Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pages From FAQ P
Pages From FAQ P
Uploaded by
paninikumar0000Copyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- PreviewpdfDocument40 pagesPreviewpdfARUN K CHOCKALINGAMNo ratings yet
- MIT5 111F14 Lec04SolnDocument2 pagesMIT5 111F14 Lec04SolnFaiza Jan IftikharNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle Inspection Quiz PDFDocument4 pagesMagnetic Particle Inspection Quiz PDFAngelica Gonzalez100% (1)
- Important Question of Class Xii Physics-Atoms and NucleiDocument17 pagesImportant Question of Class Xii Physics-Atoms and NucleiM ShawNo ratings yet
- Physics Class-Xii - Dual Nature & Radiation Revision Aissce-2020Document12 pagesPhysics Class-Xii - Dual Nature & Radiation Revision Aissce-2020PHYSICS HACKNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter - PYQ Practice Sheet (Physics)Document8 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Matter - PYQ Practice Sheet (Physics)om.dropyear2023No ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation FaqsDocument11 pagesDual Nature of Matter & Radiation Faqsdevansh9582dhyaniNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions IIDocument5 pagesPractice Questions IIPrajwol ShresthaNo ratings yet
- 2017 05 04 11 58 26 PDFDocument8 pages2017 05 04 11 58 26 PDFOm KumarNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics StudentDocument1 pageNuclear Physics Studentprashantmishra42591No ratings yet
- Important Questions Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument12 pagesImportant Questions Dual Nature of Radiation and Mattermvharshini2006No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument4 pagesPhysicsmathsbykeshavNo ratings yet
- Physics Modern Physics IDocument15 pagesPhysics Modern Physics Ianuveshr13No ratings yet
- Xii 2021 22 t2 Assign PhyDocument4 pagesXii 2021 22 t2 Assign PhyShalini JhaNo ratings yet
- Final Assessment Test - November 2016: Course: Class NBR(S) : Slot: Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 100Document2 pagesFinal Assessment Test - November 2016: Course: Class NBR(S) : Slot: Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 100VarunNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board-XII Physics - Paper and Solution - Set-IIIDocument19 pagesCBSE Board-XII Physics - Paper and Solution - Set-IIIAashray SinghNo ratings yet
- Revision Test 5 Physics Xii U Vii, Viii & Ix-1Document2 pagesRevision Test 5 Physics Xii U Vii, Viii & Ix-1victoria schoolNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 13 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22Document7 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 13 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22satyam skNo ratings yet
- Scan 22 Feb 2022Document3 pagesScan 22 Feb 2022Aditya KavalanekarNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 12 ATOMDocument1 pagePhysics Class 12 ATOMJai PrakashNo ratings yet
- Revision - EMWDocument4 pagesRevision - EMWshailendrasinghbhadoria7389No ratings yet
- UPH004Document2 pagesUPH004tjainbe23No ratings yet
- E7 - Ch02 - The Photoelectric Effect - FS - eDocument15 pagesE7 - Ch02 - The Photoelectric Effect - FS - eKenny LauNo ratings yet
- DPP Atomic Structure JH Sir-3573 PDFDocument8 pagesDPP Atomic Structure JH Sir-3573 PDFAditya RajNo ratings yet
- VG FRJ CIr YTa DUMz Y69 VMDocument6 pagesVG FRJ CIr YTa DUMz Y69 VMAyisha AfraNo ratings yet
- WB JEE Master Question Bank Chapter Wise PC-20210707093717556734Document51 pagesWB JEE Master Question Bank Chapter Wise PC-20210707093717556734PRIYANSHNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Level Practice Test-19: For JEE & NEET AspirantsDocument4 pagesJEE Main Level Practice Test-19: For JEE & NEET AspirantsSunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics - Practice Sheet (PYQ) - (Only PDFDocument2 pagesNuclear Physics - Practice Sheet (PYQ) - (Only PDFSHREYANSH RAINo ratings yet
- Exercise - V: JEE-ProblemsDocument3 pagesExercise - V: JEE-ProblemsAshu MishraNo ratings yet
- Bas 001Document6 pagesBas 001Sakkeer A VNo ratings yet
- 1modern Physics 1 - AnsDocument24 pages1modern Physics 1 - Ansrineeth22745No ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Patna, Patna: B. Tech. Online End Sem Exam March-2021Document1 pageNational Institute of Technology Patna, Patna: B. Tech. Online End Sem Exam March-2021SURAJ KUMARNo ratings yet
