Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Grade 7 Integrated Science Week 9 Lesson 2
Grade 7 Integrated Science Week 9 Lesson 2
Uploaded by
Keianna GillisOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Grade 7 Integrated Science Week 9 Lesson 2
Grade 7 Integrated Science Week 9 Lesson 2
Uploaded by
Keianna GillisCopyright:
Available Formats
MINISTRY OF EDUCTION
SECONDARY ENGAGEMENT PROGRAMME
INTEGRATED SCIENCE
GRADE 7
WEEK 9 LESSON 2
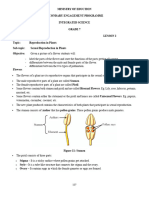
Topic: Reproduction in Plants
Sub-topic: Sexual Reproduction in Plants
Objective: Given a picture of a flower students will:
- label all the parts of the flower and state their functions correctly.
- differentiate between the male and female parts of the flower.
- differentiate between the two types of pollination.
Flowers
The flowers of a plant are its reproductive organs that participate in the sexual reproduction process.
The male reproductive parts of a plant are called Stamen.
The female reproductive parts of a plant are called Pistil.
Some flowers contain both stamen and pistil and are called Bisexual Flowers. Eg. Lily, rose, hibiscus,
petunia, mustard, etc.
Some flowers contain either the statement or the pistil and hence are called Unisexual Flowers. Eg. papaya,
watermelon, cucumber, coconut, etc.
The new plant produced contains the characteristics of both plants that participate in sexual reproduction.
The stamen consists of Anther that has pollen grains. These pollen grains produce male gametes.
Figure 11: Stamen
The pistil consists of three parts:
o Stigma – It is a sticky surface where pollen grains get attached.
o Style – It is a tube-like structure that connects the stigma and the ovary.
o Ovary – It contains eggs in which the female gametes or eggs are formed.
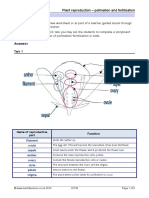
The Ovary
How the male gametes reach the female gametes in plants?
The male and female gametes fuse and form a zygote.
The male gametes reach the female gametes by the process of pollination.
The pollen grains have a tough covering which allows them to survive the different climatic conditions.
Due to their lightweight, winds and water often carry them away to different plants. Sometimes the pollen
grains also get attached to insects that carry them to different flowers.
This process of transfer of pollen grains from one stigma to another is called Pollination.
Diagram of Pollination in Flowering Plants
Pollination
There are two types of pollination:
o Self-pollination: When the pollen grains land on the stigma of the same flower.
o Cross-pollination: When the pollen grains land on the stigma of a different flower on another flower on
another plant but they are both of the same species.
Self-pollination and Cross-pollination
Reference
1. https://sites.google.com/site/scientificgreenmachine/microscopic-level/structure-of-a-leaf---internal-external
2. https://www.greenandvibrant.com/parts-of-a-flower
3. https://byjus.com/biology/flower/
You might also like
- 8461 2H QP Biology G 18nov20 AM - 2Document18 pages8461 2H QP Biology G 18nov20 AM - 2tosinNo ratings yet
- Angiosperm Life Cycle-Flowers, Fruits and SeedsDocument7 pagesAngiosperm Life Cycle-Flowers, Fruits and SeedsEunnie ChongNo ratings yet
- KEY SELECT Endosymbiotic Theory by Amoeba SistersDocument3 pagesKEY SELECT Endosymbiotic Theory by Amoeba SistersIsis Hillenberg50% (4)
- Flower and PollinationDocument3 pagesFlower and Pollinationeasylearning83No ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Plants 2Document4 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plants 2easylearning83No ratings yet
- Topic 10 Reproduction in Plants Revised Roysci Notes 2021Document14 pagesTopic 10 Reproduction in Plants Revised Roysci Notes 2021shealtielchigariso06No ratings yet
- Notebook CH 2 Q&aDocument6 pagesNotebook CH 2 Q&aumamahfarooq75No ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 12 - Learn CBSEDocument13 pagesReproduction in Plants Class 7 Notes Science Chapter 12 - Learn CBSEPrateek Kumar PatelNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerDocument30 pagesClass 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerSufiyanNo ratings yet
- Reproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)Document10 pagesReproduction-among-Flowering-Plants (Navales and Munoz)richelyn navalesNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Notes BiologyDocument12 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Class 12 Notes BiologyHarshu JiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument12 pagesReproduction in PlantsAnand Philip PrasadNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument4 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plantseasylearning83No ratings yet
