104 Project Identification 1Gail BuenaventuraNo ratings yet
- TMS Write UpDocument44 pagesTMS Write UpIdris SaheedNo ratings yet
- Types of Control in The Supply Chain.Document7 pagesTypes of Control in The Supply Chain.Lesly SalinasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document17 pagesAssignment 1pkmabshaarNo ratings yet
- Altiux Case Study - Fleet Management SolutionDocument2 pagesAltiux Case Study - Fleet Management SolutionsaloniNo ratings yet
- Logistics Information SystemDocument8 pagesLogistics Information Systemnandini_mba4870No ratings yet
- Practical No.: 5 AIM: Case Study of Supply Chain Management (SCM)Document9 pagesPractical No.: 5 AIM: Case Study of Supply Chain Management (SCM)npbachchanitNo ratings yet
- Proposal 2024Document11 pagesProposal 2024hino.neupaneNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication Management SystemsDocument8 pagesTelecommunication Management SystemsAKNo ratings yet
- Riyas 1Document39 pagesRiyas 1madhandhanabal13No ratings yet
- Supply Chain ManagementDocument98 pagesSupply Chain Managementtest1217100% (1)
- ErpDocument8 pagesErpOsama RiazNo ratings yet
- Supply Chain FinalDocument8 pagesSupply Chain FinalAbdul HadiNo ratings yet
- Admin Dashboard OverviewDocument2 pagesAdmin Dashboard OverviewRicky NavidonNo ratings yet
- Goods Transportation Management SystemDocument12 pagesGoods Transportation Management Systemneelam100% (1)
- Unit 2Document22 pagesUnit 2hejoj76652No ratings yet
- Enterprise Resource Planning ExerciseDocument7 pagesEnterprise Resource Planning Exerciseali abbasNo ratings yet
- Black Box Testing TechniquesDocument28 pagesBlack Box Testing TechniquesAshish YadavNo ratings yet
- Class4-Traffic CharacteristicsDocument16 pagesClass4-Traffic CharacteristicsYihun abrahamNo ratings yet
- StandardAero Avionics - TCAS - Traffic Alert Collision Avoidance SystemDocument1 pageStandardAero Avionics - TCAS - Traffic Alert Collision Avoidance SystemSoroush_BlasterNo ratings yet
- SAP BASIS IntroductionDocument48 pagesSAP BASIS Introductionutagore58No ratings yet
- 3CX-T-PC Precision Control (Servo) 9812/0010: ServiceDocument2 pages3CX-T-PC Precision Control (Servo) 9812/0010: ServiceRomanNo ratings yet
- JavaScript ManualDocument170 pagesJavaScript ManualNotin less24100% (1)
- Blockchain ConsensusDocument33 pagesBlockchain ConsensusROHETH SNo ratings yet
- ContainersDocument9 pagesContainerssatheesh GNo ratings yet
- Automatic Packaging MachineDocument64 pagesAutomatic Packaging Machinesajid aliNo ratings yet
- Handling Dynamic Web ElementsDocument4 pagesHandling Dynamic Web ElementsAnaghaNarayananNo ratings yet
- At6311 Ac Lab ManualDocument78 pagesAt6311 Ac Lab Manualvivek kumarNo ratings yet
- Performance Testing Vs Performance EngineeringDocument2 pagesPerformance Testing Vs Performance Engineeringkondalb100% (1)
- Requirements Engineering: COMSATS University, IslamabadDocument117 pagesRequirements Engineering: COMSATS University, IslamabadMuhammad Zaman QadirNo ratings yet
- SBR TechnologiesDocument2 pagesSBR TechnologiesTech Devils0% (1)
- OVRS-4A Cell InterfaceDocument32 pagesOVRS-4A Cell InterfaceKask84No ratings yet
- Building An Application For The Automation of On-Boarding of An EDocument48 pagesBuilding An Application For The Automation of On-Boarding of An Esridhar varmaNo ratings yet
- Duc NguyenDocument2 pagesDuc Nguyentuongng1512No ratings yet
- Datasheet AVEVA MESDocument9 pagesDatasheet AVEVA MESKuncoroNuryantoNo ratings yet
- KIT-AlerTox Sticks PeanutDocument26 pagesKIT-AlerTox Sticks PeanutLuis Miguel Matos OteroNo ratings yet
- Catalog Pm21 SIMOTION, SINAMICS S120 & SIMOTICS - SIEMENS GPO - ElECTRÓNICA INDUSTRIALDocument189 pagesCatalog Pm21 SIMOTION, SINAMICS S120 & SIMOTICS - SIEMENS GPO - ElECTRÓNICA INDUSTRIALCarlos GabrielNo ratings yet
- Online Travel Ticket BookingDocument78 pagesOnline Travel Ticket Bookingprince jhaNo ratings yet
- LMS SRSDocument2 pagesLMS SRSbusinessanalystsudheerNo ratings yet
- Model: Frequency: Fuel Type:: Generator Set Data SheetDocument3 pagesModel: Frequency: Fuel Type:: Generator Set Data SheetForesight MisrNo ratings yet
- Erwin® Mapping Manager (MM) : at A GlanceDocument2 pagesErwin® Mapping Manager (MM) : at A GlanceramanadkNo ratings yet
- Solution:: TSN2101/TOS2111 - Tutorial 4 (Process Scheduling) - SolutionsDocument4 pagesSolution:: TSN2101/TOS2111 - Tutorial 4 (Process Scheduling) - SolutionsMoonNo ratings yet
- Software Requirements SpecificationDocument42 pagesSoftware Requirements SpecificationfgokcegozNo ratings yet
- 18CS45 Model Question Paper-1 With Effect From 2019-20 (CBCS Scheme) Usn: Fourth Semester B.E. Degree Examination Object Oriented ConceptsDocument2 pages18CS45 Model Question Paper-1 With Effect From 2019-20 (CBCS Scheme) Usn: Fourth Semester B.E. Degree Examination Object Oriented ConceptsSri SriNo ratings yet