- Hpha042 Exercise (1st)Document3 pagesHpha042 Exercise (1st)piletjo phaladiNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 - DUAL NATURE AND EMW - CBSEDocument6 pagesAssignment - 1 - DUAL NATURE AND EMW - CBSEIIT ASHRAM DAHODNo ratings yet
- SEMESTER-X - Physics Questions - 2020 - AU PDFDocument7 pagesSEMESTER-X - Physics Questions - 2020 - AU PDFRaunak AnjumNo ratings yet
- DUAL NATURE TestDocument2 pagesDUAL NATURE TestChitesh MarmatNo ratings yet
- SPH2105 2016 ExDocument5 pagesSPH2105 2016 ExTrevorNo ratings yet
- PYQ of Dual Nature of Radiation & MatterDocument17 pagesPYQ of Dual Nature of Radiation & MatterrahulteliytNo ratings yet
- Atomic & MolecularDocument50 pagesAtomic & MolecularMrinal patraNo ratings yet
- Quantum Sheet by Quanta InstituteDocument130 pagesQuantum Sheet by Quanta InstituteSubhamNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023 January Session 1 Shift-2 (DT 31-01-2023) PhysicsDocument13 pagesJEE Main 2023 January Session 1 Shift-2 (DT 31-01-2023) PhysicsResonance EduventuresNo ratings yet
- PH110 2010 08Document3 pagesPH110 2010 08lyon juniorNo ratings yet
- Exercise - V: (Jee-Problems)Document4 pagesExercise - V: (Jee-Problems)Tarun KavipurapuNo ratings yet
- Physics: DPP - Daily Practice ProblemsDocument8 pagesPhysics: DPP - Daily Practice ProblemsAnonymous 9uu04elNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper Term 2 For 2021 22Document4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper Term 2 For 2021 22SUBHAM WORLDNo ratings yet
- P Ch-22 Dual+Nature+of+Radiation+and+MatterDocument4 pagesP Ch-22 Dual+Nature+of+Radiation+and+Mattermysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class X Physics Gold Series Sample Paper - 5: Time: 1 Hrs Total Marks: 80 General InstructionsDocument15 pagesICSE Board Class X Physics Gold Series Sample Paper - 5: Time: 1 Hrs Total Marks: 80 General InstructionsArijit Das GuptaNo ratings yet
- Isc Semester 2 Examination Specimen Question Paper Physics Paper 1 (Theory)Document5 pagesIsc Semester 2 Examination Specimen Question Paper Physics Paper 1 (Theory)marleyNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature Assignment1Document2 pagesDual Nature Assignment1hsofficial910No ratings yet
- Achariya World Class Education Subjective Test Xii - PhysicsDocument2 pagesAchariya World Class Education Subjective Test Xii - PhysicsSharan SNo ratings yet
- 125 PDFDocument21 pages125 PDFjconn45No ratings yet
- 3.2.2.4 Wave-Particle DualityDocument74 pages3.2.2.4 Wave-Particle Dualitynewynaw75No ratings yet
- Phy 1071 - Phy-1071 - Engineering Physics-2Document2 pagesPhy 1071 - Phy-1071 - Engineering Physics-2Challa SaiNo ratings yet
- Optics and Modern Physics Adv1Document22 pagesOptics and Modern Physics Adv1kamlesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Exercise: Violet: Iitians Spectrum EdutechDocument4 pagesExercise: Violet: Iitians Spectrum EdutechAarav ShahNo ratings yet
- Quantum MechanicsDocument100 pagesQuantum MechanicsbasedwhyteeNo ratings yet
- 861 Physics Paper 1 Sem II SpecimenDocument5 pages861 Physics Paper 1 Sem II SpecimenRahul DevNo ratings yet
- Revision - Atoms and NucleiDocument10 pagesRevision - Atoms and Nucleishailendrasinghbhadoria7389No ratings yet
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesFrom EverandX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Notes CH 3 Eco 10thDocument5 pagesNotes CH 3 Eco 10thpaninikumar0000No ratings yet
- Ray Optics 01Document13 pagesRay Optics 01paninikumar0000No ratings yet
- FAQ Physics 2020 26Document1 pageFAQ Physics 2020 26paninikumar0000No ratings yet
- Notes CH 2 Civics 10thDocument12 pagesNotes CH 2 Civics 10thpaninikumar0000No ratings yet
- 02 Kinetic Theory of Gases Practice Problem1Document2 pages02 Kinetic Theory of Gases Practice Problem1DonickGregoryDiengdohNo ratings yet
- What Is Diffraction?: Single Slit Diffraction FormulaDocument4 pagesWhat Is Diffraction?: Single Slit Diffraction FormulaChhoti Gas serviceNo ratings yet
- RSM 2008 RevisionDocument51 pagesRSM 2008 RevisionphanthanhhungNo ratings yet
- Questions 11-20Document3 pagesQuestions 11-20Samuel Francisco SinagaNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions On LN 5Document4 pagesPractice Questions On LN 5gokharNo ratings yet