- S5LT 11f 6Document8 pagesS5LT 11f 6Kristine Joy PitaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Plants & InsectsDocument9 pagesLesson Plan: Plants & InsectsGemerlyn VallesNo ratings yet
- Reproduction The Continuity of Life - CompressDocument7 pagesReproduction The Continuity of Life - CompressDaisy Jeanne Belarmino RosalesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6B BIOL5 TranscriptDocument8 pagesLecture 6B BIOL5 TranscriptHannah Fae RotairoNo ratings yet
- PERPETUATION OF LIFE NotesDocument11 pagesPERPETUATION OF LIFE NotesErnie Rosemarie T. BucalenNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Plants CLASS 10Document5 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plants CLASS 10shallowNo ratings yet
- HSRR - 3-SE 2023-PLUS TWO-BOTANY-FNLDocument34 pagesHSRR - 3-SE 2023-PLUS TWO-BOTANY-FNLuntrustedusageNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Questions With AnswersDocument6 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants Questions With AnswersPrajwal dNo ratings yet
- Plancess-Biology-Class-12 Removing Images and Watermark (3) Upto CH 10Document340 pagesPlancess-Biology-Class-12 Removing Images and Watermark (3) Upto CH 10lotus25369No ratings yet
- Class 12 Bio CH 1Document6 pagesClass 12 Bio CH 1AbhishekDwivediNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTION IN PLANTSDocument9 pagesREPRODUCTION IN PLANTSFadil AliNo ratings yet
- Worksheet. 5. Sexual Reproduction in PlantDocument4 pagesWorksheet. 5. Sexual Reproduction in PlantLeonita SwandjajaNo ratings yet
- 12 Reproduction #106. Types of ReproductionDocument18 pages12 Reproduction #106. Types of ReproductionJorifNo ratings yet
- 12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFDocument51 pages12 Reproduction Biology Notes IGCSE PDFUmair Khan Marwat50% (2)
- Plant ReproductionDocument8 pagesPlant ReproductionExceil Matthew Carpio100% (1)
- 12 Biology Notes Ch02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument7 pages12 Biology Notes Ch02 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsJatin kumar100% (1)
- Chapter-2 Notes (VKS)Document16 pagesChapter-2 Notes (VKS)Seema TrivediNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Bio Chapter Wise Topic Wise Notes Chapter-1 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument134 pagesClass 12 Bio Chapter Wise Topic Wise Notes Chapter-1 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantstanvir01virkNo ratings yet
- ANTHOPHYTEDocument3 pagesANTHOPHYTEIrish Nicole BigtasNo ratings yet
- Grade 5 LPDocument7 pagesGrade 5 LPJuhanna Lizl GustiloNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Notes PollinationDocument3 pagesBIOLOGY Notes PollinationDivy PurswaniNo ratings yet
- Science G7 Q2 W5 MODDocument8 pagesScience G7 Q2 W5 MODAveCorpuz BioCornerNo ratings yet
- Gerberas o Claveles. Es Mejor Que Las Partes de La Flor Se Puedan Observar A Simple Vista)Document4 pagesGerberas o Claveles. Es Mejor Que Las Partes de La Flor Se Puedan Observar A Simple Vista)Nohelia AriasNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument8 pagesReproduction in PlantsJada MillerNo ratings yet
- STAGE 4 SCIENCE Inside Plants Concept 3Document27 pagesSTAGE 4 SCIENCE Inside Plants Concept 3AbdoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plant 2 - 210806 - 214931Document10 pagesChapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plant 2 - 210806 - 214931Ompriya SNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants PDFDocument5 pagesReproduction in Plants PDFHasanNo ratings yet
- Lecture notes-XII-Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument11 pagesLecture notes-XII-Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plantsaditya100% (3)
- Sexual ReproductionDocument19 pagesSexual ReproductionjojopebblesNo ratings yet
- 3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5Document12 pages3.6.1 Plant Reproduction H 3.6.3 - 3.6.5George Oswald Junior CarringtonNo ratings yet
- 1. Reproduction in Lower and Higher PlantsDocument19 pages1. Reproduction in Lower and Higher Plantsshivamkadam563No ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants.Document47 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants.Prachi SinghNo ratings yet
- Science5 Q2 Mod7 ReproductioninPlants v3Document22 pagesScience5 Q2 Mod7 ReproductioninPlants v3Analee GalangNo ratings yet