- SR - No Date Test Topics of Chemistry Topics of Botany Topics of ZoologyDocument2 pagesSR - No Date Test Topics of Chemistry Topics of Botany Topics of ZoologySunita KharbandaNo ratings yet
- Phy 103, Physics-IDocument2 pagesPhy 103, Physics-ISüleymanNo ratings yet
- Dynasonics IS 4000 BrochureDocument8 pagesDynasonics IS 4000 BrochureHarris TLNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Calculations With Chemical Formulas and Equations PDFDocument8 pagesLecture 4 Calculations With Chemical Formulas and Equations PDFHani TamimiNo ratings yet
- Performance of A Portable Thermoelectric Water Cooling SystemDocument10 pagesPerformance of A Portable Thermoelectric Water Cooling SystemAnton PermanaNo ratings yet
- Ez Cleaner Ez Cleaner Ez Cleaner: REF REF REFDocument1 pageEz Cleaner Ez Cleaner Ez Cleaner: REF REF REFHussein MohamedNo ratings yet
- 80375-01 r0 Technical Data Sheet, AT-250Document1 page80375-01 r0 Technical Data Sheet, AT-250pablolz712No ratings yet
- Aeroshell Fluid 71Document2 pagesAeroshell Fluid 71mertaktayNo ratings yet
- GulfSea HT Oil 32 PDFDocument1 pageGulfSea HT Oil 32 PDFObydur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Urea-Formaldehyde ResinDocument11 pagesPreparation of Urea-Formaldehyde ResinRahul Sarma100% (3)
- Tutorial Eleven Reaction: 4 Edition, Jan. 2018Document10 pagesTutorial Eleven Reaction: 4 Edition, Jan. 2018komodiemoNo ratings yet
- Hastelloy B2 Welding Rod, Hastelloy Alloy B2 UNS N10665 Welding Rod Manufacturer in IndiaDocument3 pagesHastelloy B2 Welding Rod, Hastelloy Alloy B2 UNS N10665 Welding Rod Manufacturer in IndiaOZAIRTRADELINKNo ratings yet
- Wet Air Oxidation and Catalytic Wet Air Oxidation For Refinery Spent Caustic DegradationDocument7 pagesWet Air Oxidation and Catalytic Wet Air Oxidation For Refinery Spent Caustic DegradationSudeep MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Oxide Mineralization at The Radomiro Tomic Porphyry Copper Deposit, Northern ChileDocument14 pagesOxide Mineralization at The Radomiro Tomic Porphyry Copper Deposit, Northern Chilejunior.geologiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 10 To 12 Notes PDFDocument321 pagesChemistry 10 To 12 Notes PDFMoses NjobvuNo ratings yet
- 7790english VIII ADocument3 pages7790english VIII AAman GamingNo ratings yet
- Eaton 066166 EMT6 en - GBDocument3 pagesEaton 066166 EMT6 en - GBSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Biochemical AssDocument1 pageBiochemical AssbezNo ratings yet
- Env107 Lab Report-04: Water Quality Parameters Group-C Section-18Document6 pagesEnv107 Lab Report-04: Water Quality Parameters Group-C Section-18Araby NevaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Quantum Dots As New Hole Transport Material For Perovskite Solar CellsDocument6 pagesCarbon Quantum Dots As New Hole Transport Material For Perovskite Solar CellsZZ ChenNo ratings yet
- Density Calculations Worksheet IDocument2 pagesDensity Calculations Worksheet Iapi-218999959No ratings yet
- Sampling Steel and Iron For Determination of Chemical CompositionDocument23 pagesSampling Steel and Iron For Determination of Chemical CompositionMOHAMMADJAVAD NATEQINo ratings yet
- Geiger Counter Example Report 1Document8 pagesGeiger Counter Example Report 1emaad hamdaniNo ratings yet
Pages From FAQ P
Pages From FAQ P
Uploaded by
paninikumar0000Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pages From FAQ P
Pages From FAQ P
Uploaded by
paninikumar0000Copyright:
Available Formats
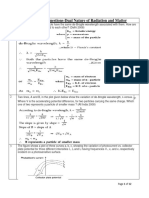
PHYSICS CLASS-XII –DUAL NATURE & RADIATION REVISION AISSCE-2020
763. X-rays of wavelength ‘ ’ fall on a photo sensitive surface, emitting electrons. Assuming that the work function of surface can be
neglected, prove that the de-Broglie wavelength of electrons emitted will be CBSE (AIC)-2017,(AI)-2004
OR
An electromagnetic wave of wavelength is incident on a photosensitive surface of negligible work function. If the photoelectrons
emitted from this surface have the de-Broglie wavelength , Prove that, =( ) CBSE (D)-2008
[ Ans. As, is negligible
⇨ = = 0= =
Now de-Broglie wavelength,
= = ⇨ = ⇨ =( )
764. A proton and an are accelerated through the same potential difference. Which on of the two has
(i) greater de-Broglie wavelength, and CBSE (AI)-2016,(D)-2014,2010,2009
(ii) less kinetic energy ? Justify your answer.
[ Ans. (i) & V = same
⇨ = X = X ⇨
(ii) ⇨
As ⇨
765. A deuteron and an are accelerated with the same accelerating potential. Which one of the two has -
(i) greater value of de-Broglie wavelength associated with it, it, and CBSE (AI)-2015,(D) -2014
(ii) less kinetic energy ? Explain.
[ Ans. (i) & V = same
⇨ = X = X 2:1 ⇨ >
(ii) ⇨
As ⇨
766. A proton and an have the same de-Broglie wavelength. Determine the ratio of-
(i) their accelerating potentials, and (ii) their speeds. CBSE (D) -2015, (DC)-2009
[ Ans. (i) ⇨ & = same
⇨ = X = X 8:1
(ii) ⇨ ⇨
⇨ = = = 4:1
767. A proton and a deuteron are accelerated through the same accelerating potential. Which one of the two has –
(i) greater value of de-Broglie wavelength associated with it, it, and CBSE (D)-2014
(ii) less momentum ? Give reasons to justify your answer .
[ Ans. (i) & V = same
⇨ = X = X
⇨ thus proton has the greater de-Broglie wavelength
(ii) ⇨ ⇨
As hence Thus proton has less momentum
SUNEEL KUMAR VISHWAKARMA PGT(PHYSICS) KV1 AFS CHAKERI KANPUR suneel19761976@gmail.com
PHYSICS CLASS-XII –DUAL NATURE & RADIATION REVISION AISSCE-2020
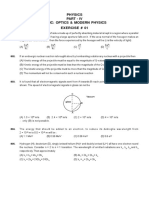
768. Two metals X and Y have work functions 2 eV & 5 eV respectively. Which metal will emit electrons, when it is
radiated with light of wavelength 400 nm & why ? CBSE (AIC)-2010
[Ans. metal X, as 3.09 eV ⇨ WX & WY
769. Monochromatic light of frequency 6.0 X Hz is produced by a laser. The power emitted is 2.0 X W.
(a) What is the energy of a photon in the light beam ? NCERT-2017
(b) Estimate the number of photons emitted per second on an average by the source. CBSE (AI)-2015,(D)-2014
[ Ans. (a) J
(b) number of photons,
770. The work function for the following metals is given : CBSE (F)-2016
: and :
(i) Which of these will not give photoelectron emission from a radiation of wavelength 3300 A0 from a laser beam ?
(ii) What happens if the source of laser beam is brought closer ?
[ Ans. (i) for 3300 A0, energy of photon, 3.75 4.175 eV
Hence Mo will not give photoelectric emission as W
(ii) In case of Na, photocurrent will increase but in case of Mo no effect
771. The work function of Cesium metal is 2.14 eV. When light of frequency 6.0 X is incident on metal surface,
photoemission of electron occurs. What is the CBSE (AIC)-2010,NCERT-2017
(i) maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons
(ii) stopping potential, and
(iii) maximum speed of emitted photoelectrons
[Ans. (i) 2.14 X 1.6 X 1.6 X (2.48 2.14) J 0.34 eV
(ii) e 0.34 eV ⇨ 0.34
(iii) 0.34 eV 0.34 X 1.6 X J ⇨ 345.8 X
0
772. Light of wavelength 2000 A falls on a metal surface of work function 4.2 eV. CBSE (F)-2011
(i) What is the kinetic energy (in eV) of the (a) fastest and (b) slowest electrons emitted from the surface ?