- Gr12 - Reproduction in PlantsDocument14 pagesGr12 - Reproduction in PlantsZelNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce - STUDENTSDocument18 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce - STUDENTSAnshika AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument9 pagesModule 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsMorgan BrownNo ratings yet
- 0 105920 Worksheet9gr9Document6 pages0 105920 Worksheet9gr9omar.hazembadawi2010No ratings yet
- It Consist Of:-: FLOWER - Itis The Fascinating Reproductive Organ of AngiospermsDocument23 pagesIt Consist Of:-: FLOWER - Itis The Fascinating Reproductive Organ of AngiospermssiddhantNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument4 pagesSexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsChandanNo ratings yet
- Biology Investigatory Project: PollinationDocument30 pagesBiology Investigatory Project: PollinationMohamed LaqinNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningDocument11 pagesCurriculum Guide: Instructional PlanningMerce Tojino ManigosNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument28 pagesSexual Reproduction in Plantsasadukimbugwe20No ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument40 pagesReproduction in PlantsMegha SainiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument40 pagesLecture 4 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsEsther Suan-LancitaNo ratings yet
- Ch.12. Reproduction in PlantsDocument7 pagesCh.12. Reproduction in PlantsSharath ChandraNo ratings yet
- Pollination and FertilisationDocument5 pagesPollination and FertilisationmihayedoNo ratings yet
- Gardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3From EverandGardener's Guide to Seed Catalogs: Gardener's Guide Series, #3No ratings yet
- Biophysics Assignment 2 PDFDocument2 pagesBiophysics Assignment 2 PDFKwasi BempongNo ratings yet
- Trichodesma Zeylanicum PDFDocument4 pagesTrichodesma Zeylanicum PDFsindysintyadewiNo ratings yet
- What Is BacteriaDocument33 pagesWhat Is Bacteriaapi-19862227100% (1)
- Chapter 7EDocument9 pagesChapter 7EChandan KumarNo ratings yet
- BotanyUG PDFDocument6 pagesBotanyUG PDFSharma DineshNo ratings yet
- Cestode NotesDocument26 pagesCestode NotesJOSEPH NDERITUNo ratings yet
- Bryophyta Pteridophyta GymnospermDocument7 pagesBryophyta Pteridophyta GymnospermVishal Jalan100% (1)
- Principles of Inheritance and VariationDocument81 pagesPrinciples of Inheritance and VariationRayan100% (2)
- 0610 w11 QP 21Document24 pages0610 w11 QP 21Muhammad Azhar HayatNo ratings yet
- Non-Mendelian GeneticsDocument3 pagesNon-Mendelian GeneticsMarlon EllamilNo ratings yet
- Crops & The Environment: Banole ProtectsDocument24 pagesCrops & The Environment: Banole ProtectsToan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Bioinformatics: Concepts and Applications: December 2019Document11 pagesBioinformatics: Concepts and Applications: December 2019Piyush GuptaNo ratings yet
- Selective Breeding in Fish and ConservatDocument9 pagesSelective Breeding in Fish and ConservatWahyu W'cas PamungkasNo ratings yet
- Swamy Et. Al. (2010)Document8 pagesSwamy Et. Al. (2010)mpd zulkifliNo ratings yet
- KS2 Science SATs Study Book PDFDocument112 pagesKS2 Science SATs Study Book PDFAzra100% (4)
- Microbiology SyllabusDocument56 pagesMicrobiology SyllabusYaswanth SinhaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument4 pagesNutrition in AnimalsAaron Dave CanteroNo ratings yet
- 8 Facts About The AmazonDocument8 pages8 Facts About The AmazonNOr JOeNo ratings yet
- Gautam PHD Dissertation 2013Document129 pagesGautam PHD Dissertation 2013sorinaNo ratings yet
- ICAR NET Question PaperDocument4 pagesICAR NET Question PaperKuttivalli Kollam100% (1)
- A1764846802 - 12964 - 21 - 2018 - Hybrid Rice BreedingDocument21 pagesA1764846802 - 12964 - 21 - 2018 - Hybrid Rice BreedingSaurabh BishnoiNo ratings yet
- Bugs in The BrainDocument4 pagesBugs in The Braingalina sokolovaNo ratings yet
- Text Detective Weird Animals WorkbookDocument22 pagesText Detective Weird Animals Workbookveronica.h.recipethisNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Lab EquipmentDocument8 pagesMicrobiology Lab EquipmentJoila AbaoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Molecular BiologyDocument39 pagesIntroduction To Molecular BiologyAbbinaya100% (9)
- Conservation Strategies of Indian MouseDocument6 pagesConservation Strategies of Indian MouseJugaadBabaNo ratings yet
- 1S00145 PDFDocument917 pages1S00145 PDFMahesh KhandareNo ratings yet
- Can Top-Down Controls Expand The Ecological Niche of Marine N Fixers?Document11 pagesCan Top-Down Controls Expand The Ecological Niche of Marine N Fixers?Neha_ Sharma08No ratings yet