(ii) What will be the change in the energy of the emitted electrons if the intensity of light with same wavelength is
doubled ?
(iii) If the same light falls on another surface of work function 6.5 eV, what will be the energy of emitted electrons ?
[Ans. (i) (a) K.E. of fastest electron
= 4.2 X 1.6 X 1.6 X (6.2 4.2) J 2.0 eV
(b) K.E. of slowest electron = 0 eV (ii) No change in the energy of emitted electrons as it does not depend on intensity
(iii) no emission as E( 6.2 eV) W (6.5 eV) ]
773. Ultraviolet light of wavelength 2271 A0 from a 100W mercury source irradiated a photocell made of Molybdenum
metal. If the stopping potential is 1.3 V, estimate the work function of the metal. How would the photocell respond
when the source is replaced by another source of high intensity (10 5 W/m2) red light of wavelength 6328 A0. Justify
your answer. CBSE (AI)-2015,(F)-2013,(D)-2005
[ Ans. e
⇨ e – 1.3 X 1.6 X 1.6 X (5.5 1.3) J 4.2 eV
Also, ⇨ 2.977 X 2977
As 6328 ) 2977 )
Hence, photocell will not respond to source of high intensity (105 W/m2) red light of wavelength 6328 A0
SUNEEL KUMAR VISHWAKARMA PGT(PHYSICS) KV1 AFS CHAKERI KANPUR suneel19761976@gmail.com
PHYSICS CLASS-XII –DUAL NATURE & RADIATION REVISION AISSCE-2020
774. Calculate the- NCERT-2017
(a) momentum, and
(b) de Broglie wavelength of the electrons accelerated through a potential difference of 56 V.
[ Ans. (a)
(b)
775. The wavelength of light from the spectral emission line of Sodium is 589 . Find the kinetic energy of electron
for which it would have the same de-Broglie wavelength. CBSE (AI)-2015
[ Ans. ⇨ 6.96 X J
776. An electron and a photon each have a wavelength 2.00 nm. Find- CBSE (D)-2011
(i) their momenta
(ii) the energy of photon, and
(iii) the kinetic energy of electron
[ Ans. (i) momentum of electron = momentum of photon = = 3.3 X kgm/s
(ii) energy of photon = = 9.945 X J.
(iii) K.E. of electron = = 6.0314 X J
777. An electron and a proton each has de-Broglie wavelength of 1.6 nm. CBSE (F)-2013
(i) write the ratio of their linear momenta
(ii) compare the kinetic energy of the proton with that of the electron.
[ Ans. (i) momentum of electron = momentum of proton = ⇨ 1: 1
(ii) ⇨ ⇨ As ⇨ >
0
778. Given the ground state energy = eV and Bohr radius = 0.53 A . Find out how the de-Broglie
wavelength associated with the electron orbiting in the ground state would change when it jump in to the first
excited state ?
[ Ans. & for ground state , for first excited state CBSE (AI)-2015
Now, as = ⇨ but ⇨
⇨ = = ⇨ =2
Hence, de-Broglie wavelength will become double
779. When an electron orbiting in hydrogen atom in its ground state moves to third excited state, show how the
de-Broglie wavelength associated with it would be affected ? CBSE (AI)-2015
[ Ans. for ground state , for third excited state
Now, as = ⇨ but ⇨
⇨ = = ⇨ =4
Hence, de-Broglie wavelength will become four times
780. When an electron in hydrogen atom jumps from the third excited state to the ground state, how would the
de-Broglie wavelength associated with the electron change ? Justify your answer. CBSE (AI)-2015
[ Ans. for third excited state , for ground state
Now, as = ⇨ but ⇨
⇨ = = ⇨ =
Hence, de-Broglie wavelength will decrease to one fourth of its value in third excited state
==================================================================================
SUNEEL KUMAR VISHWAKARMA PGT(PHYSICS) KV1 AFS CHAKERI KANPUR suneel19761976@gmail.com
You might also like
- PreviewpdfDocument40 pagesPreviewpdfARUN K CHOCKALINGAMNo ratings yet
- MIT5 111F14 Lec04SolnDocument2 pagesMIT5 111F14 Lec04SolnFaiza Jan IftikharNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Particle Inspection Quiz PDFDocument4 pagesMagnetic Particle Inspection Quiz PDFAngelica Gonzalez100% (1)
- Important Question of Class Xii Physics-Atoms and NucleiDocument17 pagesImportant Question of Class Xii Physics-Atoms and NucleiM ShawNo ratings yet
- Physics Class-Xii - Dual Nature & Radiation Revision Aissce-2020Document12 pagesPhysics Class-Xii - Dual Nature & Radiation Revision Aissce-2020PHYSICS HACKNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter - PYQ Practice Sheet (Physics)Document8 pagesDual Nature of Radiation and Matter - PYQ Practice Sheet (Physics)om.dropyear2023No ratings yet
- Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation FaqsDocument11 pagesDual Nature of Matter & Radiation Faqsdevansh9582dhyaniNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions IIDocument5 pagesPractice Questions IIPrajwol ShresthaNo ratings yet
- 2017 05 04 11 58 26 PDFDocument8 pages2017 05 04 11 58 26 PDFOm KumarNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics StudentDocument1 pageNuclear Physics Studentprashantmishra42591No ratings yet
- Important Questions Dual Nature of Radiation and MatterDocument12 pagesImportant Questions Dual Nature of Radiation and Mattermvharshini2006No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument4 pagesPhysicsmathsbykeshavNo ratings yet
- Physics Modern Physics IDocument15 pagesPhysics Modern Physics Ianuveshr13No ratings yet
- Xii 2021 22 t2 Assign PhyDocument4 pagesXii 2021 22 t2 Assign PhyShalini JhaNo ratings yet
- Final Assessment Test - November 2016: Course: Class NBR(S) : Slot: Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 100Document2 pagesFinal Assessment Test - November 2016: Course: Class NBR(S) : Slot: Time: Three Hours Max. Marks: 100VarunNo ratings yet
- CBSE Board-XII Physics - Paper and Solution - Set-IIIDocument19 pagesCBSE Board-XII Physics - Paper and Solution - Set-IIIAashray SinghNo ratings yet
- Revision Test 5 Physics Xii U Vii, Viii & Ix-1Document2 pagesRevision Test 5 Physics Xii U Vii, Viii & Ix-1victoria schoolNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 13 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22Document7 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 13 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22satyam skNo ratings yet
- Scan 22 Feb 2022Document3 pagesScan 22 Feb 2022Aditya KavalanekarNo ratings yet
- Physics Class 12 ATOMDocument1 pagePhysics Class 12 ATOMJai PrakashNo ratings yet
- Revision - EMWDocument4 pagesRevision - EMWshailendrasinghbhadoria7389No ratings yet
- UPH004Document2 pagesUPH004tjainbe23No ratings yet
- E7 - Ch02 - The Photoelectric Effect - FS - eDocument15 pagesE7 - Ch02 - The Photoelectric Effect - FS - eKenny LauNo ratings yet
- DPP Atomic Structure JH Sir-3573 PDFDocument8 pagesDPP Atomic Structure JH Sir-3573 PDFAditya RajNo ratings yet
- VG FRJ CIr YTa DUMz Y69 VMDocument6 pagesVG FRJ CIr YTa DUMz Y69 VMAyisha AfraNo ratings yet
- WB JEE Master Question Bank Chapter Wise PC-20210707093717556734Document51 pagesWB JEE Master Question Bank Chapter Wise PC-20210707093717556734PRIYANSHNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Level Practice Test-19: For JEE & NEET AspirantsDocument4 pagesJEE Main Level Practice Test-19: For JEE & NEET AspirantsSunny KumarNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics - Practice Sheet (PYQ) - (Only PDFDocument2 pagesNuclear Physics - Practice Sheet (PYQ) - (Only PDFSHREYANSH RAINo ratings yet
- Exercise - V: JEE-ProblemsDocument3 pagesExercise - V: JEE-ProblemsAshu MishraNo ratings yet
- Bas 001Document6 pagesBas 001Sakkeer A VNo ratings yet
- 1modern Physics 1 - AnsDocument24 pages1modern Physics 1 - Ansrineeth22745No ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Patna, Patna: B. Tech. Online End Sem Exam March-2021Document1 pageNational Institute of Technology Patna, Patna: B. Tech. Online End Sem Exam March-2021SURAJ KUMARNo ratings yet
- Hpha042 Exercise (1st)Document3 pagesHpha042 Exercise (1st)piletjo phaladiNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 - DUAL NATURE AND EMW - CBSEDocument6 pagesAssignment - 1 - DUAL NATURE AND EMW - CBSEIIT ASHRAM DAHODNo ratings yet
- SEMESTER-X - Physics Questions - 2020 - AU PDFDocument7 pagesSEMESTER-X - Physics Questions - 2020 - AU PDFRaunak AnjumNo ratings yet
- DUAL NATURE TestDocument2 pagesDUAL NATURE TestChitesh MarmatNo ratings yet
- SPH2105 2016 ExDocument5 pagesSPH2105 2016 ExTrevorNo ratings yet
- PYQ of Dual Nature of Radiation & MatterDocument17 pagesPYQ of Dual Nature of Radiation & MatterrahulteliytNo ratings yet
- Atomic & MolecularDocument50 pagesAtomic & MolecularMrinal patraNo ratings yet
- Quantum Sheet by Quanta InstituteDocument130 pagesQuantum Sheet by Quanta InstituteSubhamNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2023 January Session 1 Shift-2 (DT 31-01-2023) PhysicsDocument13 pagesJEE Main 2023 January Session 1 Shift-2 (DT 31-01-2023) PhysicsResonance EduventuresNo ratings yet
- PH110 2010 08Document3 pagesPH110 2010 08lyon juniorNo ratings yet
- Exercise - V: (Jee-Problems)Document4 pagesExercise - V: (Jee-Problems)Tarun KavipurapuNo ratings yet
- Physics: DPP - Daily Practice ProblemsDocument8 pagesPhysics: DPP - Daily Practice ProblemsAnonymous 9uu04elNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper Term 2 For 2021 22Document4 pagesCBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper Term 2 For 2021 22SUBHAM WORLDNo ratings yet
- P Ch-22 Dual+Nature+of+Radiation+and+MatterDocument4 pagesP Ch-22 Dual+Nature+of+Radiation+and+Mattermysoftinfo.incNo ratings yet
- ICSE Board Class X Physics Gold Series Sample Paper - 5: Time: 1 Hrs Total Marks: 80 General InstructionsDocument15 pagesICSE Board Class X Physics Gold Series Sample Paper - 5: Time: 1 Hrs Total Marks: 80 General InstructionsArijit Das GuptaNo ratings yet
- Isc Semester 2 Examination Specimen Question Paper Physics Paper 1 (Theory)Document5 pagesIsc Semester 2 Examination Specimen Question Paper Physics Paper 1 (Theory)marleyNo ratings yet
- Dual Nature Assignment1Document2 pagesDual Nature Assignment1hsofficial910No ratings yet
- Achariya World Class Education Subjective Test Xii - PhysicsDocument2 pagesAchariya World Class Education Subjective Test Xii - PhysicsSharan SNo ratings yet
- 125 PDFDocument21 pages125 PDFjconn45No ratings yet
- 3.2.2.4 Wave-Particle DualityDocument74 pages3.2.2.4 Wave-Particle Dualitynewynaw75No ratings yet
- Phy 1071 - Phy-1071 - Engineering Physics-2Document2 pagesPhy 1071 - Phy-1071 - Engineering Physics-2Challa SaiNo ratings yet
- Optics and Modern Physics Adv1Document22 pagesOptics and Modern Physics Adv1kamlesh kumarNo ratings yet
- Exercise: Violet: Iitians Spectrum EdutechDocument4 pagesExercise: Violet: Iitians Spectrum EdutechAarav ShahNo ratings yet
- Quantum MechanicsDocument100 pagesQuantum MechanicsbasedwhyteeNo ratings yet
- 861 Physics Paper 1 Sem II SpecimenDocument5 pages861 Physics Paper 1 Sem II SpecimenRahul DevNo ratings yet
- Revision - Atoms and NucleiDocument10 pagesRevision - Atoms and Nucleishailendrasinghbhadoria7389No ratings yet
- X-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesFrom EverandX-ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the Chemical and Materials SciencesNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Notes CH 3 Eco 10thDocument5 pagesNotes CH 3 Eco 10thpaninikumar0000No ratings yet
- Ray Optics 01Document13 pagesRay Optics 01paninikumar0000No ratings yet
- FAQ Physics 2020 26Document1 pageFAQ Physics 2020 26paninikumar0000No ratings yet
- Notes CH 2 Civics 10thDocument12 pagesNotes CH 2 Civics 10thpaninikumar0000No ratings yet
- 02 Kinetic Theory of Gases Practice Problem1Document2 pages02 Kinetic Theory of Gases Practice Problem1DonickGregoryDiengdohNo ratings yet
- What Is Diffraction?: Single Slit Diffraction FormulaDocument4 pagesWhat Is Diffraction?: Single Slit Diffraction FormulaChhoti Gas serviceNo ratings yet
- RSM 2008 RevisionDocument51 pagesRSM 2008 RevisionphanthanhhungNo ratings yet
- Questions 11-20Document3 pagesQuestions 11-20Samuel Francisco SinagaNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions On LN 5Document4 pagesPractice Questions On LN 5gokharNo ratings yet
- SR - No Date Test Topics of Chemistry Topics of Botany Topics of ZoologyDocument2 pagesSR - No Date Test Topics of Chemistry Topics of Botany Topics of ZoologySunita KharbandaNo ratings yet
- Phy 103, Physics-IDocument2 pagesPhy 103, Physics-ISüleymanNo ratings yet
- Dynasonics IS 4000 BrochureDocument8 pagesDynasonics IS 4000 BrochureHarris TLNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Calculations With Chemical Formulas and Equations PDFDocument8 pagesLecture 4 Calculations With Chemical Formulas and Equations PDFHani TamimiNo ratings yet
- Performance of A Portable Thermoelectric Water Cooling SystemDocument10 pagesPerformance of A Portable Thermoelectric Water Cooling SystemAnton PermanaNo ratings yet
- Ez Cleaner Ez Cleaner Ez Cleaner: REF REF REFDocument1 pageEz Cleaner Ez Cleaner Ez Cleaner: REF REF REFHussein MohamedNo ratings yet
- 80375-01 r0 Technical Data Sheet, AT-250Document1 page80375-01 r0 Technical Data Sheet, AT-250pablolz712No ratings yet
- Aeroshell Fluid 71Document2 pagesAeroshell Fluid 71mertaktayNo ratings yet
- GulfSea HT Oil 32 PDFDocument1 pageGulfSea HT Oil 32 PDFObydur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Urea-Formaldehyde ResinDocument11 pagesPreparation of Urea-Formaldehyde ResinRahul Sarma100% (3)
- Tutorial Eleven Reaction: 4 Edition, Jan. 2018Document10 pagesTutorial Eleven Reaction: 4 Edition, Jan. 2018komodiemoNo ratings yet
- Hastelloy B2 Welding Rod, Hastelloy Alloy B2 UNS N10665 Welding Rod Manufacturer in IndiaDocument3 pagesHastelloy B2 Welding Rod, Hastelloy Alloy B2 UNS N10665 Welding Rod Manufacturer in IndiaOZAIRTRADELINKNo ratings yet
- Wet Air Oxidation and Catalytic Wet Air Oxidation For Refinery Spent Caustic DegradationDocument7 pagesWet Air Oxidation and Catalytic Wet Air Oxidation For Refinery Spent Caustic DegradationSudeep MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Oxide Mineralization at The Radomiro Tomic Porphyry Copper Deposit, Northern ChileDocument14 pagesOxide Mineralization at The Radomiro Tomic Porphyry Copper Deposit, Northern Chilejunior.geologiaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 10 To 12 Notes PDFDocument321 pagesChemistry 10 To 12 Notes PDFMoses NjobvuNo ratings yet
- 7790english VIII ADocument3 pages7790english VIII AAman GamingNo ratings yet
- Eaton 066166 EMT6 en - GBDocument3 pagesEaton 066166 EMT6 en - GBSiva RamanNo ratings yet
- Biochemical AssDocument1 pageBiochemical AssbezNo ratings yet
- Env107 Lab Report-04: Water Quality Parameters Group-C Section-18Document6 pagesEnv107 Lab Report-04: Water Quality Parameters Group-C Section-18Araby NevaNo ratings yet
- Carbon Quantum Dots As New Hole Transport Material For Perovskite Solar CellsDocument6 pagesCarbon Quantum Dots As New Hole Transport Material For Perovskite Solar CellsZZ ChenNo ratings yet
- Density Calculations Worksheet IDocument2 pagesDensity Calculations Worksheet Iapi-218999959No ratings yet
- Sampling Steel and Iron For Determination of Chemical CompositionDocument23 pagesSampling Steel and Iron For Determination of Chemical CompositionMOHAMMADJAVAD NATEQINo ratings yet
- Geiger Counter Example Report 1Document8 pagesGeiger Counter Example Report 1emaad hamdaniNo ratings yet